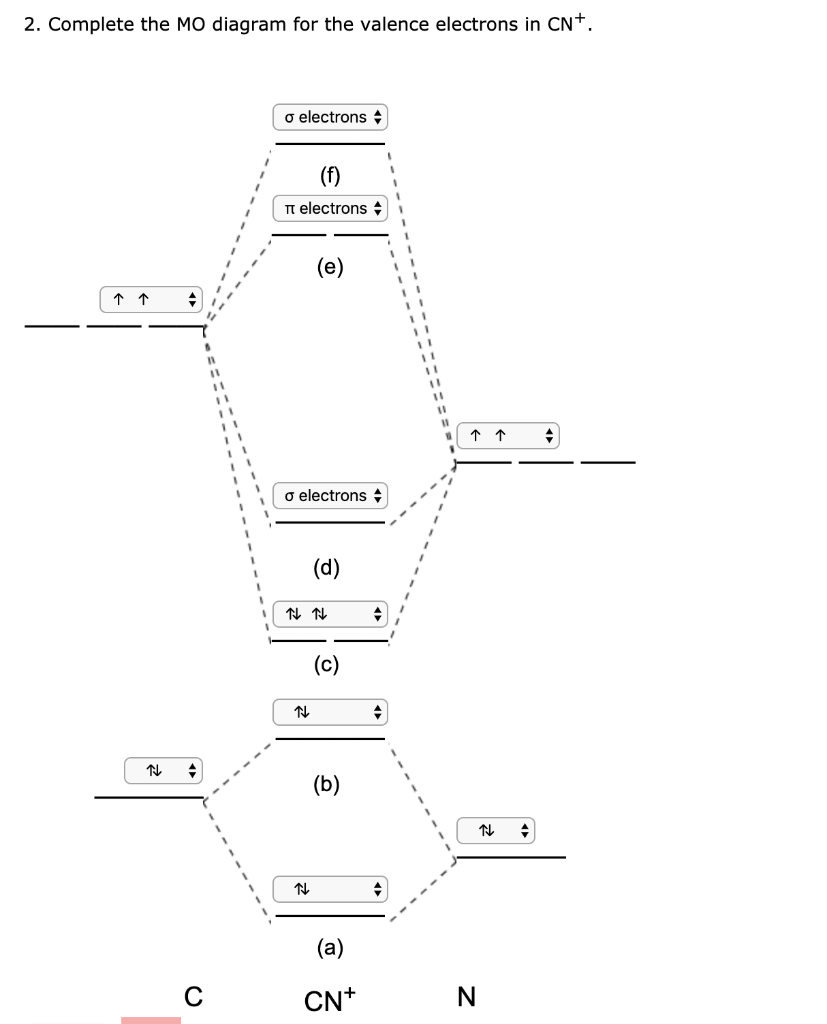
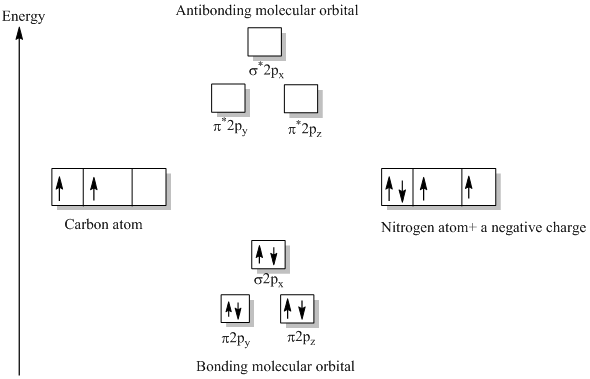
35 Mo Diagram Cn-
By writing molecular orbital configuration for NO,CO,O2 ... "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the diagram. Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of Figure \(\ PageIndex{6}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for HCl. to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). mix atomic orbitals on different atoms to get Molecular Orbitals. The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion).
