37 diagram of the sun
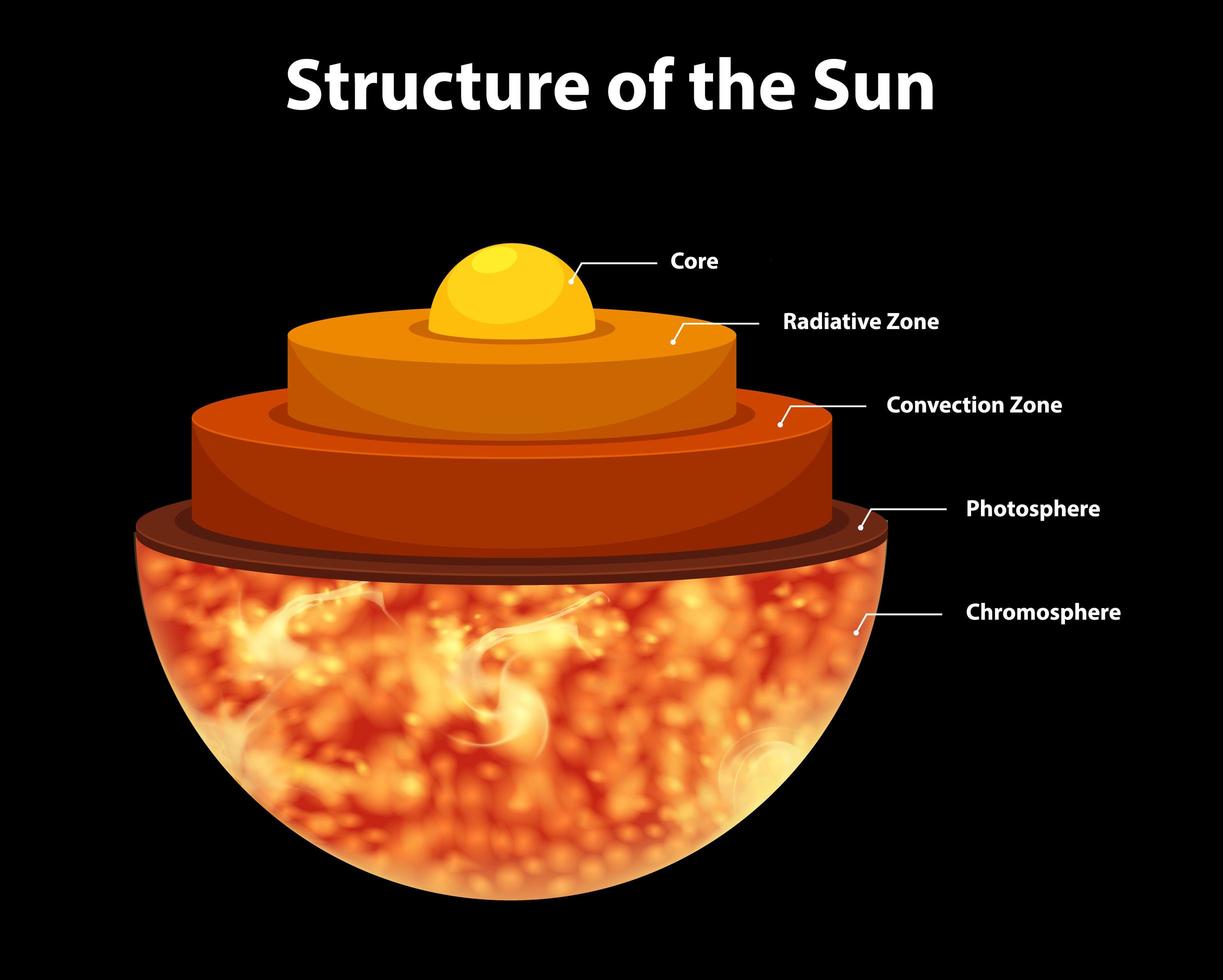
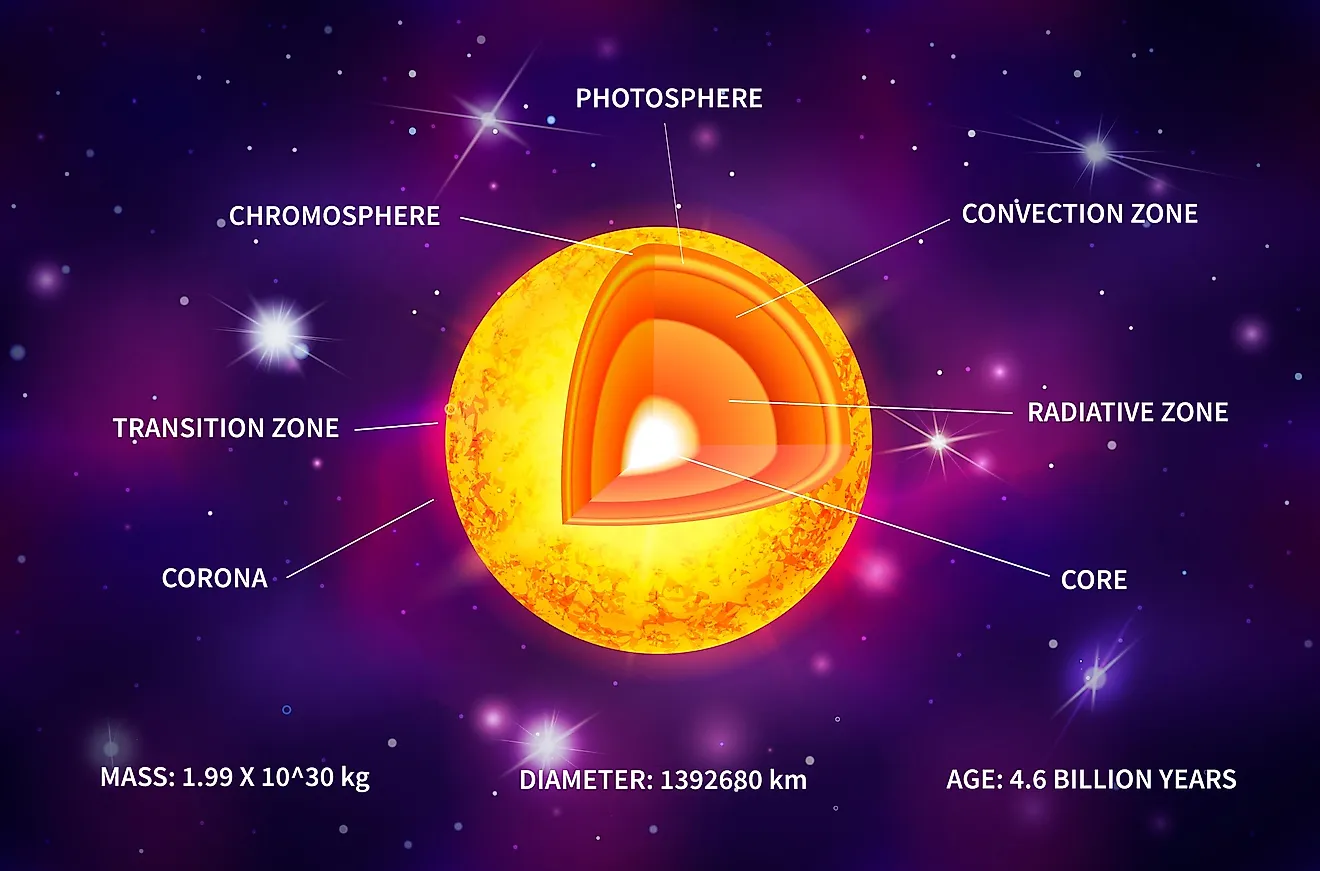
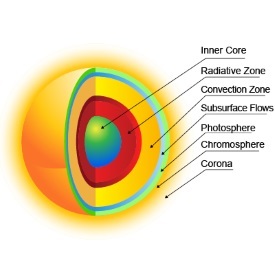
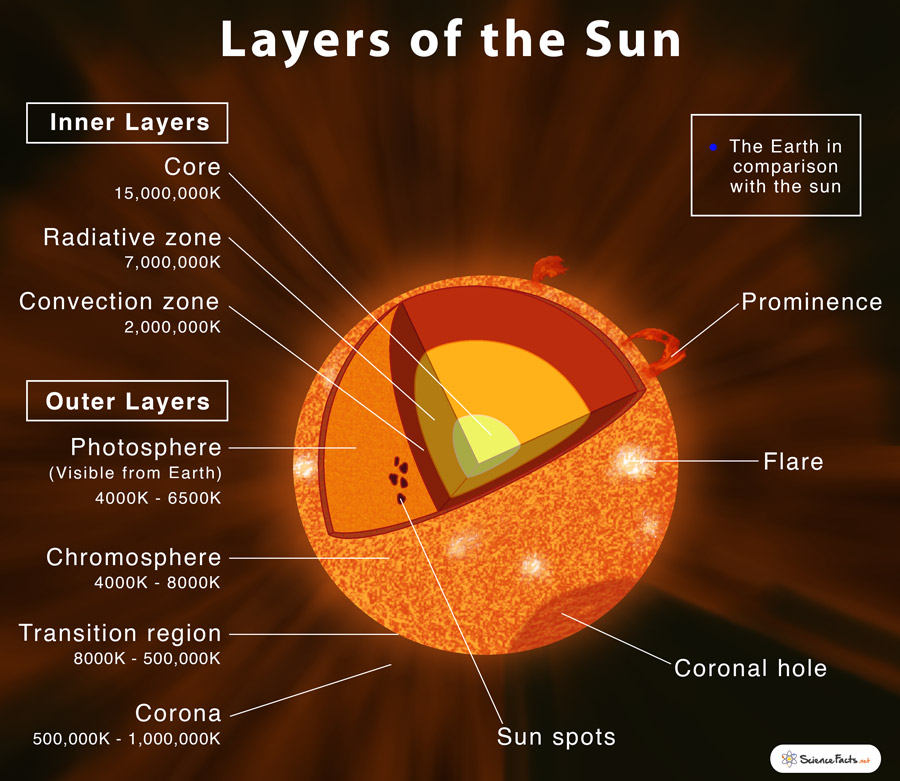
