36 electron transport chain diagram simple
3. Electron Transport Chain: The NADH may be used directly in the electron transport chain to synthesize ATP as a source of energy. This reaction has the direct effect of inhibiting the normal oxidation of fats in the fatty acid spiral and citric acid cycle. Protons are also special with respect to electron transport. Whenever a molecule is reduced by acquiring an electron, the electron (e-) brings with it a negative charge.In many cases, this charge is rapidly neutralized by the addition of a proton (H +) from water, so that the net effect of the reduction is to transfer an entire hydrogen atom, H + + e-(Figure 14-20B).
The electron transport chain. In Complex 1, NADH from glycolysis and Krebs cycle is. Image source: By Gabi Slizewska. Report. Share. 5. Like ...
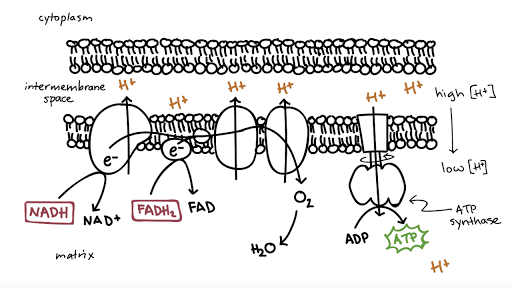
Electron transport chain diagram simple
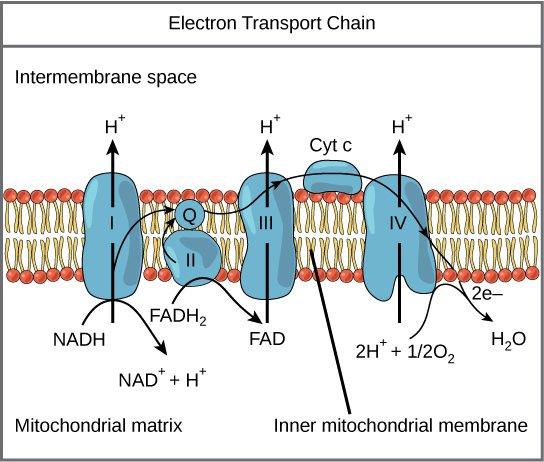
It is simply a chain of hydrogen and electron carriers of increasing redox potential. The electron carriers are found within four membrane-bound enzyme-complexes, which are imbedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Components of the electron transport chain The electron transport chain is formed of: A. Hydrogen and electron carriers B. 3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis (Stage 1) Glycolysis is the process where 1 glucose molecule, in the cell's cytoplasm, is broken down (through several steps) into 2 molecules of pyruvate, which is then used in the Kreb's Cycle (stage 2). This break down also March 1, 2021 - During aerobic respiration, coupled oxidation-reduction reactions and electron carriers are often part of what is called an electron transport chain , a series of electron carriers that eventually …
Electron transport chain diagram simple. after being done with glycolysis and the Krebs cycle we're left with 10 nadh --is 10 nadh is and 2 fadh2s and i told you that these are going to be used in the electron transport chain and they're all sitting in the matrix of our mitochondria and i said they're going to be used in the electron transport chain in order to actually generate ATP so that's what I'm going to focus on in this video ... For Higher Human Biology, discover how and where energy is made in the cell and the chemical reactions involved. The electron transport chain is an essential metabolic pathway that produces energy by carrying out a series of redox reactions. This BiologyWise article ... Electron Transport Chain is a series of compounds where it makes use of electrons from electron carrier to develop a chemical gradient. It could be used to power oxidative phosphorylation. The molecules present in the chain comprises enzymes that are protein complex or proteins, peptides and much more.
