36 pacemaker cell action potential diagram
length) A and B. In C recording is from a Intent or subsidiary pacemaker cell (upper) and true pacemaker (lower), rate of drive 300/min or 200 msec cycle length. Note the decrease in amplitude of pacemaker cell spike and the greater than normal duration of pacemaker cell action potentials after drive. The inherent pacemaker rate of the SA node is faster than the other pacemaker cells, and for that reason the SA node generates the initial action potential in a normal functioning heart. If the SA node becomes suppressed, then the other pacemaker cells are capable of generating spontaneous action potentials but at a slower heart rate.
Find out how the pacemaker cells use the movement of sodium, calcium, and potassium to get your heart beating! Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease physic...

Pacemaker cell action potential diagram
ular node, and action potentials for non-pacemaker cells such as atrial or ventricular muscle cells. Pacemaker cells are capable of spontaneous action potential generation, whereas non-pacemaker cells have to be triggered by depolarizing currents from adja-cent cells. To compare non-oscillatory and oscillatory cells, it is convenient to rewrite Browse 500 sets of term:cardiac action potential = pacemaker cells flashcards. Study sets Diagrams Classes Users. 6 Terms. tami_kunz. Cardiac Action Potentials - Pacemaker cells. Resting membrane potential. 0. 1. 2. (USMLE topics, cardiology) Cardiac action potential in pacemaker cells and contractile myocytes, electrophysiology of a heartbeat. This video is available fo...
Pacemaker cell action potential diagram. The action potential is then dispersed throughout the heart by myocardiocytes, cardiac muscle cells that contract while they conduct the current to neighboring cells. Similar to action potential initiation in neurons, and in contrast to pacemaker cells, myocardiocytes initiate rapid depolarization through voltage-gated sodium channels. Figure 17.2 Graph depicting the action potential of a pacemaker cell. ACTION POTENTIALS IN MYOCYTES osms.it/myocyte-action-potentials Myocytes Receive signal from from pacemaker cells causing them to contract Able to depolarize, spread action potentials Action potential phases: Phase 0 (depolarization phase): rapid influx of sodium into cell (inward current); responsible for rapid ... The cardiac action potential is a brief change in voltage (membrane potential) across the cell membrane of heart cells. This is caused by the movement of charged atoms (called ions) between the inside and outside of the cell, through proteins called ion channels.The cardiac action potential differs from action potentials found in other types of electrically excitable cells, such as nerves. phase of depolarization occurs (Fig 2). At the peak of the action potential, K+ channels open, K+ rushes out of the cell and the cell repolarizes. Figure 2. Slow action potential has 3 phases (0, 3 and 4). The pacemaker cells set the rate of the heart beat. They are anatomically distinct from the
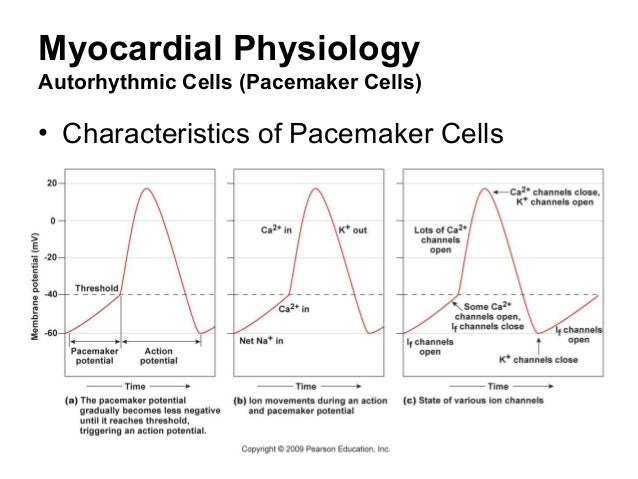
Cardiac Myocyte Action Potential. This diagram is a diagram of a cardiac myocyte - a ventricular muscle cell as apposed to a cardiac pacemaker cell. The resting membrane potential (RMP) is -90mv. A membrane potential is the difference in electrical potential between the interior and the exterior of the cell membrane. This chapter is relevant to Section G2(ii) of the 2017 CICM Primary Syllabus, which asks the exam candidate to "describe the normal and abnormal processes of cardiac excitation and electrical activity". Almost all the SAQs on this topic ask for a comparison between the action potentials of a normal cardiac myocyte and a specialised pacemaker cell, and so this chapter should probably be ... For an easy explanation of pacemaker cell action potentials, make sure to check out the EZmed blog that makes cardiac action potentials easy! Once an action potential is generated by the SA node, it will travel though the right atrium via the internodal pathway, as well as to the left atrium via Bachmann's bundle. The action potential in the SA node occurs in three phases which are discussed below. The pacemaker potential occurs at the end of one action potential and just before the start of the next. It is the slow depolarisation of the pacemaker cells e.g. cells of the sinoatrial node, towards the membrane potential threshold.
