38 d orbital energy level diagram
Alloys and compounds of the d-block elements are important components of the materials the modern world depends on for its continuing technological development, while most of the first-row transition metals are essential for life.This chapter introduces some of the key industrial and biological roles of these elements. You will learn, for example, why copper, silver, and gold …
OOPS!! "Where an atom's ELECTRONS go" is what the heading should read.Electron orbital diagrams showing energy levels (n), subshells or sublevels(s, p, d, f...
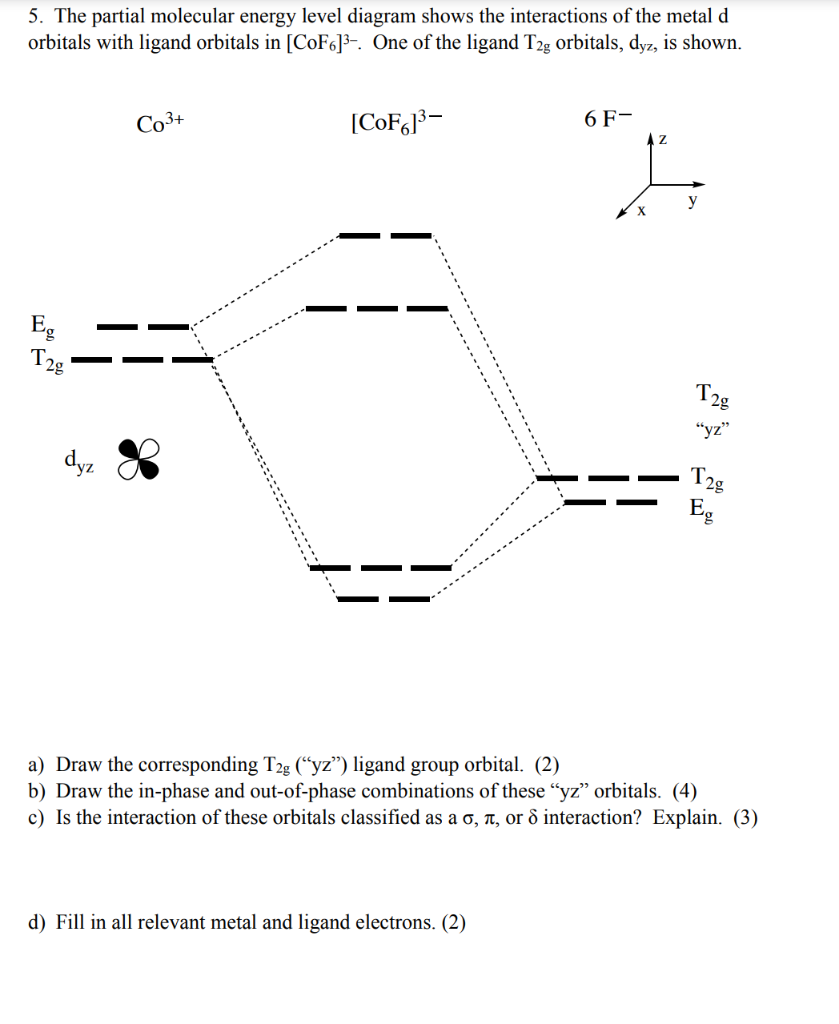
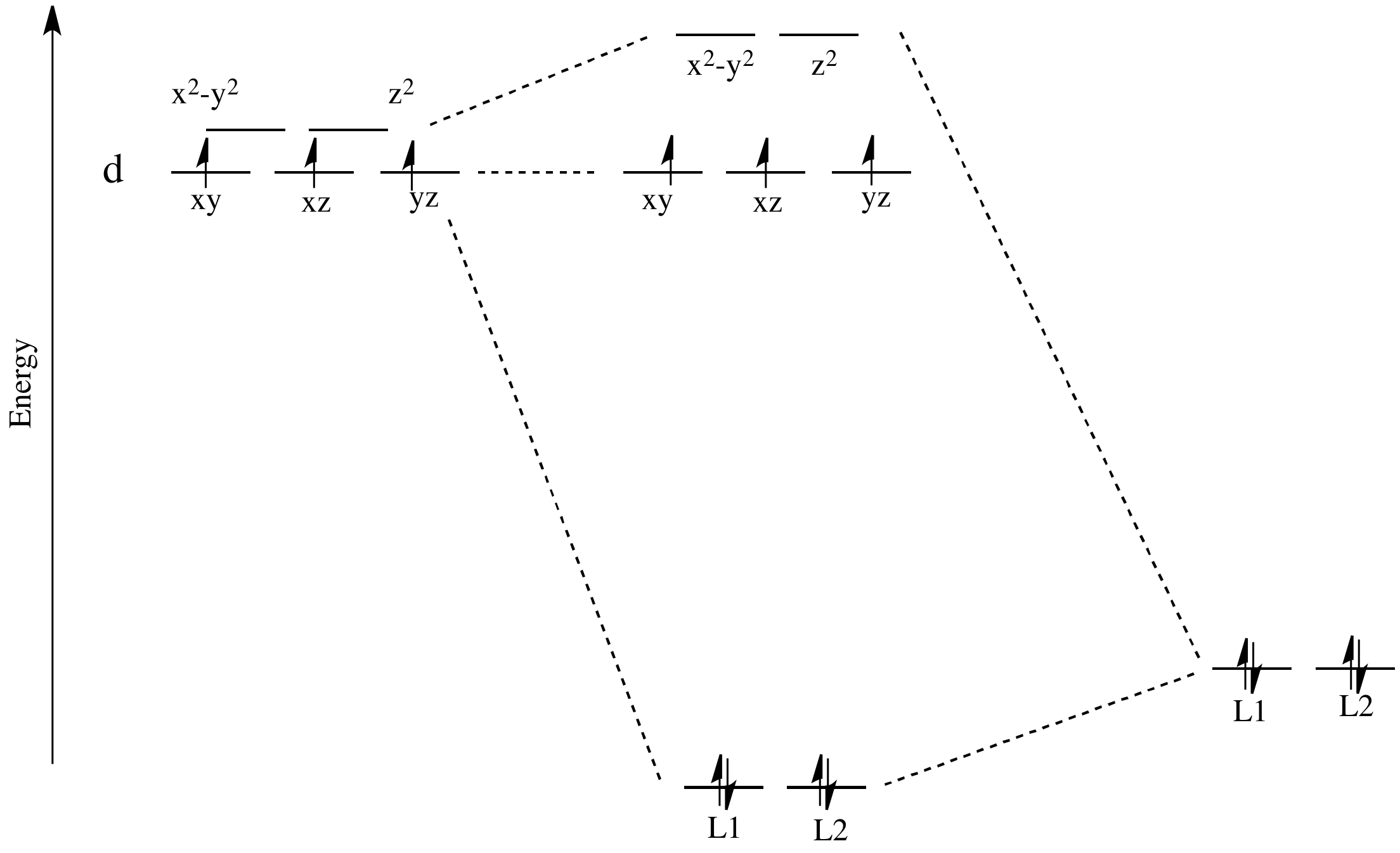
The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for σ-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Figure 10. The formation of σ-molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding and non-bonding) in octahedral complexes of transition metals. Buy the complete book with TOC navigation,
D orbital energy level diagram
All levels except the first have p orbitals. d ORBITALS. In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels. At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3px, 3py, 3pz). At ...
Electron configuration of nitrogen atom through orbital diagram. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by 'l'. The value of 'l' is from 0 to (n - 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f.
Energy Level Diagrams: Some Important Observations. The energy level diagram can help us deduce that the energy of the subshells of a specific shell is not equal. The energies of 2s and 2p, for example, are different. The subshell with the lowest value of I has the lowest energy in a given shell. 2s (I = 0) has lower energy than 2p (I = 1) in the second shell.
D orbital energy level diagram.
Answer to: Draw an orbital energy-level diagram showing the configuration of the d-electrons on the metal ion in the complex NiCl42- (tetrahedral)....1 answer · Top answer: The given coordination complex ion is [NiCl4]2−[NiCl4]2−. The central metal atom in {eq}{\left[...
So the lower energy or bills are always filled first. And here we see that we have one unfairly electron. However, it in the other complex water is a relatively weak field splitting Lagan, so the electron, the energies of the orbital's are relatively similar. So as a result of hans rule, electrons are essentially added to each of the orbital's.
