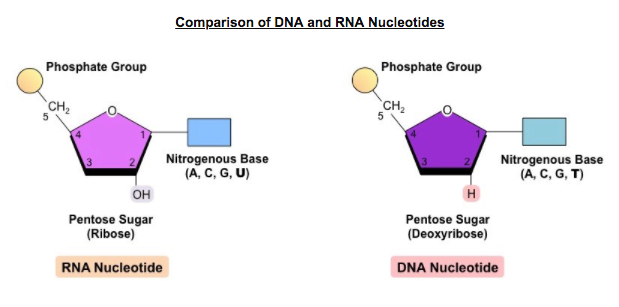
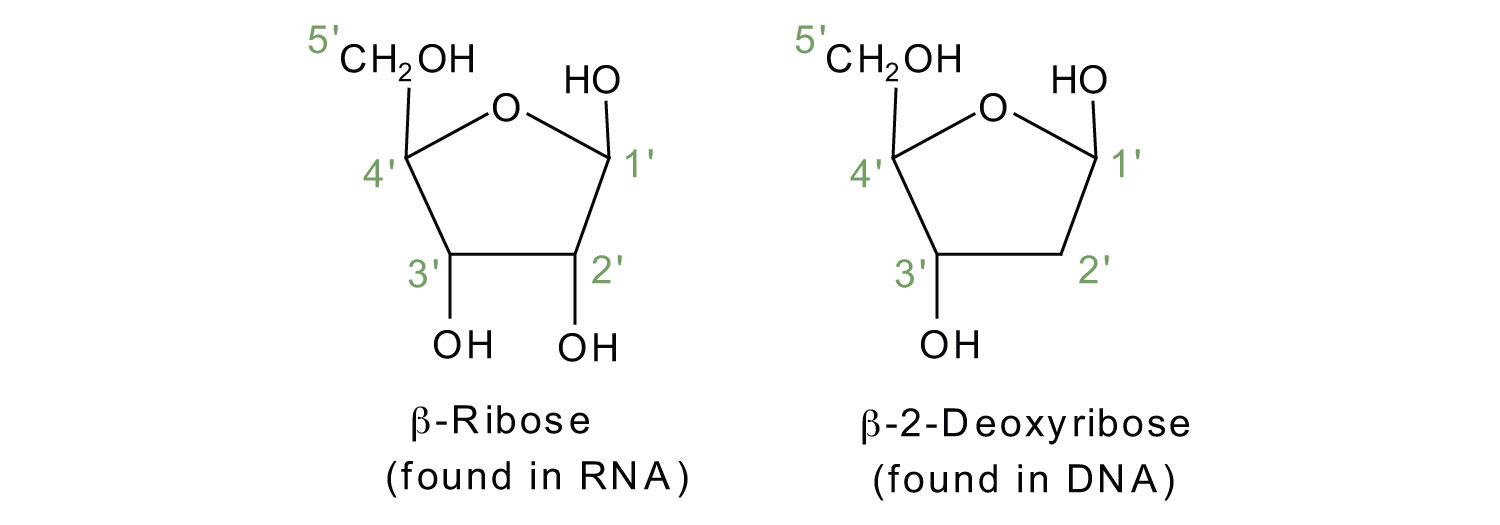
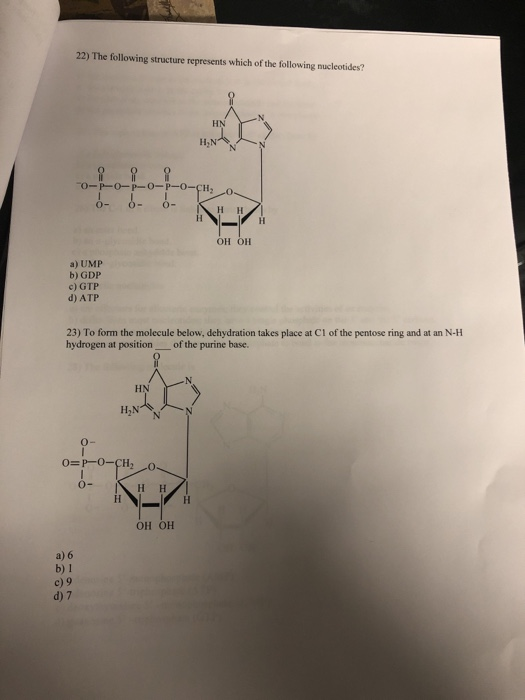
35 which sugar is present in the nucleic acid that is represented in the diagram?
