35 convex mirror ray diagram cases
Previously in Lesson 4, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by concave mirrors. The ray diagram constructed earlier for a convex mirror revealed that the image of the object was virtual, upright, reduced in size and located behind the mirror. #reflection#reflectionoflight#raydiagram#imageformation#sphericalmirror#convexmirror#concavemiror#convexmirror#regularreflection#propertiesofimagesformedbypl...
21 Posts Related to Ray Diagram For Convex Mirror 6 Cases. Convex Mirror Ray Diagram. Ray Diagram For Convex Mirror. Ray Diagram Of Convex Mirror ... Concave And Convex Mirror Ray Diagrams Chapter 17 Review. Wedding Invitation Mirror Gift. Sony Car Radio Wiring Diagram Sony Car Stereo Wiring Harness Diagram Free Download Wiring. Cat 5 E Wiring ...
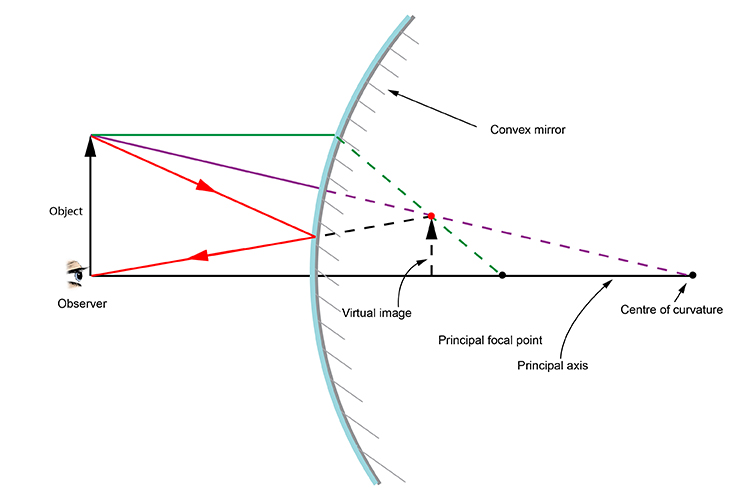
Convex mirror ray diagram cases
