39 what is a ray diagram
A ray diagram is a tool used by physicists to explain or predict the behaviour of beams of light as they pass through objects such as glass blocks or lenses ... Ray diagrams help us trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object. Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels.
This ray diagram shows the formation of a shadow by an opaque barrier. This might represent what happens when a narrow-beam torch forms the shadow of a book on a wall. This model represents the actual event in a number of ways: The light source is represented as a single point.

What is a ray diagram
A grid of points is defined at the entrance or exit pupil. of an optical system and rays are traced from the object point. through the grid points, through the observation plane. Ray diagrams It is important to be able to draw ray diagrams to show the refraction of a wave at a boundary. To draw a ray diagram: Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the... Industrial radiography is the process of inspection of interior of objects by x-Rays and photographic film the atomic arrangement within the object. Thus the material object may be identified X-Rays passing through tie objects under inspection fall on the photographic film.
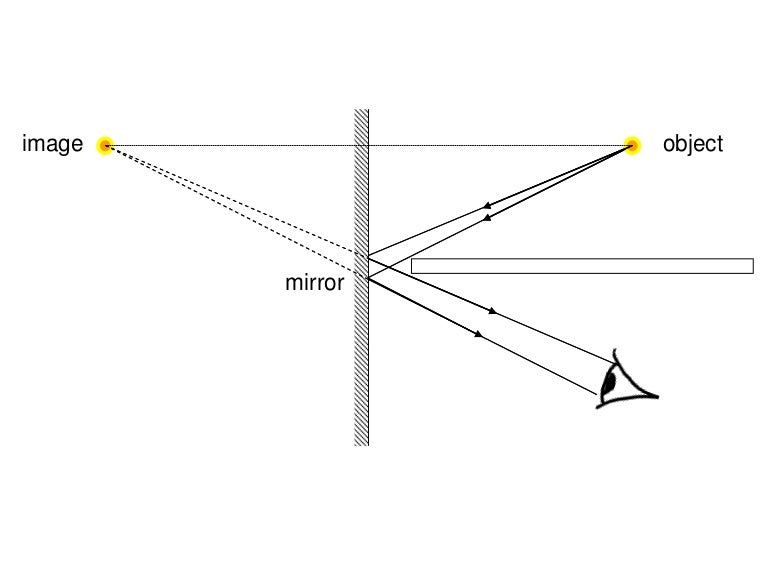
What is a ray diagram. Ray Diagrams. Jonathan is a published author and recently completed a book on physics and applied mathematics. All lenses and mirrors can use ray diagrams to find images. There are three principal rays. The first principal ray occurs when the light comes in parallel to the principle axis, it goes out through the focus. A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a ... Incident Ray: The ray of light that is incident on the interface. Reflected Ray: The ray of light that is reflected from the interface. Normal: The perpendicular to the interface. Angle of Incidence: The angle that the incident ray makes with the normal. Angle of Reflection: The angle that the reflected ray makes with the normal. Specular Reflection A ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. There are a few important things to note: Light travels in straight lines within a uniform medium (this means that light can change direction upon entering a different medium).
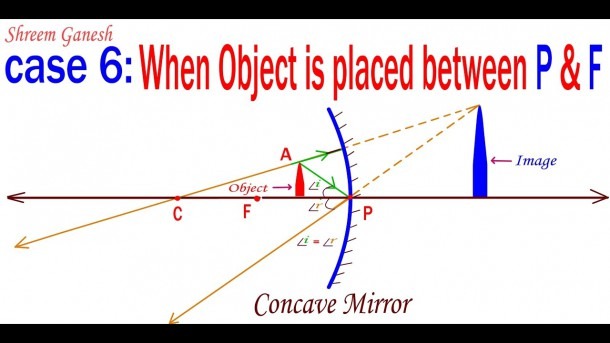
Draw a ray diagram showing the lateral displacement of a ray of light when it passes through a parallel sided glass slab. Advertisement Remove all ads. Solution Show Solution. The perpendicular distance between the path of emergent ray and the direction of the incident ray is called the lateral displacement. Plane mirror- Definition, Properties and Ray Diagram. Mirrors are defined as one side-polished surface that can reflect the light rays. Plane mirrors in physics are the ones that have a flat reflecting surface and produce always a virtual image. In this tutorial, we review the most important topics in the plane (flat) mirrors in physics ... RAY. DIAGRAM RAY DIAGRAM. Ray-diagram analyses can be used to study the effect of room shape on the distribution of sound and to identify surfaces which may produce echoes. A ray diagram is an acoustical analogy to the specular reflection of light where the angle of incidence angleiof an impinging sound wave equals the angle of reflection angler, with angles measured from the perpendicular to ... Q40) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image. What happens to the image as the object is moved away from the mirror? Looking to do well in your science exam ? Learn from an expert tutor. Book a free class! Book a free class now
Ray diagram • A ray diagram is a representation of structural formula. It provides information such as speed in each stage, the transmission ratio in each stage, The total number of speeds and its values. • As seen in fig. (a) the maxi speed and minimum speed both are higher for shaft. Ray diagrams A ray diagram shows how light travels, including what happens when it reaches a surface. In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: a straight line; with an arrowhead pointing in the... This section of Lesson 2 details and illustrates the procedure for drawing ray diagrams. Let's begin with the task of drawing a ray diagram to show how Suzie will be able to see the image of the green object arrowin the diagram below. For simplicity sake, we will suppose that Suzie is viewing the image with her left eye closed. Thus, we will focus on how light travels from the two extremities of the object arrow (the left and right side) to the mirror and finally to Suzie's right eye as she sights at the image. The four steps of the process for drawing a ray diagram are listed, described and illustrated below. 1. Draw the image of the object. 2. Pick one extreme on the image of the object and draw the reflected ray that will travel to the eye as it sights at this point. 3. Draw the incident ray for light traveling from the corresponding extreme on the object to the mirror. 4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 for all other extremities on the object. The example "Ray tracing diagram for convex lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions.
