39 pauli exclusion principle diagram
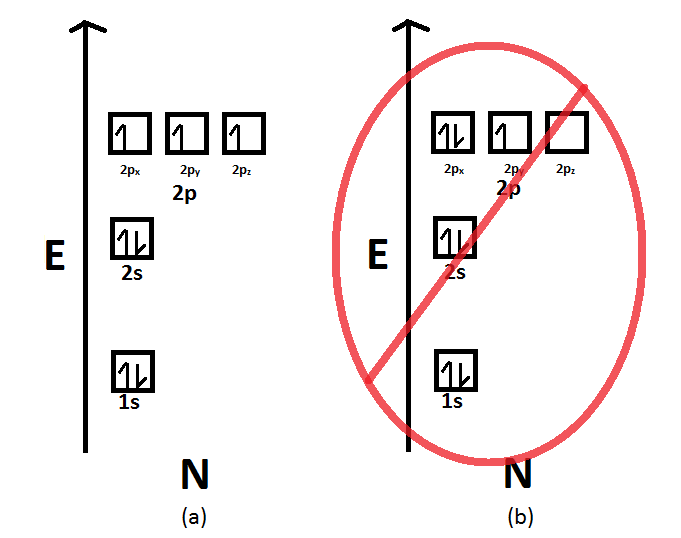
The Pauli exclusion principle dictates that no two electrons in an interacting system may have the same quantum state. If the bonding orbitals are filled, then any additional electrons will occupy antibonding orbitals. This occurs in the He 2 molecule, in which both the 1sσ and 1sσ* orbitals are filled. Since the antibonding orbital is more antibonding than the bonding orbital is bonding ... There are exceptions to Aufbau principle and Hund's Rules, but not the Pauli ... Pauli exclusion principle: |1,0,0,½> and |1,0,0,-½> ... Li Grotrian Diagram.36 pages
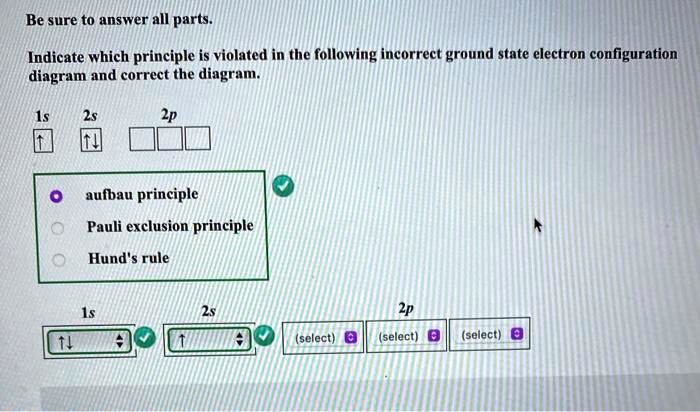
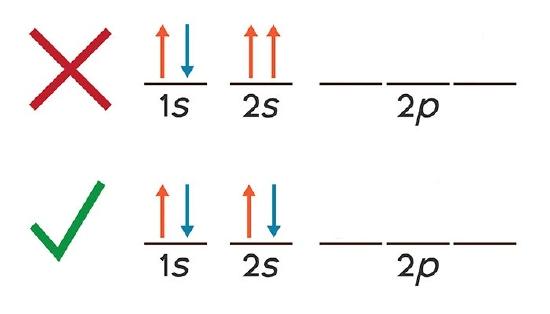
In this diagram representing the electrons in carbon, the top two images are correct distributions of electrons in the 2p subshell, and the ...11 May 2021 · Uploaded by The Study.com Video Team
Pauli exclusion principle diagram
Pauli Exclusion Principle. The Pauli exclusion principle requires that the bare scattering rate given by Eqn. (17) be modified by a factor 1−fm(k′) in the collision integral of the BTE, where fm(k′) is the one-particle distribution function for the state k′ in band (subband) m after scattering. The energy level diagram below shows sublevels to as high as the energy level of the 5f orbitals. Sublevels actually continue to higher energies than this, but 5f is a suitable place to leave an