37 fatty acid structure diagram
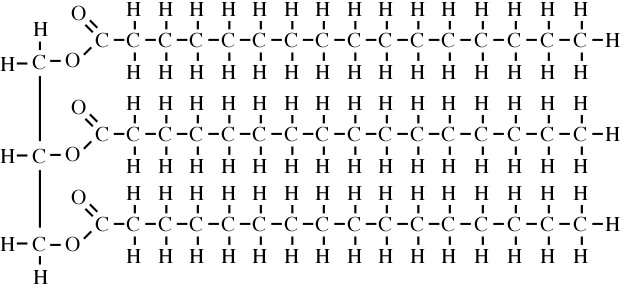
Fatty Acids: Definition, Structure, Function & Types ... Fatty Acid Structure Fatty acids are composed of carbon chains containing a methyl group at one end and a carboxyl group at the other. Fatty acid - Wikipedia Three-dimensional representations of several fatty acids. Saturated fatty acids have perfectly straight chain structure. Unsaturated ones are typically bent, unless they have a trans configuration. In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated.
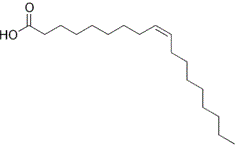
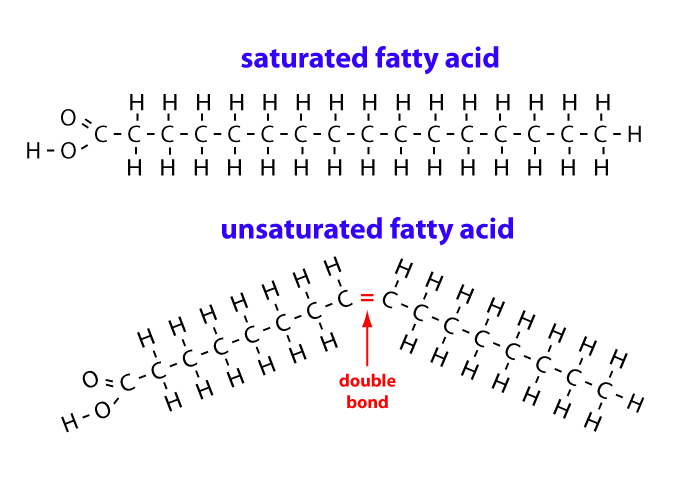
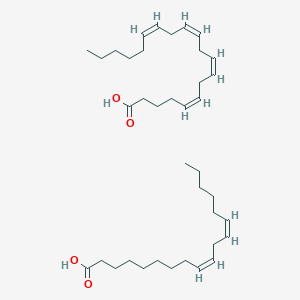
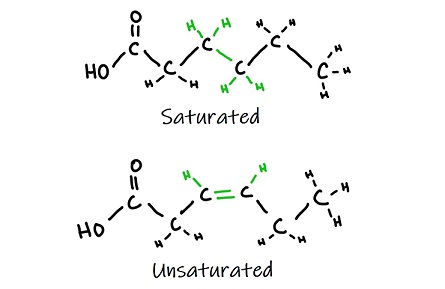
Notes on Fatty Acids (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion In unsaturated fatty acids, at least two but usually no more than six of the carbon atoms of the hydrocarbon chain are linked together by double bonds. The two most common unsaturated fatty acids are oleic acid and linoleic acid, depicted in Figure 6-1 along with the saturated fatty acid stearic acid.