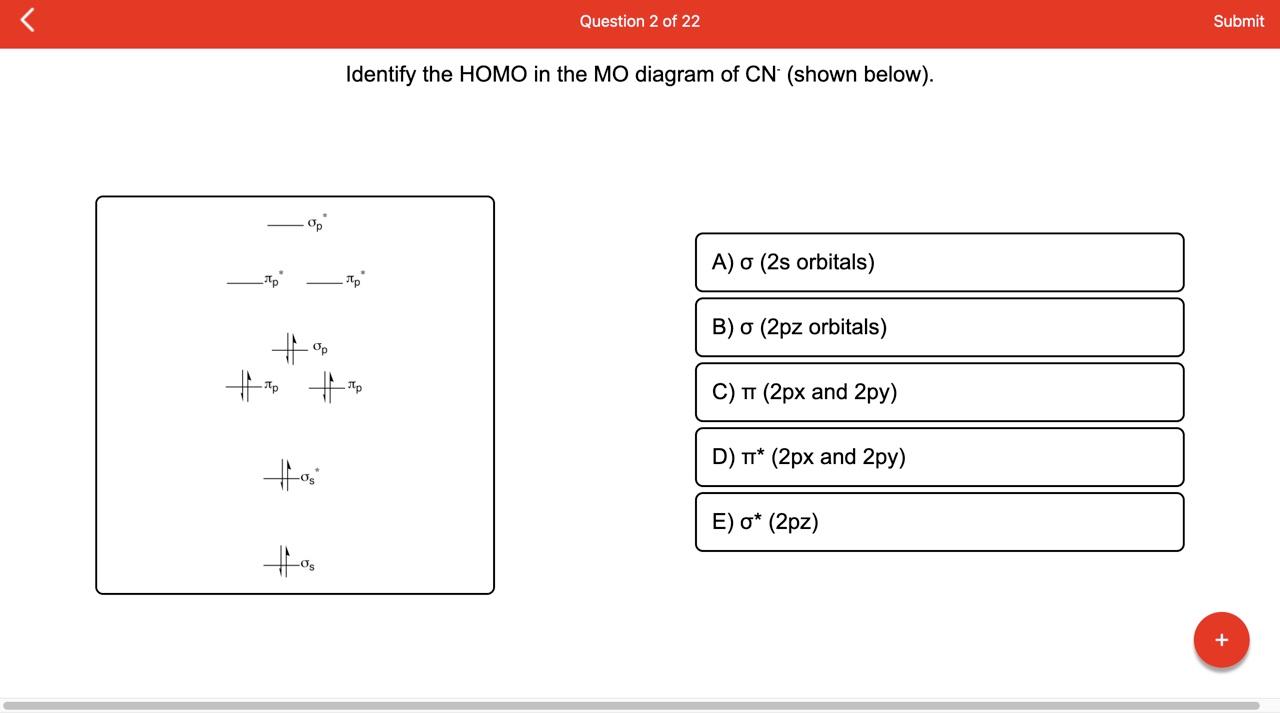
inorganic chemistry - How can one tell from the MO diagram ... The cyanide ion, when acting as a nucleophile, typically attacks via carbon as its HOMO has a greater contribution from carbon. But how can we deduce this from the MO diagram? To me it appears that the nitrogen $\mathrm{2p}$ orbitals are energetically closest to the $3\sigma$ HOMO, so its coefficient should be larger in the HOMO.
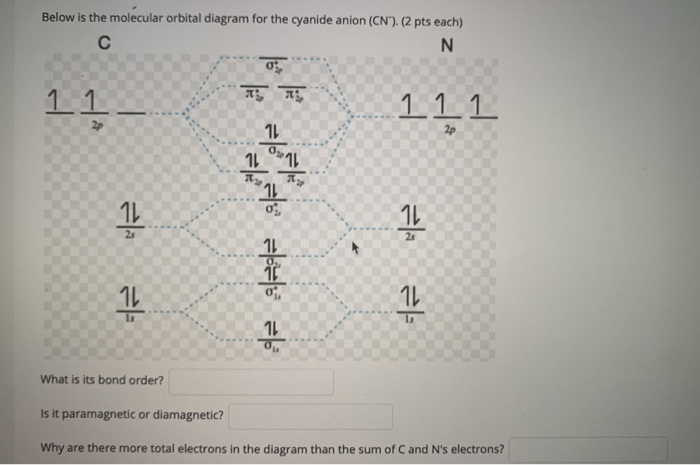
Mo diagram cn-
PDF SALCS for Common Geometries bonding) Example: Constructing a MO for Hexammine 2+Ruthenium, [[(Ru(NH 3) 6] NH 3 NH 3 2+ H 3N Ru NH 3 point group = O h H 3N NH 3 h 48 Ru bonding AOs O h E 8C 3 6C 2 6C 4 3C 2 i6S 4 8S 6 3 h 6 d /h 60 02 20004 2 = A 1g: 5s T 1u: (5p x , 5p y, 5p z) E g: (4dx2‐y2, 4dz2) A 1g 6001260001212481 A 2g 6 0 0 -12 6 0 0 0 12 -12 0 0 E g 1200012000240 48 1 Pd non‐bonding AOs CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. It belongs to the cyano group and consists of carbon and a nitrogen atom having a triple bond. It carries a charge of -1 and is a conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide (HCN). [Solved] Compare the MO diagram of Pt(CN)4 2- and Pt ... Compare the MO diagram of Pt(CN)4 2- and Pt(pyridine)4 2+. Assume the pyridine molecules are all flat in the xy plane. Pyridine is a pi acceptor, but it doesn't have as many pi orbitals as CN- does.
