39 laws of reflection diagram
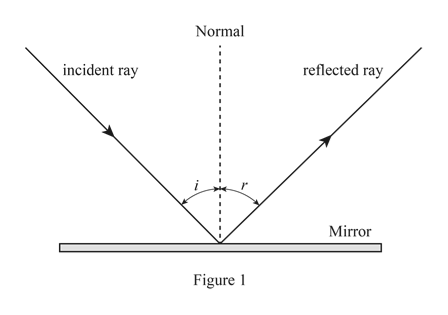
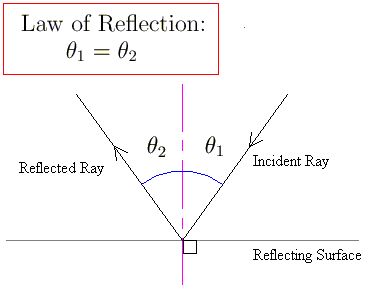
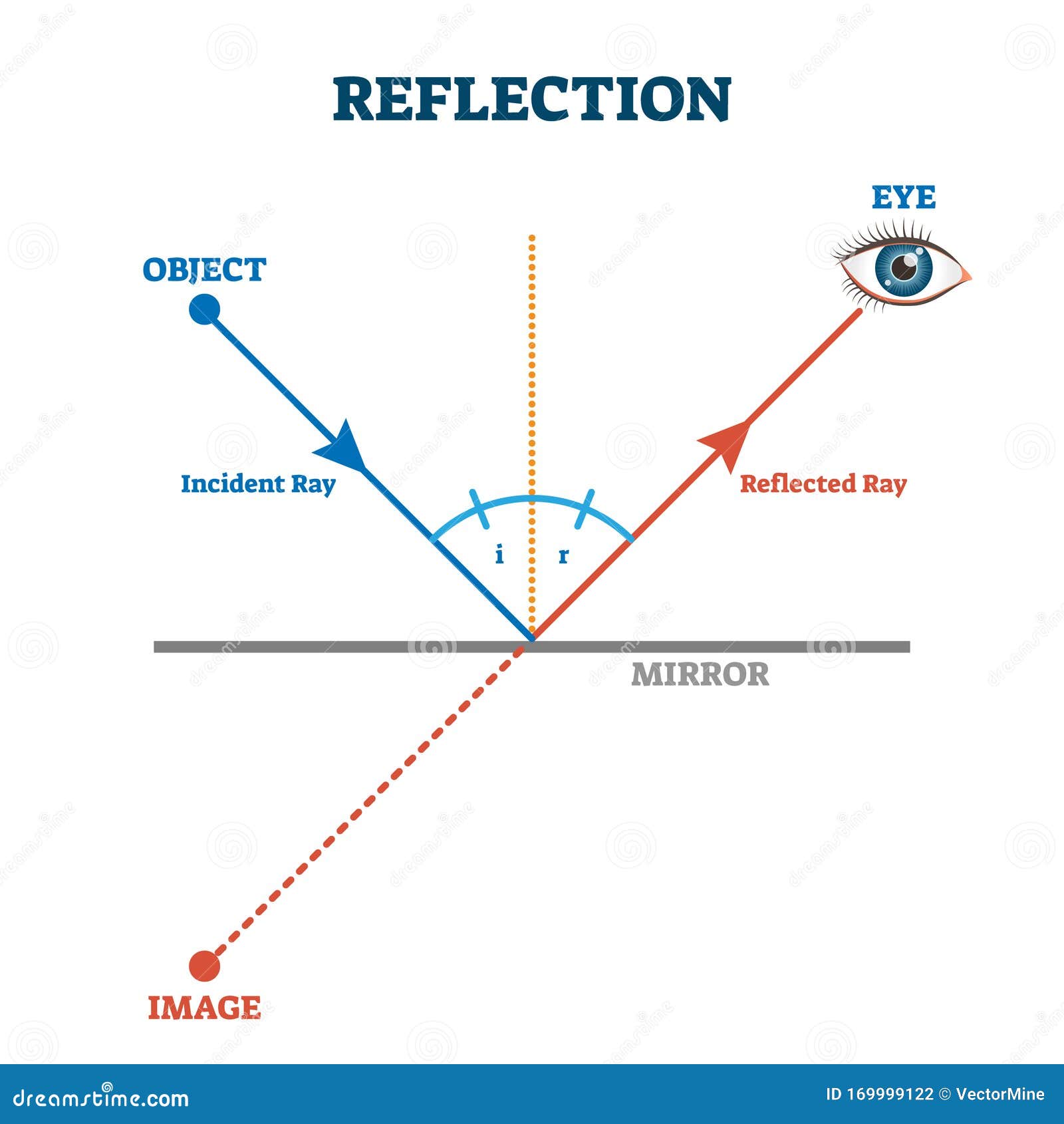
When light is reflected from a surface, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection, where both angles are measured from the path of the light to the normal to the surface at the point at which light strikes the surface. This equality is known as the law of reflection. Sample Problem 1: According to the law of reflection, when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The reflected ray always meets the surface normal at the point of contact between the incident ray and the plane defined by the incident ray and the surface normal.