Fatty acid structure diagram
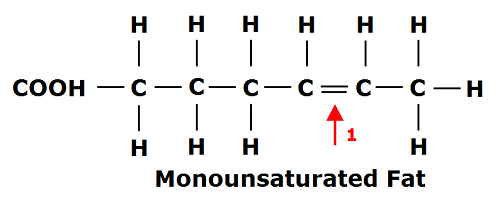
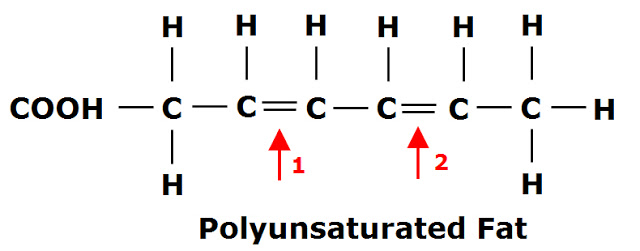
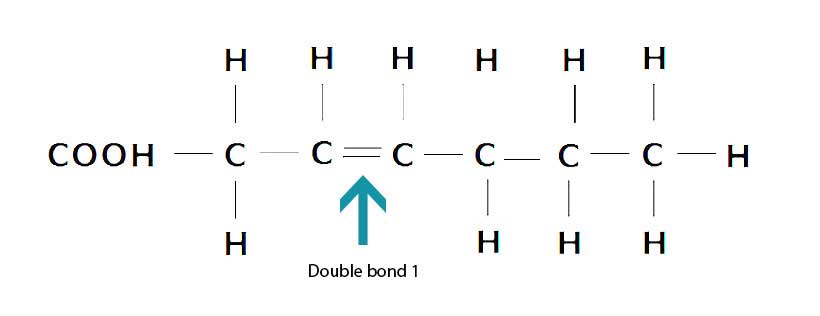
The Benefits of Monounsaturated Fatty Acids To illustrate this, the diagram below shows the chemical structure of a monounsaturated fatty acid; The chemical structure of a monounsaturated fatty acid, showing the double carbon bond. As you can see, there is a double bond between two carbon (C) atoms instead of those carbon atoms being bound to hydrogen (H). Biologicial molecules Flashcards - Quizlet (c) Olestra is an artificial lipid. It is made by attaching fatty acids, by condensation, to a sucrose molecule. The diagram shows the structure of olestra. The letter R shows where a fatty acid molecule has attached. (i) Name bond X. (1) Solved Section Short Questions (26 marks) 1. The diagram ... The diagram shows a structure of a lipid molecule. (Total 5 marks) a. What is the name of this type of lipid? (1 mark) b. How many ester bonds are present in this molecule? (1 mark) c. After the lipid molecule above is fully hydrolysed, the polyunsaturated fatty acid enters B-oxidation How many rounds of B-oxidation
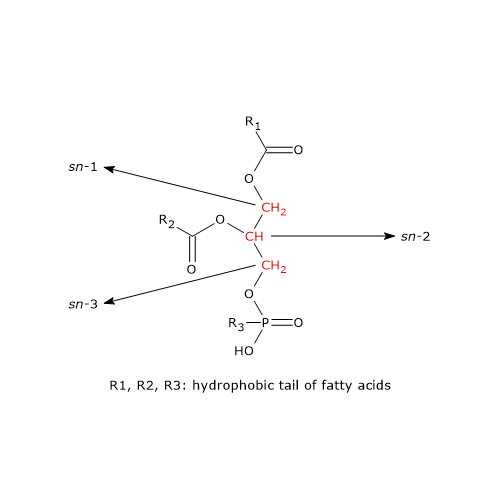
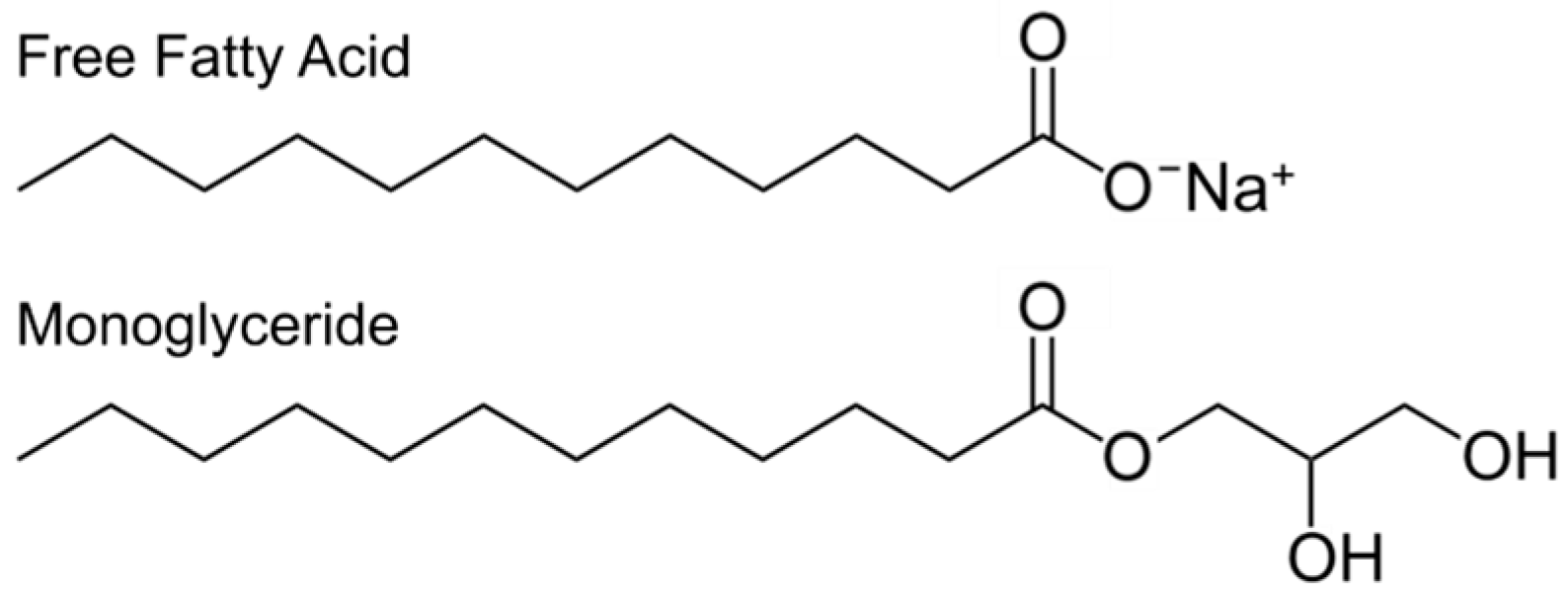
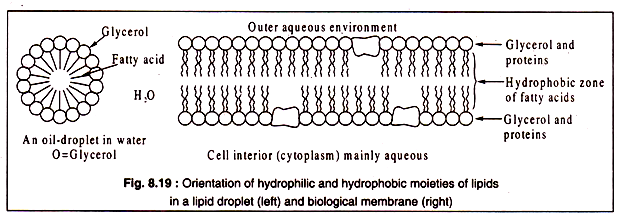
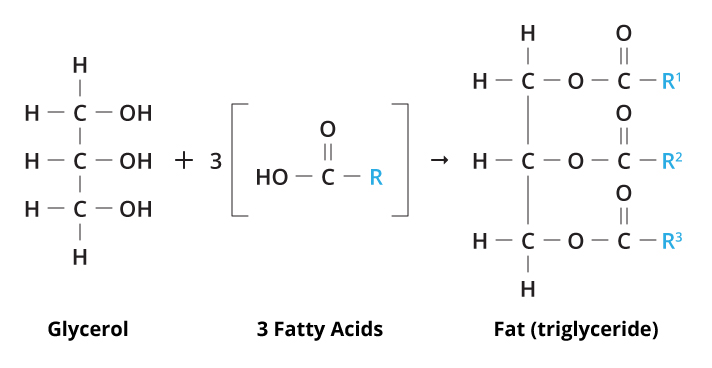
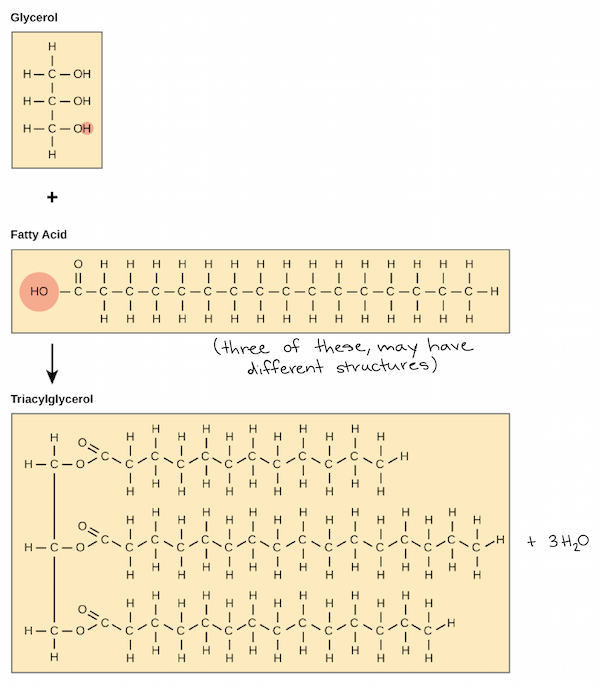
