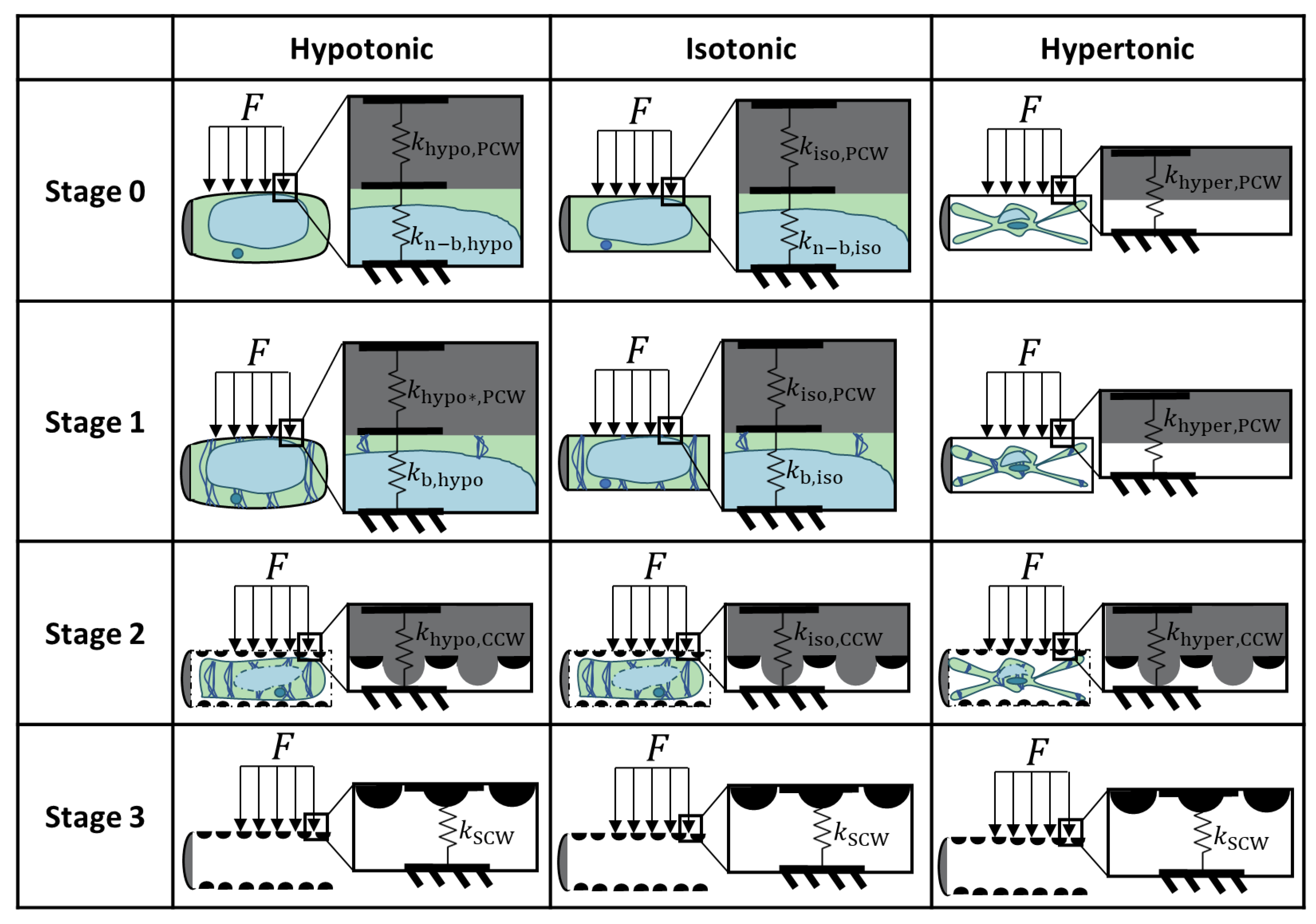
38 in the diagram, which one represents a hypertonic solution
Intravenous Fluids in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Flow Diagram of Patient Selection. CKD V = stage V chronic kidney disease; ICU = intensive care unit. TREATMENT WITH INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS AND LOOP DIURETICS. Patients received intravenous fluid therapy in 11% of hospitalizations, of which 80% involved normal saline solution as the only fluid treatment and 91% involved furosemide as the only loop diuretic (Table 2). For … Determinants of hypokalemia following hypertonic sodium ... Hypertonic NaHCO 3 infusion (1 N, 5 mmol/kg) to unanesthetized dogs with normal acid-base status or one of the four chronic acid-base disorders decreased plasma potassium concentration ([K +] p) at 30 min in all study groups (Δ[K +] p, − 0.16 to − 0.73 mmol/L), which remained essentially unaltered up to 90-min postinfusion.
