39 draw a ray diagram of the lens system in part d
Replacement parts, accessories, and software for Sony® products can be obtained from Sony Parts and Accessories. Go to Parts and Accessories.. NOTE: If the item that you are looking for has been discontinued or is not available from the Sony Parts and Accessories department, you may also be able to find it by doing an online search or at online retailers like Amazon.com. CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 5 for Practice. (i) The question paper comprises four sections A, B, C and D. There are 36 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory. (ii) Section-A - question no. 1 to 20 - all questions and parts there of are of one mark each. These questions contain multiple choice questions ...
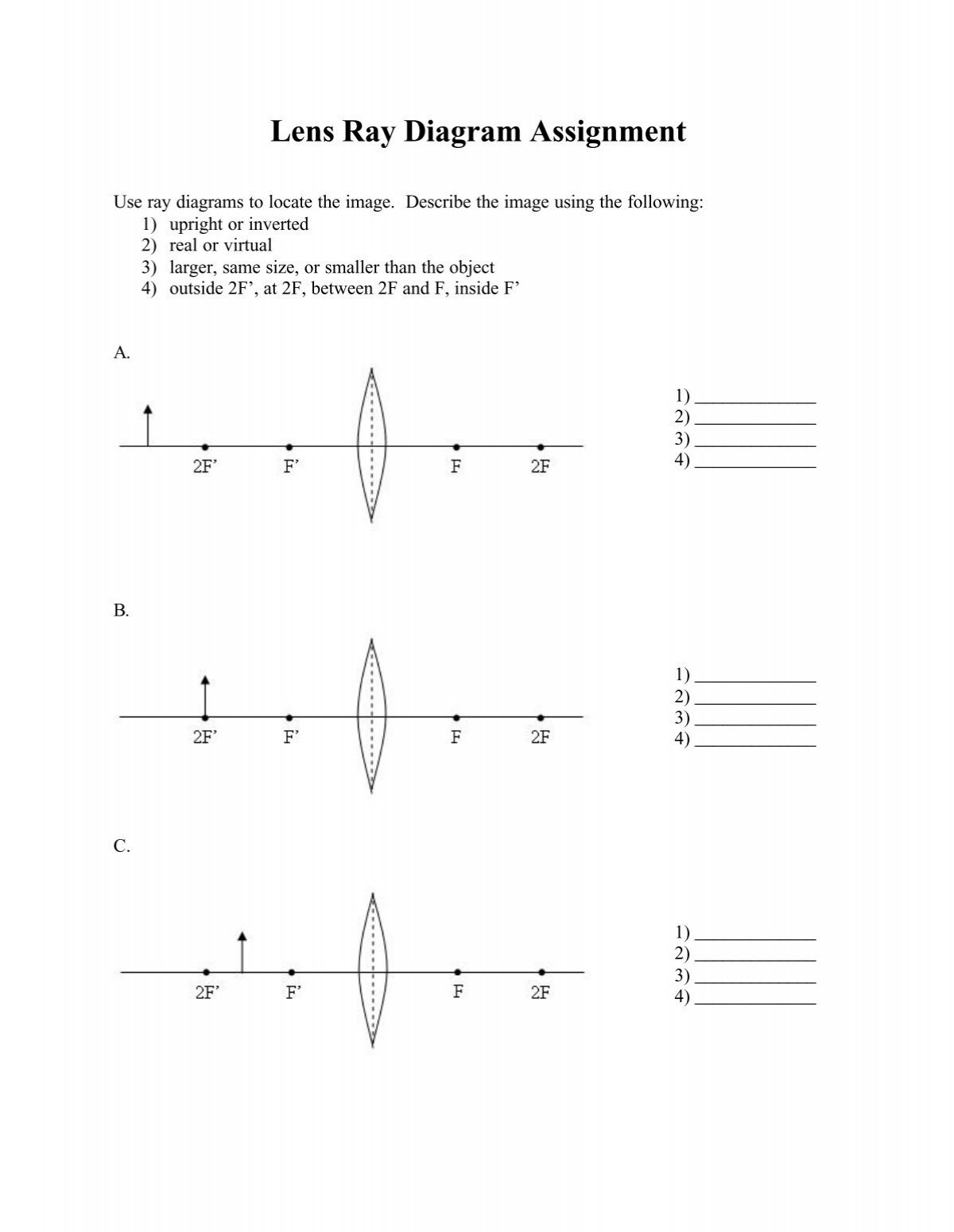
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed: (i) between the optical center and principal focus of a convex lens. (ii)anywhere in front of a concave lens. (iii)At 2F of a convex lens. State the signs and values of magnifications in the above-mentioned cases (i) and (ii). Ans.