The interactive diagram provides a focus for the attention of the whole class. Your job here is to talk through each of the steps of constructing the ray diagram, engaging the pupils in discussion as you proceed. First, hang the ball from a metre rule and hold it in the beam of light between the light source and the screen.
Find out information about ray diagram. A diagram showing the paths of selected rays through an optical system. McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific & Technical Terms, 6E, Copyright © 2003 by The...
A ray diagram is a diagram that traces the path that light takes in order for a person to view a point on the image of an object. On the diagram, rays (lines with arrows) are drawn for the incident ray and the reflected ray. What is focal length in a ray diagram? 1a A simple ray diagram for a converging convex lens.
A ray diagram is a diagram that traces the path that light takes in order for a person to view a point on the image of an object. On the diagram, rays (lines with arrows) are drawn for the incident ray and the reflected ray. Complex objects such as people are often represented by stick figures or arrows 38 views Related Answer Wes Phillips
A ray diagram is a diagram used to trace the path that light takes in order for a person to view a point on the image an object. Ray diagrams are commonly constructed to follow light rays through...
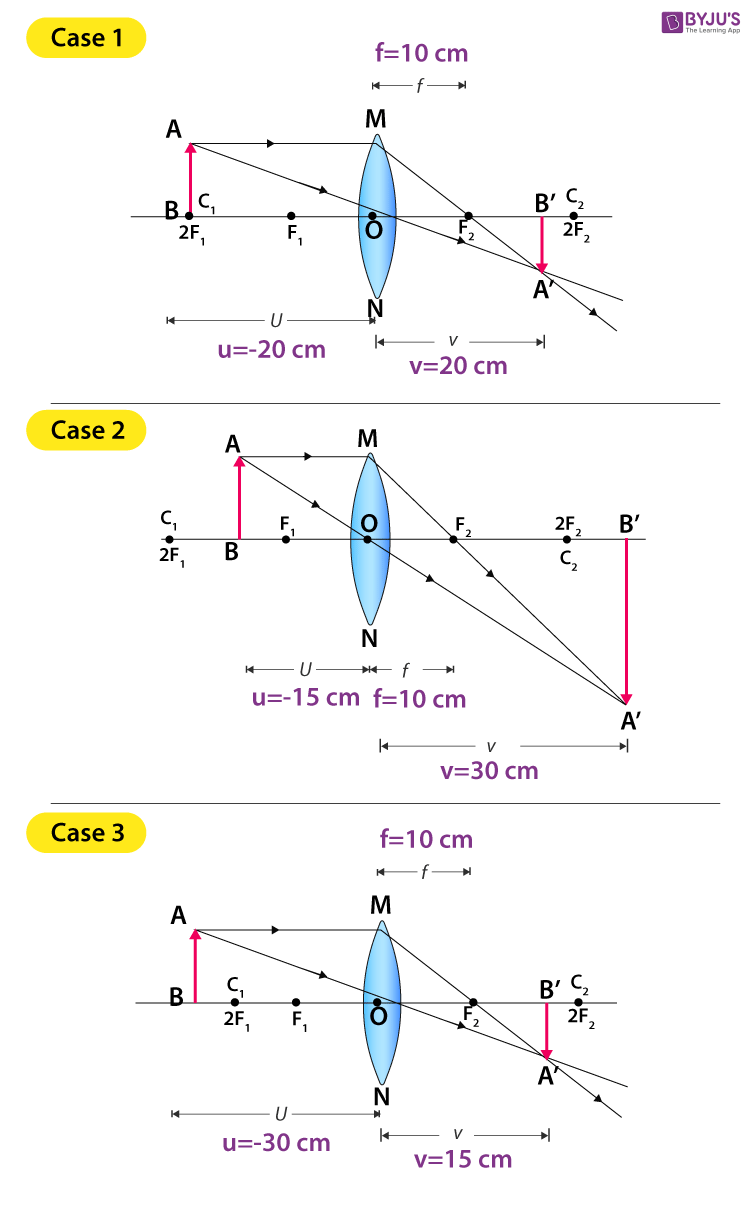
This video covers:- How to draw ray diagrams for convex and concave lenses - How to comment on whether an image is real or virtual, upright or inverted, and ...