introductory description. Naming the Subshells/Sublevels. Electron sublevels are known by the letters s, p, d, and f. So, for example, electrons in the s sublevel of shell 3 have a different … Asymmetry energy (also called Pauli Energy). An energy associated with the Pauli exclusion principle . Were it not for the Coulomb energy, the most stable form of nuclear matter would have the same number of neutrons as protons, since unequal numbers of neutrons and protons imply filling higher energy levels for one type of particle, while leaving lower energy levels vacant for …
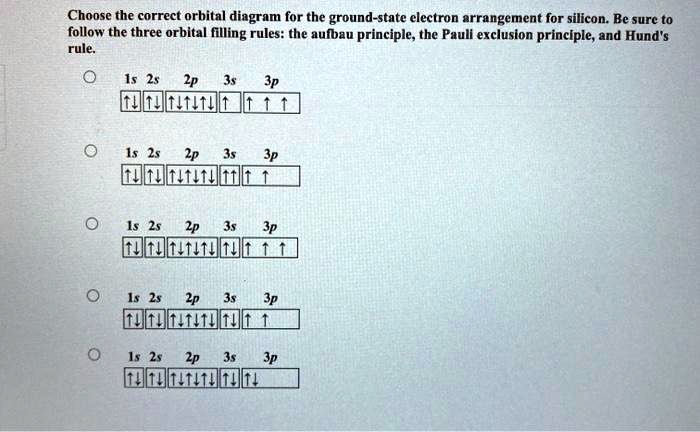
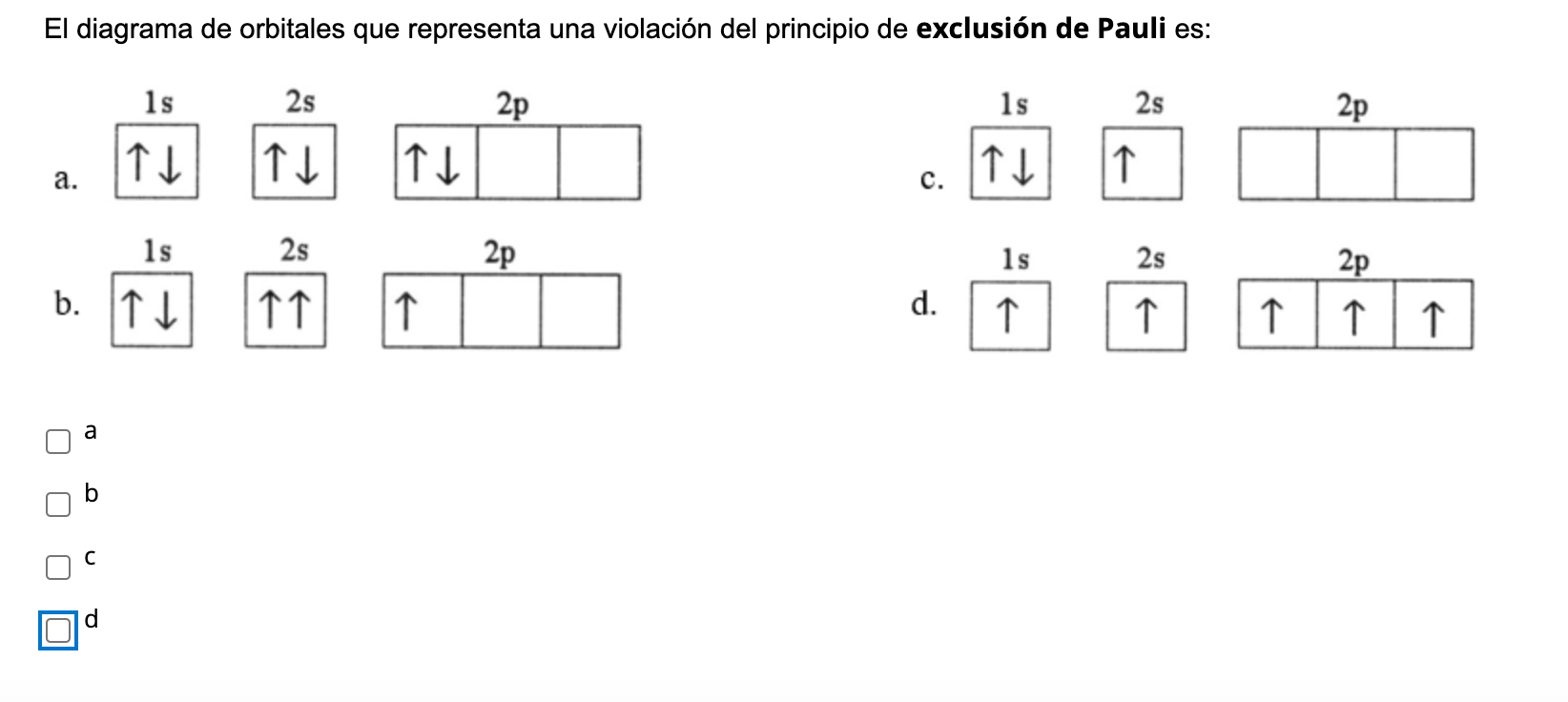
Pauli exclusion principle diagram. Pauli Exclusion Principle, Aufbau Principle and Hund's Rule ... Which of the rules do each of the following electron energy diagrams violate? 18 Apr 2021 — The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that, in an atom or molecule, no two electrons can have the same four electronic quantum numbers. 10 Dec 2016 — Pauli Exclusion Principle: no two electrons can be identified by the ... do a lot of work with electron configurations and energy diagrams.1 answer · • Aufbau Principle: lower energy orbitals fill before higher energy orbitals. • Hund's Rule: one electron goes into each until all of them are half ... Three principles explain the process of filling electrons in subsequent levels, namely the Pauli-exclusion Principle, Aufbau