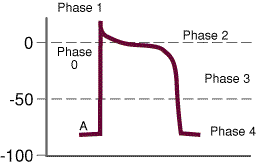
An action potential in one cell will cause all neighbouring cells to depolarize, allowing the heart chambers to act as a unit. Dominance : the cell with the highest inherent rate of pacemaker activity will therefore also set the heart rate, as all other pacemaker cells will be depolarized and rendered inactive by this stimulus. The cardiac cell action potential, like action potentials in nerves, is divided into five phases, numbered 0 through 4. Two of these, phase 2 (the plateau phase) and phase 4 (the diastolic interval) are marked by little to no change in voltage. Sodium, potassium and calcium are the primary ions. 1. Pacemaker Potential • An autorhythmic cell has the unique ability to depolarize spontaneously, resulting in a pacemaker potential. 2. Depolarization and Reversal of the Membrane Potential • Once threshold is reached, an action potential is initiated, which begins with further depolarization and leads to reversal of the membrane potential ... The contraction of cardiac muscle (heart muscle) in all animals is initiated by electrical impulses known as action potentials.The rate at which these impulses fire controls the rate of cardiac contraction, that is, the heart rate.The cells that create these rhythmic impulses, setting the pace for blood pumping, are called pacemaker cells, and they directly control the heart rate.
An action potential is caused by either threshold or suprathreshold stimuli upon a neuron. It consists of four phases: depolarization, overshoot, and repolarization. An action potential propagates along the cell membrane of an axon until it reaches the terminal button.
the blood pressure in a vessel is 10 units at point A and 10 units at point B. Flow between those points is ____. stopped. the blood pressure in a vessel is 20 units at point A and 10 units at point B. One minute later, the pressure is 15 units at point A and five units at point B. Flow between those points is _____.
The SA node is considered to be the pacemaker for the heart. Its depolarization generates the action potential that leads to depolarization of all other cardiac muscle cells. The discharge rate of the SA node determines the heart rate, the number of times the heart contracts per minute.
Identify structure "A" on the heart diagram. ... The plateau phase seen during the action potential of a cardiac muscle cell is due to the. continuing to have open calcium channels. ... When a pacemaker potential in the SA node reaches threshold, many voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open.
(b) Draw the action potential curves of a typical neuron, a pacemaker cell, and a cardiomyocyte, separately. Include all essential labeling, be careful with unit and legend. (c) How to identify whether a given action potential curve is obtained from a neuron, cardiomyocyte, or pacemaker cell, i.e. what are the characteristics of different cells ...
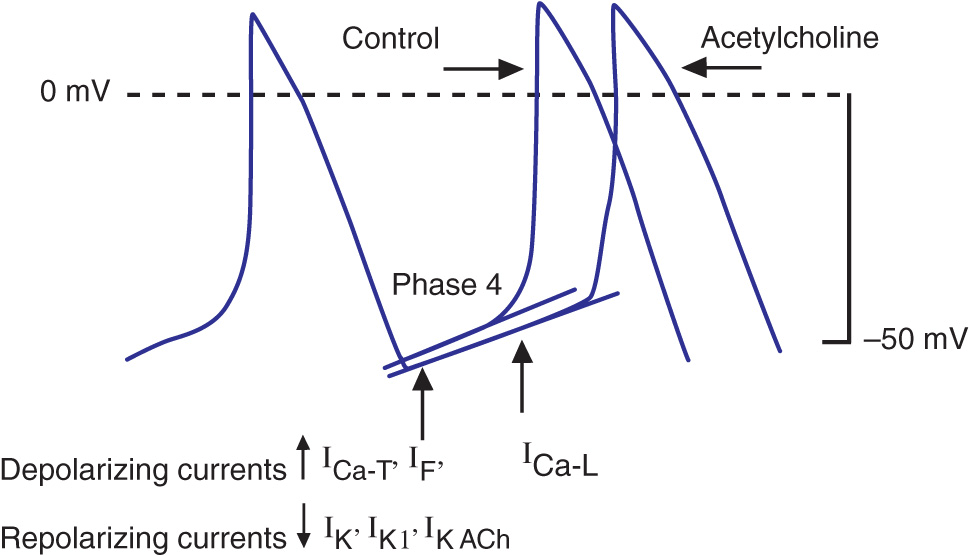
Cells within the sinoatrial (SA) node are the primary pacemaker site within the heart. These cells are characterized as having no true resting potential, but instead generate regular, spontaneous action potentials.Unlike non-pacemaker action potentials in the heart, and most other cells that elicit action potentials (e.g., nerve cells, muscle cells), the depolarizing current is carried into ...