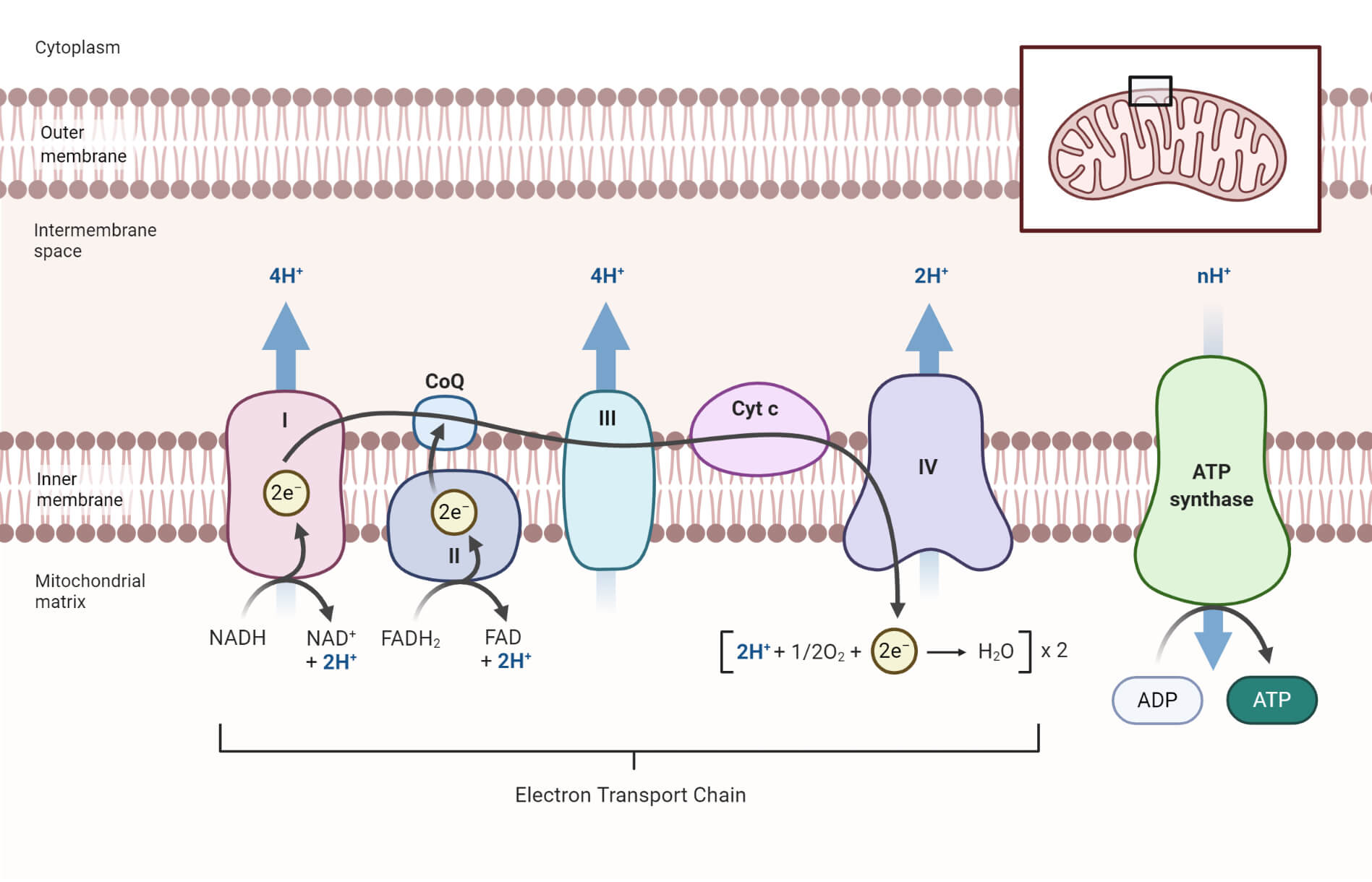
Electron Transport Chain Steps Explained with Diagram. The electron transport chain is an essential metabolic pathway that produces energy by carrying out a series of redox reactions. This BiologyWise article provides a simple explanation of this pathway. Electron Transport Chain Definition. The electron transport chain is a cluster of proteins that transfer electrons through a membrane within mitochondria to form a gradient of protons that drives the creation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is used by the cell as the energy for metabolic processes for cellular functions. In the following description, we assume all of the hydrogen and electrons are available from these reactions. In reality, some are lost and not used to create ATP. Other descriptions of the electron transport chain have additional sites and are omitted here for simplicity. July 27, 2020 - Note: Electrons from FADH2 enter the electron transport chain at the fourth protein complex, succinate-Q reductase. This protein complex contains succinate dehydrogenase which was responsible for generating FADH2 from the reaction converting succinate into fumarate.