Principle, and Hund’s Rule. Degenerate Orbitals Example. Here is a degenerate orbitals example that will help students to understand the degenerate orbital meaning more clearly. Example: An atom has four orbitals, namely s, p, d, and f. The p orbital …
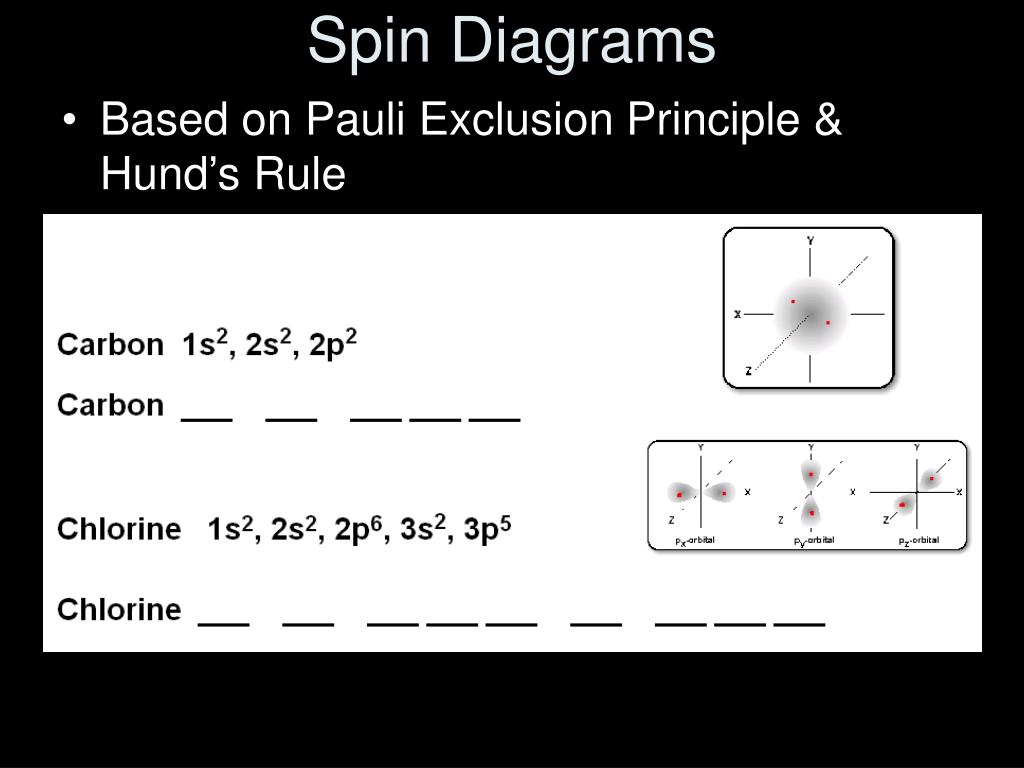
Explain the Pauli exclusion principle and its application to the atom. ... Diagram illustrating the components of the expression 2 times p to the third ... The diagram below really shows the overlap of the Principal Energy Levels. on to Sublevels and the Periodic Table. Electrons and Sublevels Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Writing Electron Configurations Box and Arrow Configurations using Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund's Rule Quantum Numbers. ... Fermi-Dirac statistics is the branch of quantum statistics, that describes the distribution of particles in energy states that contains identical particles obeying Pauli-Exclusion Principle. Since F-D statistics is applied to particles with half-integer spin, these are called fermions. The Aufbau principle can be used to understand the location of electrons in an atom and their corresponding energy levels. For example, carbon has 6 electrons and its electronic configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2. It is important to note that each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons (as per the Pauli exclusion principle).