Fatty acid structure diagram. 9.1 Terminology for Vegetable Oils and Animal Fats | EGEE ... Animal fats tend to have more free fatty acids than vegetable oils do. Chemically, fats and oils are also called "triglycerides." They are esters of glycerol, with a varying blend of fatty acids. Figure 9.1 shows a generic diagram of the structure without using chemical formulas. Solved Sketch the block diagram for a phospholipid. Drag ... Chemistry questions and answers. Sketch the block diagram for a phospholipid. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Glycerol Secondary protein structure Glycerol Fatty acid Phosphate. Question: Sketch the block diagram for a phospholipid. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Lipid Structures And Functions | A-Level Biology Revision ... Lipid structures. The structure of the fatty acids influences the structure of the lipid. In the fatty acid chains, the carbon atoms could have single bonds between them making the lipid "saturated".This generates fats that are usually solid at room temperature.. Alternatively, if one or more of the bonds between the carbon atoms are double bonds, the lipid is said to be "unsaturated". Fatty Acid Structure | Saturated Fatty Acid Structure ... The fatty acids structure are chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms that are linked together. They are linear chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms. There is a carboxyl group at the end of the fatty...
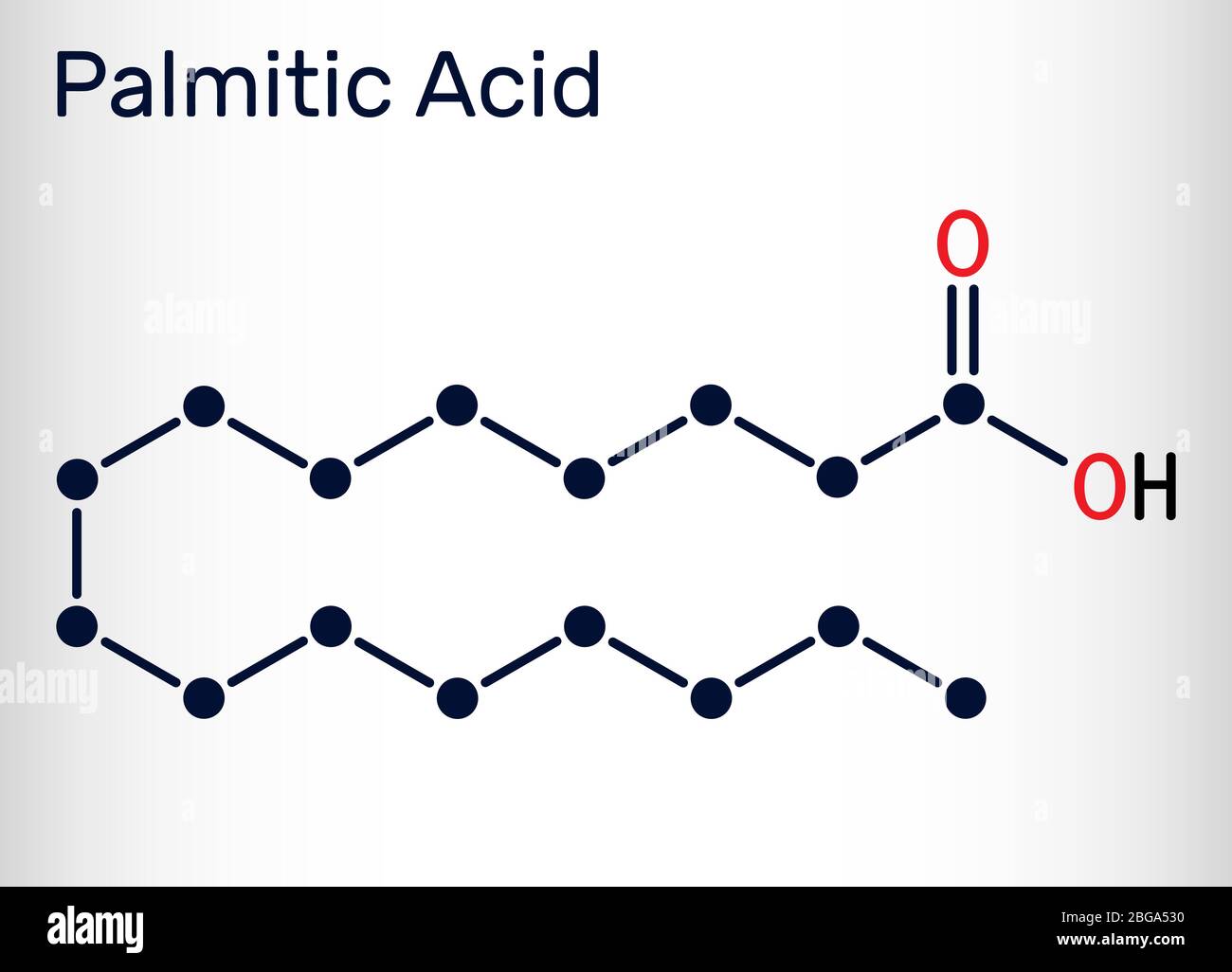
