39 diverging lens ray diagram image
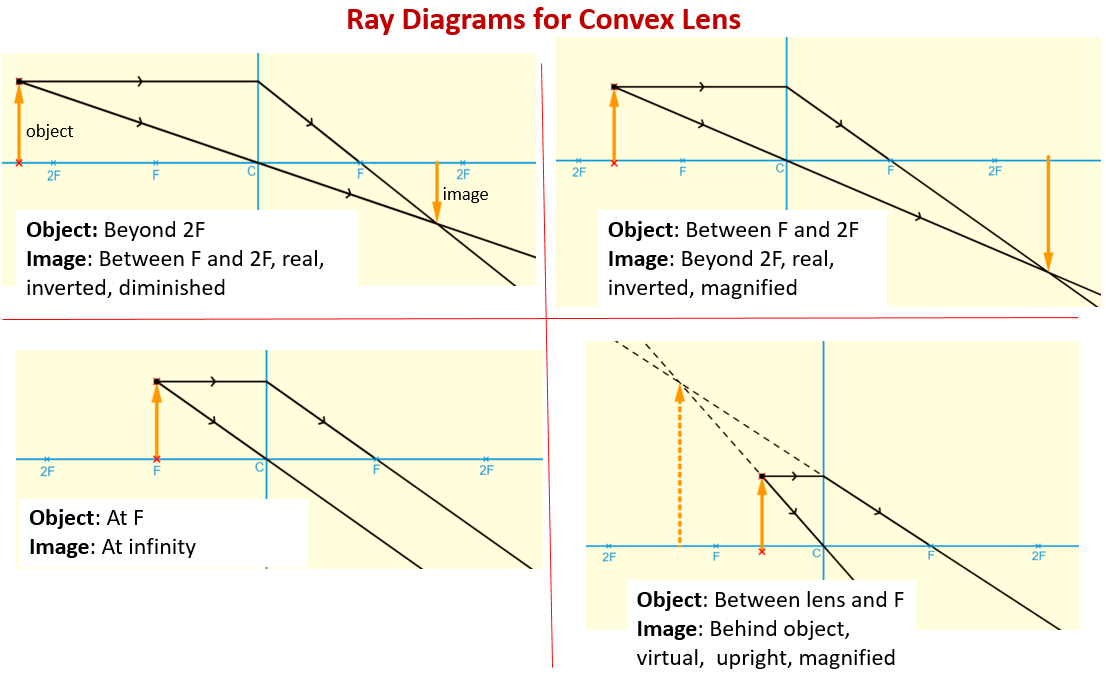
A diverging lens ray diagram follows three basic rules: Any ray of light that is parallel to the principal axis of the lens will pass through its focal point after refraction. Any incident ray of light that passes through the focus of the lens before getting refracted will emerge parallel to the principal axis on refraction. A ray diagram is a tool used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a lens. Ray diagrams for double convex lenses were drawn. Converging lenses can produce both real and virtual images while diverging . The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below.Image formation by convex lens ...
Diverging Lenses As such, the rules for how light behaves when going through a diverging lens is a little bit different. You will be expected to be able to draw a Ray Diagram of a converging and diverging lens on our upcoming test without the rules.
Diverging lens ray diagram image
First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. So, it passes through focus after refraction. We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center. So, the ray will go through without any deviation. Where both rays meet is point A'. And the image formed is A'B'. This image is formed between F 2 and 2F 2. We can say that. In a ray diagram, a convex lens is drawn as a vertical line with outward facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens. The distance from the lens to the principal focus is called the focal length . Image Construction: Ray 1: A ray parallel to the lens axis passes through the far focus of a converging lens or appears to come from the near focus of a diverging lens. Ray 1: Ray 1: A ray parallel to the lens axis passes through the far focus of a converging lens or appears to come from the near focus of a diverging lens. Converging Lens
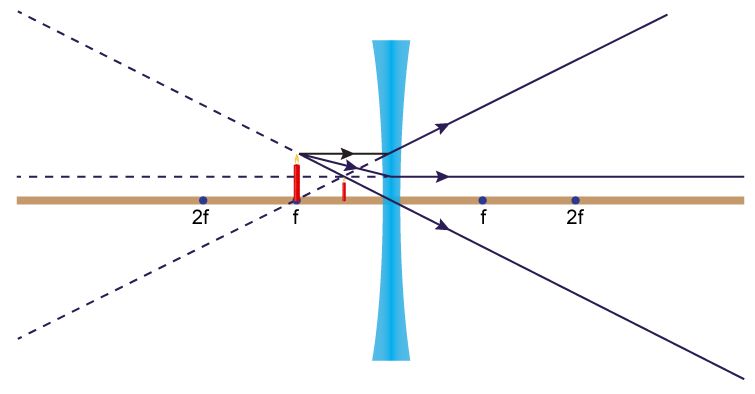
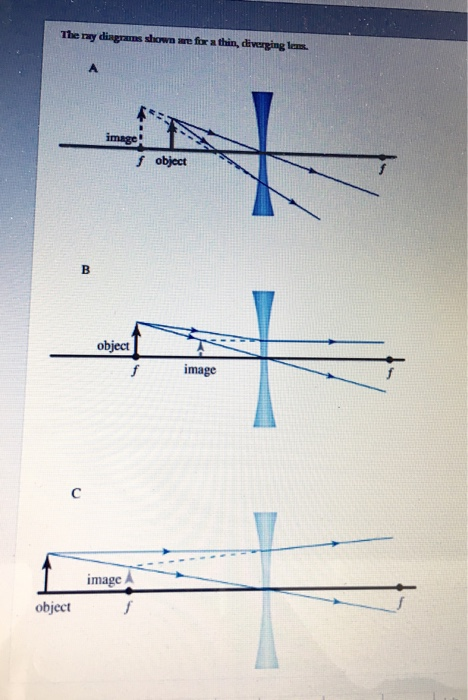