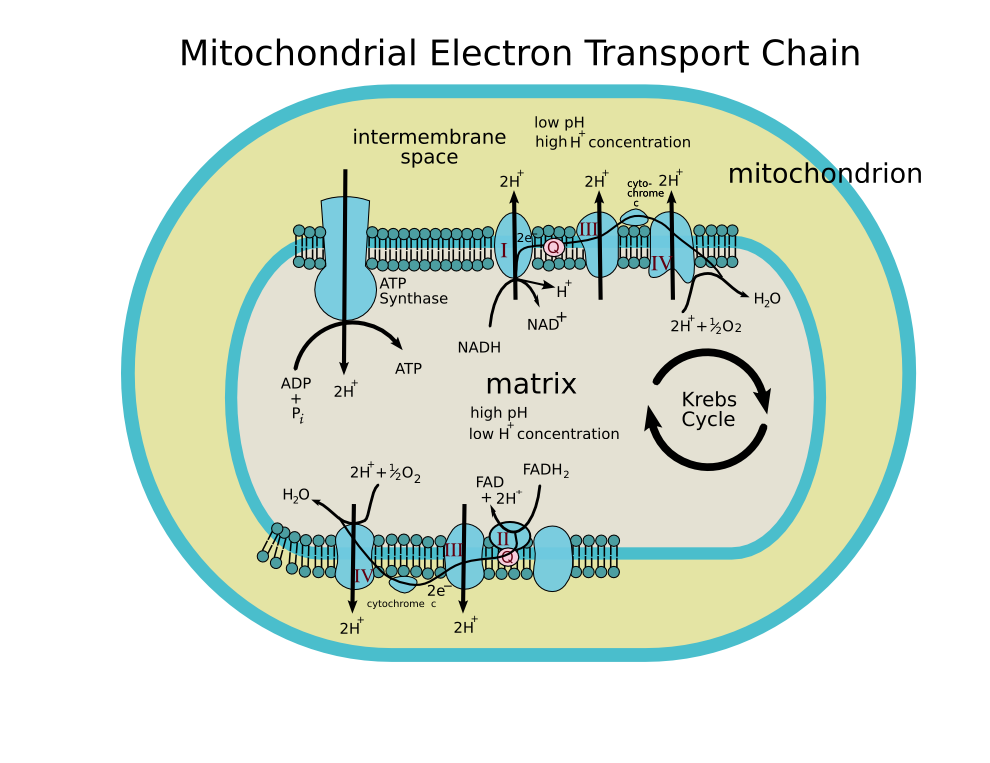
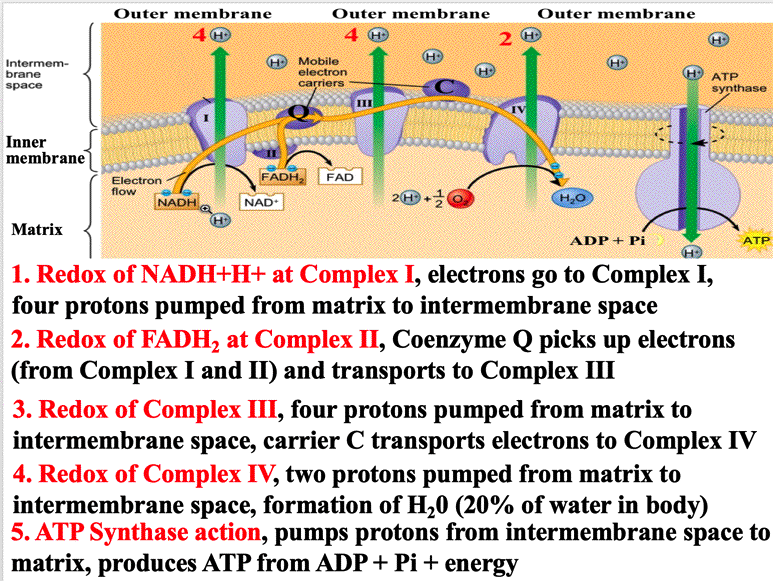
Oxidative phosphorylation is made up of two closely connected components: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. In the electron transport chain, electrons are passed from one molecule to another, and energy released in these electron transfers is used to form an electrochemical gradient. In chemiosmosis, the energy stored in the ... The first stage of the electron transport chain is a form of active transport. The electron carriers NADH and FADH2 that were produced during the Krebs cycle interact with proteins embedded in the cristae. This interaction causes the proteins to pump hydrogen ions from one side of the membrane to the other. Electron Transport Chain Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed through a series of electron acceptors present in the inner membrane of mitochondria. 2 NADH produced during glycolysis, 2 NADH, produced during pyruvic acid oxidation, & 6 NADH AND 2 FADH2, produced during Kreb cycle. Four enzyme complexes of ETC. Complex I - NADH ... Electron Transport Chain Definition. The electron transport chain is a crucial step in oxidative phosphorylation in which electrons are transferred from electron carriers, into the proteins of the electron transport chain which then deposit the electrons onto oxygen atoms and consequently transport protons across the mitochondrial membrane.This excess of protons drives the protein complex ATP ...