element meaning "into, in, on, upon" (also im-, il-, ir- by assimilation of -n- with following consonant), from Latin in- "in," from PIE root *en "in." In Old French (and hence in Middle English) this often became en-, which in English had a strong tendency to revert to Latin in-, but not always, which accounts for pairs such as enquire/inquire. There was a native form, which in West Saxon usually appeared as on- (as in Old English onliehtan "to enlighten"), and some of those verbs survived into Middle English (such as inwrite "to inscribe"), but all now seem to be extinct. Not related to in- (1) "not," which also was a common prefix in Latin, causing confusion: to the Romans impressus could mean "pressed" or "unpressed;" inaudire meant "to hear," but inauditus meant "unheard of;" in Late Latin investigabilis could mean "that may be searched into" or "that cannot be searched into." Latin invocatus was "uncalled, uninvited," but invocare was "to call, appeal to." The trouble has continued in English; the hesit
Marine biogeochemical cycles are biogeochemical cycles that occur within marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries.These biogeochemical cycles are the pathways chemical substances and elements move through within the marine environment. In addition, substances and elements can be imported into or exported from the marine ...
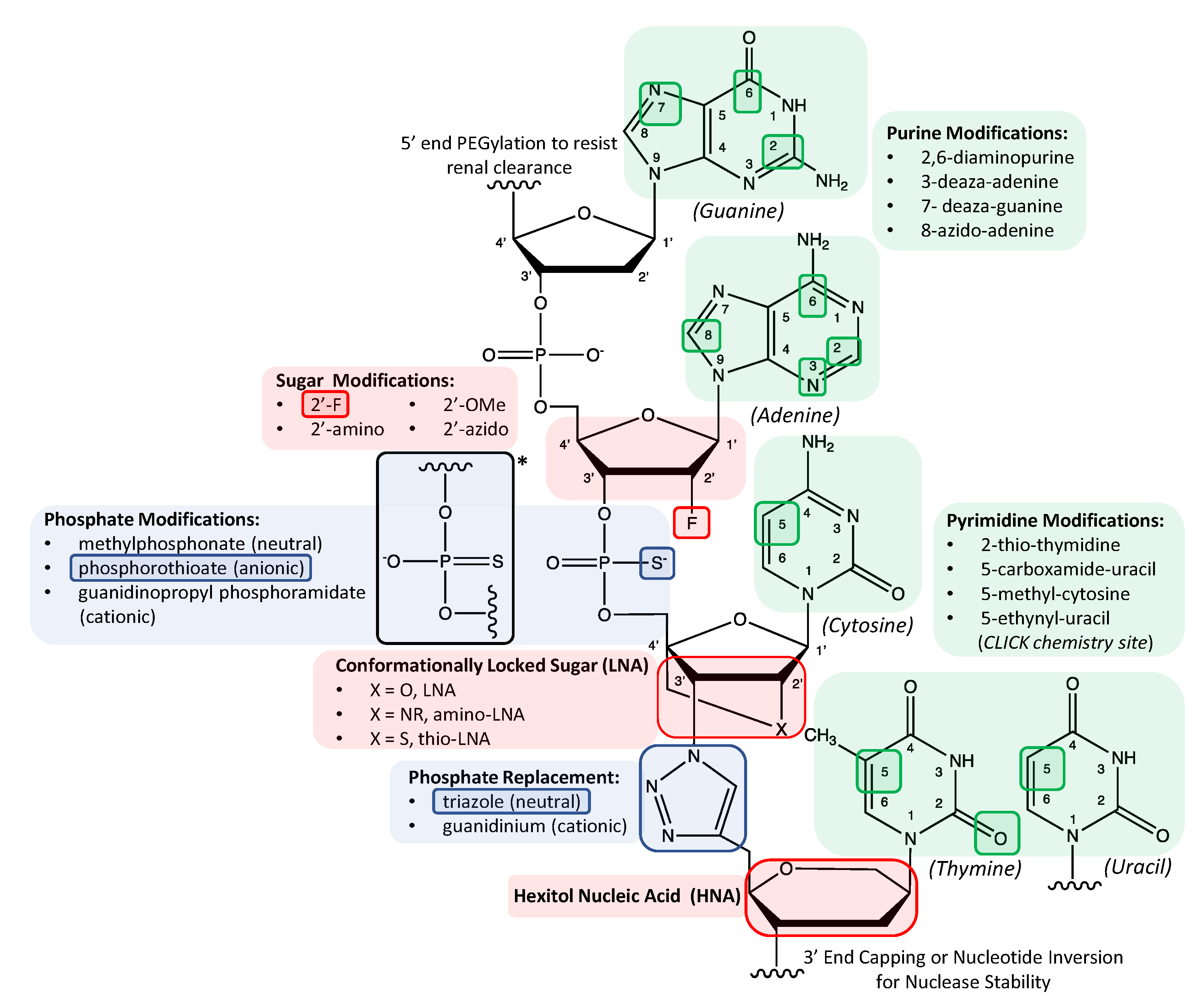
They are all polyfunctional bases, and may exist in tautomeric forms. ... As shown in the following diagram, the sugar component of RNA is ribose, ...
