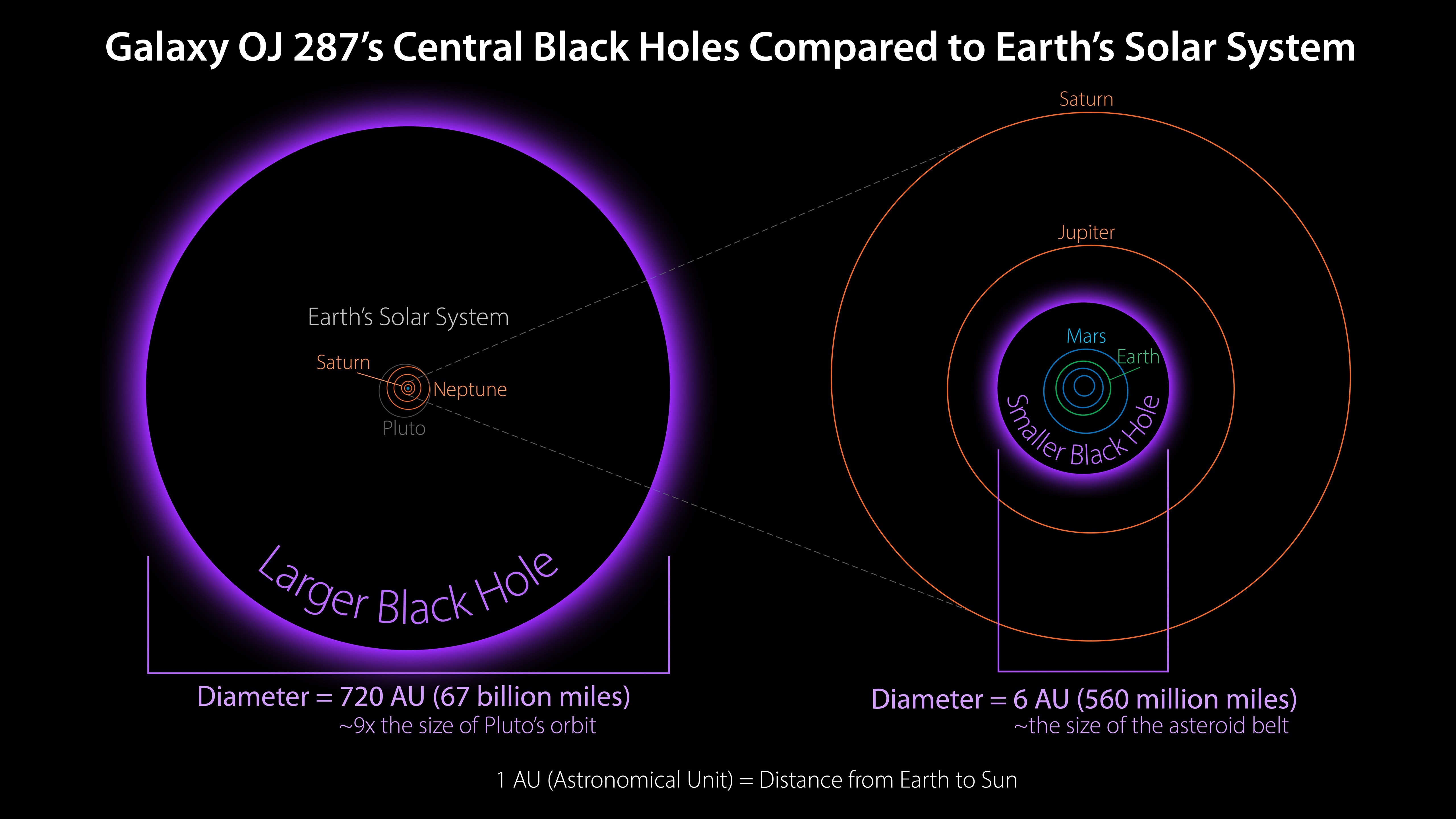
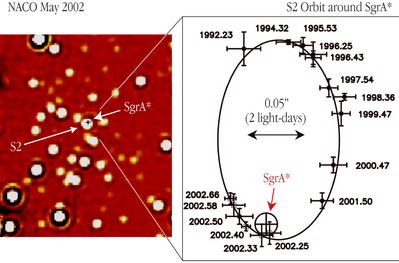
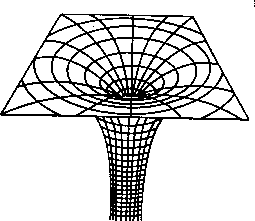
39 diagram of black hole
black hole | Definition, Formation, Types, Pictures, & Facts | Britannica black hole, cosmic body of extremely intense gravity from which nothing, not even light, can escape. A black hole can be formed by the death of a massive star. When such a star has exhausted the internal thermonuclear fuels in its core at the end of its life, the core becomes unstable and gravitationally... Black Hole Information Paradox: An Introduction | Of Particular... This article represents a lightning introduction to the black hole information paradox. Many details are omitted for brevity; longer articles will (eventually) explain them. Also, caution! the current understanding of the problem is so confused that the very last portion of this article should not be considered reliable...