Lipids and It's Types (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The fatty acid is called an acyl group when it is a part of ester. In biological systems, fatty acids usually contain an even number of carbon atoms, typically between 14 and 24. The most common fatty acids have 16-18 carbon and 0-3 double bonds. For example, plamitic (C16), stearic (C18), oleic (C18), linoleic (C18) etc. ADVERTISEMENTS: PDF (2) (1) (c) Olestra is an artificial lipid. It is made by attaching fatty acids, by condensation, to a sucrose molecule. The diagram shows the structure of olestra. The letter R shows where a fatty acid molecule has attached. (i) Name bond X. _____ (1) fatty acid | Definition, Structure, Functions, Properties ... fatty acid, important component of lipids (fat-soluble components of living cells) in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Generally, a fatty acid consists of a straight chain of an even number of carbon atoms, with hydrogen atoms along the length of the chain and at one end of the chain and a carboxyl group (―COOH) at the other end. It is that carboxyl group that makes it an acid ... Fatty Acid Structure | Examples | Types | Physical ... Fatty acids are composed of long hydrocarbon chains terminated by carboxylic acid groups. Fatty acids are basically the primary derivative of lipids. Chain length from 4 to usually 24C atoms. They contain even number of C atoms majority of fatty acids are those containing 16 and 18 C atoms. Fatty Acid Structure Described Below.
Saturated Fatty Acid: Structure, Formula & Example - Video ... Lauric Acid Another way to draw the fatty acid above - lauric acid - is illustrated below. Instead of writing each carbon and hydrogen atom, they are replaced with a zigzag line. Each edge of the... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Revisited: Structure Elucidation ... Fatty acids are primary metabolites synthesized by complex, elegant, and essential biosynthetic machinery. Fatty acid synthases resemble an iterative assembly line, with an acyl carrier protein conveying the growing fatty acid to necessary enzymatic domains for modification. ... 2VZ8) structure with a diagram below of the domain organization ... The diagram shows the general structure of a lipid, which ... The diagram shows the general structure of a lipid, which consists of two main parts. The part that is circled is the fatty acid carboxyl group. -Lipids is one of the four important biomolecules, others being, nucleic acid, carbohydrates, and proteins. -Lipids are made of glycerol and fatty acids. Fatty acids consist of a carboxylic acid (-C=O ... PDF Fatty Acids: Structures and Introductory article Properties The influence of a fatty acid's structure on its melting point is such that branched chains and cis double bonds will lower the melting point compared with that of equiv-alent saturated chains. In addition, the melting point of a fatty acid depends on whether the chain is even- or odd-numbered; the latter have higher melting points.
Fatty acids: definition, structure, and classification Fatty acids (FAs) are a class of lipids consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, arranged as a linear carbon chain skeleton of variable length, generally with an even number of atoms, with a carboxyl group at one end.