Which sugar is present in the nucleic acid that is represented in the diagram?
The diagram shows a tiny bit of a DNA double helix. ... The full name of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, gives you the name of the sugar present - deoxyribose.
also instore, 1954, from in (prep.) + store (n.). In Middle English, instore was a verb meaning "to restore, renew," from Latin instaurare.
word-forming element meaning "not, opposite of, without" (also im-, il-, ir- by assimilation of -n- with following consonant, a tendency which began in later Latin), from Latin in- "not," cognate with Greek an-, Old English un-, all from PIE root *ne- "not." In Old French and Middle English often en-, but most of these forms have not survived in Modern English, and the few that do (enemy, for instance) no longer are felt as negative. The rule of thumb in English has been to use in- with obviously Latin elements, un- with native or nativized ones.
Which sugar is present in the nucleic acid that is represented in the diagram?.
The full length of cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of Mm-Smad 3. The frames represented the start codon, the stop codon, and the polyadenylation signal sequence. The double line is the polyA tail. The * represents the end of the protein translation. The double underlined bold part is the functional domains of MH1.
Which sugar is present in the nucleic acid that is represented in the diagram? WRONG. phosphate. Rating: 2.2 · 9 reviews
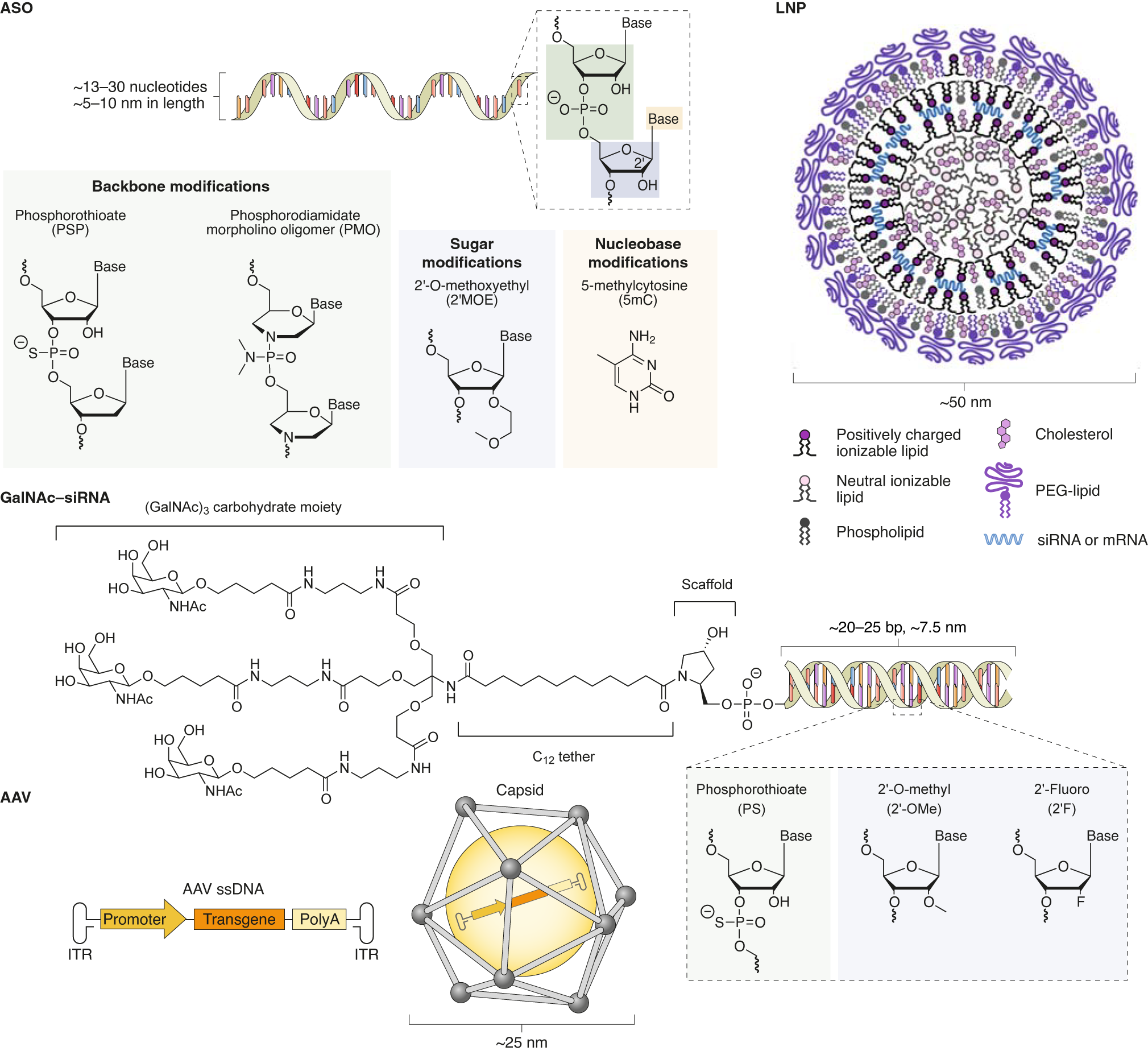
Each nucleotide is made up of three components: a nitrogenous base, a pentose (five-carbon) sugar, and a phosphate group (Figure 1). Each nitrogenous base in a ...