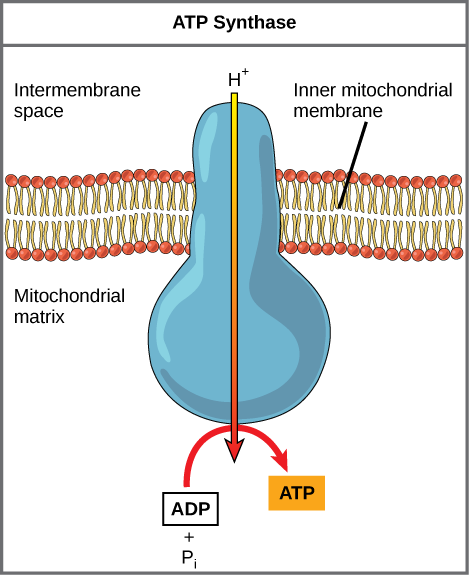
Transfer of electrons between carriers in the electron transport chain in the membrane of the cristae is coupled to proton pumping AND In chemiosmosis protons diffuse through ATP synthase to generate ATP AND Oxygen is needed to bind with the free protons to maintain the hydrogen gradient, resulting ...
The electron transport chain (ETC; respiratory chain) is a series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H + ions) across a membrane.The electron transport chain is built up of peptides, enzymes, and other ...
August 16, 2021 - In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation
We are pleased to provide you with the picture named Diagram Of Simple Electron Transport Chain.We hope this picture Diagram Of Simple Electron Transport Chain can help you study and research. for more anatomy content please follow us and visit our website: www.anatomynote.com. Anatomynote.com found Diagram Of Simple Electron Transport Chain from plenty of anatomical pictures on the internet.
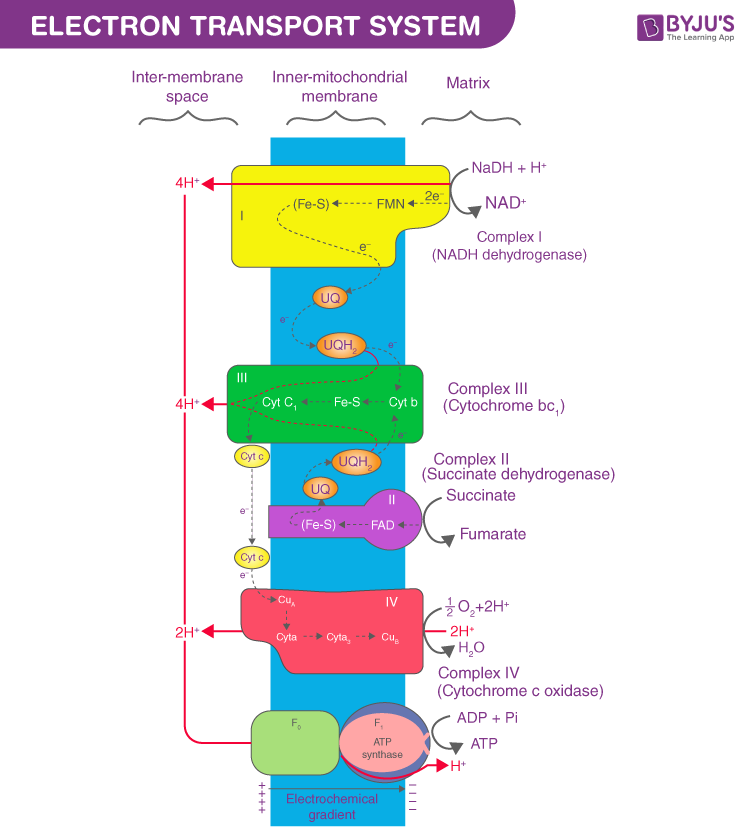
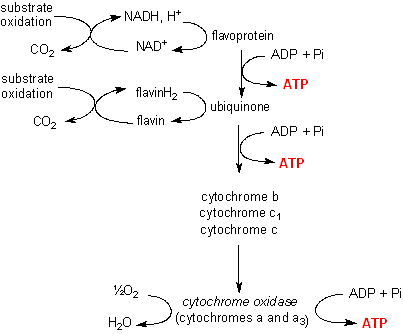
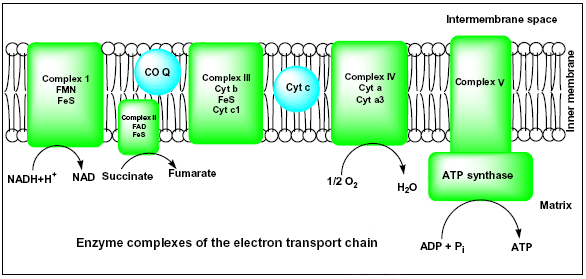
The electron transport chain is also called the Cytochrome oxidase system or as the Respiratory chain. The components of the chain include FMN, Fe–S centers, coenzyme Q, and a series of cytochromes (b, c1, c, and aa3). The energy derived from the transfer of electrons through the electron transport chain is used to pump protons across the ...