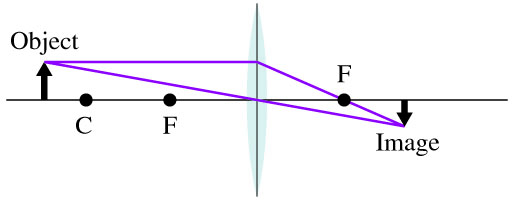
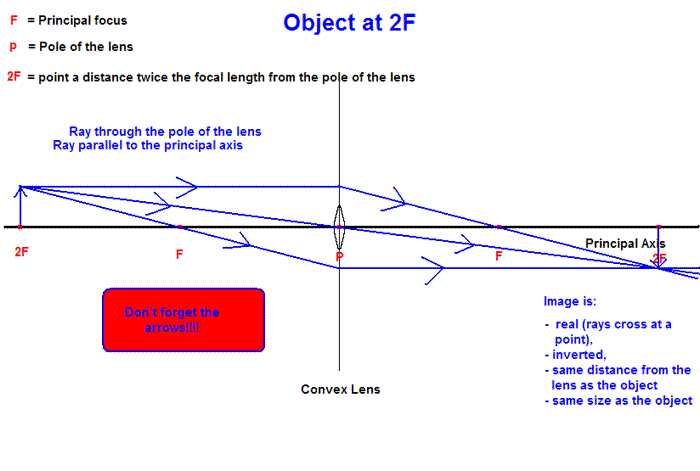
One goal of a ray diagram is to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image that is formed by the double convex lens. Typically, this requires ...
A ray diagram is a specialized pictorial representation used to trace the path of light rays. The rules used for drawing ray diagrams are as follows.
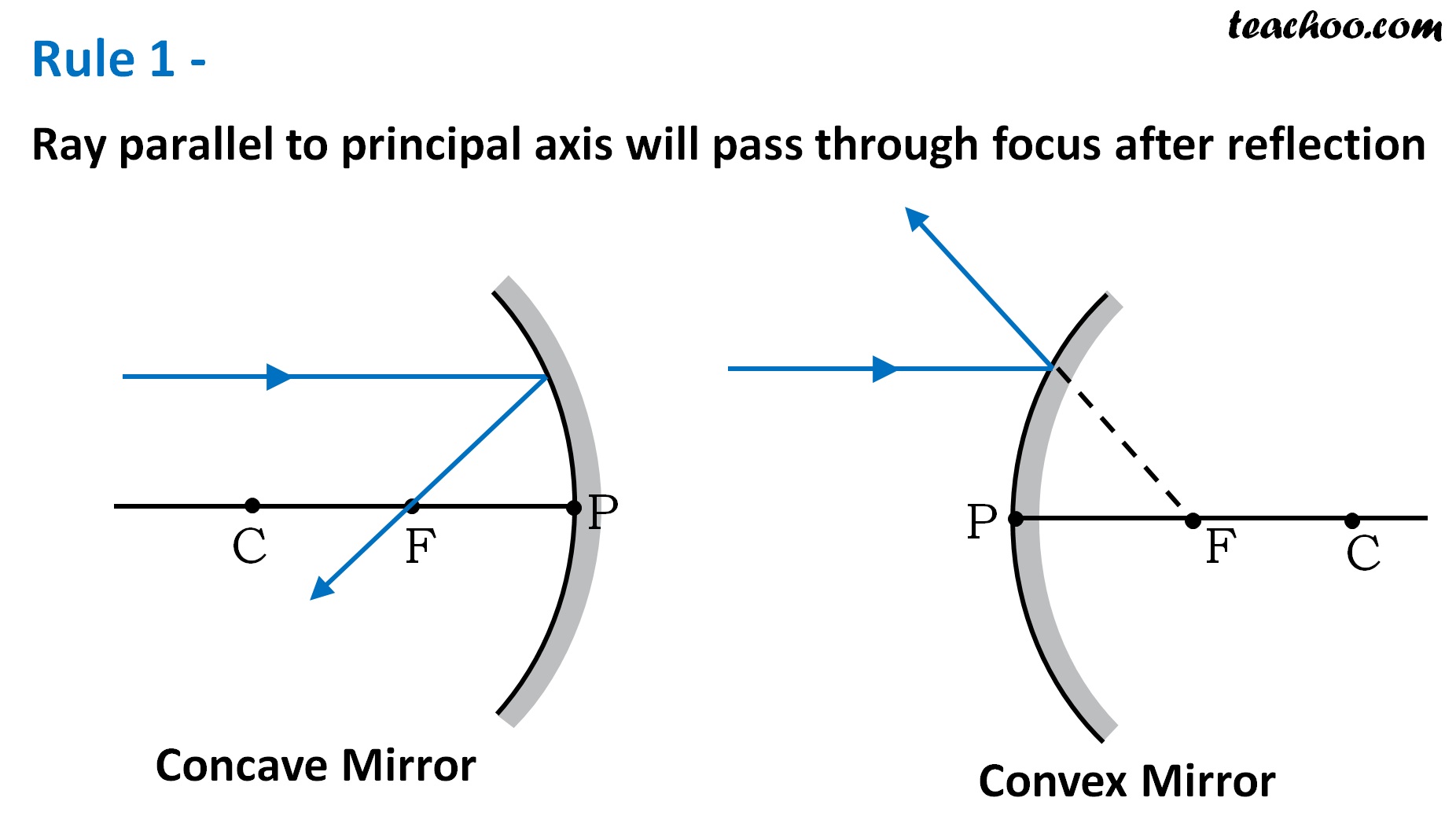
There are some rules which we use to obtain images in a ray diagramLet's look at themRule 1 - Ray parallel to principal axis will pass through focus after reflectionFor aconcave mirror,we see that ray passes through focus after reflectionFor aconvex mirror,since focus is on the right side,itappearst
This physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging lens, diverging l...
Ray diagrams are a basic optical skill and a skill that you would use throughout a career in optics. One needs to know where the image will be and what the magnification is. Ray diagrams will tell you. Hey, and making them is kinda fun, too. 1.2K views Jeff Johnston , Ph.D. Physicist with 20+ years industrial experience
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope. Definition: The cathode ray oscilloscope is the instrument which generates the waveform of any electrical quantity. The waveform is generated in such a way that the amplitude of the signal is represented along Y-axis and the variation in the time is represented along X-axis. CRO is the measuring device as well as it ...
The theme of this unit has been that we see an object because light from the object travels to our eyes as we sight along a line at the object. Similarly, we see an image of an object because light from the object reflects off a mirror and travel to our eyes as we sight at the image location of the object. From these two basic premises, we have defined the image location as the location in space where light appears to diverge from. Ray diagrams have been a valuable tool for determining the path taken by light from the object to the mirror to our eyes. In this section of Lesson 3, we will investigate the method for drawing ray diagrams for objects placed at various locations in front of a concave mirror.