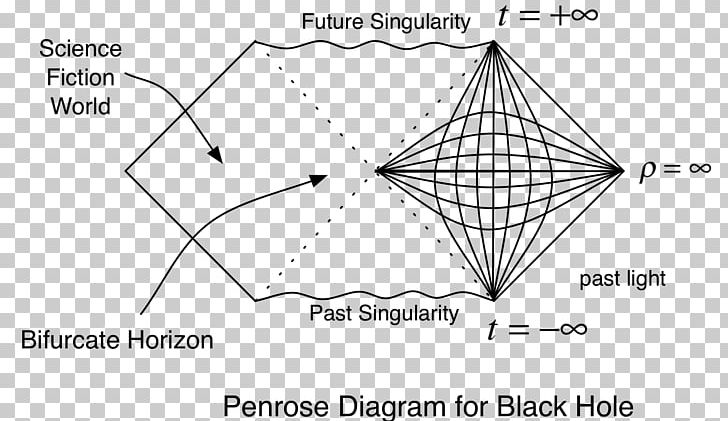
PDF Black holes and | Penrose Diagram of an Eternal Black Hole Early History of the Black Hole Concept. 1783 John Michell of Cambridge University suggested the possibility. 1796 Laplace calculated the mass needed for the escape velocity to equal the velocity of light. 1916 Karl Schwarzchild discovered a static sperically symmetric solution to Ein-stein's equation.

Diagram of black hole
Black Holes Black Hole Conditions. After collapse to the neutron star stage, stars with masses less than 2-3 solar masses should remain neutron stars, gradually radiating away their energy, because there is Once they collapsed past a certain radius, the "event horizon", then even light could not escape: black hole. Black Holes Might Lead to the Birth of New Universes | IE Black holes are one of the most tremendous destructive forces in the universe. And while opposites in magnetism attract, the concepts of creation Using two mathematical representations of the big bang and black holes — called the Penrose diagrams of expanding cosmology, and the Penrose diagram... PDF Hole Nonetheless, it is clearly a black hole: it has an event horizon and (in the rotating case) an inner horizon, it appears as the nal state of As in the case of the Kerr black hole, an innite number of such Kruskal patches may be joined together to form a maximal solution, whose Penrose diagram is shown.
Diagram of black hole. PDF Black holes from uid mechanics maps black holes on the gravitational side to the deconned phase of the dual gauge theory. When we put this together with the general lore that eld theories at Figure 1.2: Possible phase diagrams of black objects in D ≥ 6 dimensions. compactify the extended direction on a circle, this only occurs if the... PDF Black Hole Math The Nearest Stellar Black Holes The Nearest Supermassive Black Holes Exploring the Size and Mass of a Black Hole The Earth and Moon as Black Diagraming a Star Collapsing Into a Black Hole Light Cones Inside and Outside a Black Hole Black Holes that Rotate Exploring a Penrose Diagram... PDF Lectures on black holes Black holes and null hypersurfaces. A first definition of black holes. The event horizon as a null hypersurface. Kruskal-Szekeres coordinates in Schwarzschild spacetime. Standard (singular) Carter-Penrose diagram of Schwarzschild spacetime. How Building a Black Hole for 'Interstellar' Led to an Amazing... | WIRED This particular black hole is a simulation of unprecedented accuracy. It appears to spin at nearly the speed of light, dragging bits of the Thorne's diagram of how a black hole distorts light. Diagrams courtesy of Kip Thorne. Their success with the wormhole emboldened the effects team to try the same...