The electron transport system refers to the "Electron transport chain" or "ETS" (in abbreviated form) that is present in the inner mitochondrial membrane.ETS involves electron transfer through a series of protein complexes from higher (NADH +) to lower energy state (O 2) by releasing protons into the cytosol.. A movement of proton or H + from a matrix to cytosol generates a proton ...
The electron transport chain has two essential functions in the cell: Regeneration of electron carriers: Reduced electron carriers NADH and FADH 2 pass their electrons to the chain, turning them back into NAD + and FAD. This function is vital because the oxidized forms are reused in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) during cellular respiration.
Electron transport chain tricks easy to remember - This lecture explains about the easy way to remember the electron transport chain pathway. This lecture wi...
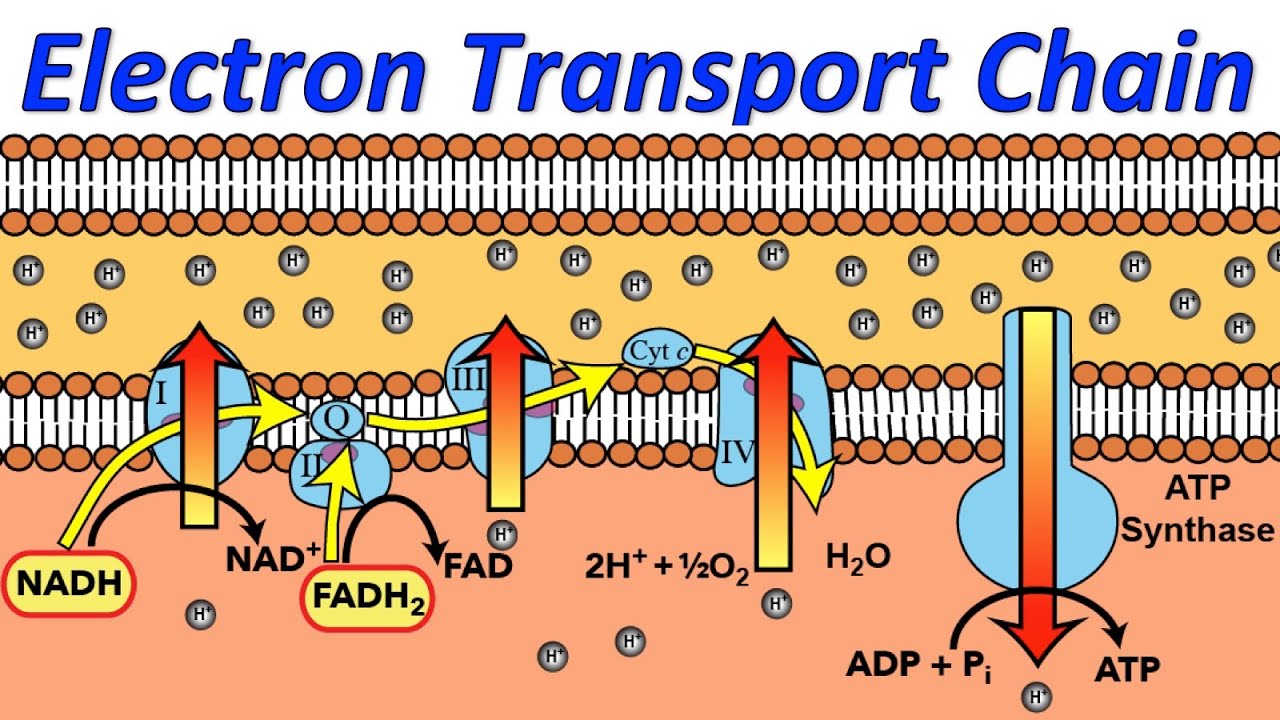
December 2, 2020 - The electron transport chain uses the electrons from electron carriers to create a chemical gradient that can be used to power oxidative phosphorylation.