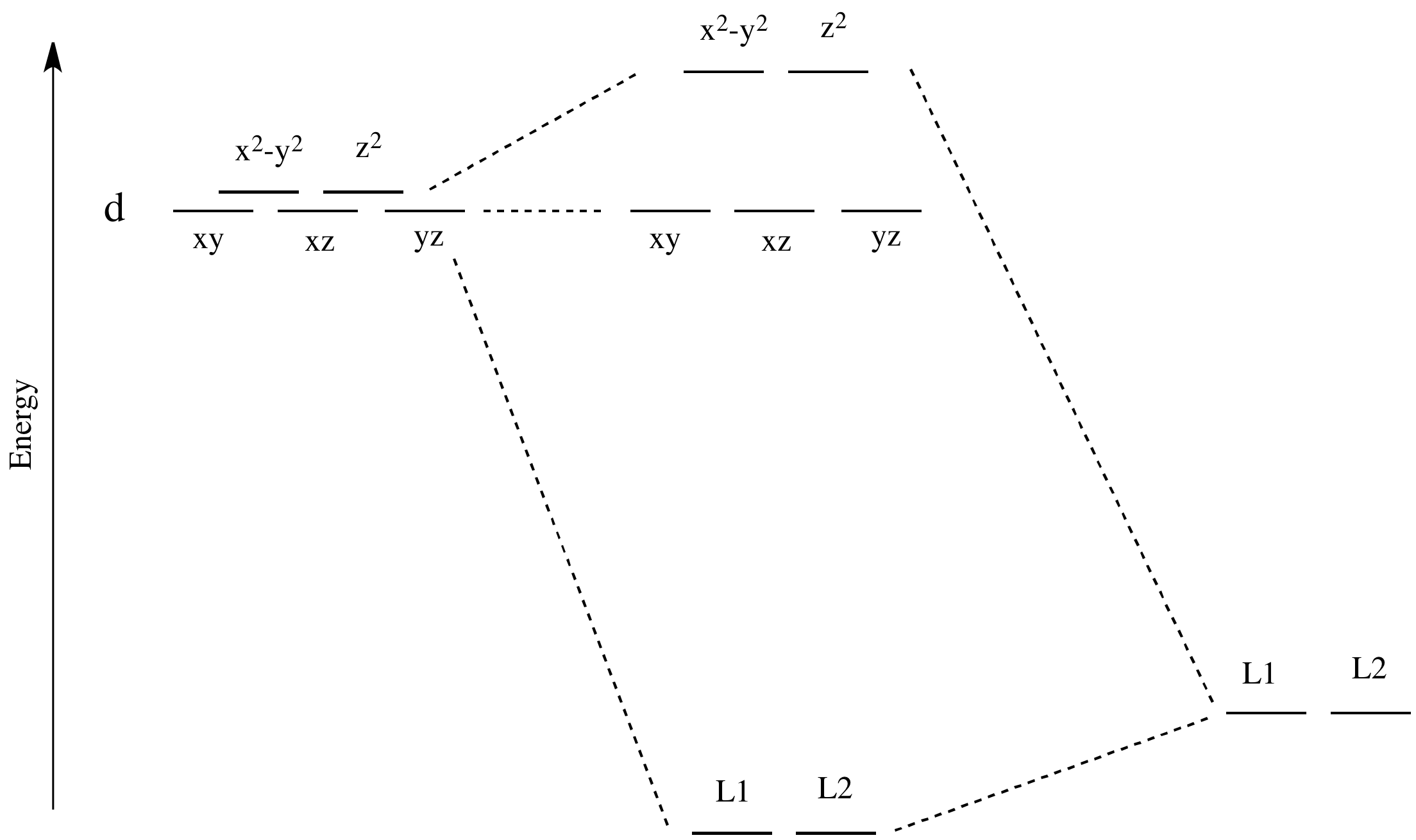
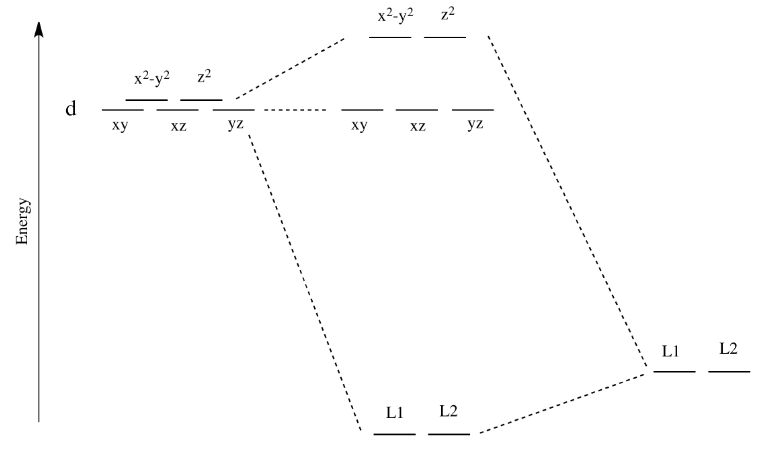
Like all ligand-metal interaction diagrams, the energy levels of the ligands by themselves are shown on one side. The metal's electronic energy levels are shown on the other side. The result of their interaction, a metal-ligand complex, is shown in the middle. The d orbital splitting diagram is shown in a box.
