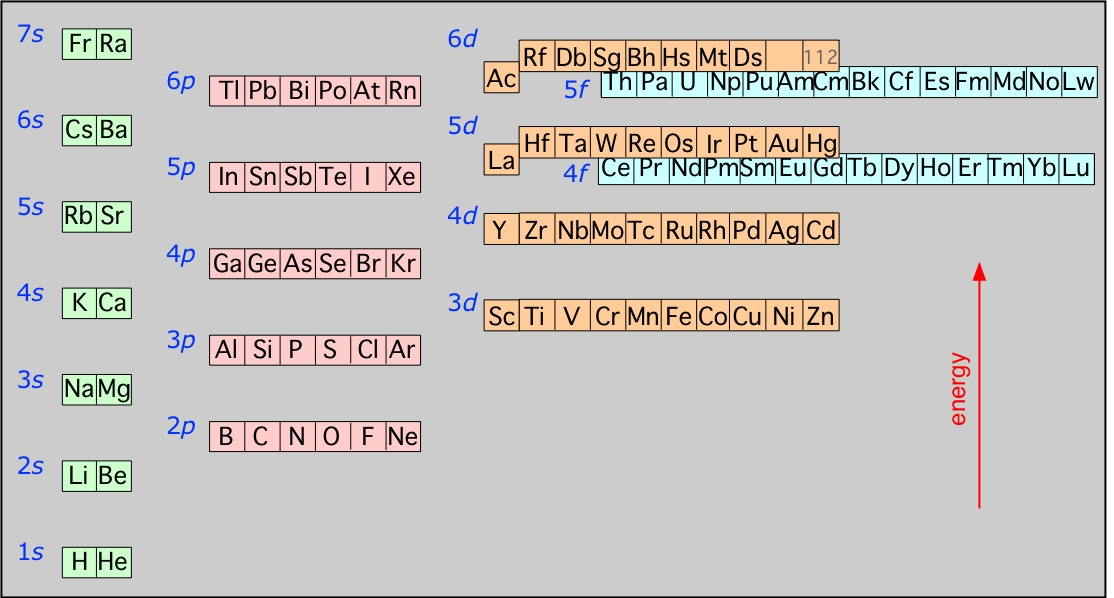
38 orbital diagram for lead
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics. Two atomic orbitals in phase create a larger electron density, which leads to the σ orbital. If the two 1s orbitals are not in phase, a node between them causes a jump in energy, the σ* orbital. From the diagram you can deduce the bond order, how many bonds are formed between the two atoms. For this molecule it is equal to one.
Use partial orbital diagrams to show how the atomic orbitals of the central atom lead to hybrid orbitals in (a) GeCl 4: (b) BCl 3; (c) CH 3+. Step-by-step solution Step 1 of 4 (a) In molecule, the electron group arrangement around 'Ge' atom is tetrahedral. Hence, 'Ge' is (central atom) hybridized. The 'Ge' atom has four half-filled orbitals.

Orbital diagram for lead
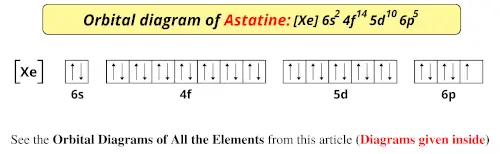
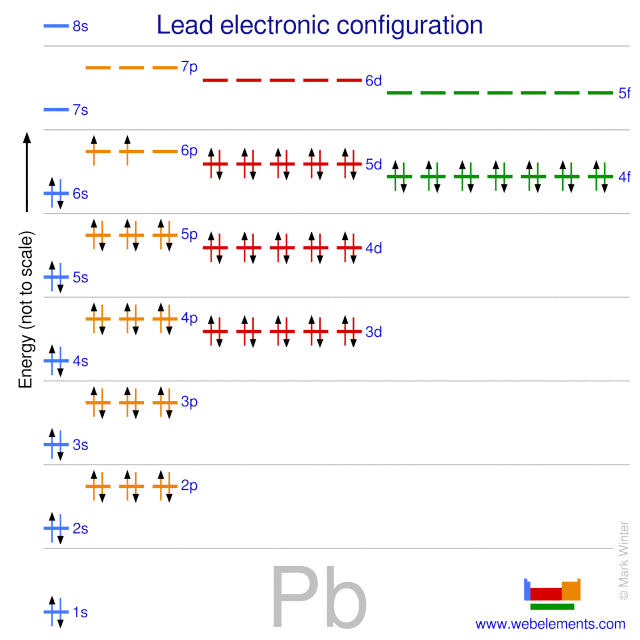
This is the orbital diagram of lead: But in science, it's pretty difficult to work with these diagrams; not to mention that are utterly wrong. Instead, electron configurations are used. Lead (Pb) has an atomic number (Z) of 82. That means it has 82 protons on it's nucleus. On Pb's fundamental state, Z equals the number of electrons. Figure 8.3 The effect of nuclear charge on orbital energy. Figure 8.4 Shielding and orbital energy. Figure 8.5 Penetration and orbital energy. Illustrating Orbital Occupancies The electron configuration n l # of electrons in the sublevel as s, p, d, f The orbital diagram (box or circle) Figure 8.6 Order for filling energy sublevels with electrons. Orbital diagram of Lead (Pb) 83: Orbital diagram of Bismuth (Bi) 84: Orbital diagram of Polonium (Po) 85: Orbital diagram of Astatine (At) 86: Orbital diagram of Radon (Rn) 87: Orbital diagram of Francium (Fr) 88: Orbital diagram of Radium (Ra) 89: Orbital diagram of Actinium (Ac) 90: Orbital diagram of Thorium (Th) 91:
Orbital diagram for lead. Answer (1 of 3): Orbital Diagrams Many times it is necessary to see all the quantum numbers in an electron configuration, this the purpose of the orbital diagram. In addition to listing the principle quantum number, n, and the subshell, ℓℓ, the orbital diagram shows all the different orientation... There are atomic orbitals in chemistry and the role of electronic configuration is that it tells us how many electrons are divided in their respective atomic orbitals. If we talk about the electronic configuration of lead or Pb, then we may write it as; Electronic configuration For Lead (Pb): 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 6 4d 10 4f 14 ... orbitals have one electron. Then additional electrons enter each orbital until 2 . electrons are in each orbital. Once all orbitals in a sublevel are filled (each with 2 . electrons), the next electron enters the next higher energy sublevel. The Aufbau diagram below illustrates the order of filling orbitals and sublevels. p orbital lobes are in the plane of the paper. p orbital lobe is in back of the paper. p orbital lobe is in front of the paper. H C C H Each line represents a bond. While the three simple lines of the triple bond appear equivalent, we know that the first bond formed is a sigma bond of overlapping sp hybrid orbitals. The