Laws of Reflection Consider the diagram below to understand the laws of reflection: 1. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection when light is reflected on a plane surface. 2. The incident ray reflected the ray and the normal lie on the same plane. Image Formation Through a Plane Mirror

Laws of reflection diagram
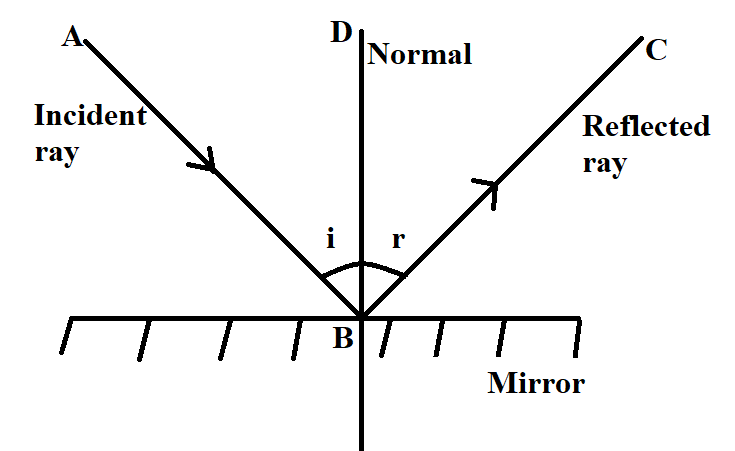
the angle of reflection, r, is the angle between the normal and reflected ray. The law of reflection states that: angle of incidence i = angle of reflection r. For example, if a light ray hits a... Solution: The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection (where both angles are measured from the normal line to the surface). The normal line is shown as the dashed line in the figure. Let's add angle ?3 to the figure; note that this angle is 90° - ?1. This is basically what the law of reflection is all about. Here's a diagram to help you visualize the law of reflection a bit better: Angle of incidence and angle of reflection In the diagram above, the light ray approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray, while the one that bounces off the mirror is called the reflected ray.
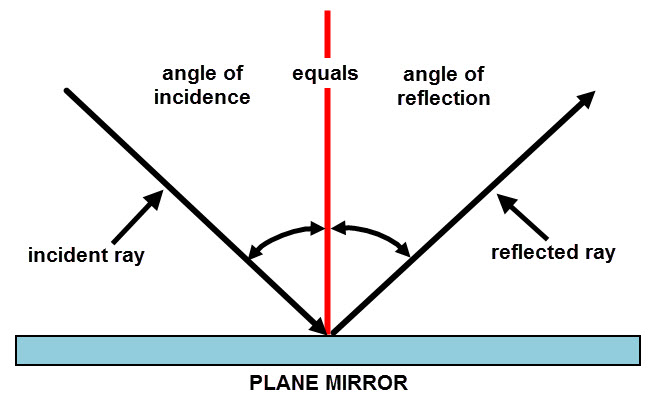
Laws of reflection diagram. The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The ray of light that leaves the mirror is known as the reflected ray (labeled R in the diagram). that the incoming ray makes with a line (dashed in the diagram) normal to the surface is called the angle of incidence. The angle θ r for the reflected ray is called the angle of reflect. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, or, stated mathematically. Start studying Law of Reflection diagram. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, i = r. It works for any angle. For example: the angle of reflection is 30° if the angle of incidence is 30 ...