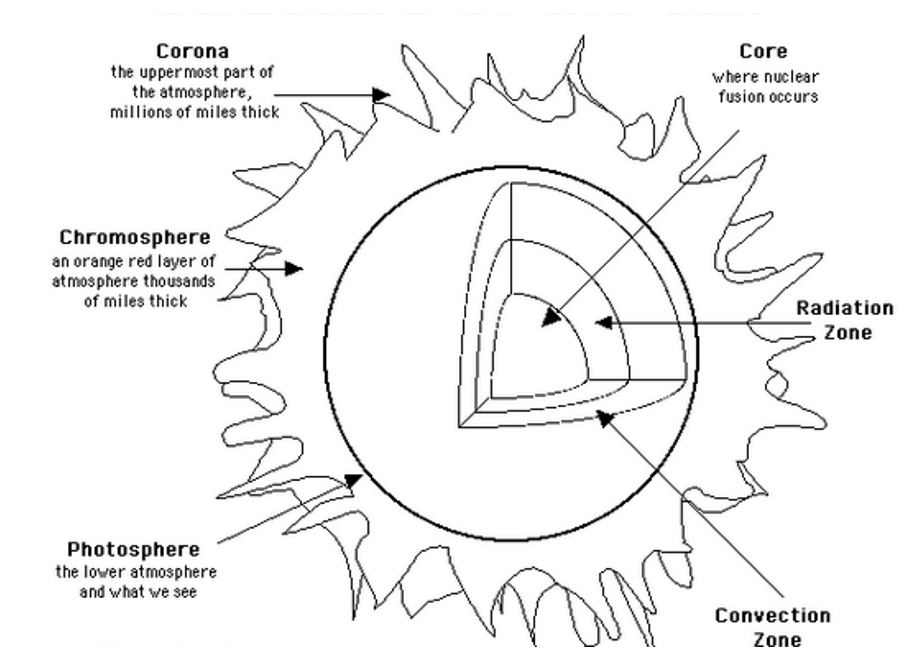
The Sun is the largest object in our solar system. It is composed of seven layers: three inner layers and four outer layers. The inner layers are the core, the radiative zone and the convection zone, while the outer layers are the photosphere, the chromosphere, the transition region and the corona. See the fact file below for more information ...