The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. In the former, the electrons come from breaking down organic molecules, and energy is released.
June 30, 2021 - Electrons can leak out of electron transport chain and can reduce oxygen, which can produce free radicals such as superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. By OpenStax College [CC BY 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons · Fig 1 – Diagram to summarise the electron ...
The electron transport chain is the last stage of the respiration pathway and is the stage that produces the most ATP molecules. The electron transport chain is a collection of proteins found on ...
The electron transportation chain is the last aerobic respiration portion and is the only part of the glucose metabolism that uses atmospheric oxygen. Oxygen continuously passes through plants; it enters the body via the respiratory system of animals. Electron transport is a sequence of redox reactions that mimic a relay race or bucket brigade ...
GET LECTURE HANDOUTS and other DOWNLOADABLE CONTENT FROM THIS VIDEOSUPPORT US ON PATREON OR JOIN HERE ON YOUTUBE.https://www.patreon.com/medsimplifiedElectro...
April 8, 2012 - This is shown by the diagram below. Complex I-IV each play a role in transporting electrons( hence the name electron transport chain), and establishing the proton gradient. The exact mechanism of each Complex can be overwhelming so I will save that for a future post.
An electron transport chain (ETC) is how a cell gets energy from sunlight in photosynthesis.Electron transport chains also occur in reduction/oxidation ("redox") reactions, such as the oxidation of sugars in cellular respiration.. In aerobic respiration, each molecule of glucose leads to about 34 molecules of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) being produced by the electron transport chain.
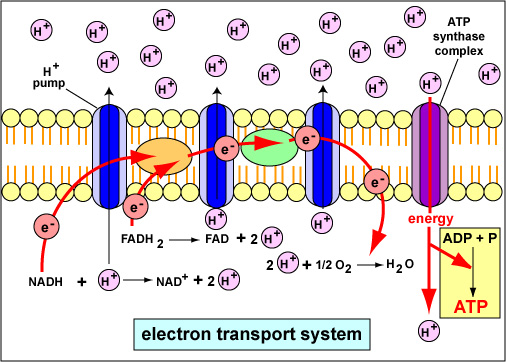
The electron transport chain is a series of molecules that accept or donate electrons easily. By moving step-by-step through these, electrons are moved in a specific direction across a membrane. The movement of hydrogen ions are coupled with this. This means that when electrons are moved, hydrogen ions move too.
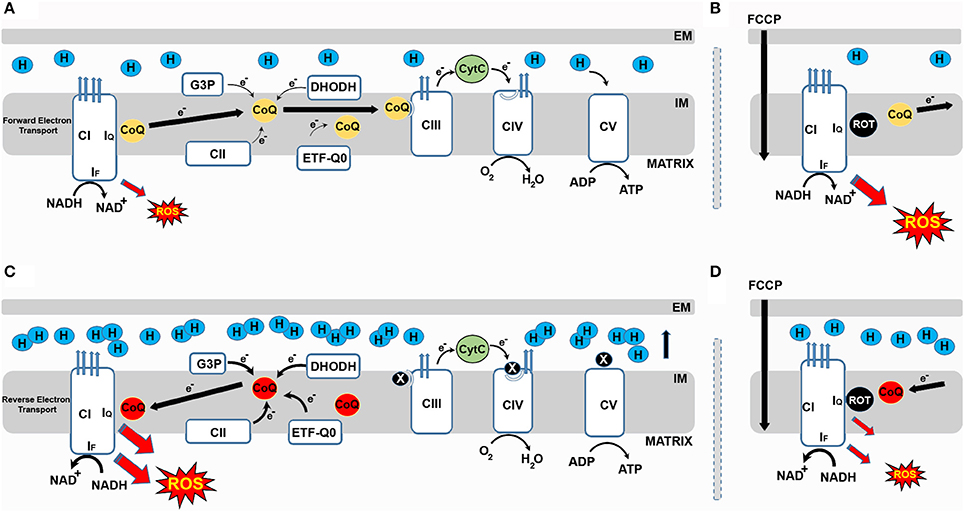
Frontiers Role Of Mitochondrial Reverse Electron Transport In Ros Signaling Potential Roles In Health And Disease Physiology
cellular respirationI. Energy flow & chemical cyclinga. Autotrophs -- producersi. Solar energy à chemical energy b. Heterotrophs -- consumersi. Live off chem...