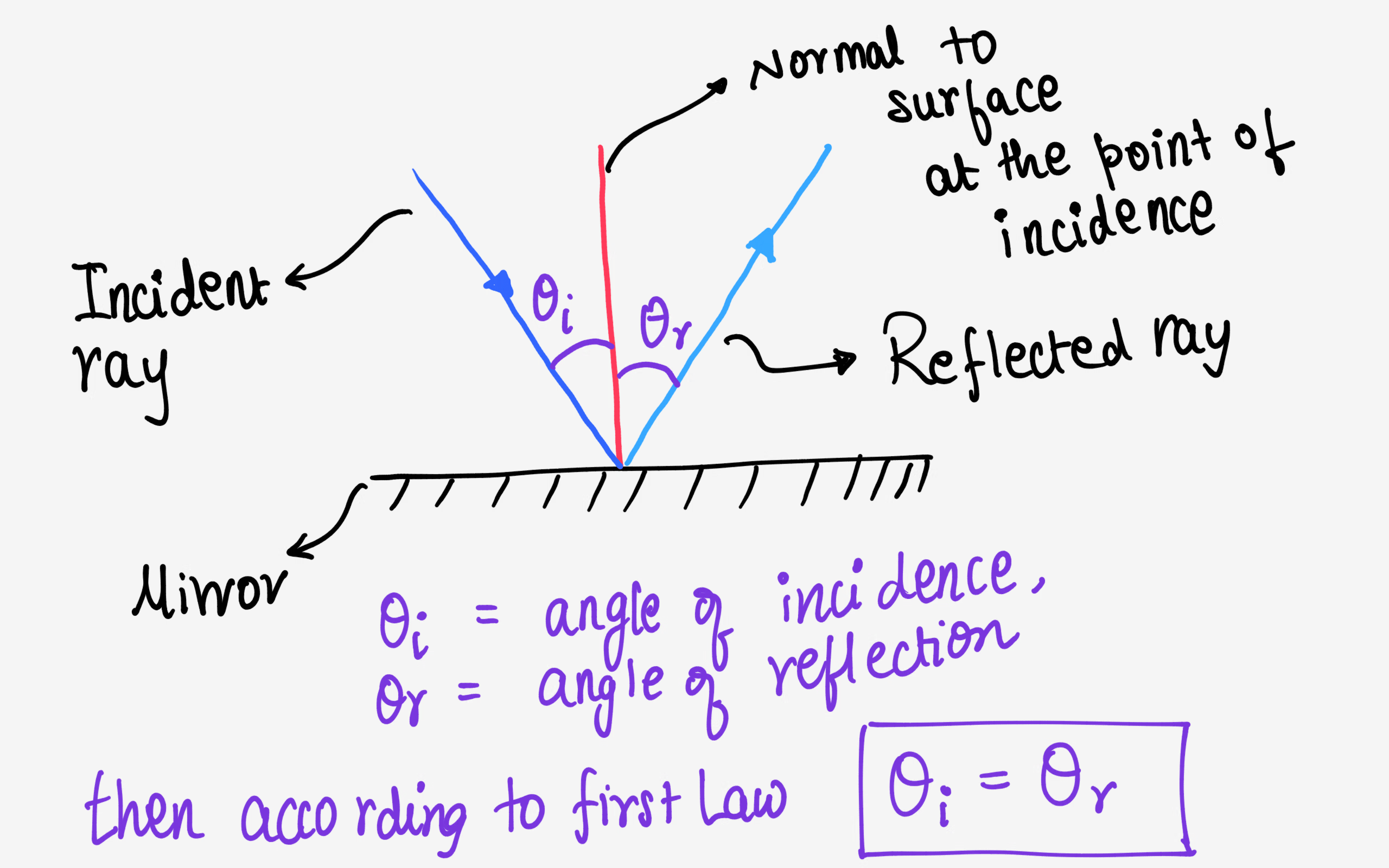
From the diagram, it can be seen that the incident ray and the reflected ray lie on either side of the normal at the point of incidence. Similarly the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane i.e. plane of the paper. Hence laws of reflection are proved. Following laws of reflection are valid for smooth surfaces like mirror,still water surface etc. (1)the incident ray, Normal and reflected ray all lie in same plane. (2)incident ray and reflected ray always lie in opposite to the Normal (3) angle of incidence is always equal to angle of angle of reflection. 10.8K views View upvotes With the help of a diagram, state the laws of reflection. asked Dec 4, 2020 in Light by Zabya (57.5k points) light; class-7; 0 votes. 1 answer. Assertion (A): A convex mirror always forms a diminished and virtual image. Reason (R): The laws of reflection are not applicable in the case of shphe. asked Aug 12, 2020 in Physics by Chiranjeev (98.4k ... State the laws of Reflection along with a suitable diagram. Easy Solution Verified by Toppr I = Incident ray R = Reflected ray N = Normal ∠ i = angle of incidence ∠ r = angle of reflection There are two basic laws of reflection of light - (i) The incident ray the reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting
The three laws of reflection Any mirror obeys the three laws of reflection, flat, curved, convex or concave. The three laws of reflection are 1. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal 2. The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray are all in the same plane 3. According to the Law of Reflection, θ = θ r Hence, Angle of Reflection = 60° Q2: A light ray strikes a reflective plane surface at an angle of 54° with the surface. (i) Calculate the angle of incidence. (ii) Calculate the angle of reflection. (iii) Calculate the angle made by the reflected ray and the surface. We use the diagram shown below to answer the questions. a) angle of incidence: i = 90 - 56 = 34 °. b) angle of reflection r = i = 34 ° (by the law of reflection) c) q = 90 - r = 90 - 34 = 56 °. d) i + r = 34 + 34 = 68 °. Example 2: A ray of light is reflected by two parallel mirrors (1) and (2) at points A and B. The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. What is reflection example?