The Aufbau principle tells you that the lowest-energy orbitals fill first, but the specific order isn't sequential in a way that's easy to memorize. See Resources for a diagram showing the filling order. Note that the n = 1 level only has s orbitals, the n = 2 level only has s and p orbitals, and the n = 3 level only has s, p and d orbitals.
Oct 11, 2021 · 1 answer(a) The complex ion, [Ni(en)3]2+ is octahedral. Since en is a strong ligand there is pairing of electrons. Number of unpaired electrons = n ...
For example, the orbital 1s (pronounced as the individual numbers and letters: "'one' 'ess'") is the lowest energy level (n = 1) and has an angular quantum number of ℓ = 0, denoted as s. Orbitals with ℓ = 1, 2 and 3 are denoted as p, d and f respectively.
by RJ Deeth · 2020 — Qualitative MO theory predicts degenerate dπ orbitals for planar coordination complexes with formally σ-only ligands and the splitting energy, ...
Therefore, the electron energy levels of these five d-orbitals in mechanics forming a set five-fold degenerate energy level and the shape diagram dimensions of these orbitals identify by the principal, azimuthal, magnetic, spin quantum number or numbers of the atom for physics or chemistry courses.
Below is a blank energy level diagram which helps you depict electrons for any specific atom. At energy level 2, there are both s and p orbitals. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. The three dashes in 2p subshells represent the same energy. 4s has lower energy when compared to 3d. Therefore, the order of energy level is as follows: s ...
Molecular Orbital Theory: Energy level diagram for molecular orbitals. Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mullikan in 1932. This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in molecules, atomic orbitals lose their identity and the electrons in molecules are present in new orbitals called molecular orbitals.