Structure of the human fatty acid synthase KS-MAT didomain ... The human fatty acid synthase (FAS) is a key enzyme in the metabolism of fatty acids and a target for antineoplastic and antiobesity drug development. Due to its size and flexibility, structural studies of mammalian FAS have been limited to individual domains or intermediate-resolution studies of th …
PDF Fatty Acid Biosynthesis - California State University ... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis 4 Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS) • FAS is a polypeptide chain with multiple domains, each with distinct enzyme activities required for fatty acid biosynthesis. •ACP: Recall that CoA is used as an activator for β-oxidation. For fatty acid biosynthesis, the activator is a protein called the acyl carrier protein (ACP).
Structure of Fatty Acids | Download Scientific Diagram Download scientific diagram | Structure of Fatty Acids from publication: Technical Note 101 | | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
Fatty Acids -- Overview - University of Utah Overview The elements of fatty acid structure are quite simple. There are two essential features: A long hydrocarbon chain The chain length ranges from 4 to 30 carbons; 12-24 is most common. The chain is typically linear, and usually contains an even number of carbons. A carboxylic acid group
Trans fatty acids: definition, structure, health effects ... Unsaturated fatty acids most commonly have their double bonds in cis configuration; the other, less common configuration is trans. Cis bond causes a bend in the fatty acid chain, whereas the geometry of trans bond straightens the fatty acid chain, imparting a structure more similar to that of saturated fatty acids. CONTENTS
FATTY ACIDS | Biology - Quizizz Q. The diagram shows the structure of palmitic acid. What type of fatty acid is palmitic acid? (apply knowledge using the picture)
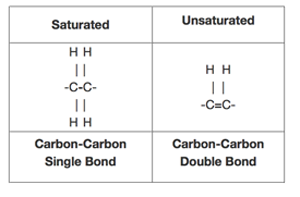
structure fatty acid Flashcards and Study Sets | Quizlet fatty acid structure. saturated fatty acid have. all the available bonds in a saturated…. unsaturated fatty acids have. the double bonds makes the. a single bond between carbons in the hydrocarbon chain. are saturated with hydrogen. double bonds between carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain. molecule bends which means they cannot pack ...
Structure of unsaturated fatty acids in 2D system The behaviour of Langmuir monolayers corresponding to unsaturated fatty acids belonging to the omega-9 (oleic acid), omega-3 (α-linolenic and stearidonic acids) and omega-6 (linoleic, γ-linolenic and eicosadienoic acids) series was studied in order to get insight into the influence of various factors (such as subphase temperature, length, degree of unsaturation and position of the double ...
Fatty Acids - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Fatty acids consist of a long hydrocarbon chain (-CH 2 -CH 2 -) with a carboxyl group, typically at the terminus of the molecule. The hydrocarbon chain can be saturated or unsaturated (containing double bonds) depending on the origin of the fatty acid.
Structure of Fatty Acids | Download Scientific Diagram Analysis of fatty acid profiles showed iso-C15:0, anteiso-C15:0, C16:0, C18:1 ω9c, and iso-C17:0 3OH as the major fatty acids for all three strains and additionally C16:0 3OH for AN421T and AN502.
Solved Section Short Questions (26 marks) 1. The diagram ... The diagram shows a structure of a lipid molecule. (Total 5 marks) a. What is the name of this type of lipid? (1 mark) b. How many ester bonds are present in this molecule? (1 mark) c. After the lipid molecule above is fully hydrolysed, the polyunsaturated fatty acid enters B-oxidation How many rounds of B-oxidation
Biologicial molecules Flashcards - Quizlet (c) Olestra is an artificial lipid. It is made by attaching fatty acids, by condensation, to a sucrose molecule. The diagram shows the structure of olestra. The letter R shows where a fatty acid molecule has attached. (i) Name bond X. (1)
The Benefits of Monounsaturated Fatty Acids To illustrate this, the diagram below shows the chemical structure of a monounsaturated fatty acid; The chemical structure of a monounsaturated fatty acid, showing the double carbon bond. As you can see, there is a double bond between two carbon (C) atoms instead of those carbon atoms being bound to hydrogen (H).




















/carboxylic_acid-56a12b445f9b58b7d0bcb431.jpg)
0 Response to "37 fatty acid structure diagram"
Post a Comment