Diverging lens ray diagram image. Ray Diagram for Object Located in Front of the Focal Point. In the three cases described above - the case of the object being located beyond 2F, the case of the object being located at 2F, and the case of the object being located between 2F and F - light rays are converging to a point after refracting through the lens. In such cases, a real image is formed. Ray Diagrams for Diverging Lenses 1106 Chapter 36 Image Formation Figure 36.24 is useful for obtaining the signs of p and q, and Table 36.3 gives the sign conventions for thin lenses. These sign conventions are the same as those for refracting surfaces (see Table 36.2). Various lens shapes are shown in Figure 36.25. Notice that a converging lens is Description of how to draw ray diagrams for diverging lenses for grade 10 science. Find out how an image is formed when light passes through a diverging lens. This tutorial shows how the ray diagram is constructed from object to image.The n...
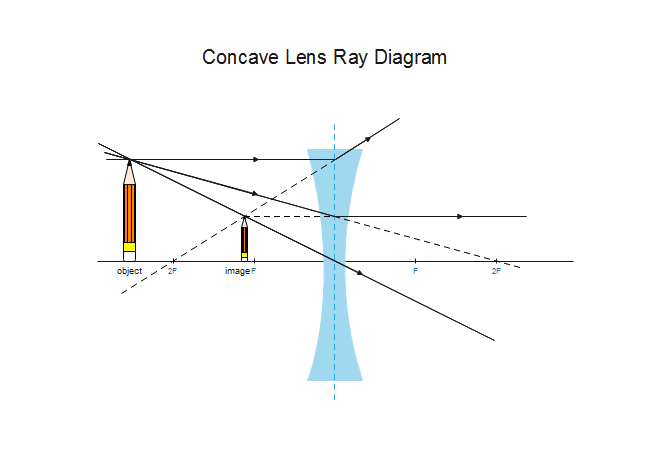
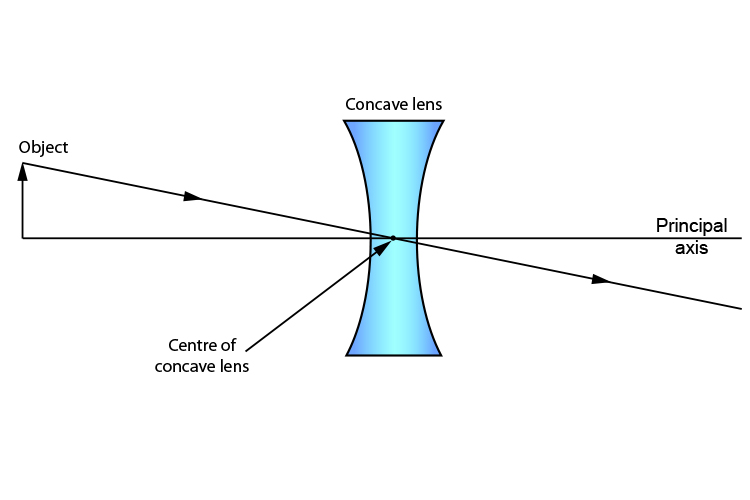
Convex Lens Ray Diagrams For lenses, the following three rays are typically used in ray diagrams. Keep in mind that an inflnite number of rays actually form the image. Ray # 1 For a lens, the flrst ray starts from the top of the object and extends parallel to the optical axis to the center of the lens. This ray, for a converging (convex) lens, A diverging lens always form an upright virtual image. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object: A ray passing through the center of the lens will be undeflected. A ray proceeding parallel to the principal axis will diverge as if he came from the image focal point F'. Virtual images ... The ray diagram constructed earlier for a diverging lens revealed that the image of the object was virtual, upright, reduced in size and located on the same side. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such. Ray diagram for a diverging lens. Consider now the ray diagram for a diverging lens. Diverging lenses come in a few different shapes, but all diverging lens are fatter on the edge than they are in the center. A good example of a diverging lens is a bi-concave lens, as shown in the diagram.