Diagram of the Solar System [/caption] This image contains all of the largest objects in the Solar System. You can print this diagram of the Solar System, as well as this handy list of all the...
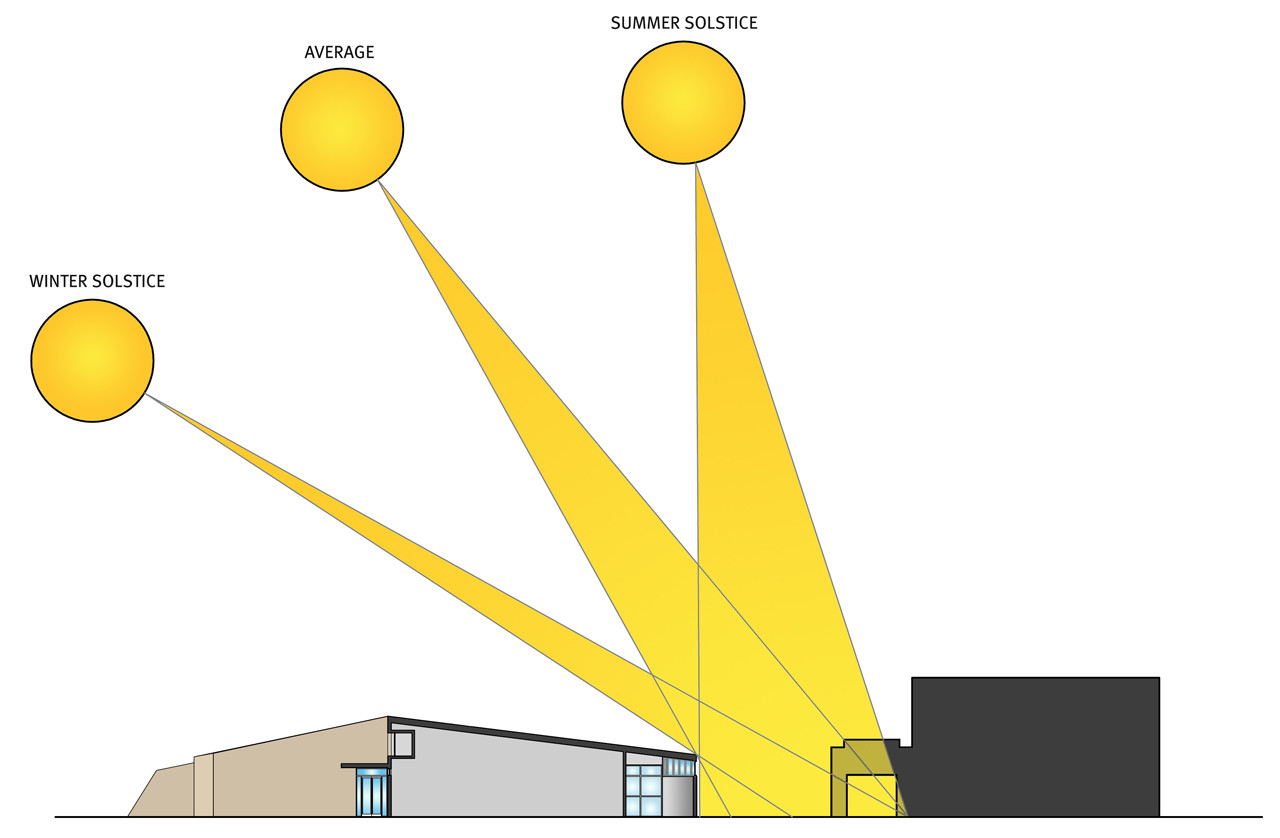
Sun chart Sun path charts can be plotted either in Cartesian (rectangular) or Polar coordinates. Cartesian coordinates where the solar elevation is plotted on Y axis and the azimuth is plotted on the X axis. Polar coordinates are based on a circle where the solar elevation is read on the various concentric circles, from 0° to 90° degrees, the azimuth is the angle going around the circle from ...

