38 converging lens ray diagram simulation
Converging lens: A converging lens focuses diverging or blurry light rays from a distant object by refracting (bending) the rays twice. Its curvature converts rays to a focal point behind the lens so that a sharper image can be seen or captured on a screen or camera sensor. Ray diagrams for converging lens cases. Here is a video from Khan Academy that shows the ray geometry that explains the image formation for four different object distances relative to the lens and its focal points. A few key concepts are: YouTube. Light is reflecting from the o bject in all directions, but the only rays shown are the ones that ...
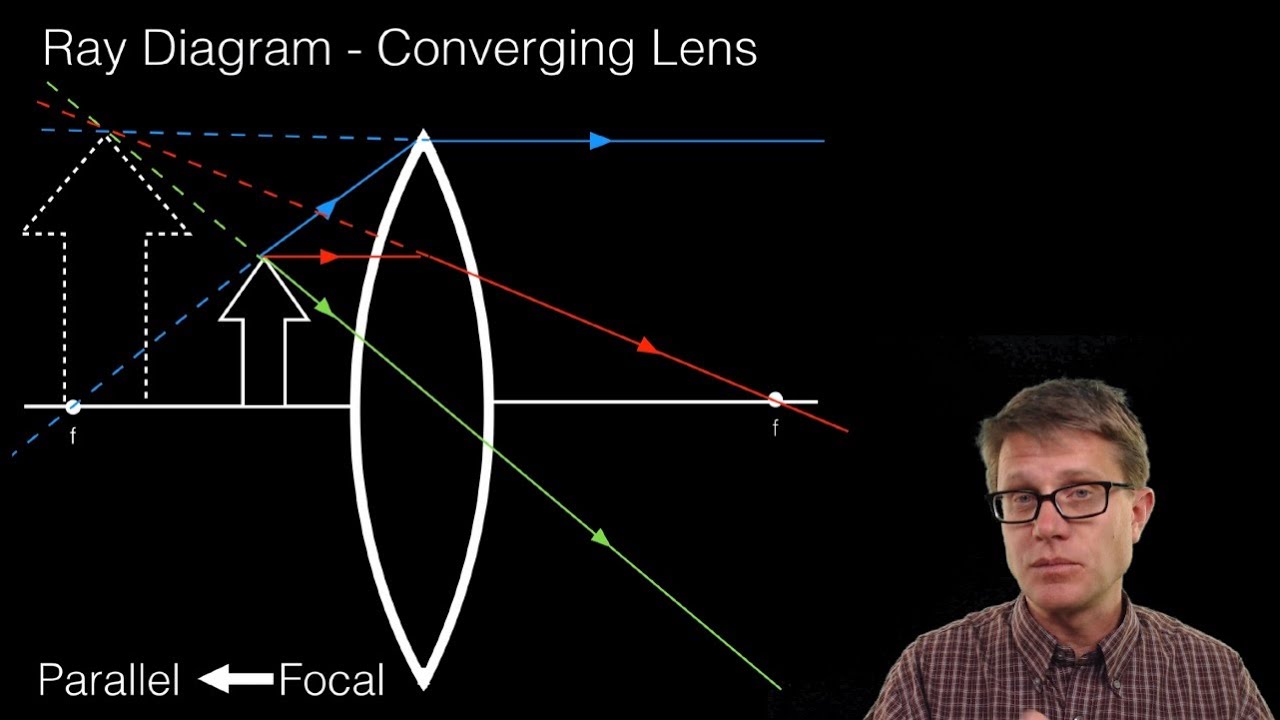
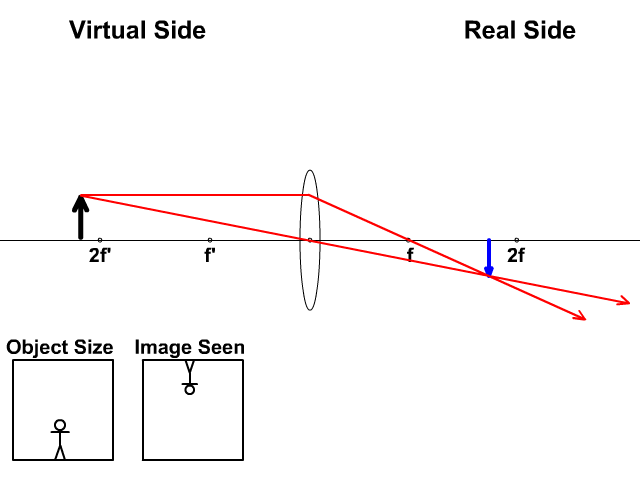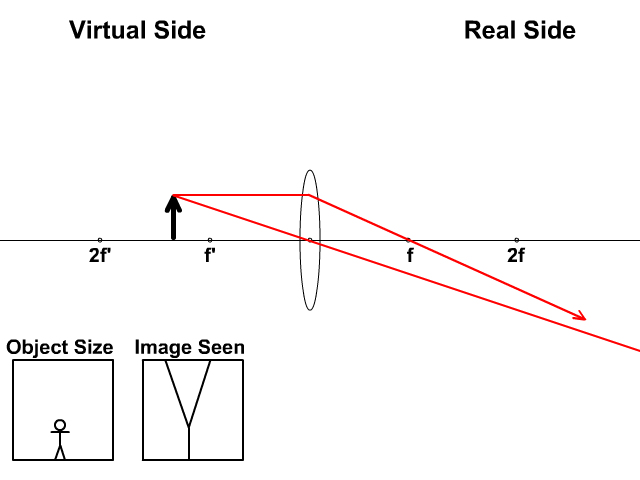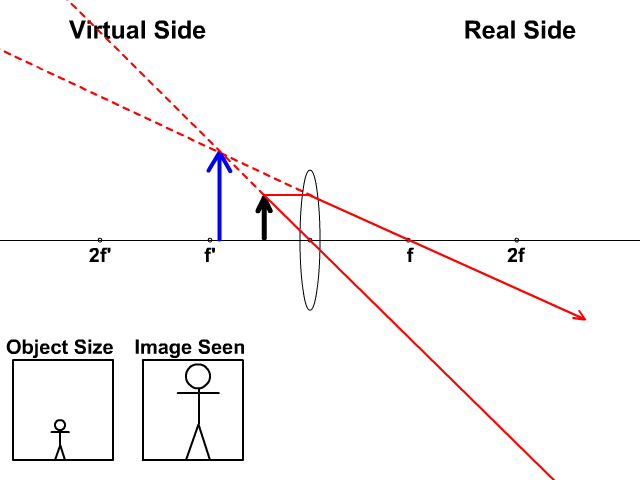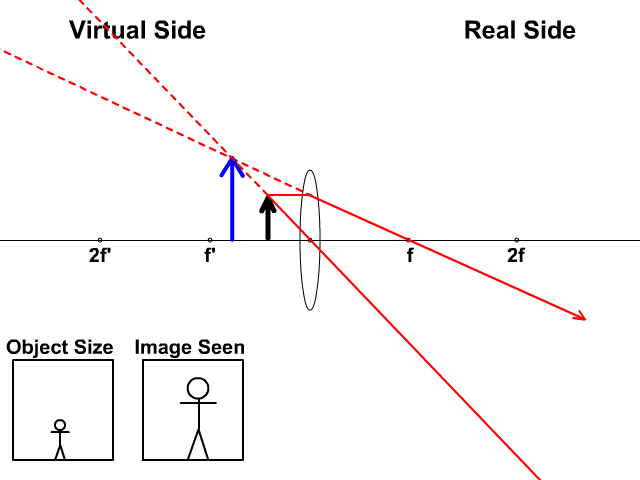
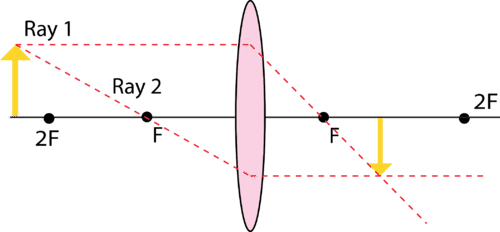
A ray entering a converging lens through its focal point exits parallel to its axis. ... The ray diagram in Figure 13 shows that the image is on the same side of the lens as the object and, hence, cannot be projected—it is a virtual image. Note that the image is closer to the lens than the object.