The pacemaker cells within the SA node generate action potentials at 60-100 beats per minute. The action potential travels from the SA node through the right atrium via the internodal pathway, and to the left atrium via Bachmann's bundle. As the action potential travels through the atria, the atria depolarize and contract.

Figure 2 From The Cardiac Conduction System Generation And Conduction Of The Cardiac Impulse Semantic Scholar
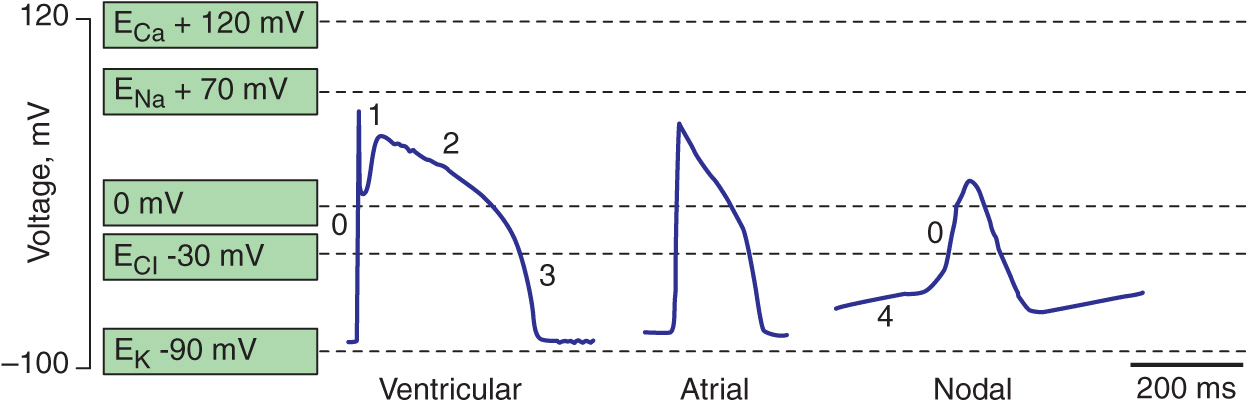
Cardiac action potentials differ from the APs found in other areas of the body. Typical neural AP duration is around 1ms and those of skeletal muscle are roughly 2-5ms, whereas cardiac action potentials range from 200-400ms. Nervous and muscle cells (as well as non-pacemaker cardiac cells) use the opening of Na channels to facilitate the depolarisation phase, whereas cardiac pacemaker cells ...
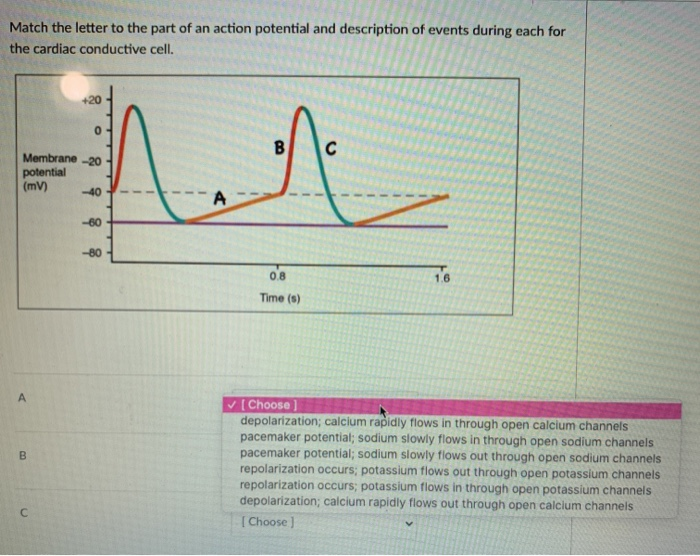
Label the diagram according to the events of an autorhythmic (pacemaker) cell. Membrane Potential (mV) is on the Y axis and Time is on the X axis. Threshold baseline is at -40, it starts at -60, peaks at 20, drops to -60 and the goes up to -55 at the end of the line.