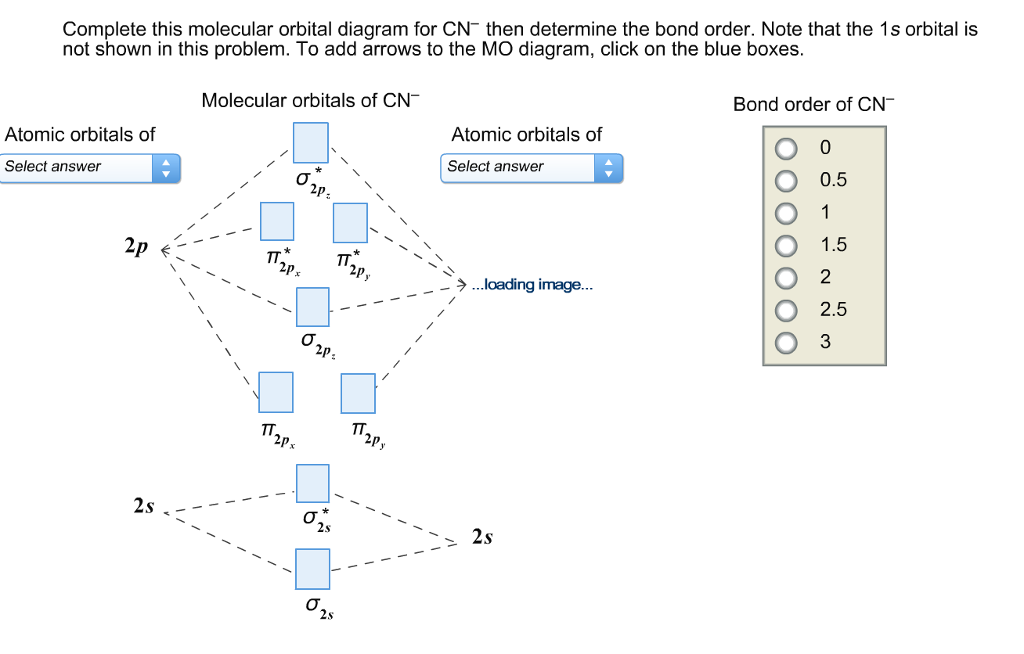
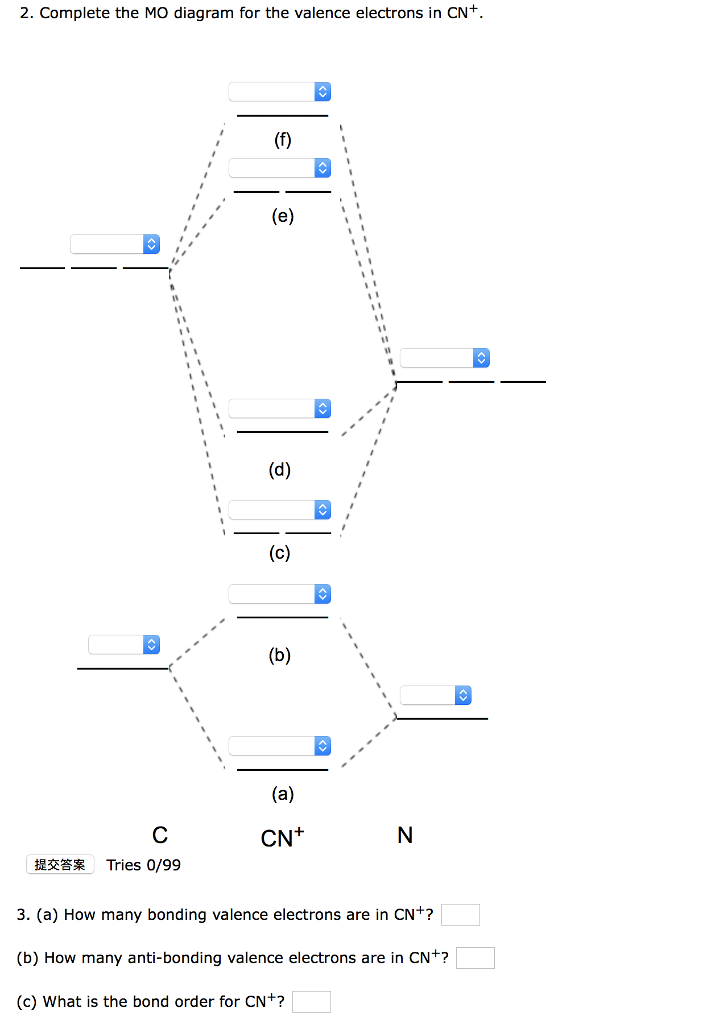
Mo diagram cn-. Can you please describe the MO diagram of CN? Tania Havenga. University of South Africa. Here is the MO for CN-, just take away a single electron from the MO since CN is neutral. Vijayta Gupta is right, the N atom is lower in energy. http ... (Get Answer) - Consider the molecular orbital diagram for ... Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. To add arrows to the MO diagram, click on the blue boxes. Bond order of CN O 0 O 0.5 Molecular orbitals of CN Atomic... PDF Lecture 6 4 coordinate complexes, summary, typical exam ... Walsh diagram OH 2, SH 2, NH 2 8 Bent-, FH2 + NH 2, PH 2, CH 2 7 Bent-, OH2 + CH 2, SiH 2, BH 2 6 Bent-, NH2 + BH 2, AlH 2, CH 2 5 Bent BeH 2, BH 2+ 4 Linear LiH 2, BeH 2+ 3 Linear LiH 2+ 2 Bent No. of Shape valence electrons Molecular species Known shape of some AH 2 molecules Recall: a molecule adopts the structure that best stabilises the HOMO. Solved: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the cyanide ... Chemistry (1st Edition) Edit edition. This problem has been solved: Solutions for Chapter 7 Problem 66QP: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the cyanide ion (CN−). (Assume the ordering of moleculer orbitals to be like that in N2.) Write the electron configuration of the cyanide ion (CN−).…. Get solutions.
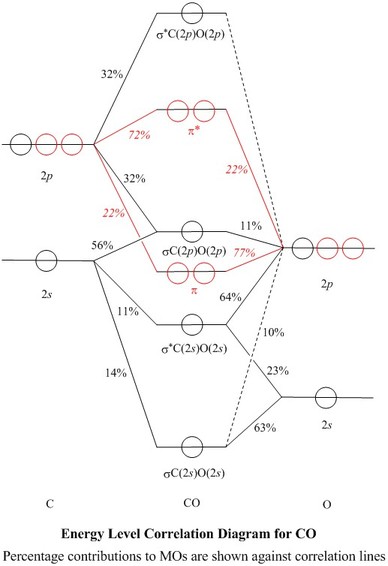