Draw a ray diagram of the lens system in part d
Ray Optics: spherical mirrors and lens. A thin double convex lens of focal length f = +15 centimeters is located at the origin of the x-axis, as shown in the attachment. An object of height 8 centimeters is placed 45 centimeters to the left of the lens. a.) On the figure in attachment, draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image by ... d. When the object is placed between principal focus and center of the curvature e. When the object is placed at the principal focus f. When the object is placed between the pole and principal focus. Concave Mirror Diagram. The ray diagram of concave mirrors based on the object placement stated above are given below: Source: NCERT Book (b) Draw a ray diagram to show how his legs appear shorter. (c) If the depth of the pool is 0.8 m, calculate the distance of the image of his feet as seen from the surface of the water. [Refractive index of water = 1.33] Solution:
Draw a ray diagram of the lens system in part d. Since the refractive index of most glasses is ~1.5, this means that our radius of curvature for a biconvex lens is equal to the inverse of the lenses power, which is also the focal length of the system!. Now we can construct our lens and visualize it with the draw function in the tinygfx package (installed as part of the PyRayT distribution). # import the Ray Tracer Package import pyrayt ... Input and Output Devices: Types, Examples and Uses. The main functioning of a computer system is based on the combined usage of both input and output devices. Utilizing an input device, a user can give directions to the computer to run and the device reverts to the user's action through an output device. Let's understand first what is an ... CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 1 with Solutions. (i) The question paper comprises four sections A, B, C and D. There are 36 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory. (ii) Section-A - question no. 1 to 20 - all questions and parts there of are of one mark each. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror. Answer: For locating the image formed by a concave mirror, minimum two rays are required. Following is the ray diagram for the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror: Q14.
Dissecting microscope (Stereo microscope) These are also known as stereoscopic microscopes. This is a type of digital optical microscope designed with a low magnification power (5x-250x), by use of light reflected from the surface of the specimen, and not the light reflected the specimen. Eyeball (Bulbus oculi) The eye is a highly specialized sensory organ located within the bony orbit.The main function of the eye is to detect the visual stimuli (photoreception) and to convey the gathered information to the brain via the optic nerve (CN II).In the brain, the information from the eye is processed and ultimately translated into an image. (b) Draw a ray diagram to show the defect in the above case. (c) Mention the type of lens used by him for the correction of the defect and calculate its power. Assume that the near point for the normal eye is 25 cm. (d) Draw a labelled diagram for the correction of the defect in the above case. Optics Drawing Templates. The Optics Drawing Software includes some pre-defined shapes such as convex lens, spherical surface, mirror, body, ray, bulb, light source and glass. Only drag them into the view and start your work. Every shape can be edited and rearranged.
Parallel beam of light after refraction from convex lens converge at the focus of convex lens. In question it is given light after refraction pass through concave lens becomes parallel. Therefore light refracted from convex lens virtually meet at focus of concave lens. According to above ray diagram d = f A - f B = 20 - 5 = 15 cm 12. Spec Sheet Lookup Rule 3 - Ray passing through Optical Center will emerge without deviation. For a both convex and concave lens, we see that ray passing through Optical center emerges without deviation. Next: Convex Lens - Ray diagram→. Facebook Whatsapp. Course on Science: Full Syllabus - Part II Get subscription. CBSE Class 10. Plus. Syllabus. Science. PREVIEW. English. Course on Science: Full Syllabus - Part II Bhavana Bisht. In this course, Bhavana Bisht will cover the important concepts under Science and this course will be beneficial for aspirants preparing for CBSE Class 10. Learners at ...