Electron Transport Chain Definition. The Electron Transport System also called the Electron Transport Chain, is a chain of reactions that converts redox energy available from oxidation of NADH and FADH 2, into proton-motive force which is used to synthesize ATP through conformational changes in the ATP synthase complex through a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
Electron Transport Chain (overview) • The NADH and FADH2, formed during glycolysis, β-oxidation and the TCA cycle, give up their electrons to reduce molecular O2 to H2O. • Electron transfer occurs through a series of protein electron carriers, the final acceptor being O2; the pathway is called as the electron transport chain.
Electron transport chain 1. M.Prasad Naidu MSc Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research Scholar 2. ETC is the 4th and final stage of aerobic respiration. Through ETC, the E needed for the cellular activities is released in the form of ATP. ETC is an O2 dependent process which occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Electron Transport Chain of Bacteria (With Diagram) The electron transport chains of bacteria (prokaryotes) operate in plasma membrane (mitochondria are absent in prokaryotes). Some bacterial electron transport chains resemble the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Paracoccus denitrificans is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic soil ...
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes and electron carrier molecules within the inner membrane of mitochondria that generate ATP for energy.; Electrons are passed along the chain from protein complex to protein complex until they are donated to oxygen.
The electron transport chain is the portion of aerobic respiration that uses free oxygen as the final electron acceptor of the electrons removed from the intermediate compounds in glucose catabolism. The electron transport chain is composed of four large, multiprotein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane and two small ...
Download scientific diagram | Schematic diagram of the electron transport chain (ETC) of mitochondria. Complex (C) I, II, III, IV, and V represent each complex in the ETC chain. The ETC uses NADH and FADH2 to make ATP. These reducing equivalents for ETC are generated during glycolysis, fatty ...
March 1, 2021 - During aerobic respiration, coupled oxidation-reduction reactions and electron carriers are often part of what is called an electron transport chain , a series of electron carriers that eventually …
3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis (Stage 1) Glycolysis is the process where 1 glucose molecule, in the cell's cytoplasm, is broken down (through several steps) into 2 molecules of pyruvate, which is then used in the Kreb's Cycle (stage 2). This break down also
It is simply a chain of hydrogen and electron carriers of increasing redox potential. The electron carriers are found within four membrane-bound enzyme-complexes, which are imbedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Components of the electron transport chain The electron transport chain is formed of: A. Hydrogen and electron carriers B.
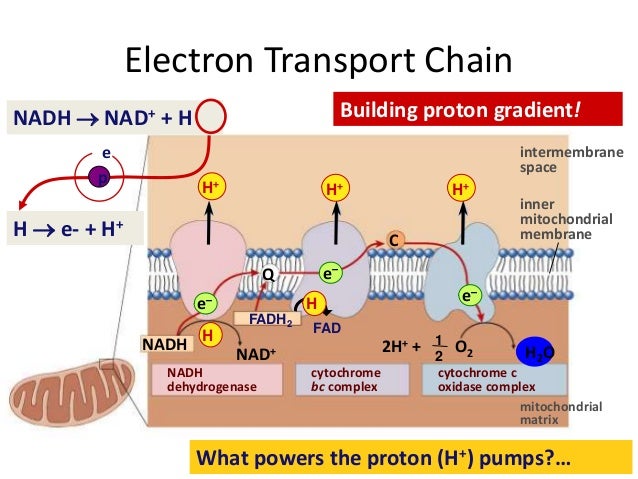
/electron-transport-chain-58e3be435f9b58ef7ed96112.jpg)

















0 Response to "36 electron transport chain diagram simple"
Post a Comment