Diagram of the sun
the layer of the sun's atmosphere that gives off visible light the layer of the sun's atmosphere that has a reddish glow the layer of the sun's atmosphere that looks like a halo during an eclipse areas of gas on the sun's surface that are cooler than the gases around them reddish loops of gas that link parts of sunspot regions
In the 101 Diagrams of the sun above, the detail parts and structures of the sun are illustrated clearly. Much like the earth, the Sun has many different layers that define its structure. Unlike the earth, the Sun is completely gaseous, there is no solid surface on the Sun. More diagrams of the sun are posted in the following images.
sun. When the moon is directly in front of the earth, light from the sun is hitting directly on the backside of the moon. The moon is not visible resulting in a new moon. Reasoning (Explain how your evidence supports your claim. Describe the position of the moon, earth, and sun.) - Because of the moon's position around the earth,
Diagram of the sun.
Diagram of the Sun. Students' understanding of the sun is developed in this lesson which explores the very center of our solar system and the different elements of the sun. $2.99 . Info. Share Wish List. $2.99 . by Education.com.
The sun's atmosphere consists of the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona. The inner layer of the sun's atmosphere is called the photosphere. Photo means "light," so the photosphere is the sphere that gives off visible light. ... Label the diagram of the sun below.
Find sun earth diagram energy stock images in HD and millions of other royalty-free stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the Shutterstock collection.
diagrams are a way of showing the path that you would see the sun follow during the day. We'll look at how the sun's path changes during the course of the year at Tucson, and we'll also see how the sun's path is different at different locations on the globe. We'll come to understand better why the largest seasonal changes
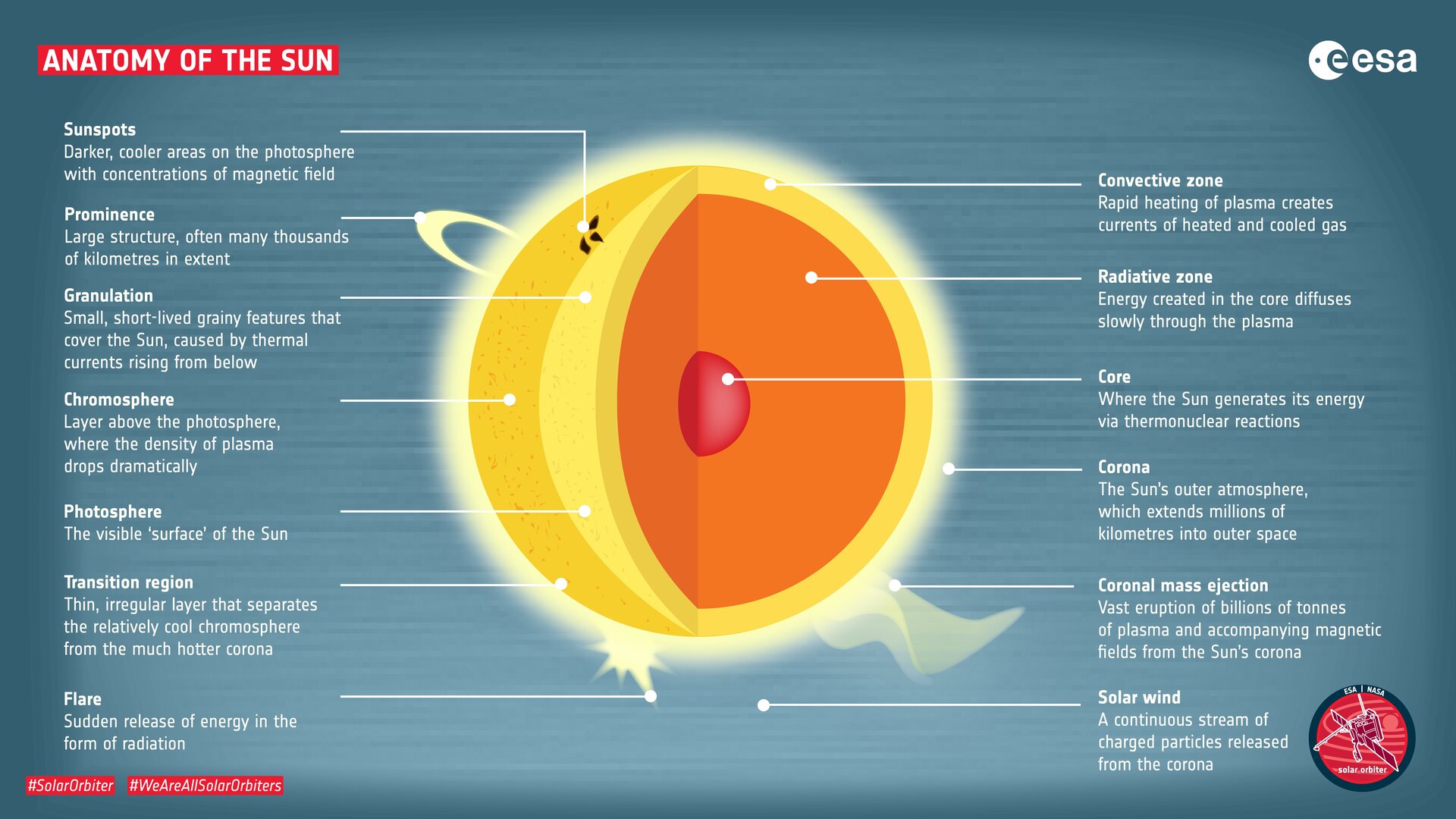
Photosphere - The photosphere is the deepest layer of the Sun that we can observe directly. It reaches from the surface visible at the center of the solar disk to about 250 miles (400 km) above that. The temperature in the photosphere varies between about 6500 K at the bottom and 4000 K at the top (11,000 and 6700 degrees F, 6200 and 3700 ...
Solar system vector infographic, education diagram. Planets Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune in order of distance from the sun with names.
2015-11-2 - Explore w Tresdin's board "sun diagram" on Pinterest.
Draw the Sun near the left side of the page. The sun is the largest body in the solar system, so draw a large circle to represent it. Then, color it in with orange, yellow, and red to represent the hot gases that it's made up of. Remember to leave enough space on the page to draw all of the planets.
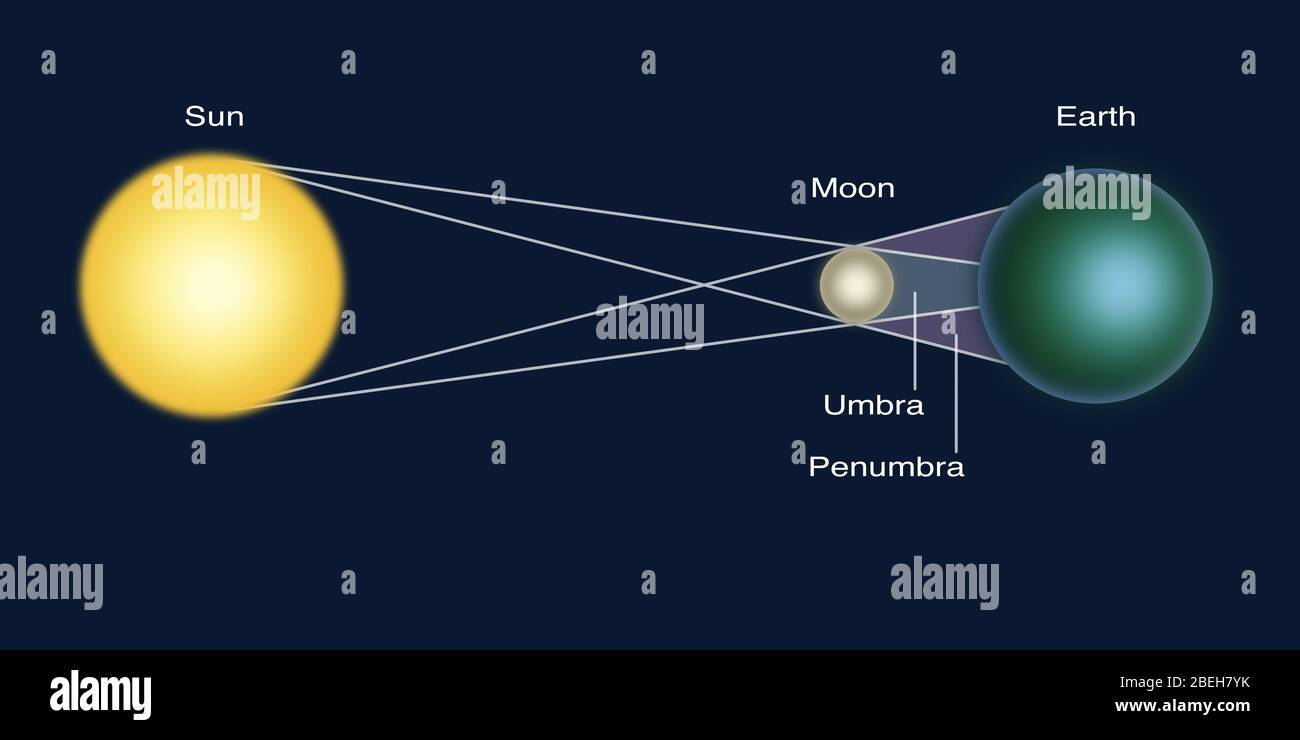