Draw diagrams to show the refraction of light from (i) air to glass, (ii) glass to air. In each diagram, label the incident ray, refracted ray, the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r). Answer 2
Draw a labelled ray diagram for the formation of image by a convex lens of focal length 15 cm when the object is placed at a distance of 25 cm from the lens. Determine the size of the image formed, if the size of the object is 4 cm.
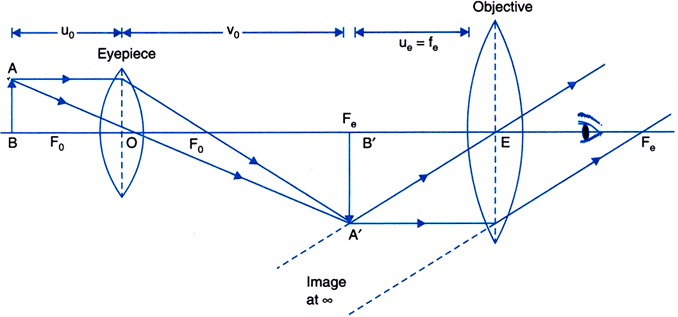
Draw A Ray Diagram Of A Compound Microscope Write The Expression For Its Magnifying Power From Physics Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Class 12 Cbse
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. With the help of ray diagrams, we can understand how images are formed in concave mirrors. We should consider at least 2 incident rays coming from an object to understand the image formation in Concave Mirrors. The intersection of 2 rays after reflection provides the image position of an object.
Focal Length. This schematic shows an example of a convex lens on the top and a concave lens on the bottom. The focal point (F) is the point at which parallel light rays cross.
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays. A ray of light, incident obliquely on a face of a rectangular glass slab placed in air, emerges from the opposite face parallel to the incident ray.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in this case. A ray of light, incident obliquely on a face of a rectangular glass slab placed in the air, emerges from the opposite face parallel to the incident ray. State two factors on which the lateral displacement of the emergent ray depends.
The iris is actually that part of the eye which gives the eye its distinctive colour. 4) Behind pupil is the eye-lens. The eye-lens is a convex lens made of a transparent and flexible material like jelly. The eye-lens is actually a living lens because it is made up of transparent living cells which allow light to pass through them.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to show image formation by the defective eye? (iv) Draw a ray diagram showing a corrected eye using the proper lens. NOTE: The links given below for Download Class 10 Science Sample Paper in pdf format.