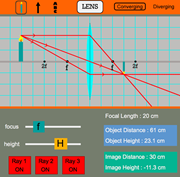
Converging lens ray diagram simulation
Lens and Mirror Lab. Category. Optics, Physics. Change the location of the object and use the ray diagrams to determine the location of the image. The following lab was created by Nick Donovan. Thanks Nick! Recommended Lab: Converging Lens Image Formation. The Converging Lens Image Formation Interactive provides learners with a virtual light box for exploring the refraction of light through converging lenses and the manner in which such refraction leads to the formation of an image of a complex object. Learners tap on various points upon an object. Lenses are traditionally shaped as sections of spheres, such that the radius of curvature of the sphere of which they are comprised can describe the lens' curvature. The diagram of an eye and lens to the right demonstrates this concept. Lenses show up in nature in the eyes of animals.
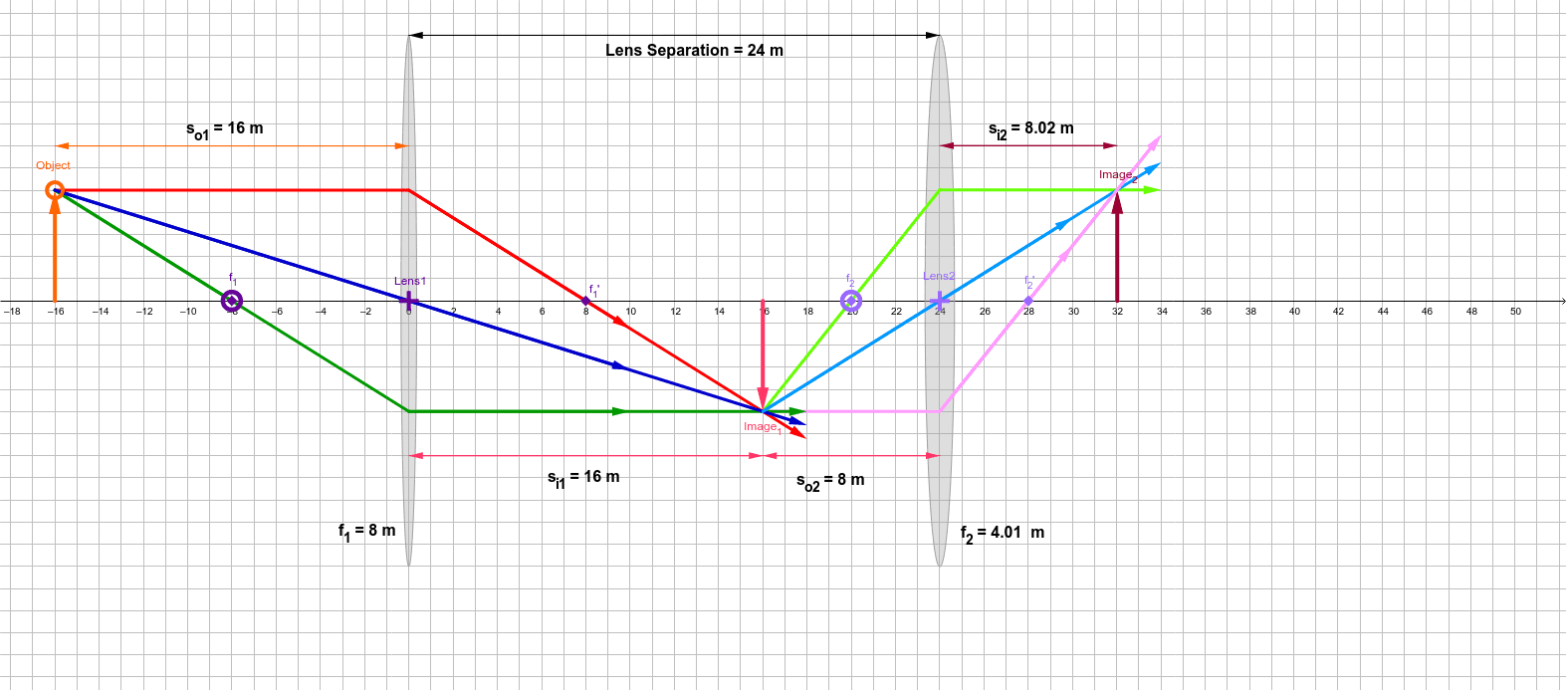
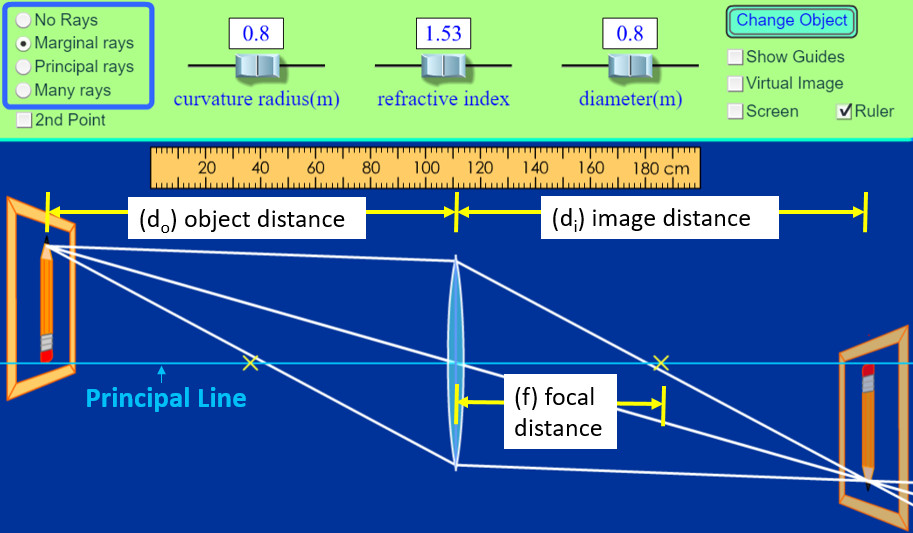
Converging lens ray diagram simulation. oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Concave and Convex Mirrors. Concave and Convex Mirrors - GeoGebra Materials. Description. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror. This interactive tutorial utilizes ray traces to explore how images are formed by the three primary types of converging lenses, and the relationship between the object and the image formed by the lens as a function of distance between the object and the focal points. Lens Combinations - 1 Diverging & 1 Converging. Author: Barb Newitt. This simulation shows a diverging lens in combination with a converging lens. Adjust the position of the orange circle to adjust the object position. Adjust the position of the purple focal point circles to adjust the focal lengths of the two lenses. Adjust the position of the purple Lens2 + to adjust the position of Lens 2. Re: Request for converging lens ray diagram with an adjustable screen. Most simulatuions only show the ray tracing of light paths for converging lens and indicate where the real/virtual image will be formed. If a screen is located at the real image focus point, image will be seen.