Lunar Eclipse Diagram. This shows the geometry of a lunar eclipse. When the Sun, Earth, and Moon, are precisely aligned, a lunar eclipse will occur. During an eclipse the Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the Moon. Earth creates two shadows: the outer, pale shadow called the penumbra, and the dark, inner shadow called the umbra.
Get to know Earth's star with with this diagram and vocabulary worksheet! Children will learn important solar terminology and trivia as they review a ...
Diagram of the regions of the Sun. The solar interior includes the core, radiative zone and convective zone. The photosphere is the visible surface of the ...
The parts of the inner layer are: 1. Core. It is the innermost layer of the sun, which is extremely dense where nuclear fusion generates energy in terms of photons by converting hydrogen into helium. The core is approximately 20% of the size of the solar interior and is found to be the hottest part of the sun. 2.
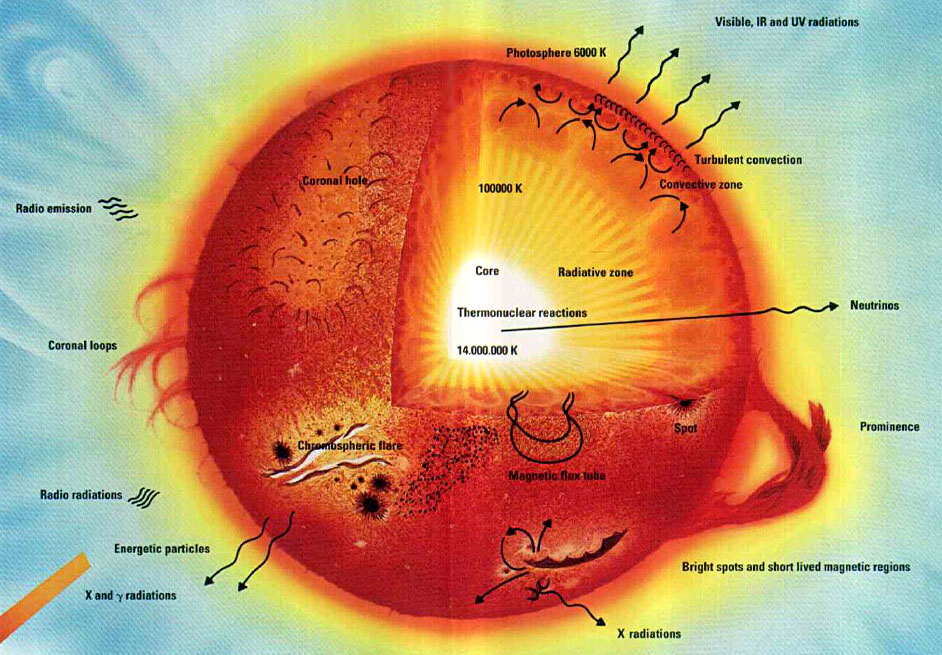
Diagram: Below is a diagram of the Sun, originally developed by NASA for educational purposes. Visible, IR and UV radiation - The light that we see coming from the Sun is visible, but if you ...
The Sun (and, of course, the rest of our solar system) is located near the Orion arm, between two major arms (Perseus and Sagittarius). The diameter of the Milky Way is about 100,000 light-years and the Sun is located about 28,000 light-years from the Galactic Center. You can see a drawing of the Milky Way below which shows what our Galaxy ...