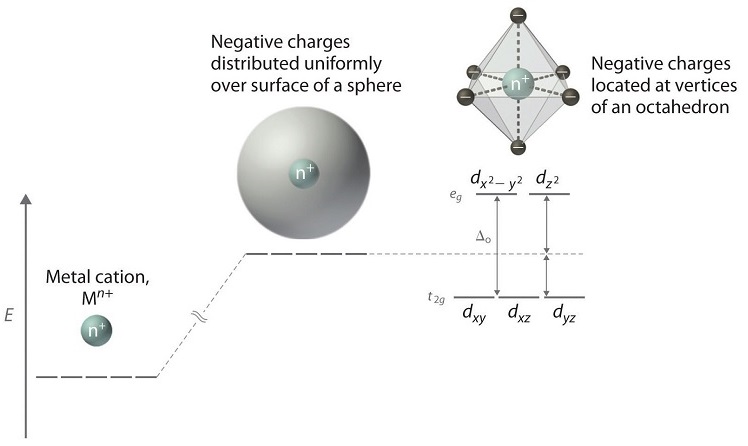
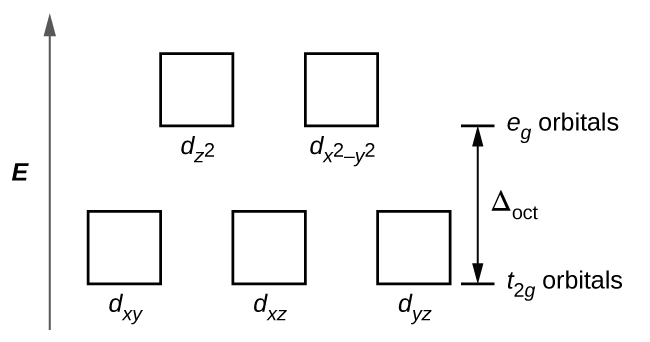
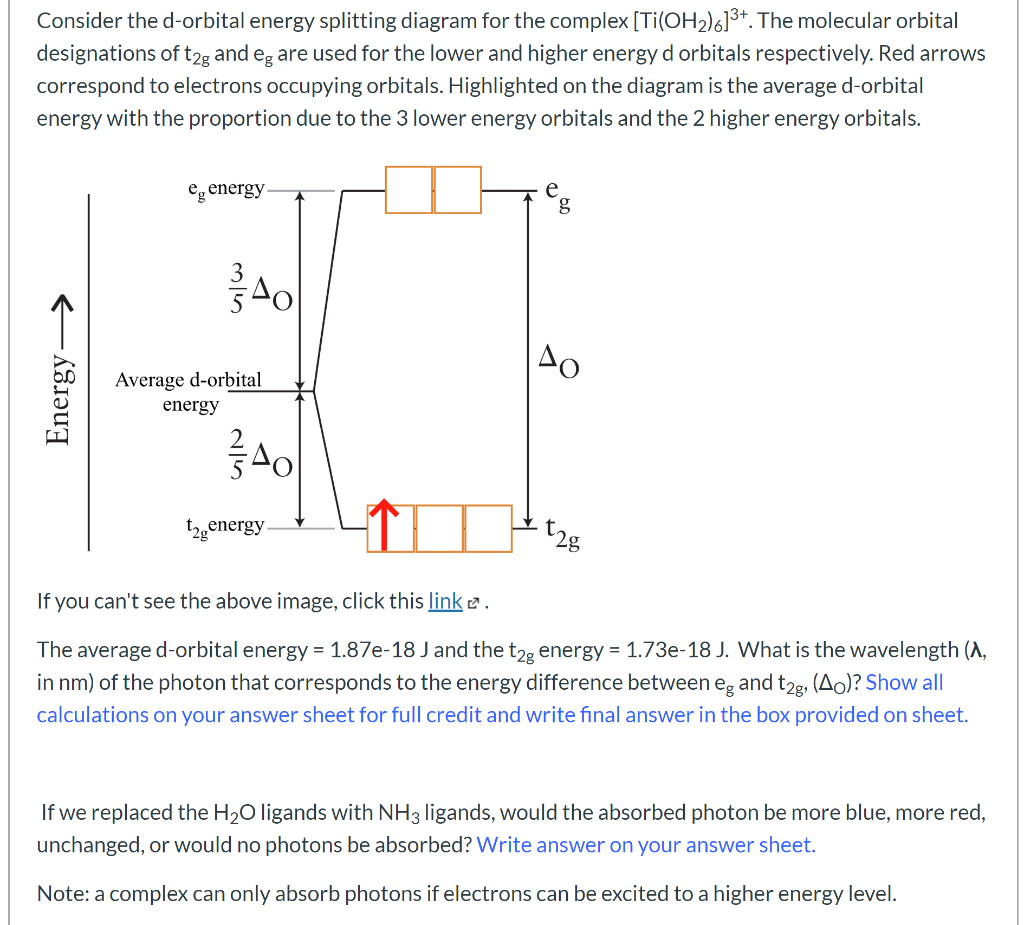
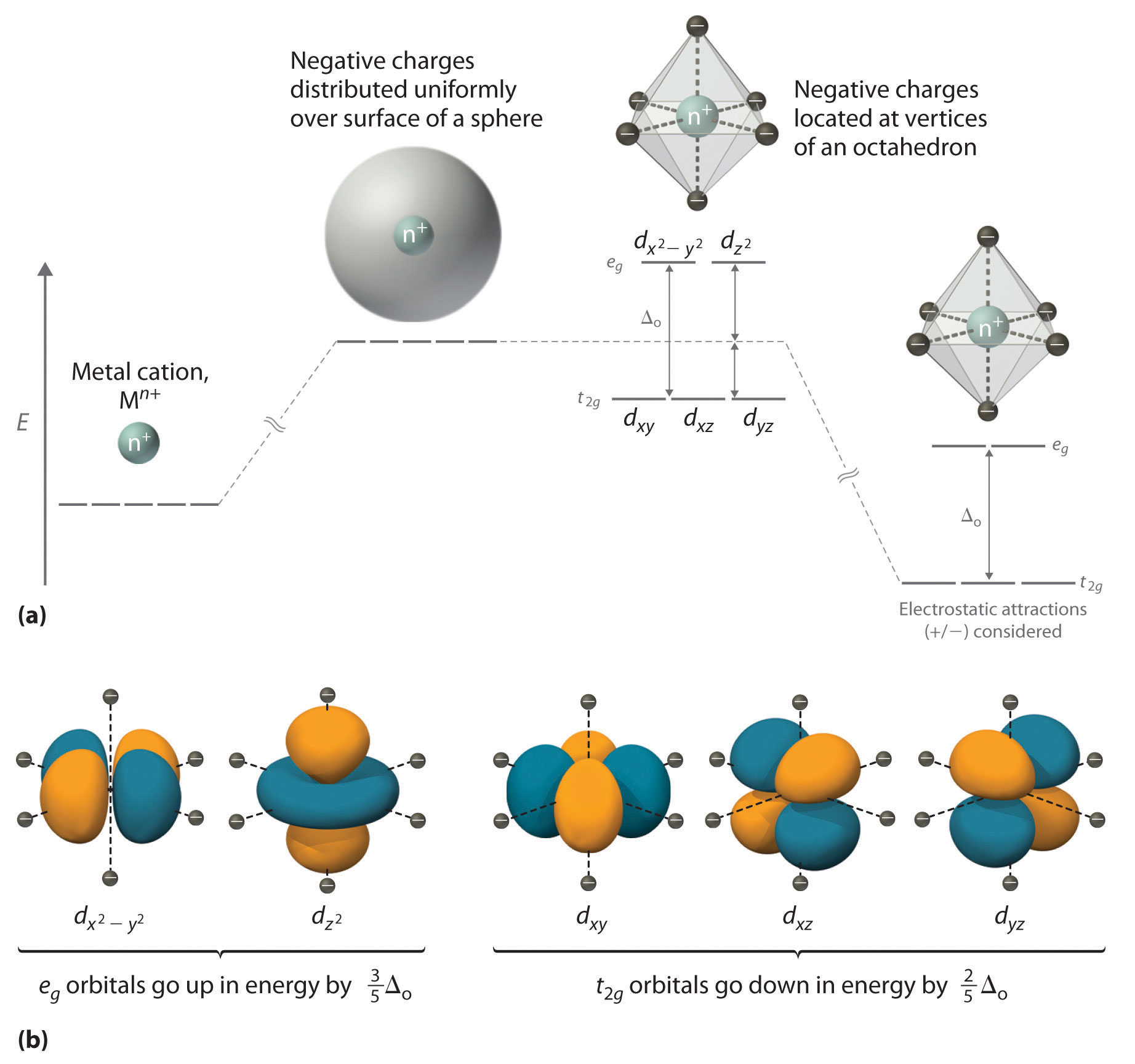
• The energy increase of the e g orbitals and the energy decrease of the t 2g orbitals must be balancedrelative to the energy of the hypotheticalsphericalfield(aka the barycenter).• The energy of each of the two orbitals of the e g set rises by +3/5 o (+6 Dq) while the energy of eachof the three t 2g orbitalsfallsby ‐2/5 o(‐4Dq). • Thisresults inno netenergy changefor the system:
The molecular, sp 3 orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedron, with bond angles of 109.5 o. Each of the 1s orbitals of H will overlap with one of these hybrid orbitals to give the predicted tetrahedral geometry and shape of methane, CH 4. Hybridization also changes the energy levels of the orbitals. The 2s orbital of carbon is lower in energy than the 2p orbitals, since it is more penetrating.