Solution for What is the orbital diagram of the atom Lead Pb 82. close. Start your trial now! First week only $4.99! arrow_forward. learn. write. tutor. study resourcesexpand_more. Study Resources. We've got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. ... 0 Comments. on Orbital Diagram For Germanium. orbital. Because an electron can have either one of two spins, any orbital can hold a maximum of four . The orbital diagram for germanium is. 1s. 2s. 2p. 3s. Oxidation States, +4,2. Electrons Per Shell, 2 8 18 4. Electron Configuration, [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p2. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p2. Pb (Lead) is an element with position number 82 in the periodic table. Located in the VI period. Melting point: 327.5 ℃. Density: 11.34 g/cm 3 . Electronic configuration of the Lead atom in ascending order of orbital energies: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 2. Electronic configuration of the Lead ... Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory (continued 1) • Filling of MOs with electrons is governed by the same rules as for atomic orbitals • Aufbau principle - Fill MOs beginning with the lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital • Pauli exclusion principle - No more than two electrons can be accommodated in a MO, and their spins must be paired
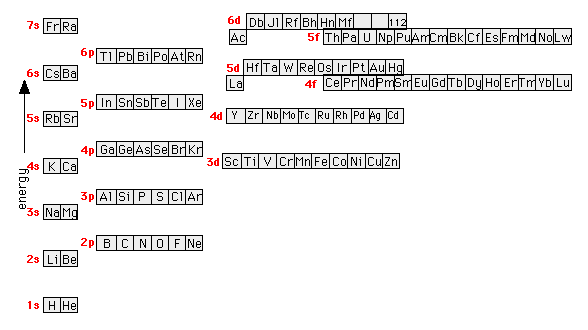
1. The Pauli principle: No more than two electrons can occupy a given orbital. If there are two electrons in an orbital, their spins must be paired (one must have m s = 1 2 and the other, m s = − 1 2). 2. The aufbau (building-up) principle: When electrons are filled in to orbitals in an atom, the orbitals with lower energy are filled first. Electron configuration and orbital diagram worksheet The goal of introducing quantity numbers has shown that similarities in the electronic arrangement or electronic configurations lead to the similarities and differences of the element's properties. But writing the proportion numbers of electrons to an element in notation set such as {2.1.1 ... Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Use partial orbital diagrams to show how the atomic orbitals of the central atom lead to hybrid orbitals in (a) BF4-; (b) PO43-; (c) SO3.. The 1s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of .. Rb+, Se2−. The first orbital (an s orbital) can contain only two electrons.. Rubidium.