Lens - The biconvex lens is placed above the stage and its function is to magnify the size of the object being examined. By manipulating it (moving up and down by the frame), you will be able to enlarge the image. (1, 8, and 10) A simple microscope is a device that only has one lens for magnification. It functions the same way as the ...
The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position, and size of the image. Also, find its magnification. Write the positions of the objects in each case. Draw ray diagrams to show the image formation in each case. How will the following be affected on cutting this lens into two halves along the principal axis? Focal length
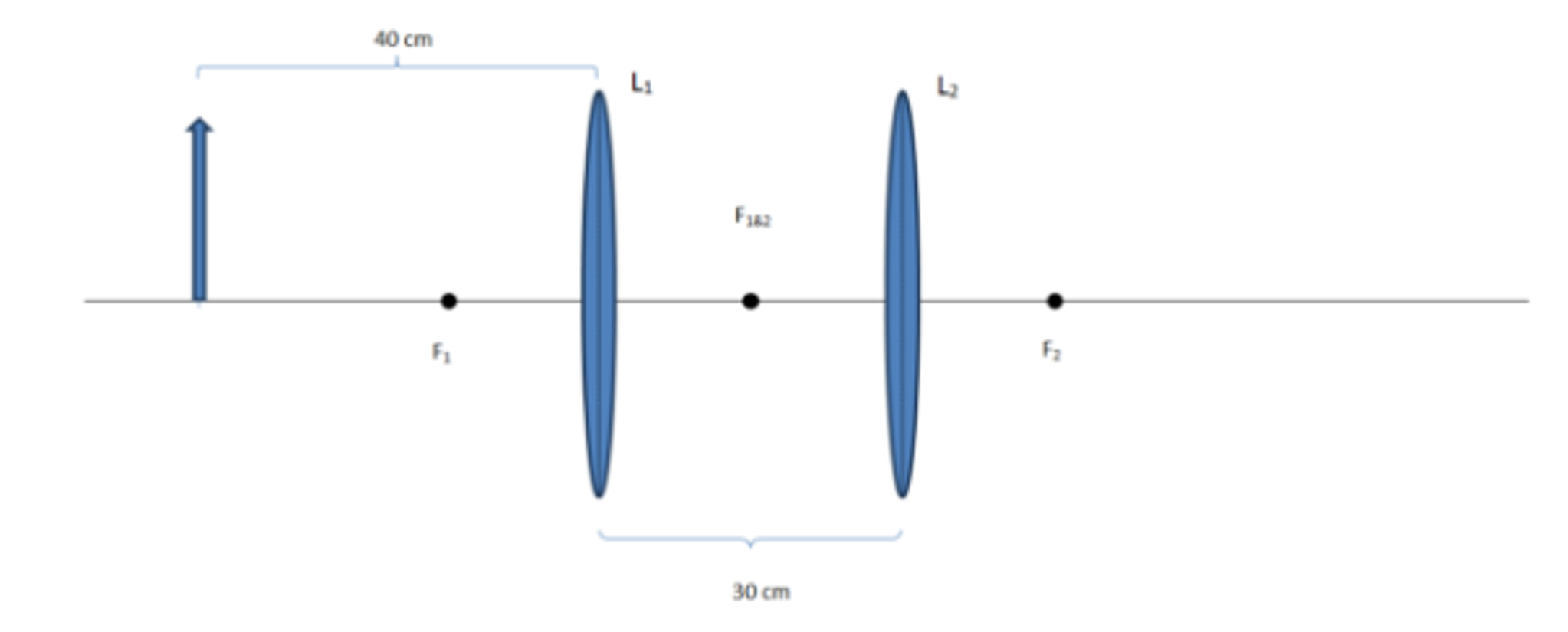
Two-lens system. We can use the lens formula for a two lens system with the object distance for the second lens equal to the image distance from the first lens. The Lens Equation is: 1/focal ...
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show how his legs appear shorter. (c) If the depth of the pool is 0.8 m, calculate the distance of the image of his feet as seen from the surface of the water. [Refractive index of water = 1.33] Solution:

Does The Position Of The Final Image In A Multiple Lens System Found By The Thin Lens Formula Always Agree With The Ray Diagrams Physics Stack Exchange
d. When the object is placed between principal focus and center of the curvature e. When the object is placed at the principal focus f. When the object is placed between the pole and principal focus. Concave Mirror Diagram. The ray diagram of concave mirrors based on the object placement stated above are given below: Source: NCERT Book
Ray Optics: spherical mirrors and lens. A thin double convex lens of focal length f = +15 centimeters is located at the origin of the x-axis, as shown in the attachment. An object of height 8 centimeters is placed 45 centimeters to the left of the lens. a.) On the figure in attachment, draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image by ...