CN- lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram, and, bond ... So, in this article, we have learned about How to draw CN– lewis structure, its molecular orbital diagram (MO), formal charges, hybridization, and bond order. Here is a quick review of this article. Hybridization of CN is Sp. The bond order of CN- is 3. CN– formal charge is -1 according to its lewis structure. Molecular Orbitals for Carbon Monoxide - Newcastle University The Molecule. CO is a very stable 10-valence-electron molecule, isoelectronic with [CN] - and with N 2, which has a slightly lower bond dissociation energy than CO. The formal bond order of CO is 3, from about one σ- bond and two π- bonds. Its most important property is burning in air to give CO 2 , in the combustion of fossil fuels. MO Diagrams - GitHub Pages #3. Draw the MO diagram for `O_2^+` This is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. Recall that a cation indicates a loss of `1` electron. `O_2^+` is just the ionized form of `O_2`; that is, it's `O_2` with `1` missing electron. The MO diagram will be the same as the MO diagram of `O_2`, except with `1` less electron. MO Diagram of CN-< - Hunt Research Group MO Diagram of CN-< Theoretical chemistry research group focusing on development of methods, and calculations in the areas of ionic liquids, photochemistry and catalysis The process Write down as far as you can remember the steps that we will need to go through ... for example the first step will be to draw a set of axes ... answer
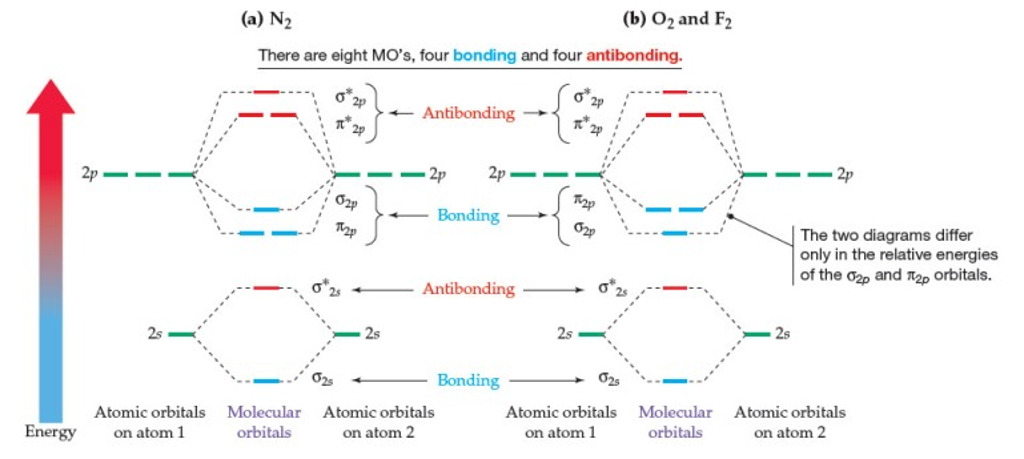
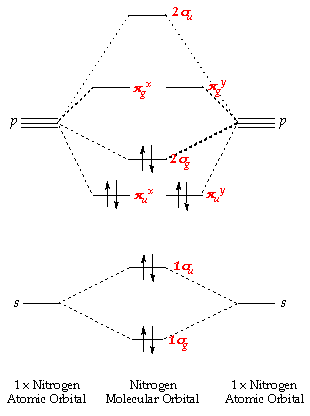