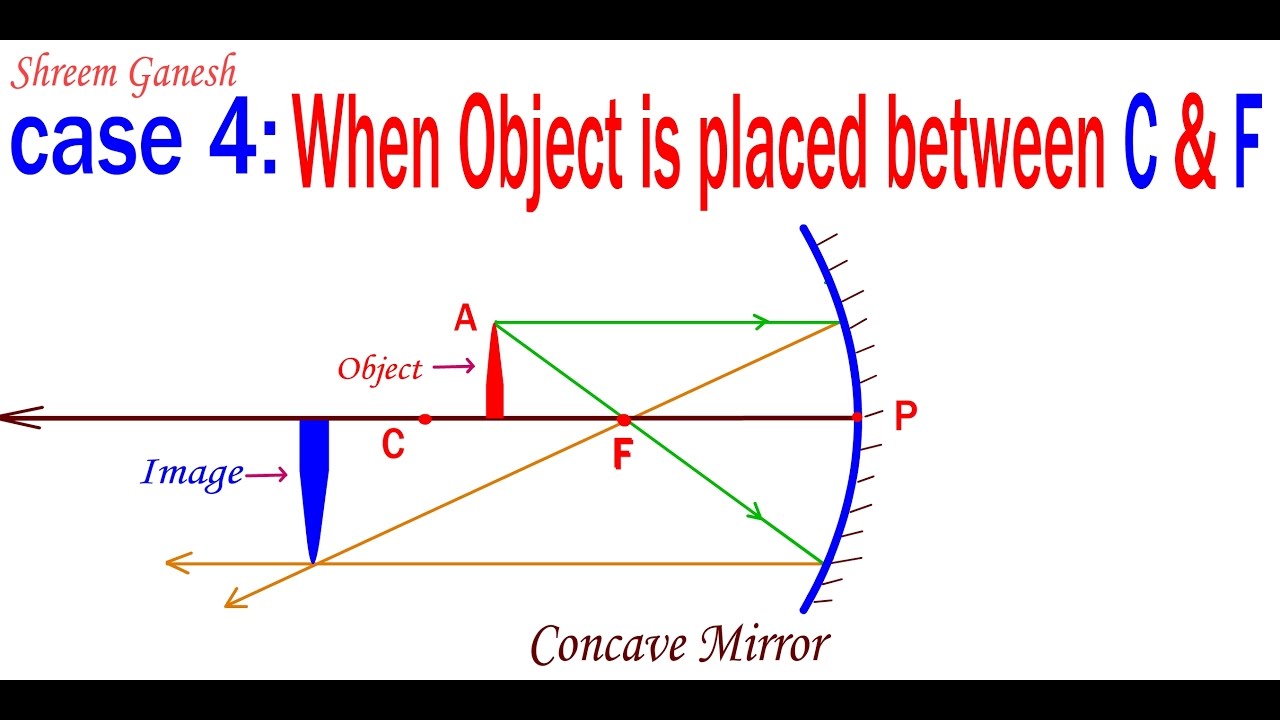
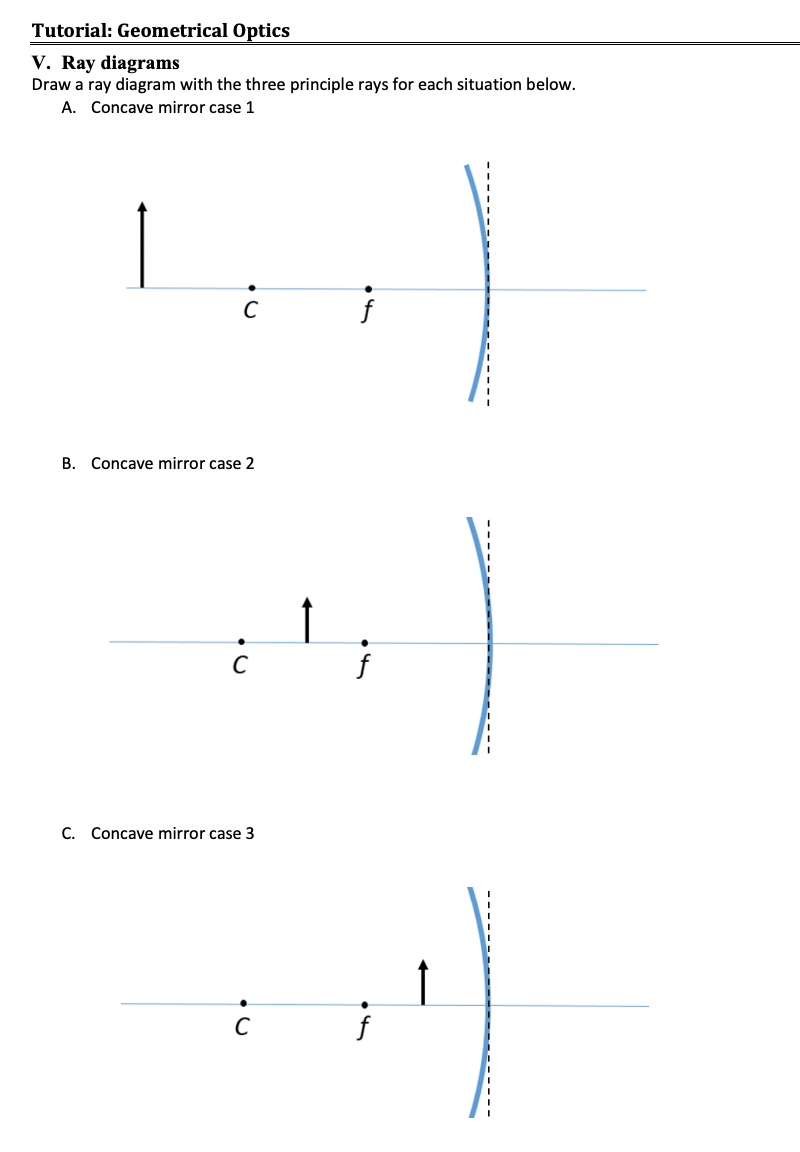
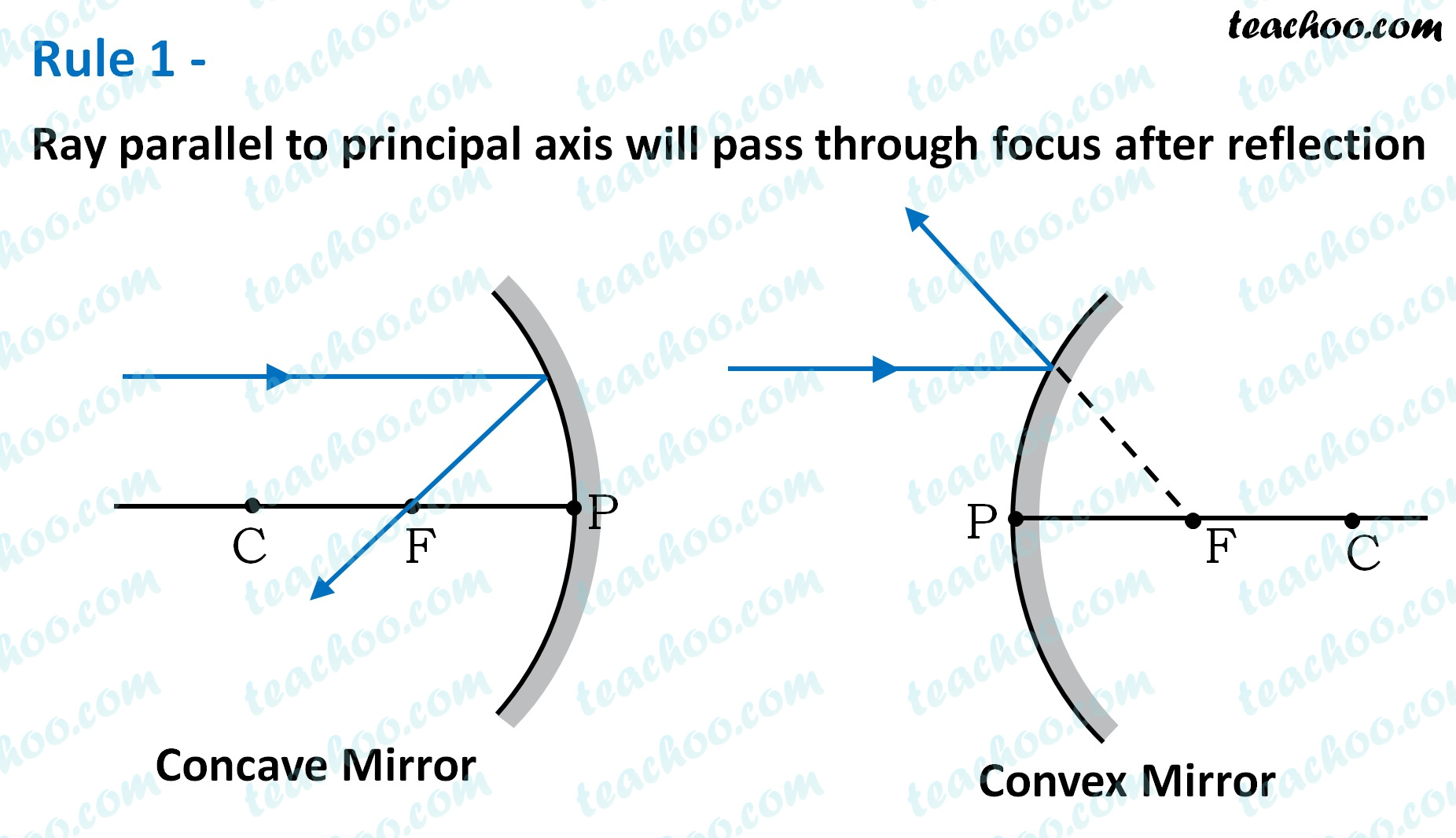
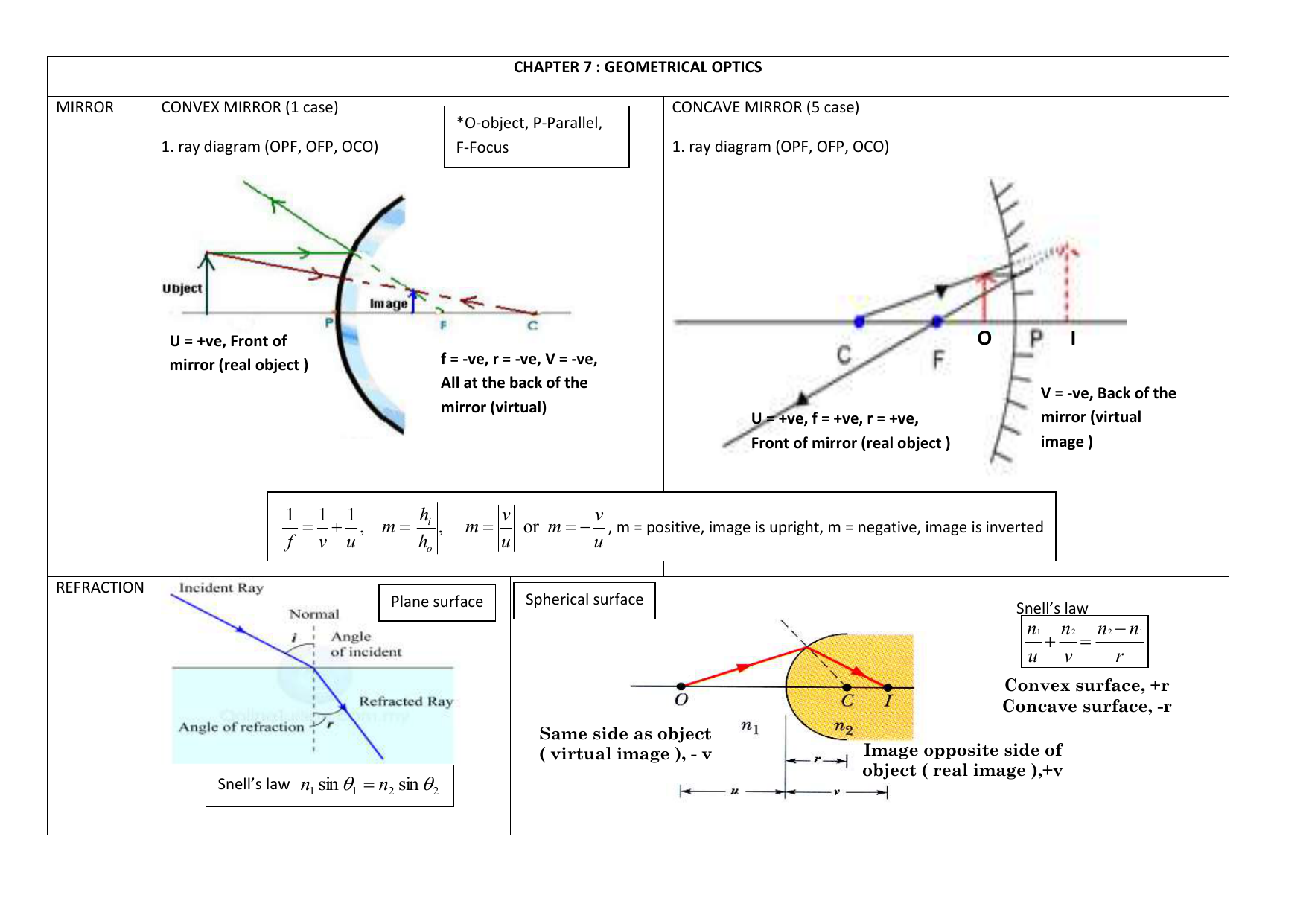
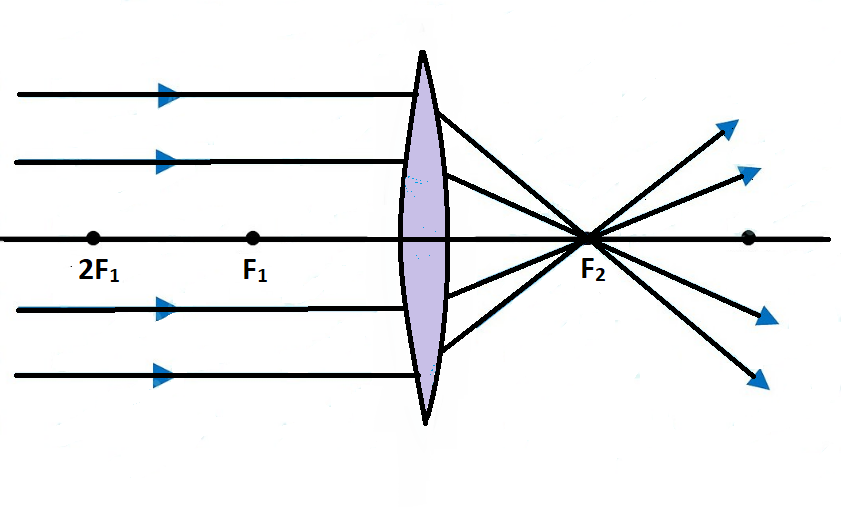
For a Convex Mirror,The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirrorSo, there will only be 2 cases.They areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Principal axis and InfinityCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (al Ray diagrams can be used to determine the image location, size, orientation and type of image formed of objects when placed at a given location in front of a mirror. The use of these diagrams was demonstrated earlier in Lesson 3 and in Lesson 4.Ray diagrams provide useful information about object-image relationships, yet fail to provide the information in a quantitative form. A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.