What are black holes? Facts, theory & definition. | Space Simulated view of a black hole in front of the Large Magellanic Cloud. (Image credit: Alain R. | Wikimedia Commons). Journey into a realistic black hole The black hole is intended to model the 4 million solar mass supermassive black hole at the center of our Galaxy, the Milky Way. As its Penrose diagram shows, in the Reissner-Nordström geometry ingoing and outgoing geodesics do in fact exceed the speed of light relative to each other, and cross... Black Holes and Quantum Gravity | Aurélien Barrau | Inference Might black holes provide a key? Aurélien Barrau claims that black holes are integral laboratories for the Although black holes were first imagined in the late eighteenth century, it was not until That singularity is represented as a horizontal line in the Penrose diagram of a Schwarzschild black hole... Singularities and Black Holes (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy) Black holes are regions of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. A typical black hole is the result of the gravitational force becoming so strong Such black holes generically contain a spacetime singularity at their center; thus we cannot fully understand a black hole without also...
7. the schwarzschild solution and black holes Also, the Penrose diagram for a collapsing star that forms a black hole is what you might expect, as shown on the next page. With that out of our system, we now turn to electrically charged black holes. These seem at first like reasonable enough objects, since there is certainly nothing to stop us... PDF notes.dvi | 2 Dynamical black holes Black holes and white holes Consider timelike paths that start in region I outside the r = 2M region.13 In a Penrose-Carter diagram, these have slope of But if II is a black hole, then what is III? Region III is in casual contact with I+, but note that it is not in future of I−. Also note that: It is impossible for any... (PDF) Properties of black holes and their searches at the LHC We presented the main properties of black holes and their evolution from macro to micro black holes. We considered Kruskal-Szekeres diagram representing the evolution of time in the form of hypersurfaces and stressed that the transition between the Universes is connected with the so-called... Black Holes What are Black Holes? A black hole is a region of space packed with so much matter that its own gravity prevents anything from escaping — even a ray of light. Although we can't see a black hole, the material around it is visible. Material falling into a black hole forms a disk...
PDF Black Holes and String Theory BH and WH mean black hole and white hole. +, − mean future and past null innity respectively, and i+, i− mean future and past timelike innity whilst i0 is spatial innity. Labels are left-right symmetric. Interpretation of the diagram and event horizon- example of null hypersurface.
Black hole - Wikipedia Part of a series of articles about. General relativity. Introduction. History. Mathematical formulation. Tests. v. t. e. A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing—no...
Conformal diagrams: stationary black holes - Universe in Problems In the context of black hole spacetimes there are many subtly distinct notions of horizons, with the most useful being different from those used in cosmology. In particular, particle horizons do not play any role.
Are black holes 4-dimensional? - Quora Penrose diagram of a Schwarzschild black hole. The properties of spacetime inside a black hole are entirely different from outside, space and time flows towards a singularity axis of black hole i.e space collapses and time flows in a reverse direction due to very strong gravity.
Loop Quantum Black Hole Extensions Within the Improved Dynamics . 3 Painlevé-Gullstrand Coordinates: Black Hole to White Hole Transition. We are interested in spatial slicings that are horizon penetrating and asymptotically FIGURE 1 . Penrose diagram of the effective geometry determined by the slicing in Eq. 3.1 . Black and green lines indicate low and high curvature...
PDF Particle Creation by Black Holes Thus black holes of this size would be absorbing radiation faster than they emitted it and would be increasing in mass. 3. The Penrose diagram of a spherically symmetric collapsing body producing a black hole. The vertical dotted line on the left represents the non-singular centre of the body.
Black Holes Black Holes. Homework for tomorrow's class. When a massive star runs out of fuel, its core collapses from the size of the Earth to a compact ball of Black Holes. If the core of a star contains only two or three solar masses of material when it collapses, the neutron degeneracy pressure -- that is, the...
PDF 6 The laws of black hole thermodynamics 3 Schwarzschild black holes. There is a classic set of black hole solutions in four dimensions. The innite size of the Penrose diagram implies that the r = Q hypersurface of an extremal Reissner-Nordstr¨om black hole is a Cauchy horizon.
What Is a Black Hole? Black holes are points in space that are so dense they create deep gravity sinks. Beyond a certain region, not even light can escape the powerful tug of a black hole's gravity. And anything that ventures too close—be it star, planet, or spacecraft—will be stretched and compressed like putty in a...
Kerr black holes images and videos White holes and antihorizons. Tying many universes together with the Carter-Penrose diagram. Some remarks about real black holes. A black hole in general is a region of space from which nothing, not even light, can escape the gravitational pull (or, to put things in a different way, clearer though...