According to the Pauli exclusion principle, each new electron occupies the lowest energy subshell available, subject to the constraints imposed by the allowable quantum numbers. Only after lower-energy subshells have been filled to capacity do electrons enter higher-energy subshells. Share . aufbau principle diagram. Consider the electron arrangement of carbon, an … 005 - Electron ConfigurationIn this video Paul Andersen explains how to write out the electron configuration for atoms on the periodic table. More important... The Pauli exclusion principle states that in a single atom no two electrons will have an identical set or the same quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms). To put it ... Asymmetry energy (also called Pauli Energy). An energy associated with the Pauli exclusion principle . Were it not for the Coulomb energy, the most stable form of nuclear matter would have the same number of neutrons as protons, since unequal numbers of neutrons and protons imply filling higher energy levels for one type of particle, while leaving lower energy levels vacant for …
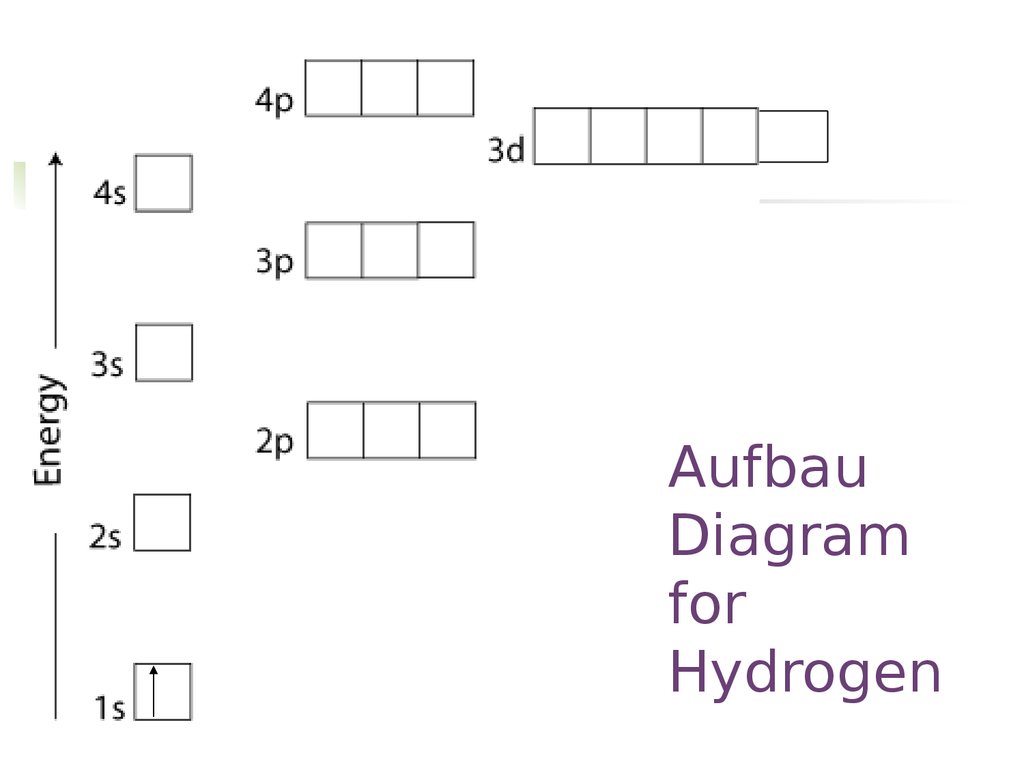
The energy level diagram below shows sublevels to as high as the energy level of the 5f orbitals. Sublevels actually continue to higher energies than this, but 5f is a suitable place to leave an introductory description. Naming the Subshells/Sublevels. Electron sublevels are known by the letters s, p, d, and f. So, for example, electrons in the s sublevel of shell 3 have a different …
Pauli Exclusion Principle. The Pauli exclusion principle requires that the bare scattering rate given by Eqn. (17) be modified by a factor 1−fm(k′) in the collision integral of the BTE, where fm(k′) is the one-particle distribution function for the state k′ in band (subband) m after scattering.






















0 Response to "39 pauli exclusion principle diagram"
Post a Comment