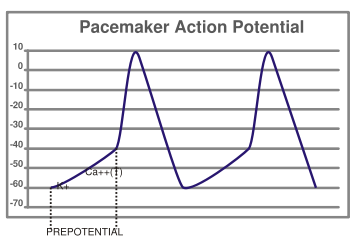
Pacemaker potential. In the pacemaking cells of the heart (e.g., the sinoatrial node ), the pacemaker potential (also called the pacemaker current) is the slow, positive increase in voltage across the cell 's membrane (the membrane potential) that occurs between the end of one action potential and the beginning of the next action potential.
Figure 1. The action potential in the sinoatrial node and in contractile myocardial cells. Phase 4 of the action potential in the sinoatrial node is called 'pacemaker potential', because it is responsible for the spontaneous repetitive depolarization. The depolarization spreads from the sinoatrial node to the atrial and ventricular myocardium.
(USMLE topics, cardiology) Cardiac action potential in pacemaker cells and contractile myocytes, electrophysiology of a heartbeat. This video is available fo...
Browse 500 sets of term:cardiac action potential = pacemaker cells flashcards. Study sets Diagrams Classes Users. 6 Terms. tami_kunz. Cardiac Action Potentials - Pacemaker cells. Resting membrane potential. 0. 1. 2.
ular node, and action potentials for non-pacemaker cells such as atrial or ventricular muscle cells. Pacemaker cells are capable of spontaneous action potential generation, whereas non-pacemaker cells have to be triggered by depolarizing currents from adja-cent cells. To compare non-oscillatory and oscillatory cells, it is convenient to rewrite
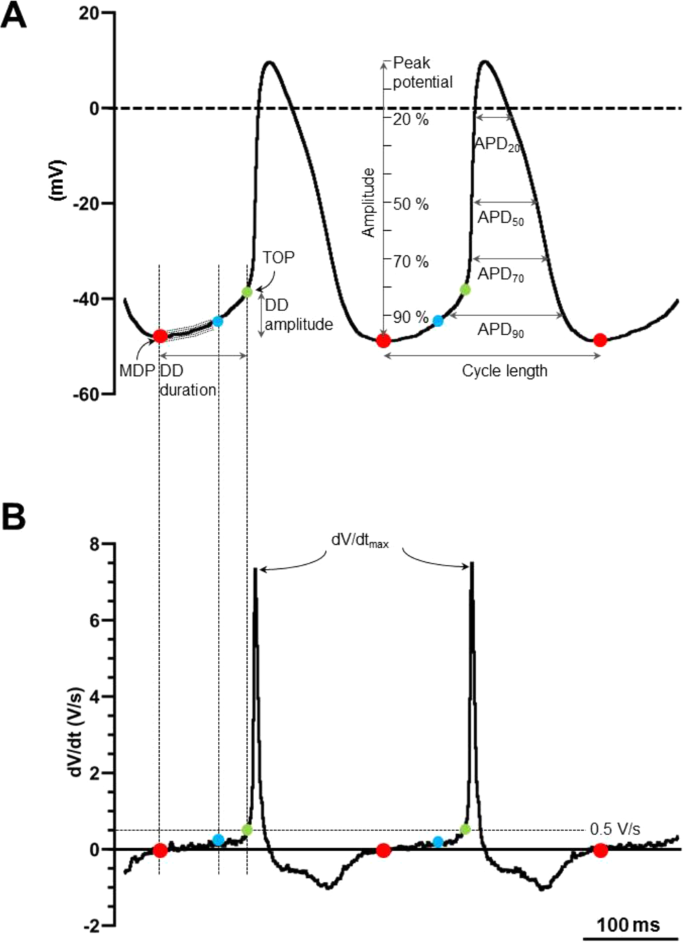
Sinus Node Like Pacemaker Mechanisms Regulate Ectopic Pacemaker Activity In The Adult Rat Atrioventricular Ring Scientific Reports


















0 Response to "36 pacemaker cell action potential diagram"
Post a Comment