To figure out where the image of this object is located, a ray diagram can be used. In a ray diagram, rays of light are drawn from the object to the mirror, along with the rays that reflect off the mirror. The image will be found where the reflected rays intersect. Note that the reflected rays obey the law of reflection.
Purpose To develop an understanding of the Law of Reflection, to apply the Law of Reflection to finding images formed by plane and spherical mirrors, and to learn to draw ray diagrams to assist in predicting the locations of images formed by spherical concave mirrors. Hypothesis According to the Law of Reflection, the angle of […]
The Law of Reflection; Specular vs. Diffuse Reflection; Light is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a predictablelawknown as thelaw of reflection. The diagram below illustrates the law of ...

Pavings Floor is representative of earth, in it the darkness and the light are both alike, black and white flooring and is described as “a celestial canopy of diverse colours, even the heavens.
The Law of Reflection states that when waves are reflected from an interface, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. The purpose of this lab is to experimentally verify this outcome. Given below are a sample screen capture and an accompanying image showing an example of the corresponding ray and angle constructions.
In your earlier classes, you have learnt the laws of reflection at a plane surface. Let us recall these laws : Law 1 -The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence always lie in the same plane. Law 2 -The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection : ∠i = ∠r
Laws of reflection The laws of reflection determine the reflection of incident light rays on reflecting surfaces, like mirrors, smooth metal surfaces, and clear water. Following are the laws of reflection: The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface of the mirror all lie in the same plane.
Two Rules of Reflection for Concave Mirrors. Light always reflects according to the law of reflection, regardless of whether the reflection occurs off a flat surface or a curved surface. Using reflection laws allows one to determine the image location for an object. The image location is the location where all reflected light appears to diverge ...
Laws of reflection: The first law of reflection states that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface of the mirror, all lie in the same plane. The second law of reflection states that the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. Both angles are measured with respect to the normal to the mirror.
These are laws of reflection. Law 1 The first law of reflection states that the reflection angle is always equivalent to the angle of incidence. If the incident ray falls on the plane mirror along the normal, i.e. 90°, the reflected ray will travel along the same path Law 2
The reflection of light follows two laws: 1. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. 2. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane. We often express the first law in short as
Reflection is a phenomenon in which a wave traveling through a medium reflects at the interface of another medium. In optics, reflection takes place when light is incident at the interface of the two media. The ray of light returns to the first medium without any change in velocity. Reflection Example. Image Courtesy: Satyam Bhuyan.
This is basically what the law of reflection is all about. Here's a diagram to help you visualize the law of reflection a bit better: Angle of incidence and angle of reflection In the diagram above, the light ray approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray, while the one that bounces off the mirror is called the reflected ray.
Solution: The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection (where both angles are measured from the normal line to the surface). The normal line is shown as the dashed line in the figure. Let's add angle ?3 to the figure; note that this angle is 90° - ?1.
the angle of reflection, r, is the angle between the normal and reflected ray. The law of reflection states that: angle of incidence i = angle of reflection r. For example, if a light ray hits a...


















0 Response to "39 laws of reflection diagram"
Post a Comment