› articles › ncomms1714Intracellular temperature mapping ... - Nature Communications Feb 28, 2012 · The cell pellets (0.5 ml) were collected and resuspended in hypertonic buffer (2.5 ml, containing 0.42 M KCl, 50 mM HEPES (4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid)-KOH, 5 mM MgCl 2, 0.1 ...
In the diagram, which one represents a hypertonic solution
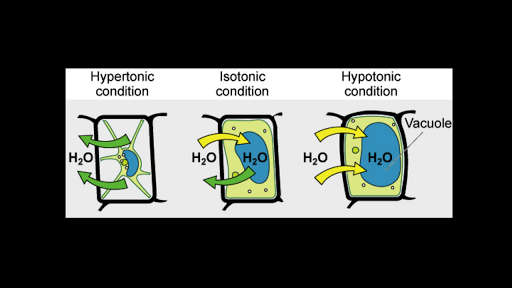
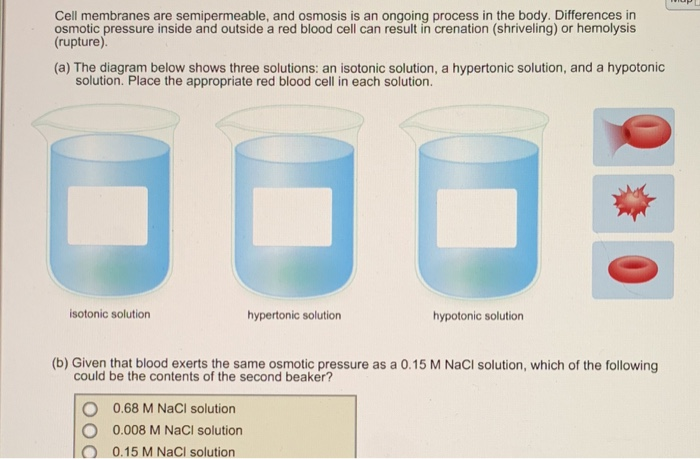
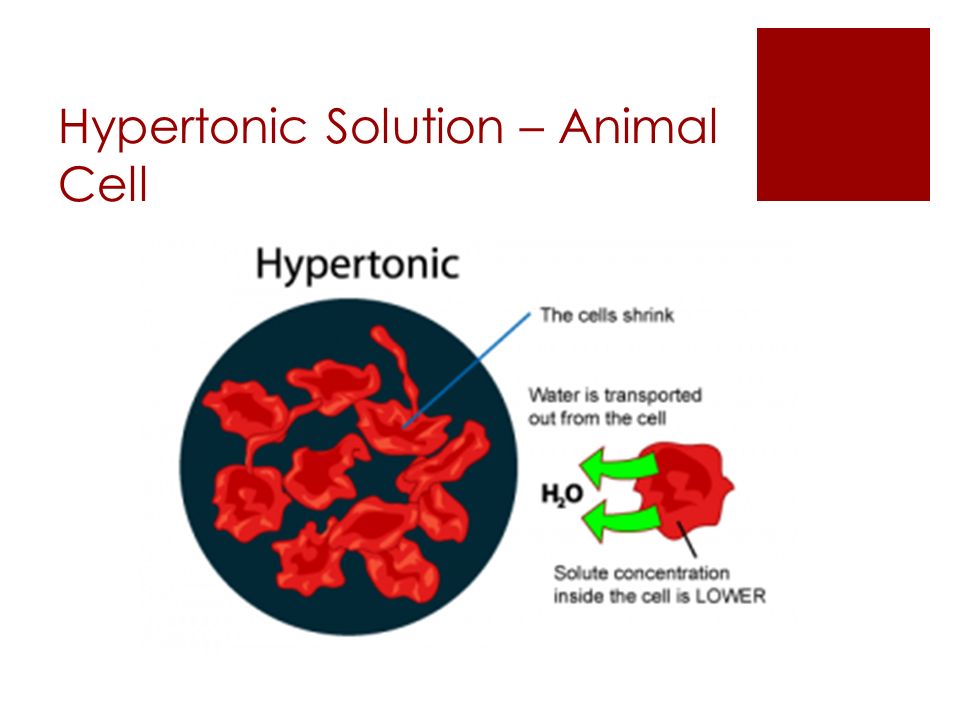
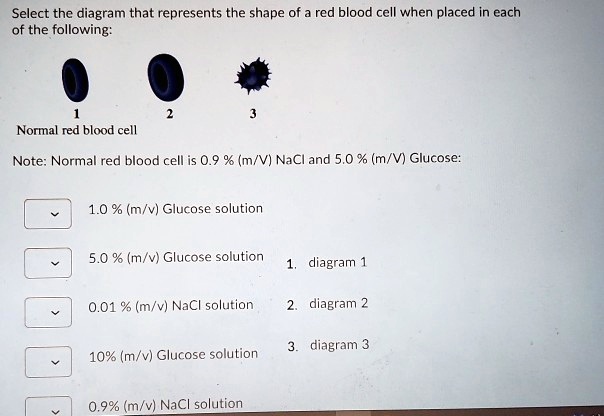
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 3 Test Bank Flashcards - Quizlet in diagram, which one represents hypertonic solution a. A b. B c. C d. both B & C e. all choices are correct. ... red blood cells are in osmotic equilibrium when they are in a 0.9% NaCl solution. rapid osmotic efflux of water will occur if a cell is placed in a _____ NaCl solution. rapid osmotic influx of water will occur if a cell is placed in ... Comparison of red blood cell morphology in isotonic ... Hypertonic solution: Water leaves the cells and the cells appear shriveled. Isotonic solution: Equal movement of water in and out of the cell and cells appear circular with indentions in the middle. Hypotonic solution: Water moves into the cells and cells appear larger, with one cell exploding. Prasanna - Page 76 - HSSLive Guru The diagram below shows the cells placed in hypertonic solution and hypotonic solution. If the diagram 'B' is 'turgid' what will be diagram 'A'? Answer: A - Flaccid. Question 16. The excess of one element may inhibit the uptake of another element. What is this effect called? Answer: Toxicity of micronutrients. Question 17.
In the diagram, which one represents a hypertonic solution. cosmo-kasino350.de › 8[email protected] - cosmo-kasino350.de The last one is the 18 th Remember your alphabet is different from the English one. Grade 4. radiate from the cell center 4. 12 to answer questions a and b. Worksheets are Accounting, Grade 8 ems accounting booklet 2020, Accounting grade 8 exam and answer, Grade 8 ems june exam, Economic and management sciences grade 8, Accounting basics part 1 ... Biology Questions and Answers - Form 1 End Term 3 2022 ... The diagram below represents the digestive system in man. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow Label the part K ,L, S and salivary glands M and P (5rnks) Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Kangundo Subcounty ... Give one reason in each case for the results obtained in the tubes kept at: 0ºc (1mk) 50ºc (1mk) Suggest the time it would take amylase to digest starch if the temperature is kept at 00c (1mk) The diagram below represents an organ from the body of a fish. Study it and answer the questions that follow. Passive And Active Transport Venn Diagram - Studying Diagrams Explain the differences between hypotonic isotonic and hypertonic solutions. Ahmed makes a Venn diagram to compare active transport and passive transport across the cell membrane. Which label belongs in the region marked x. 2 Draw a picture in the appropriate section which represents passive and active transport.