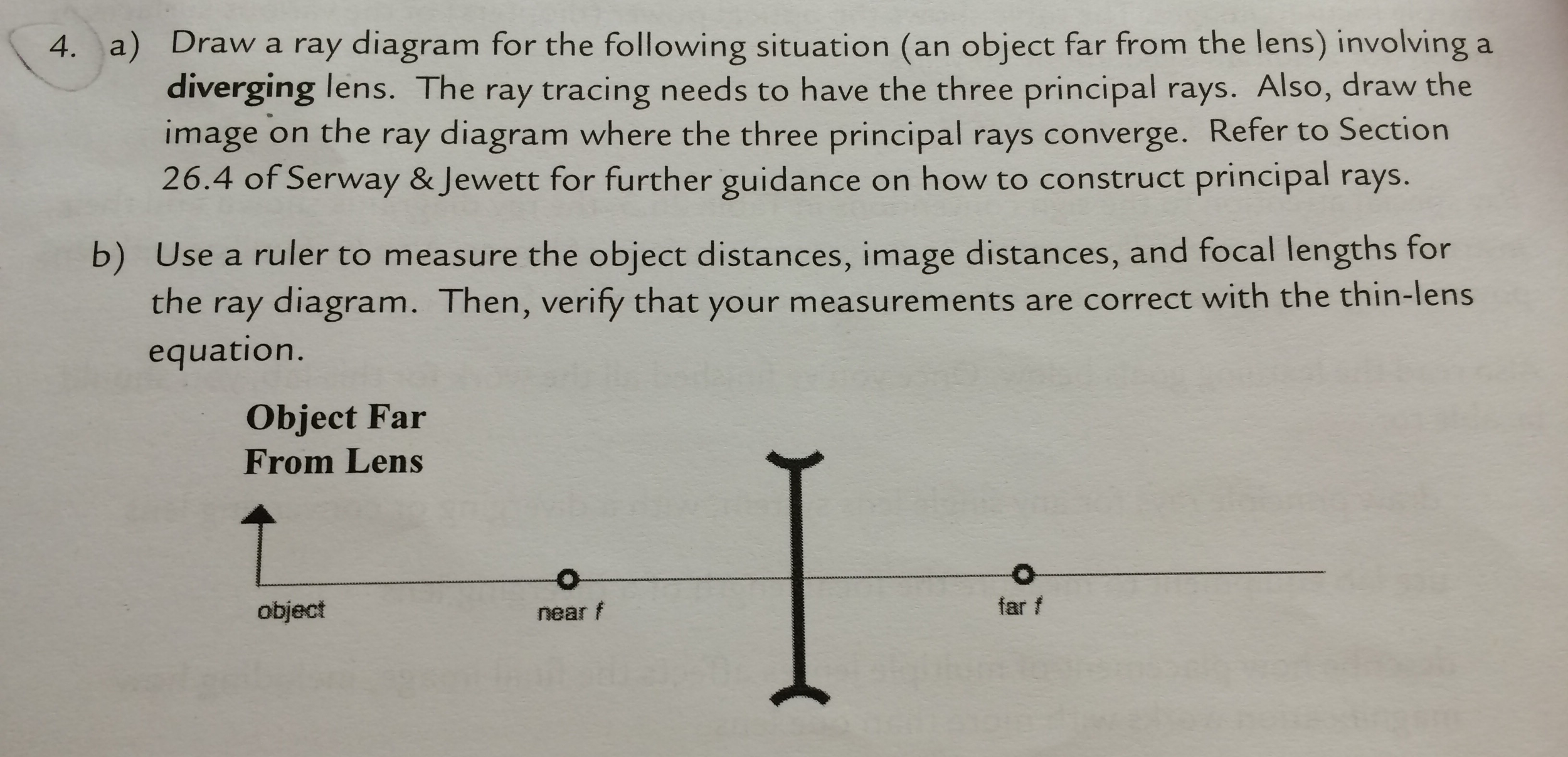
Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams H Om E A Bout Te Rm S Cre Dits Fe E Dback T He P Hysics C La Ss Room P

Convex Lens Concave Lens How To Determine Focal Length Ray Diagrams Image Properties Real Virtual Inverted Size Correction Of Eye Defects Causes Of Long Sight Short Sight Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes

Draw A Ray Diagram In Each Of The Following Cases To Show The Formation Of Image When The Object Is Placed I Between Optical Centre And Principal Focus Of A Convex Lens Ii

Which Of The Following Ray Diagrams Is Correct For The Ray Of Light Incident On A Lens Shown In Fig 10 7

Draw A Ray Diagram To Show The Image Formation By A Combination Of Two Thin Convex Lenses To Contact Obtain The Expression For The Power Of This Combination In Terms Of The Focal Lengths Of The Lenses















0 Response to "39 draw a ray diagram of the lens system in part d"
Post a Comment