A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases ...
RNA is a string of nucleotides, and it is present in some form or another in all living things, including viruses. In HIV, it carries the genetic information that allows the virus to copy itself inside a host—the human body. HIV RNA comprises about 9,800 nucleotides.
the adverb in attached to a verb as a word-forming element, by 1960, abstracted from sit-in, which is attested from 1941 in reference to protests and 1937 in reference to labor union actions (which probably was influenced by sit-down strike) but was popularized in reference to civil disobedience protests aimed at segregated lunch counters. As a word-forming element at first of other types of protests, extended by 1965 to any sort of communal gathering (such as love-in, 1967).
16.12.2021. Allegro CL 10.1 Documentation Introduction and Overview
word-forming element in chemistry, usually indicating a neutral substance, antibiotic, vitamin, or hormone; a modification and specialized use of -ine (2).
Nov 8, 2016 — The sugar present in DNA is deoxyribose sugar, which shows presence of a hydrogen atom, instead of an hydroxyl group (-OH group). Thus, the ...2 answers · Top answer: Well, to determine the type of sugar that is present and serves to play an important role ...
The article presents the results of biochemical and QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) analysis of dry matter content, nutrient and biologically active compounds: sugars, ascorbic acid, chlorophylls a and b, anthocyanins and carotenoids in populations of doubled haploid lines of leaf, root crops, and oilseeds of the Brassica rapa L. species grown in optimal light culture conditions, but with ...
1740, Latin, literally "in its (original) place or position," from ablative of situs "site" (see site (n.)).
a Middle English merger of Old English in (prep.) "in, into, upon, on, at, among; about, during;" and Old English inne (adv.) "within, inside," from Proto-Germanic *in (source also of Old Frisian, Dutch, German, Gothic in, Old Norse i), from PIE root *en "in." The simpler form took on both senses in Middle English. Sense distinction between in and on is from later Middle English, and nuances in use of in and at still distinguish British and American English (in school/at school). Sometimes in Middle English shortened to i. The noun sense of "influence, access (to power or authorities)," as in have an in with, is first recorded 1929 in American English. to be in for it "certain to meet with something unpleasant" is from 1690s. To be in with "on friendly terms with" is from 1670s. Ins and outs "intricacies, complications of an action or course" is from 1660s. In-and-out (n.) "copulation" is attested from 1610s.
Cyanobacteria present remarkable variability in terms of morphology: from unicellular and colonial to filamentous forms. Filamentous forms exhibit functional cell differentiation such as heterocysts (for nitrogen fixation), akinetes (resting stage cells), and hormogonia (reproductive, motile filaments). These, together with the intercellular connections they possess, are considered the first ...
"that is within, internal," 1590s, from in (adv.). Sense of "holding power" (the in party) first recorded c. 1600; that of "exclusive" (the in-crowd, an in-joke) is from 1907 (in-group); that of "stylish, fashionable" (the in thing) is from 1960.
also inflight, "during or within a flight," 1945, from in (prep.) + flight.
"easy winner" (especially in politics), 1939, from earlier sense "horse that wins a race by pre-arrangement" (1928); the verb phrase shoo in in this sense is from 1908; from shoo (v.) + in (adv.).




![Solved] The diagram shows a nucleic acid in the shape of a ...](https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d22/a0b26d1236efe2f0cbf271c73a0ee055.jpg)
/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)













0 Response to "35 which sugar is present in the nucleic acid that is represented in the diagram?"
Post a Comment