Test Bank - Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 12th ... In the diagram, which one represents facilitated diffusion? a. A b. B c. C d. Both a and c e. Both b and c Ans: E Difficulty: easy Feedback: 3.3 62. In the diagram, which one represents a hypertonic solution? a. A b. B c. C d. Both b and c e. Please click on the following link to fill out the survey ... If the concentration of solute is not equal, hypotonic describes the side with a lower concentration of solute and hypertonic describes the solution with a higher concentration of solute. Use the questions below to practice using these terms. 10. The diagram to the right depicts a cell submerged in a solution. CH103 – Chapter 8: Homeostasis and Cellular Function ... Osmotic pressure is a measure of the tendency of water to move into one solution from another by osmosis. The higher the osmotic pressure of a solution the more water wants to go into the solution. The kidneys are used to remove excess ions (such as Na +, K + and Ca 2+) from the blood, thus affecting the osmotic pressure. These are then expelled as urine. The kidneys are … Saline irrigation for allergic rhinitis - PMC 22/06/2018 · Tonicity of saline solution (hypertonic, isotonic and hypotonic solutions). There is some evidence in other conditions that tonicity may have an effect on the efficacy of nasal saline Berjis 2011; Rabago 2005). Alkalinity of saline solution. There is evidence that increased alkalinity of the saline solution improves some nasal symptoms (Chusakul 2013). Participant …
Test Bank - Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 12th ... Test Bank - Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 12th Edition, by Bryan Derrickson, Gerald Tortora. Test bank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B Difficulty: easy Feedback: 1.1 2. This is defined as a group of cells with similar structure ... What happens to a animal cell placed in a hypotonic solution Hypotonic solution is a solution which, contains lesser solute concentration. If animal and plant cells are kept in a hypotonic solution then endosmosis will occur. Endosmosis is a process in which the water molecules move from outside of the cell of lower solute concentration to the inside of the cell of higher solute concentration through the ... Frank Chapter 4 Absorption by Roots ICSE Solutions Class ... 21. The diagram given below represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Guidelines 1 to 5 indicate the following: 1. Strong sugar solution 2. Cell wall 3. Protoplasm 4. Large vacuole 5. Nucleus Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow: (i) What is the state of the cell shown in the diagram? Absorption by Roots ICSE Class-10 Concise ... - ICSEHELP Question 1. Name the following: (a) The condition of a cell placed in a hypotonic solution. (b) Process by which intact plants lose water in the form of droplets from leaf margins. (c) Process by which water enters root hairs. (d) The tissue concerned with upward conduction of water in plants. (e) The term for the inward movement of solvent ...
Cell Biology Questions and Answers - Study.com Cell Biology Questions and Answers. Get help with your Cell biology homework. Access the answers to hundreds of Cell biology questions that are explained in …
Week 3: Membrane Transport Flashcards & Practice Test ... Start studying Week 3: Membrane Transport. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Hypertonic Solution: Definition, Effect & Example - Video ... With its salt content, seawater is considered to be a hypertonic solution. A hypertonic solution will do just the opposite to a cell since the concentration of solutes is greater outside of the...
Growth of Microorganisms: 6 Factors - Biology Discussion Water is one of the most essential requirements for life. Thus, its availability becomes most important factor for the growth of microorganisms. The availability of water depends on two factors — the water content of the surrounding environment and the concentration of solutes (salts, sugars, etc.) dissolved in the water. In most cases, the cell cytoplasm possesses higher solute ...
History of cell membrane theory - Wikipedia Cell theory has its origins in seventeenth century microscopy observations, but it was nearly two hundred years before a complete cell membrane theory was developed to explain what separates cells from the outside world. By the 19th century it was accepted that some form of semi-permeable barrier must exist around a cell. Studies of the action of anesthetic molecules led to …
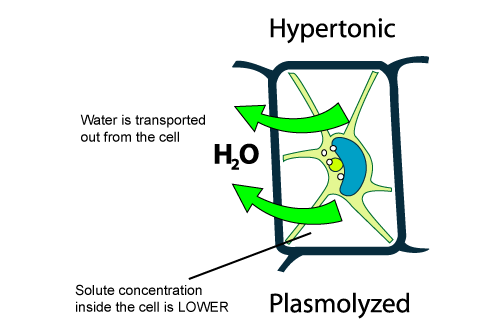
Diagram Of Plant Cell In Hypertonic Solution - Studying ... Diagram of plant cell in hypertonic solution. If you place an animal or a plant cell in a hypertonic solution the cell shrinks because it loses water water moves from a higher concentration inside the cell to a lower concentration outside.
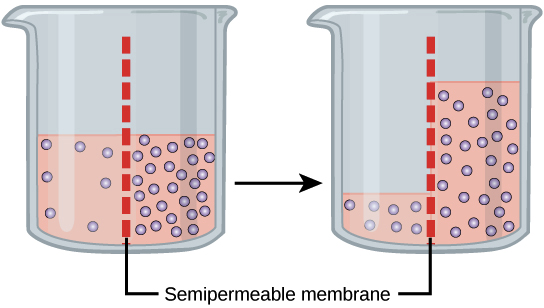
What is Osmosis: Definition, Diagram, Examples and Explanation What is Osmosis? By definition, osmosis is the movement of any solvent through a selectively permeable membrane into an area of higher solute concentration, the result of which will be an equalizing of solute concentration on either side of the membrane.. This equilibrium is important for the efficient and optimized function of cells; as mentioned before, balance is the preferred state in a ...