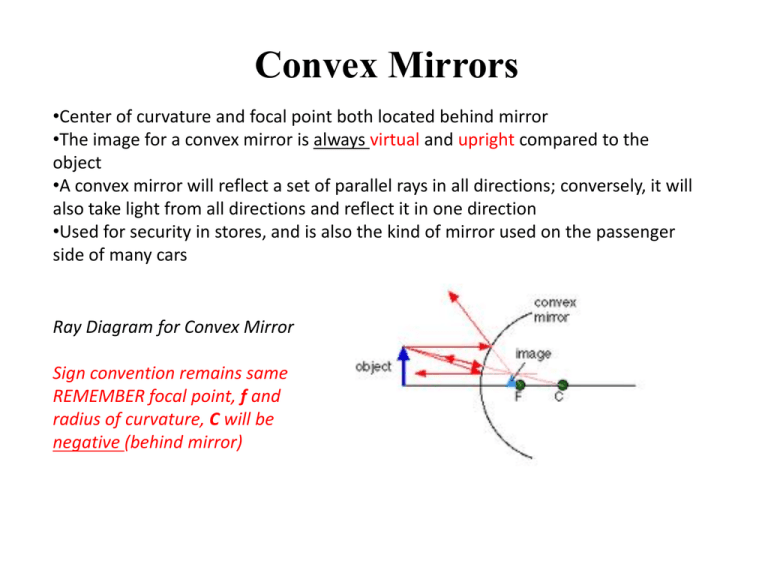
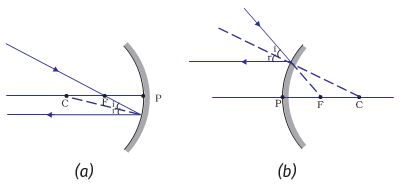
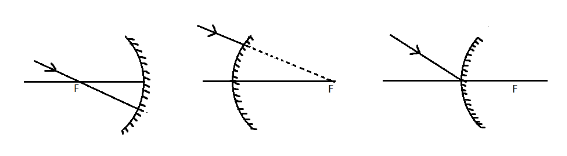
Convex mirror ray diagram cases. Virtual, erect, and diminished images are always formed with convex mirrors, irrespective of the distance between the object and the mirror. Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors. Guidelines for Rays Falling on the Concave and Convex Mirrors. When a ray strikes concave or convex mirrors obliquely at its pole, it is reflected obliquely. Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a convex mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and to learn the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. The intersection of these two reflected rays gives the position of an image of the object. In case of a convex mirror any ... Ray Diagram for a Convex Mirror ¥ The object is in front of a convex mirror ¥ The image is Ðvirtual Ðupright Ðsmaller than the object (reduced) Notes on Images ¥With a concave mirror, the image may be either real or virtual ¥With a convex mirror, the image is always virtual and upright ¥An image is real when the rays are passing through ... A ray diagram that shows the position and the magnification of the image formed by a convex mirror. The animation illustrates the ideas of magnification, of real and virtual images. Click and drag the candle along the optic axis. Click and drag its flame to change its size.