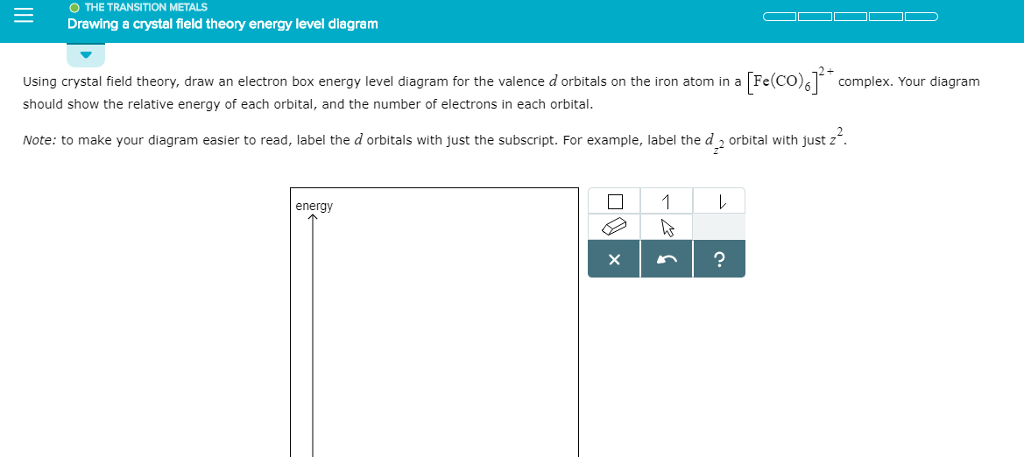
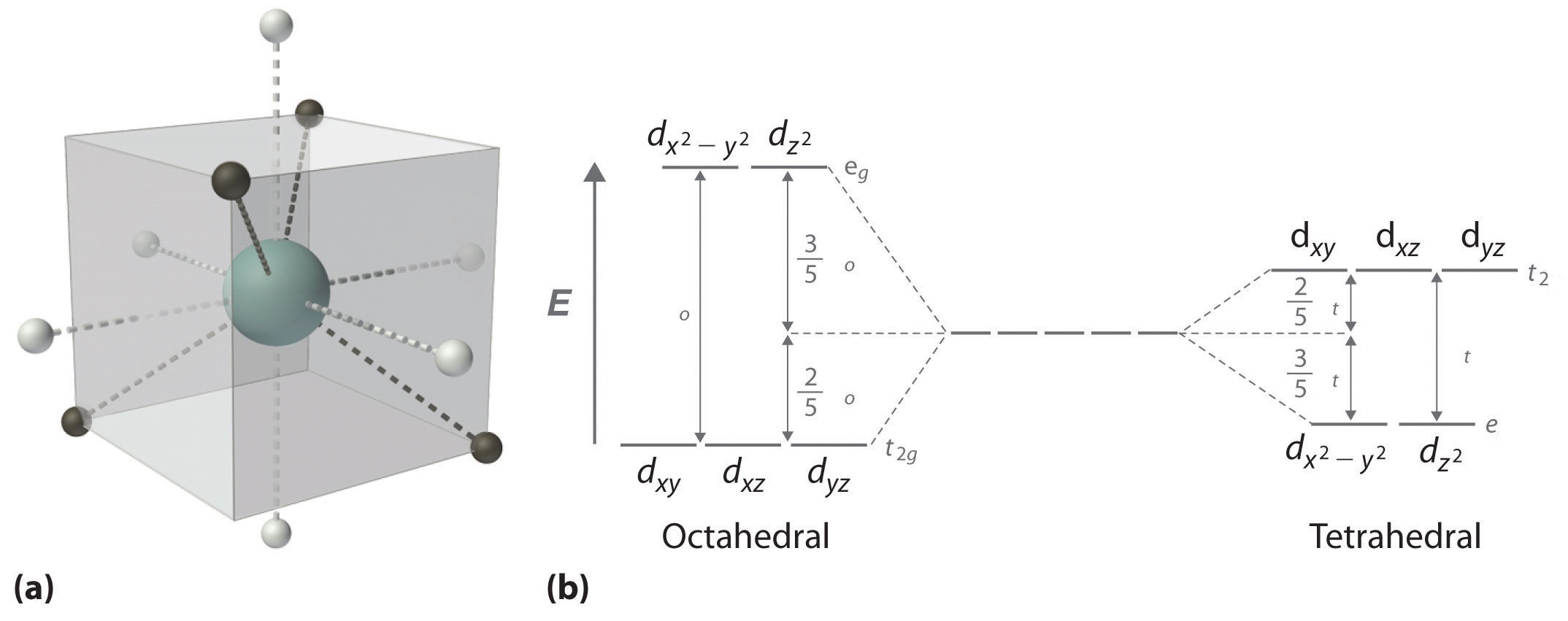
Transcribed image text: Using crystal field theory, draw an electron box energy level diagram for the valence d orbitals on the cadmium atom in a tetrahedral「C14_-complex. Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electrons in each orbital Note: to make your diagram easier to read, label the d orbitals with just the subscript.
A P-Orbital in the second energy level is a 2p orbital ( 2p(x), 2p(y), 2p(z) ) A P-Orbital in the third energy level is a 3p orbital ( 3p(x), 3p(y), 3p(z) ) etc. In addition, the third and subsequent energy levels each contain five D-Orbitals, the fourth and subsequent energy levels contain seven F-Orbitals and so on.
molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the NO molecule. We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is 2.5. Figure 9.42: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure 9.43: A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule.
Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electron in each orbital. Question: Using crystal field theory, draw an electron box energy level diagram for the valence d orbital on the cobalt atom in a [CoBr_6]^3- complex. Your diagram should show the relative energy of each orbital, and the number of electron ...
The fifth 3d orbital, called the 3 d z 2 orbital, has a unique shape: it looks like a 2p z orbital combined with an additional doughnut of electron probability lying in the xy plane. Despite its peculiar shape, the 3 d z 2 orbital is mathematically equivalent to the other four and has the same energy.
Download scientific diagram | Energy level ordering of d -orbitals in (a) tetrahedral and (b) octahedral crystal field environments. from publication: ...
degenerateHaving the same quantum energy level. ... The electrons in the d orbitals of the central metal ion and those in the ligand repel each other due to ...
The d orbitals also split into two different energy levels. The top three consist of the dxy, ...May 6, 2021 · Uploaded by Chuck WightCrystal Field Stabilization Energy · Introduction to Crystal Field...
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. ... If N b = Na,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals. 2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order.
This video explains s, p, d, and f orbitals, sublevels, and their shapes. It discusses the 4 quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. n represents the energy leve...
Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram . For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right.
with the. d. orbital being one level lower than the energy level it is on. orbital diagram for arsenic see more ideas approximately from diagram electron configuration gallery & create your house design images related to pictures as well help you in locating the solution are seeking about itOrbital diagram for arsenic.
The molecular orbital energy- level diagram that results is constructed by putting the molecular orbitals in order of increasing number of internuclear nodal planes, the orbital with no such nodal plane lying at lowest energy and the orbital with nodal planes between all the atoms lying at highest energy. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO ...
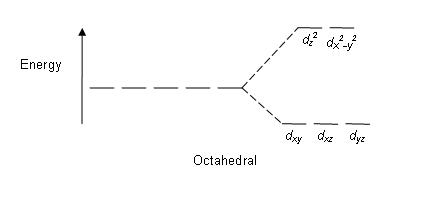
The octahedral ion [Fe(NO2)6]3−, which has 5 d-electrons, would have the octahedral splitting diagram shown at right with all five electrons in the t2g level.Overview of crystal field theory · Crystal field stabilization energy
Electron configuration of sodium atom through orbital diagram. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by 'l'. The value of 'l' is from 0 to (n - 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f.
Figure 46. The splitting pattern of d-orbital energy levels of d3-metal complexes in tetragonal distortion. 2. Rhombic distortion: The unequal amount of elongation or compression along two four-fold axes of rotation in octahedral complexes produces rhombic distortions. The common examples of rhombic distortion are high-
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
Explanation of Degenerate Orbitals with Diagram. Orbitals in the 2p sublevel are degenerate orbitals - Which means that the 2p x, 2p y, and 2p z orbitals have the exact same energy, as illustrated in the diagram provided below. Similarly, the 3p x, 3p y, and 3p z are degenerate orbitals. And at the 3d energy level, the 3d xy, 3d xz, 3d yz, 3d ...
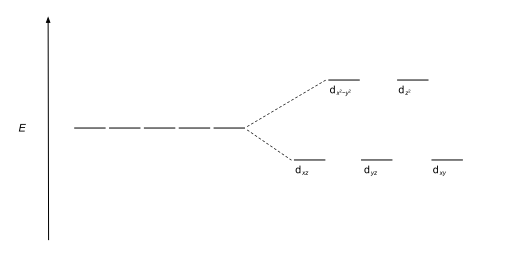
We can use the d-orbital energy-level diagram in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) to predict electronic structures and some of the properties of transition-metal complexes. We start with the Ti 3 + ion, which contains a single d electron, and proceed across the first row of the transition metals by adding a single electron at a time.
d and f orbitals. In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels. At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3p x, 3p y, 3p z). At the third level there are a total of ...
18.03.2020 · We can use the d-orbital energy-level diagram in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) to predict electronic structures and some of the properties of transition-metal complexes. We start with the Ti 3 + ion, which contains a single d electron, and proceed across the first row of the transition metals by adding a single electron at a time.











![d-orbital energy levels in planar [M II F 4 ] 2− , [M II (NH 3 ...](https://pubs.rsc.org/image/article/2020/DT/d0dt02022b/d0dt02022b-f1_hi-res.gif)










0 Response to "38 d orbital energy level diagram"
Post a Comment