lowing orbitals on two atoms: (a) the 2s orbital on each, CQ (b) the 2pz orbital on each (assume that the atoms are on the z-axis), (c) the 2s orbital on one and the 2pz orbital on the other. 9.41 Consider the bonding in an MgH2 molecule. (a) Draw a Lewis structure for the molecule, and predict its molec- ular geometry.
Now for the pain of doing the orbital filling diagram of lead: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 6 6s 2 4f 14 5d 10 6p 2. The rules are the same, so I'll just bite the metaphorical bullet and write it out here: And with that, you should officially know what you're doing!
The sum of the number of protons and neutrons of an atomic nucleus. In other words, it's the sum of the number of nucleons in an atom. Relative Atomic Mass. The ratio of the average mass per atom of an isotope to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Relative atomic mass is also known as atomic weight (symbol: A r ).
The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is. 13. The orbital diagram for a ground-state oxygen atom is. 14. The orbital diagram for a ground state carbon atom is ... lead E) tin. 17. Which ground-state atom has an electron configuration described by the following orbital diagram? A) phosphorus B) nitrogen C) arsenic D) vanadium E ...
Use partial orbital diagrams to show how the atomic orbitals of the central atom lead to the hybrid orbitals in (W/ Ground State Configuration and Excited State Configuration) fullscreen Expand Transcribed Image Text
Use partial orbital diagrams to describe how mixing of the atomic orbitals of the central atom(s) leads to hybrid orbitals in each of the following: (a) Methanol, CH 3 OH (b) Sulfur tetrafluoride, SF 4 (a) CH 3 OH The electron- group arrangement is tetrahedral around both the C and the O atom. 11-20 Sample Problem 11.1 2s 2 p isolated C atom sp 3
The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is A) A B) B C) C D) D see chart. A. The orbital diagram for a ground-state oxygen atom is ... lead E) tin. E) tin. Which ground-state atom has an electron configuration described by the following orbital diagram? A) phosphorus B) nitrogen C) arsenic D) vanadium E) none of these. A) phosphorus.
lead (Pb; Z = 82) PLAN: The atomic number gives the number of electrons, and the periodic table shows the order for filling orbitals. The partial orbital diagram includes all electrons added after the previous noble gas except those in filled inner sublevels.
It is in the minimum energy state. This partial penetration of the orbital is known as orbital overlap. The extent of overlap depends on the two participating atoms, their size and the valence electrons. In general, the greater the overlap, stronger is the bond formed between the two atoms. Thus, according to the orbital overlap concept, atoms ...
Electron binding energies for lead. All values of electron binding energies are given in eV. The binding energies are quoted relative to the vacuum level for rare gases and H 2, N 2, O 2, F 2, and Cl 2 molecules; relative to the Fermi level for metals; and relative to the top of the valence band for semiconductors. Label Orbital eV [literature ...
Orbital diagram of Lead (Pb) 83: Orbital diagram of Bismuth (Bi) 84: Orbital diagram of Polonium (Po) 85: Orbital diagram of Astatine (At) 86: Orbital diagram of Radon (Rn) 87: Orbital diagram of Francium (Fr) 88: Orbital diagram of Radium (Ra) 89: Orbital diagram of Actinium (Ac) 90: Orbital diagram of Thorium (Th) 91:
Figure 8.3 The effect of nuclear charge on orbital energy. Figure 8.4 Shielding and orbital energy. Figure 8.5 Penetration and orbital energy. Illustrating Orbital Occupancies The electron configuration n l # of electrons in the sublevel as s, p, d, f The orbital diagram (box or circle) Figure 8.6 Order for filling energy sublevels with electrons.
This is the orbital diagram of lead: But in science, it's pretty difficult to work with these diagrams; not to mention that are utterly wrong. Instead, electron configurations are used. Lead (Pb) has an atomic number (Z) of 82. That means it has 82 protons on it's nucleus. On Pb's fundamental state, Z equals the number of electrons.

























0 Response to "38 orbital diagram for lead"
Post a Comment