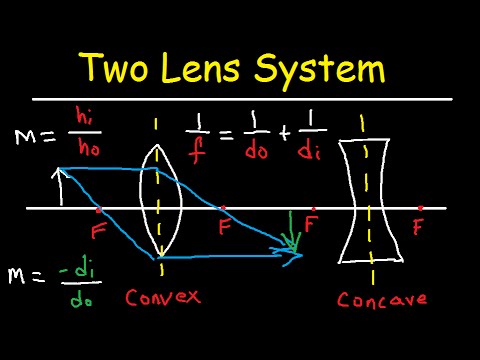
This physics video tutorial focuses on a multiple two lens system that contains a diverging lens and a converging lens. It provides the thin lens equation n... Real images occur when objects are placed outside the focal length of a converging lens (s>f). If the lens is converging but the distance from the object to the lens is smaller than the focal length, the image will be virtual. Diverging lenses always produce virtual images. This calculator shows a ray diagram when the image is real. Magnification A converging lens is an optical lens that converges all rays of light passing through it. The primary purpose of a converging lens is to focus the incoming rays from an object and converge them to form an image. The image can be magnified, diminished, or remain the same depending on the distance of the object from the lens. Type of lens: Check here to show multiple rays This work by Andrew Duffy is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
Ray Optics Simulation. An open-source web application to simulate reflection and refraction of light. ... , including prisms and "spherical" lenses. Glass (Ideal lens) An ideal lens which obeys exactly the thin lens equation (1/p + 1/q = 1/f). The focal length (in pixels) can be set directly. ... This collection of interactive simulations allow learners of Physics to explore core physics concepts by altering variables and observing the results. This section contains more than 70 simulations and the numbers continue to grow. Ray diagram for a converging or diverging lens; Nice variation of the previous simulation by John Welch, showing the lens changing shape; Test yourself - what's behind the curtain? (Lenses) Puzzle - find the focal length of the lens (I) Puzzle - find the focal length of the lens (II) Puzzle - find the focal length of the lens (III) • Construct ray diagrams to accurately show how an image is formed ... A converging lens could be used to create an image with .=−2. B. A diverging lens could be used to create an image ... Run two scenarios using the hidden lens simulation. If the frame does not open properly in your Pivot window, in a new window.