An Introduction to Black Holes Black holes are objects in the universe with so much mass trapped inside their boundaries that they have incredibly strong gravitational fields. In fact, the gravitational force of a black hole is so strong that nothing can escape once it has gone inside.
PDF Hole Nonetheless, it is clearly a black hole: it has an event horizon and (in the rotating case) an inner horizon, it appears as the nal state of As in the case of the Kerr black hole, an innite number of such Kruskal patches may be joined together to form a maximal solution, whose Penrose diagram is shown.
Black Holes Might Lead to the Birth of New Universes | IE Black holes are one of the most tremendous destructive forces in the universe. And while opposites in magnetism attract, the concepts of creation Using two mathematical representations of the big bang and black holes — called the Penrose diagrams of expanding cosmology, and the Penrose diagram...
Black Holes Black Hole Conditions. After collapse to the neutron star stage, stars with masses less than 2-3 solar masses should remain neutron stars, gradually radiating away their energy, because there is Once they collapsed past a certain radius, the "event horizon", then even light could not escape: black hole.
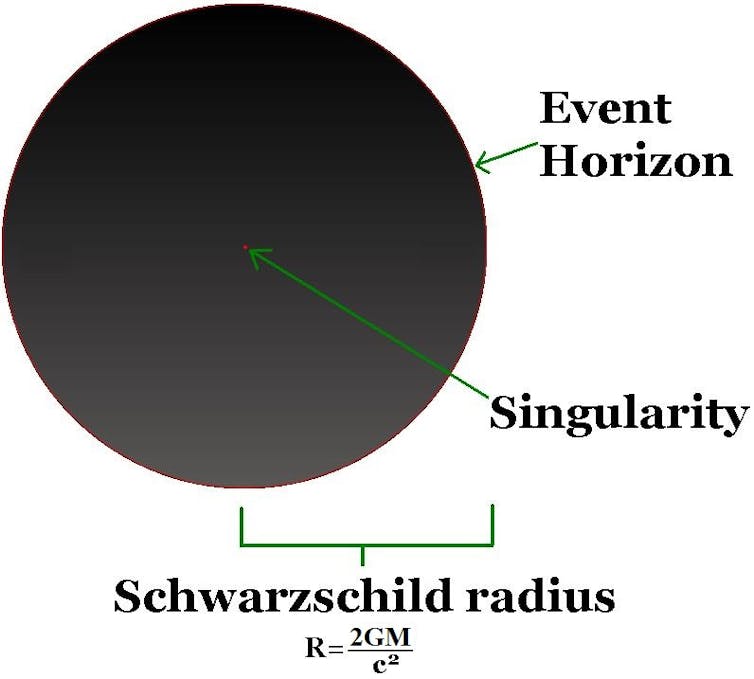
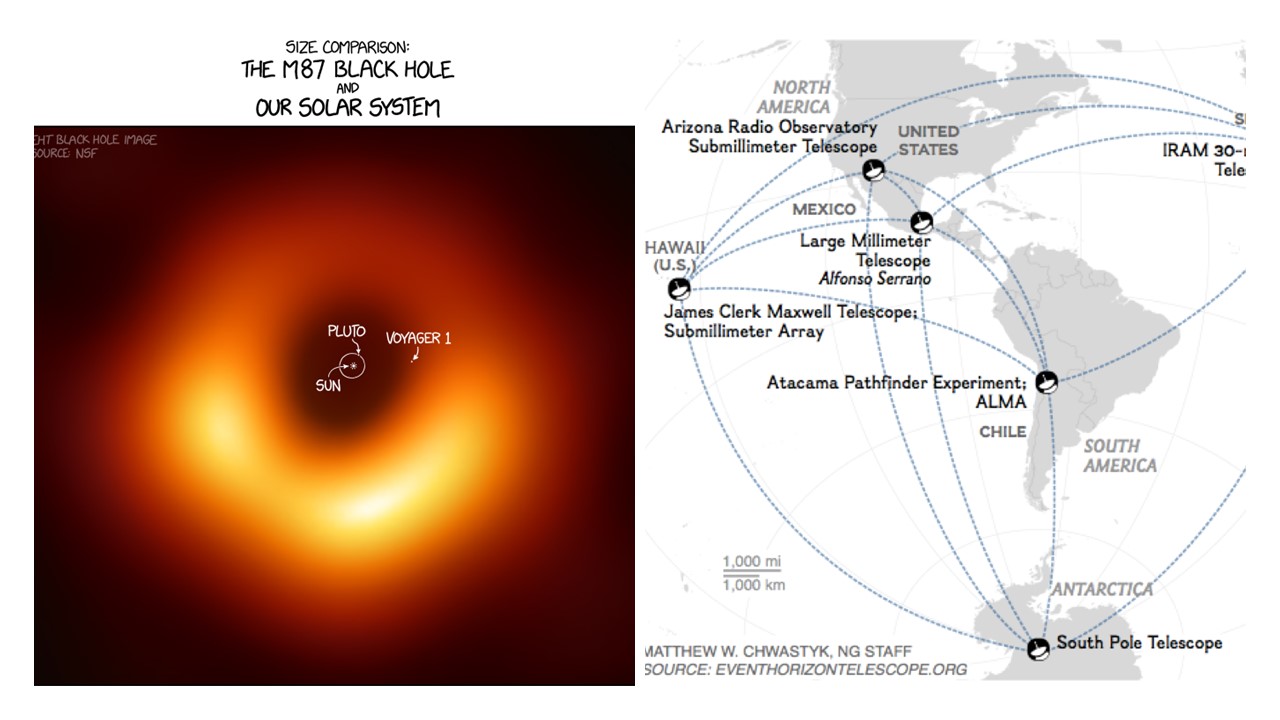






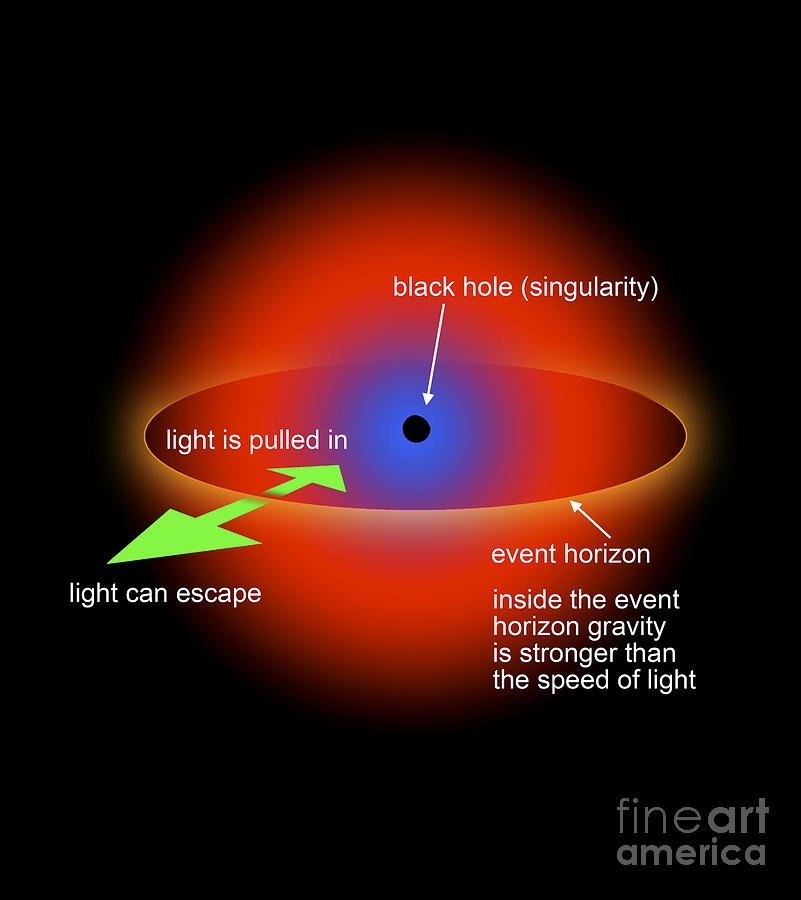








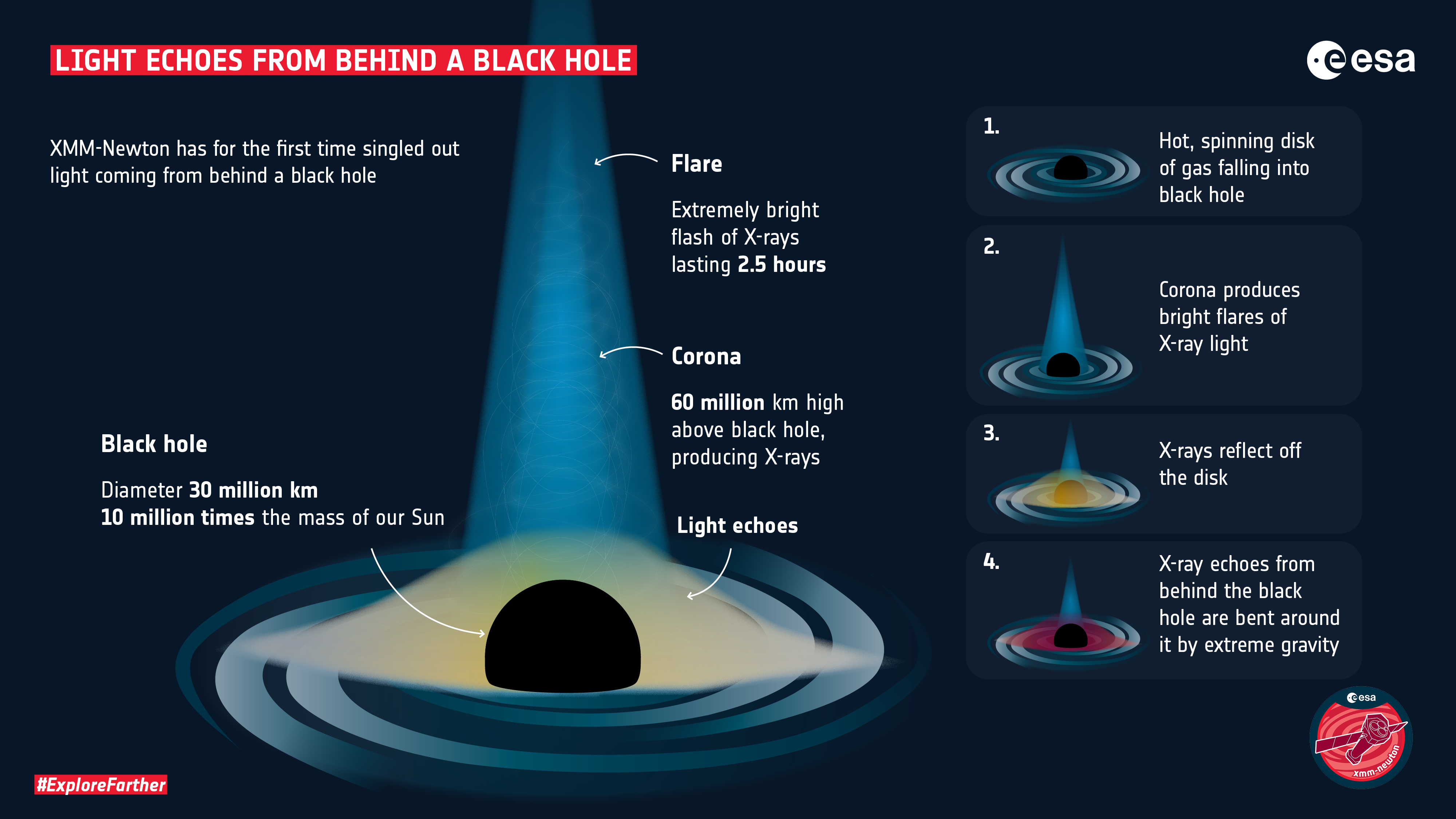



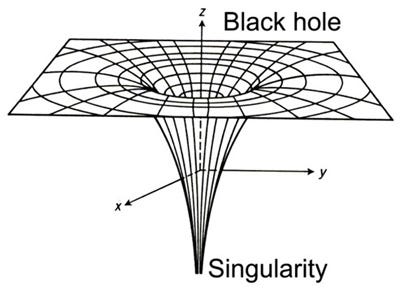



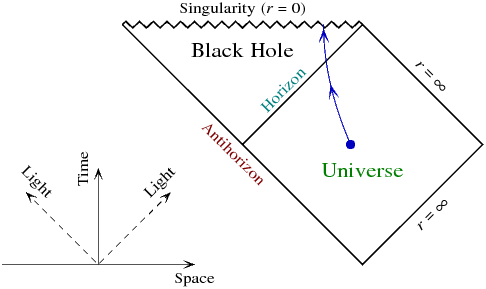

0 Response to "39 diagram of black hole"
Post a Comment