PDF Bonding in transition metal complexes Example: Constructing a MO diagram for Chromium Hexacarbonyl, Cr(CO) 6 Cr ππππ-bonding AOs T2g:(3dxy,3dxz,3dyz) T1u:(4px,4py,4pz) • T2g previouslyconsiderednon-bondingin σ-bondingscheme • T1ucombineswith T1u SALCin in σ-bondingscheme • T1g, T2u π-SALCs are non-bonding Cr non-bonding AOs T2g: (3 dxy, 3dxz, 3dyz) Cr σσσσ-bonding ... MO Diagrams for First Row Diatomic Molecules - Chemistry ... MO Diagrams. Now we're ready to look at MO diagrams for the first row series. Note that the molecules that aren't common and stable might still be more stable in the gas phase than single atoms. For instance, in a gas of Li metal, diatomic molecules will form. The figure shows a summary of the energy levels, so we can see how they change. Diatomic Species | MO theory | Chemogenesis The MO diagram for the diatomic carbon monoxide, CO, shows it to be isoelectronic with nitrogen, N 2: The heteronuclear diatomic ions cyanide ion, CN -, and nitrosonium ion, NO +, are also electronic with nitrogen, N 2, and carbon monoxide. The only difference between the MO diagrams are the relative energies of the orbitals. MO Diagram #3 - CN- - YouTube This video is about MO Diagram #3 - CN-
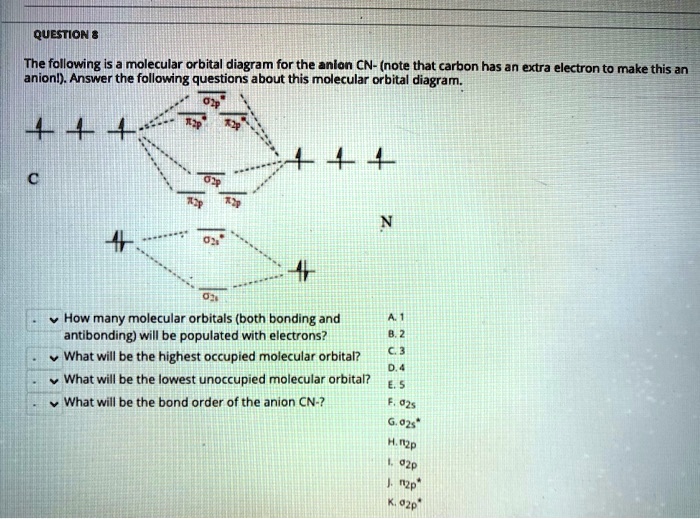
Molecular nitrogen, carbon monoxide, and c ... - Clutch Prep Q. Draw Lewis structures and MO diagrams for CN+, CN, and CN-. According to the Lewis model, which species is most stable? Q. Use molecular orbital theory to complete this table. Q. What is the ground-state electron configuration of O2^-? 1. (δ2s)^2(δ2s*)^2(π2p)^3(π2p*)^1 2.