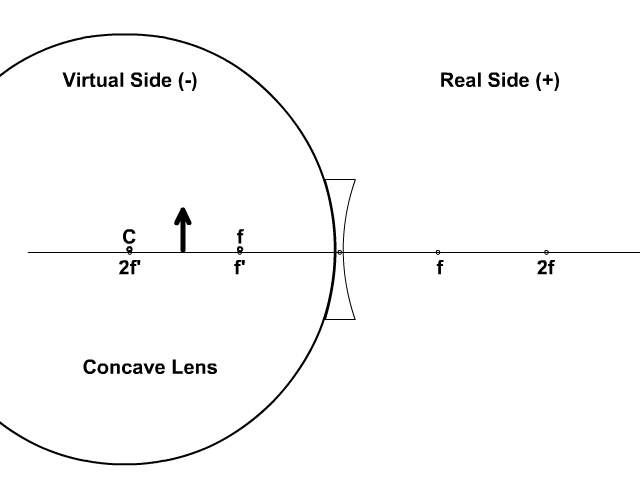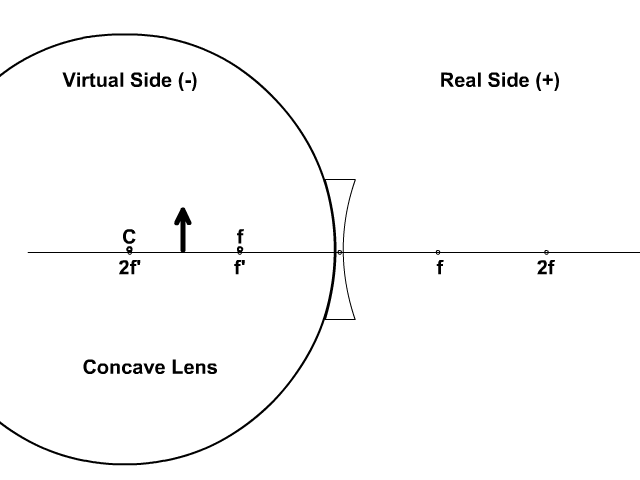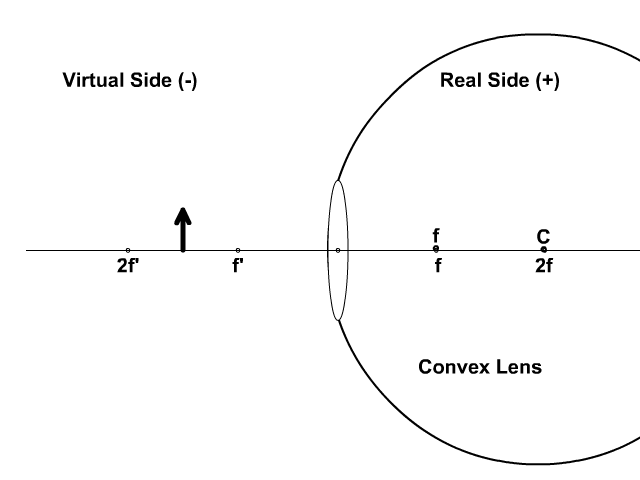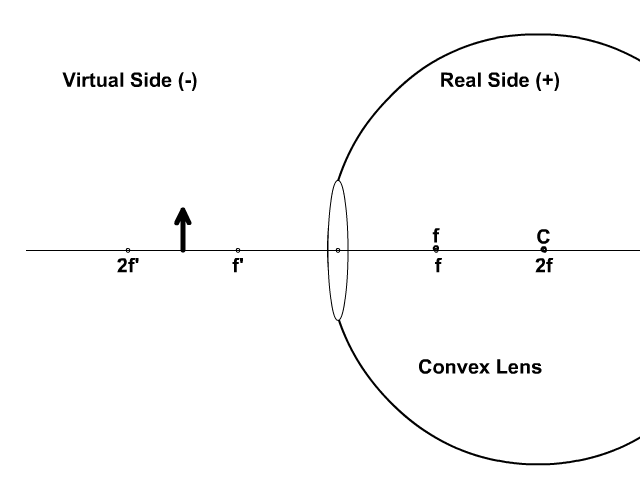
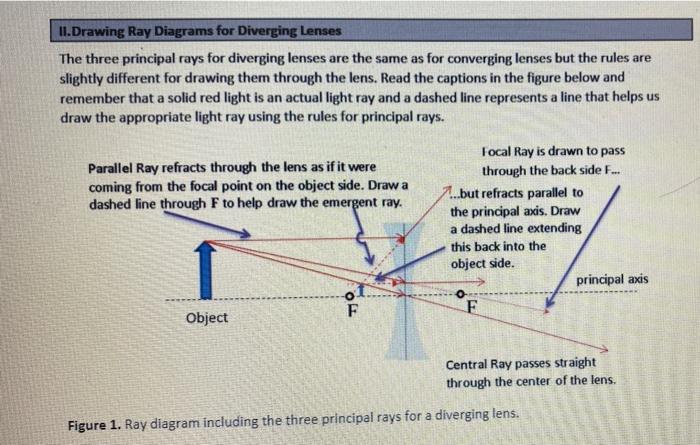
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a diverging lens. A diverging lens always form an upright virtual image. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object: A ray passing through the center of the lens will be undeflected. A ray proceeding parallel to the principal axis will diverge as if he came from the ...
The top diagram shows the formation of the virtual object where converging rays are prevented from meeting by the diverging lens. enter image. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such.Ray Diagrams for Lenses.
Description. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave lens.
• Any ray can be traced through the lens system using the oblique-ray method • For example, trace the axial ray - point of intersection with axis in image space gives image location L1 L2 F1 F1' F2 F2' Object parallel a x i a l r a y Image parallel second focal plane of lens1 second

Open Source Physics Singapore Thin Converging Diverging Lens Ray Diagram Lens Javascript Html5 Applet Simulation Model By Fu Kwun Hwang And Loo Kang Wee