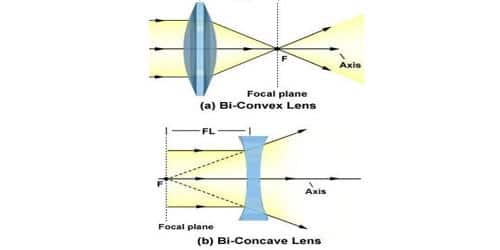
There are some rules which we use to obtain images in a ray diagramLet's look at themRule 1 - Ray parallel to principal axis will pass through focusFor aconvex lens,we see that ray passes through focus on right sideFor aconcave lens,we see that ray appears to pass through focus on left sideRule 2 -
A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Incident rays - at least two - are drawn along with their corresponding reflected ...
Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results: an erect virtual imagesmaller than the object. The image is always formed inside the focal length of the lens. Ray diagrams for lenses Index Lens concepts HyperPhysics*****Light and Vision R Nave Go Back
A ray of light falling on a plane mirror is reflected at the same angle as the angle of incidence. As a result, the image formed by the mirror is sharp and undistorted. This image is not real but virtual because the image formed behind the mirror by extending the diverging reflected rays backward.
Ray diagrams · A ray diagram shows how light travels, including what happens when it reaches a surface. · In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: · Remember to use ...
Industrial radiography is the process of inspection of interior of objects by x-Rays and photographic film the atomic arrangement within the object. Thus the material object may be identified X-Rays passing through tie objects under inspection fall on the photographic film.
Ray diagrams It is important to be able to draw ray diagrams to show the refraction of a wave at a boundary. To draw a ray diagram: Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the...
A grid of points is defined at the entrance or exit pupil. of an optical system and rays are traced from the object point. through the grid points, through the observation plane.




.png)

















0 Response to "39 what is a ray diagram"
Post a Comment