MO Diagram of CN-< - Hunt Research Group This means that very occasionally an occupied MO can move up in energy as long as the occupied MOs move down more in energy. If only two MOs mix then one always goes up and one down, and the one that goes up better be unoccupied. However, once a third MO starts mixing strongly the situation is extremely complex, and this is what has happened here.
Molecular Orbital diagram of CN- - YouTube
PDF MO Diagrams for More Complex Molecules MO Theory • MO diagrams can be built from group orbitals and central atom orbitals by considering orbital symmetries and energies. • The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection.
PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Module Two Chem 101 Problems Flashcards - Quizlet Module Two Chem 101 Problems. TestNew stuff! Carbon dioxide is a _____ compound composed two types of _____ atoms. Carbon dioxide is a molecular compound composed of two oxygen atoms with covalent double bonds to a central carbon atom. Both C and O are to the right of the "staircase" on the periodic table, as nonmetals.
PDF Lecture 3 - chem.tamu.edu Lecture 3 Ligands and Bonding and Electron Counting in Organo-Transition Metal Compounds . Stable electronic configurations: MO Energy Level Diagrams Reviewed
Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram - schematron.org A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. In this answer of Martin's, you can find a molecular orbital diagram of $\ce {CO}$.
11.5: Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry LibreTexts Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact with only one hydrogen ...
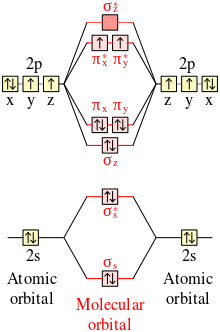
What is the bond order of CN-? - Quora Answer (1 of 6): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here's a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i...
Complete this molecular orbital diagram fo... | Clutch Prep We're being asked to complete the molecular orbital diagram of CN-and then determine the bond order. To do so, we shall follow these steps: Step 1: Calculate the total valence electrons present. Step 2: Fill the molecular orbitals with electrons. Step 3: Determine the bond order. Step 1: Calculate the total valence electrons present. Group ...
[Solved] Compare the MO diagram of Pt(CN)4 2- and Pt ... Compare the MO diagram of Pt(CN)4 2- and Pt(pyridine)4 2+. Assume the pyridine molecules are all flat in the xy plane. Pyridine is a pi acceptor, but it doesn't have as many pi orbitals as CN- does.
CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. It belongs to the cyano group and consists of carbon and a nitrogen atom having a triple bond. It carries a charge of -1 and is a conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide (HCN).
PDF SALCS for Common Geometries bonding) Example: Constructing a MO for Hexammine 2+Ruthenium, [[(Ru(NH 3) 6] NH 3 NH 3 2+ H 3N Ru NH 3 point group = O h H 3N NH 3 h 48 Ru bonding AOs O h E 8C 3 6C 2 6C 4 3C 2 i6S 4 8S 6 3 h 6 d /h 60 02 20004 2 = A 1g: 5s T 1u: (5p x , 5p y, 5p z) E g: (4dx2‐y2, 4dz2) A 1g 6001260001212481 A 2g 6 0 0 -12 6 0 0 0 12 -12 0 0 E g 1200012000240 48 1 Pd non‐bonding AOs














0 Response to "35 Mo Diagram Cn-"
Post a Comment