Converging Lens. Diverging Lens. F. Ray 1. F Ray 1. Ray 2. Ray 2. Ray 3 Ray 3. Images' ' Tracing Points Draw an arrow to represent the location of an object, then draw any two of the rays from the tip of the arrow. The image is where lines cross. Draw an arrow to represent the location of an
Simulation of image formation by a mirror ... Ray diagram for a converging lenses Object Image A converging lens can form real and virtual images converging light ... An object is placed 30 cm in front of a converging lens with focal length 10 cm. Find the object distance and magnification. Ray diagram.
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray.
Converging Lenses A convex lens is a converging lens which bends light rays into focus. The focal length, f, is the distance to the focal point where parallel rays converge as shown. A Ray Diagram is a simple picture using only 2 or 3 light rays reflected off an object to visualize how images are formed.
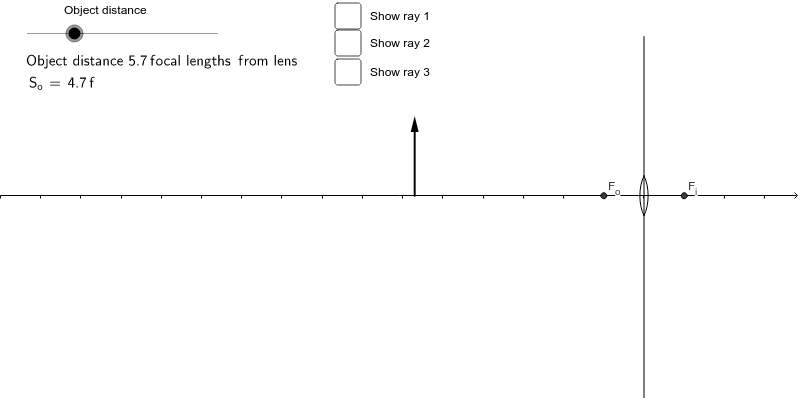
Diverging lens. Author: Ray Tuck. This simulation shows a ray diagram for a diverging lens. Use the slider to set the position of the object. The object is shown by a black arrow. Use the check boxes to choose which rays to show. You need any two to fix the position of the image. The image is shown by the red arrow.