Maharashtra Board Class 12 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 2 ... If π B is greater than π A, then the solution B is a hypertonic solution with respect to the solution A. Hence, if C A and C B are their concentrations, then C B > C A. Hence, for equal volume of the solutions, n B > n A. Question iii. A solvent and its solution containing a nonvolatile solute are separated by a semipermable membrane.
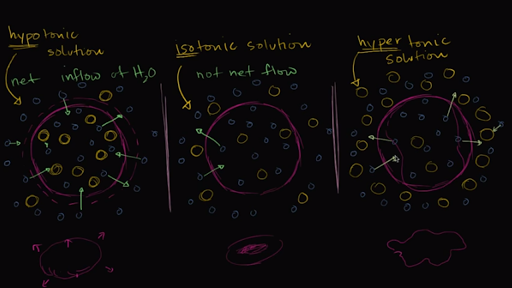
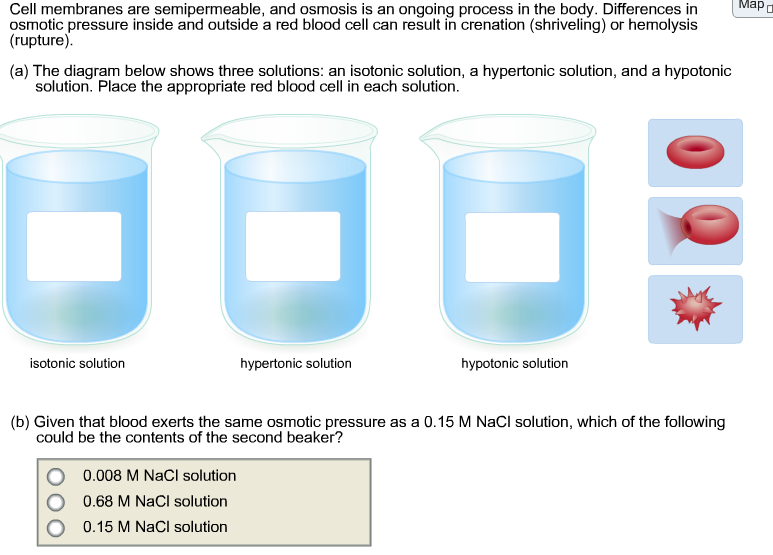
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is the ... A solution in which the concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside of a cell is a solution: * hypertonic hypotonic isotonic None of the above. Answers: 3 Show answers Another question on Biology. Biology, 21.06.2019 20:40 ...
Which diagram best represents the - Brainly.com Which diagram best represents the ... In a hypertonic solution, a bacterial cell will typically:. ... I identify a producer, a consumer and a decomposer and give one justification for your answer. b.From the list of observation and noted organism,Describe how each of the organism interacted with the system.
Module_4_HW BIO 111.pdf - BIO 111 Module 4 HW Chapter 5 ... The below picture represents diffusion of molecules. ... Hypotonic Hypertonic Hypertonic If a hypertonic solution is used water will flow out of the brain and release pressure. ... Place the labels "hypertonic" and "hypotonic" in your diagram. One label should be for the gummy bears and one label should be for the water. 5.
Crystalloid Fluids - StatPearls - NCBI ... - NCBI Bookshelf Crystalloid fluids are a subset of intravenous solutions that are frequently used in the clinical setting. Crystalloid fluids are the first choice for fluid resuscitation in the presence of hypovolemia, hemorrhage, sepsis, and dehydration. Further clinical applications include acting as a solution for intravenous medication delivery, delivering maintenance fluid in patients with limited or no ...
Form 1 Biology End Term 2 Exams Plus Marking Schemes ... The diagram below represents a set up that was used to investigate a certain process in a plant. State the aim of the experiment.(1mk) State a factor that would affect the process.(1mk) State the importance of nucleic acids to an organisms.(1mk) State the significance of the following to a leaf:-Thinness(1mk) Presence of air spaces(1mk)
What Happens When You Put Salt Water On An Onion Cell ... Explanation: Adding salt solution to the onion cells causes water to diffuse out of the cell (salt does not diffuse). Water diffused into the cell because there was a higher concentration of water outside of the cell than inside of the cell SEE DIAGRAM 2.
quizlet.com › 475043076 › prokaryotic-and-eukaryoticProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Flashcards | Quizlet 3) Which of the following statements best describes what happens when a bacterial cell is placed in a solution containing 5% NaCl? A) Sucrose will move into the cell from a higher to a lower concentration. B) The cell will undergo osmotic lysis. C) Water will move out of the cell. D) Water will move into the cell.