The diagram above shows all the planets and dwarf planets (and also the moon and the asteroid belt) in order from the sun. It also includes information on the diameter, mass and orbital period of each body and also a diagram showing the orbit of each body from the sun.
The Sun is found on the main sequence with a luminosity of 1 and a temperature of around 5,400 Kelvin. Astronomers generally use the HR diagram to either summarise the evolution of stars, or to investigate the properties of a collection of stars. In particular, by plotting a HR diagram for either a globular or open cluster of stars, astronomers ...
SunCalc is a little app that shows sun movement and sunlight phases during the given day at the given location. You can see sun positions at sunrise, specified time and sunset. The thin orange curve is the current sun trajectory, and the yellow area around is the variation of sun trajectories during the year.
The motions of the Moon around the Earth and of the Earth around the Sun are complex. The motions involved in revolutions are superimposed on the movements involved in rotations. The Earth and the Moon both turn on their own axis (rotation), but both also move around another object (revolution). The rotation of the Earth (24 hours) explains the alternation of day and night.
Anatomy of the Sun. The Sun's Core - Energy is generated via thermonuclear reactions creating extreme temperatures deep within the Sun's core. The Convection Zone - Energy continues to move toward the surface through convection currents of the heated and cooled gas. The Chromosphere - This relatively thin layer of the Sun is sculpted by ...
3D Diagram of the Solar System. ... An orrery is a model of the solar system that shows the positions of the planets along their orbits around the Sun. The chart above shows the Sun at the centre (the yellow ball), surrounded by the solar system's innermost planets. Click and drag the chart to rotate the camera angle, or use your mouse wheel to ...
The Sun's track is low in the sky and we have fewer hours of daylight than nighttime. It is winter, dark and cold. Your model shows this as the shortest cord. After the winter solstice, the Sun starts working its way back up to the northeast and the pattern repeats.
A Map of Every Object in Our Solar System. The path through the solar system is a rocky road. Asteroids, comets, planets and moons and all kinds of small bodies of rock, metals, minerals and ice are continually moving as they orbit the sun. In contrast to the simple diagrams we're used to seeing, our solar system is a surprisingly crowded place.
The construction of sunspot butterfly diagrams was first carried out by E.W. Maunder in 1904, and proceeds as follows: one begins by laying a coordinate grid on, for example, a solar white light or calcium image, with, as in the case of geographic coordinates on Earth, the rotation axis defining the North-South vector.
I Earth-Sun Relations: Figure 1 below shows that the orbit of the Earth about the sun is not circular. The path is elongated or ellipitcal. This means that the distance from the Earth to the sun varies through the year. Two special events are depicted in the diagram. Aphelion (July 4) is when the Earth is as far away from the sun as it ever gets.
A Scale Model of the Solar System (Developed by Dr. David H. Hathaway, NASA/MSFC) Background: From 1959 to the present the National Aeronautics and Space Administration has sent a number of spacecraft to explore our solar system. Many different types of spacecraft are
Temperatures in the Solar Atmosphere: On this graph, temperature is shown increasing upward, and height above the photosphere is shown increasing to the ...
Explain the structure of the sun with a diagram. · Solution · Convection Zone. The convection zone is the outer-most layer of the interior. It extends from a ...
Illustration about an image of the 3d layers of the Sun. Illustration of core, sphere, colorful - 26160182. More like this. This interactive diagram from ...
The Earth revolves around the Sun once every 365 and quarter days (one year), The rotation of the Earth around the Sun causes the sequence of the four seasons (the summer - the spring - the autumn - the winter). The sequence of the four seasons. The Earth's axis is inclined and this causes the difference in the length of the day and the ...
The Sun's rotation rate differs according to latitude: as seen from the Earth, the equatorial region rotates with a period of about 27 days, while the rotational period closer to the poles is about 32 days (Table 2-1). _____ * The Sun's rotational period as observed from Earth is known as the synodic period . Because the Earth moves about






















0 Response to "37 diagram of the sun"
Post a Comment