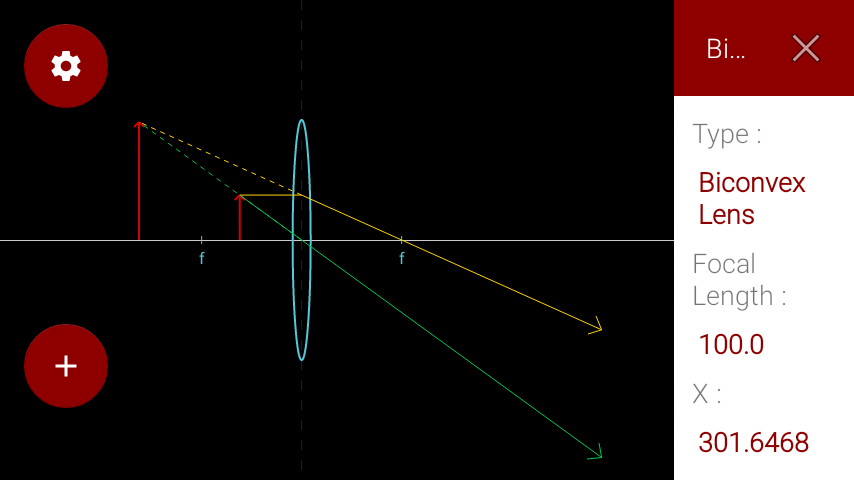
This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The rays parallel to the principal axis and the ray through the center of the lens are drawn.Locators allow you to drag both the object and the lens. You can change the focal length using a slider.
Steps to a Convex Lens Ray Diagram Look below and not at the animation to see the numbered steps for two scenarios and the analysis of the image produced. Start the First Ray : Start with your pencil on the top of the object (black thick arrow tip) and draw a line parallel to the principle axis to the center of the lens.
This physics tutorial shows you how to use the thin lens equation / formula to calculate variables such as the image height and image distance in addition to...
Molecular Expressions: Image Formation with a Converging Lens This simulation uses ray traces to explore how images are formed by converging lenses. Move the object back & forth along the optical axis to see the effects on the image size and placement. Object distance (p) and image distance (q) are automatically generated.

Converging Lens Optics Flash Animation For Optics Learning Interactive Physics Simulations Interactive Physics Animations Interactive Flash Animation To Learn How To Get An Clear Image Of An
physics-simulation. A collection of interactive physics simulations. Fork on GitHub. Elastic Collision. Simulates an elastic collision between two particles. Thin Lens. Draws the ray diagram for a thin converging or diverging lens.
Lenses are traditionally shaped as sections of spheres, such that the radius of curvature of the sphere of which they are comprised can describe the lens' curvature. The diagram of an eye and lens to the right demonstrates this concept. Lenses show up in nature in the eyes of animals.
Converging Lens Image Formation. The Converging Lens Image Formation Interactive provides learners with a virtual light box for exploring the refraction of light through converging lenses and the manner in which such refraction leads to the formation of an image of a complex object. Learners tap on various points upon an object.
Lens and Mirror Lab. Category. Optics, Physics. Change the location of the object and use the ray diagrams to determine the location of the image. The following lab was created by Nick Donovan. Thanks Nick! Recommended Lab:

Refraction Lenses Types Of Lenses Image Formation Via Refraction By Thin Lenses Thin Lenses Are Those Whose Thickness Is Small Compared To Their Radius Ppt Download

How To Use The Convex Lens Interactive Simulation Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng

Lens Any Transparent Object Having Two Nonparallel Curved Surfaces Or One Plane Surface And One Curved Surface Converging Lenses Thicker In Middle Than Ppt Download













0 Response to "38 converging lens ray diagram simulation"
Post a Comment