Onion and Cheek Cells (Theory) : Class 9 : Biology ... Onion Cell. An onion is a multicellular (consisting of many cells) plant organism. As in all plant cells, the cell of an onion peel consists of a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus and a large vacuole. The nucleus is present at the periphery of the cytoplasm. The vacuole is prominent and present at the centre of the cell.
TN Board 11th Bio Botany Important Questions Chapter 11 ... What happens if a plant cell is treated with a hypertonic solution? Answer: When a plant cell is kept in a hypertonic solution, water leaves the cell due to exosmosis. As a result of water loss, protoplasm shrinks and the cell membrane is pulled away from the cell wall and finally, the cell becomes flaccid. This process is named plasmolysis.
Hypotonic Solution: Definition, Example & Diagram - Video ... A solution can be labeled one of three ways when it is compared to another solution. First, it may be considered an isotonic solution, meaning it has an equal amount of solute and water when...
BIOLOGY FORM ONE NOTES FREE - Educationnewshub.co.ke 08/03/2022 · This is the process where solvent molecules (water) move from a lowly concentrated solution (dilute) to a highly concentrated solution across a semi-permeable membrane. Diagram fig 4.6. The highly concentrated solution is known as Hypertonic Solution. The lowly concentrated solution is called Hypotonic solution.
MCQ Absorption by Roots for ICSE Class-10 Biology - ICSEHELP (c) 5%% sugar solution (d) Isotonic solution. Answer (d) Isotonic solution. Question 11 : Cell slightly enlarges or bursts when kept in (a) Hypertonic solution (b) Hypotonic solution (c) Isotonic solution (d) Pond water. Answer (b) Hypotonic solution. Question 12 : The diagram represents two liquids, separated by a membrane through which ...
Absorption by Roots Class 10 Biology ICSE ... - ICSE Solutions (ii) Hypertonic solution (iii) (1) Nucleus, (2) Sugar drops, (3) Small vacuole, (4) Large vacuole. (iv) Plant cell (1) Presence of cell wall, (2) Presence of large vacuole. (v) It has to be placed in a hypotonic solution. Question 4: The below diagram represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Guidelines 1 to 5 ...
Cell Biology - Wiki - Scioly.org 08/10/2021 · In the diagram of maltodextrin, this is shown by placing the monomer (in this case, ... DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is one of two long molecules known as nucleic acids, which code for the genetic information found within cells. It is made up of molecules known as nucleotides, which are made up of a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a deoxyribose sugar. The …
Bacterial Cell Walls Function & Parts | What is a ... 27/01/2022 · A bacterial cell represents a hypertonic solution, in contrast to the hypotonic solution surrounding it. There is always a risk of water …
Extracellular Osmolarity and Cell Volume - Body Function Solutions containing greater than 300 mOsm of nonpenetrating solutes (hypertonic solutions) cause cells to shrink as water diffuses out of the cell into the fluid with the lower water concentration. Note that the concentration of nonpenetrating solutes in a solution, not the total osmolarity, determines its tonicity —hypotonic, isotonic, or ...
Prasanna - Page 76 - HSSLive Guru The diagram below shows the cells placed in hypertonic solution and hypotonic solution. If the diagram 'B' is 'turgid' what will be diagram 'A'? Answer: A - Flaccid. Question 16. The excess of one element may inhibit the uptake of another element. What is this effect called? Answer: Toxicity of micronutrients. Question 17.
Comparison of red blood cell morphology in isotonic ... Hypertonic solution: Water leaves the cells and the cells appear shriveled. Isotonic solution: Equal movement of water in and out of the cell and cells appear circular with indentions in the middle. Hypotonic solution: Water moves into the cells and cells appear larger, with one cell exploding.
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 3 Test Bank Flashcards - Quizlet in diagram, which one represents hypertonic solution a. A b. B c. C d. both B & C e. all choices are correct. ... red blood cells are in osmotic equilibrium when they are in a 0.9% NaCl solution. rapid osmotic efflux of water will occur if a cell is placed in a _____ NaCl solution. rapid osmotic influx of water will occur if a cell is placed in ...
/GettyImages-112706652-58980a3c5f9b5874eed738d1.jpg)























0 Response to "38 in the diagram, which one represents a hypertonic solution"
Post a Comment