A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram. Ray diagrams can be used to determine the image location, size, orientation and type of image formed of objects when placed at a given location in front of a mirror. The use of these diagrams was demonstrated earlier in Lesson 3 and in Lesson 4.Ray diagrams provide useful information about object-image relationships, yet fail to provide the information in a quantitative form. For a Convex Mirror,The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirrorSo, there will only be 2 cases.They areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Principal axis and InfinityCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (al
Draw The Ray Diagram And Find The Position Nature And Size Of Image Formed By A Convex Mirror If The Object Is Placed I At Infinity Ii Between Infinity And The Pole
Draw A Labeled Ray Diagram To Show The Formation Of Image Of An Object By A Convex Mirror Studyrankersonline
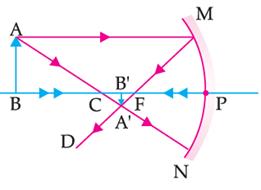
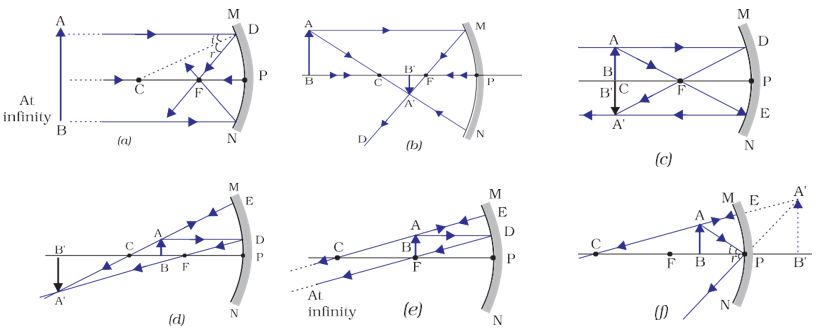
Following Figure Illustrates The Ray Diagram For The Formation Of Images By A Concave Mirror The Position Of The Object Is Beyond The Centre Of Curvature Of The Concave Mirror On The
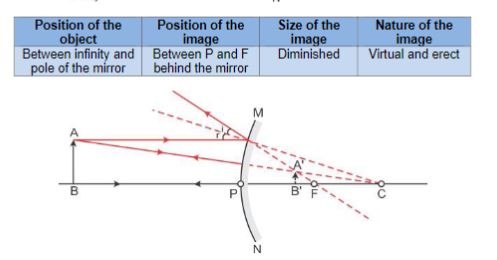
Name The Mirror That Shows Virtual Erect And Diminished Image And Draw A Ray Diagram Using The Same Mirror Physics Topperlearning Com 2d5vewkk

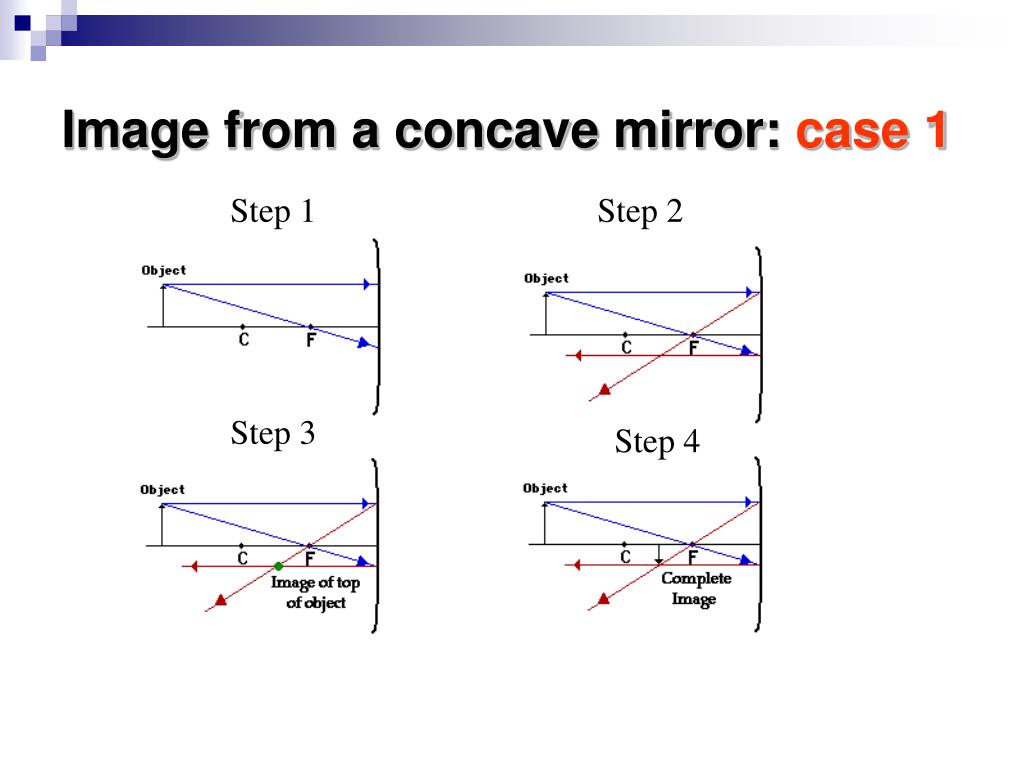
Drawing Ray Diagrams Concave And Convex Mirrors And Double Concave And Double Convex Lenses By Vincent Sapone Ppt Download
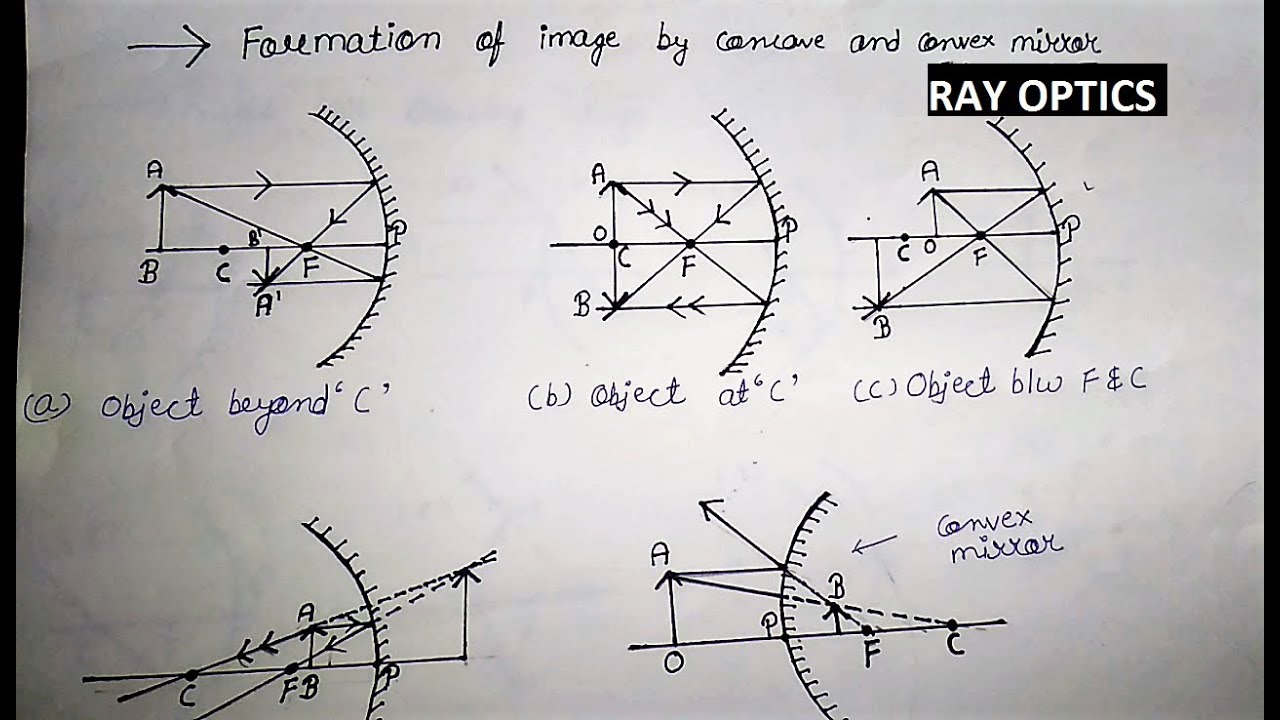
Very Important Five Cases Of Concave And Convex Mirror On Which The Whole Ray Optics Is Based Youtube











0 Response to "35 convex mirror ray diagram cases"
Post a Comment