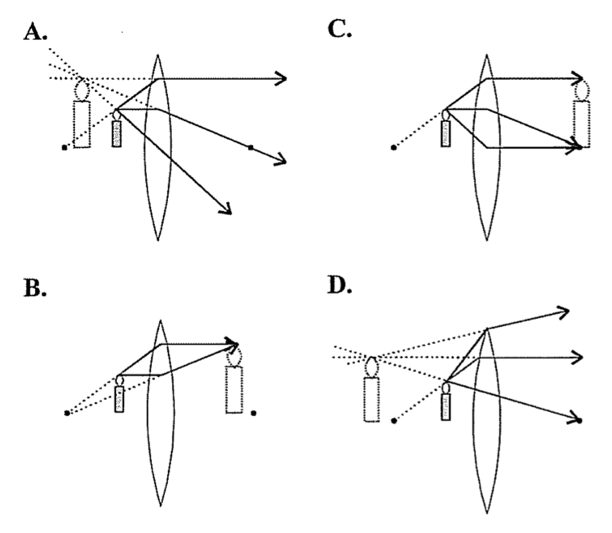
The image size is the object size What is the image; Question: Print Info Diverging Lens Region 1 Region 2 Region 3 If an object is located in region 1, then answer the following questions about the image which is formed with a diverging lens. Please draw the ray diagram to visualize the problem. The image is located on the side as the object. The ray diagram constructed earlier for a diverging lens revealed that the image of the object was virtual, upright, reduced in size and located on the same side. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such. The top diagram shows the formation of the virtual object where converging rays are prevented from meeting by the diverging lens. Then those converging rays are made to diverge by the lens and so a virtual image is formed. A ray diagram is a tool used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a lens. Ray diagrams for double convex lenses were drawn in a previous part of Lesson 5. In this lesson, we will see a similar method for constructing ray diagrams for double concave lenses.
Steps to a Convex Lens Ray Diagram Look below and not at the animation to see the numbered steps for two scenarios and the analysis of the image produced. Start the First Ray : Start with your pencil on the top of the object (black thick arrow tip) and draw a line parallel to the principle axis to the center of the lens.
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are:
What Is The Ray Diagram Of Concave Lens When Object Is Placed At Focus Please Explain In Detail Physics Topperlearning Com Yqq7t00
Drawing a ray diagram for a two-lens system Pick one configuration of lenses and viewing screen from your measurements on the diverging lens and draw a complete ray diagram to scale showing the formation of the intermediate image from the converging lens and the final image of the diverging lens. Ray diagrams for single converging
If the lens is converging but the distance from the object to the lens is smaller than the focal length, the image will be virtual. Diverging lenses always produce virtual images. This calculator shows a ray diagram when the image is real. Magnification The magnification m of an image is the ratio between the image and object height. It can be ...
The lens in a film, slide or video projector is a converging lens. In this diagram the lens produces a real image, which can be projected on a screen. You can see that the image is upside down (inverted) and magnified.
ray diagram that shows how light will travel from the object to the eye by reflecting from the mirror in illustration 2 identify the position of the image first measure how far the object is in front of the answer is no you have a virtual image, diverging lenses ray diagrams this page from the physics classroom uses images
Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. image is always virtual, upright and reduced O F I F' Ray diagram for diverging lens • point object A, source of light • reflected rays appear to come from A' ...
What are converging and diverging lens with diagram? Converging and Diverging Lens - diagram Converging lens is convex lens whereas diverging lens is a concave lens. Converging lens converge and focus the light ray to meet at a single point whereas diverging lens, diverge the light falling on its surface and not meet at a single point.
While diverging lenses always produce virtual images, converging lenses are capable of producing both real and virtual images. A virtual image is formed if the object is located less than one focal length from the converging lens. To see why this is so, a ray diagram can be used. What causes an image to be inverted?
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. Three principal rays can be used to locate and size the image formed by a single lens, with examples for converging and diverging lenses. The three principal rays are:. A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the centerline perpendicular to the lens, passing through the principal focal point beyond the lens.
diverging lens focal length f optic axis A B A´ image distance q object distance p Figure 7.3: Using a ray diagram to locate the virtual image formed by a diverging lens. The dotted lines show the trajectories that the photons appear to follow, according to the observer. The gray lines indicate the relationships between the second and third ...
Image Construction: Ray 1: A ray parallel to the lens axis passes through the far focus of a converging lens or appears to come from the near focus of a diverging lens. Ray 1: Ray 1: A ray parallel to the lens axis passes through the far focus of a converging lens or appears to come from the near focus of a diverging lens. Converging Lens
In a ray diagram, a convex lens is drawn as a vertical line with outward facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens. The distance from the lens to the principal focus is called the focal length .
First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. So, it passes through focus after refraction. We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center. So, the ray will go through without any deviation. Where both rays meet is point A'. And the image formed is A'B'. This image is formed between F 2 and 2F 2. We can say that.

---teachoo.png)


















0 Response to "39 diverging lens ray diagram image"
Post a Comment