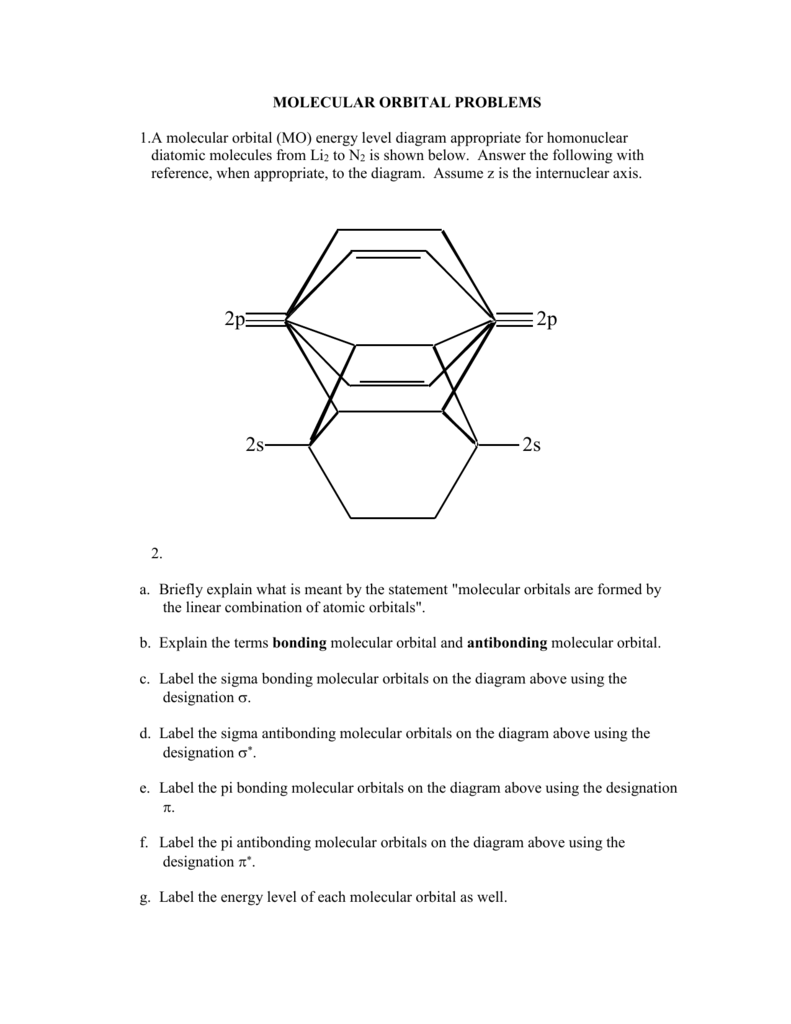
34 c2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
Bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons present in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Bond Order = ½ ( N b - Na) The molecule is stable if N b > Na ie. bond order is positive. The molecule is unstable if N b < Na i.e. the bond order is negative or zero. 3) Relative stability of molecule in terms of ... referring to the molecular orbital diagram in question 1, which of the following statements is true? a) the dicarbon cation, C2+, has a bond order of 1 and is less stable than C2 b) the dicarbon cation, C2+, has a bond order of 1 and is more stable than C2 c) the dicarbon anion, C2- has a bond order of -1 and does not exist
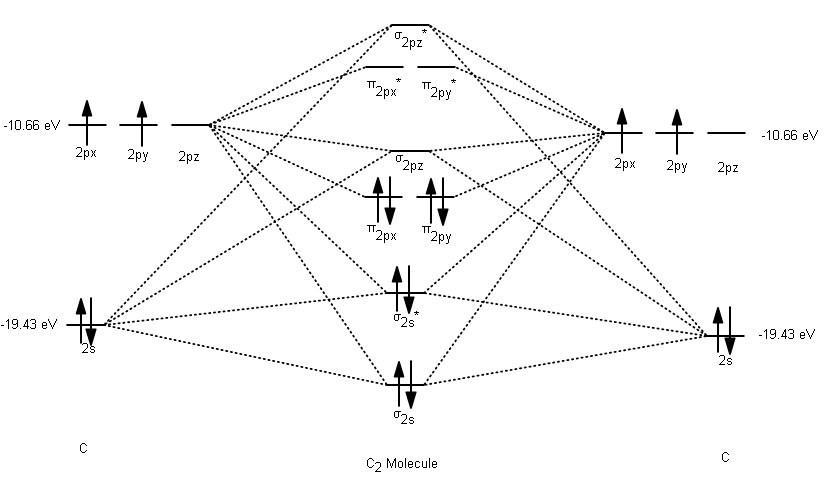
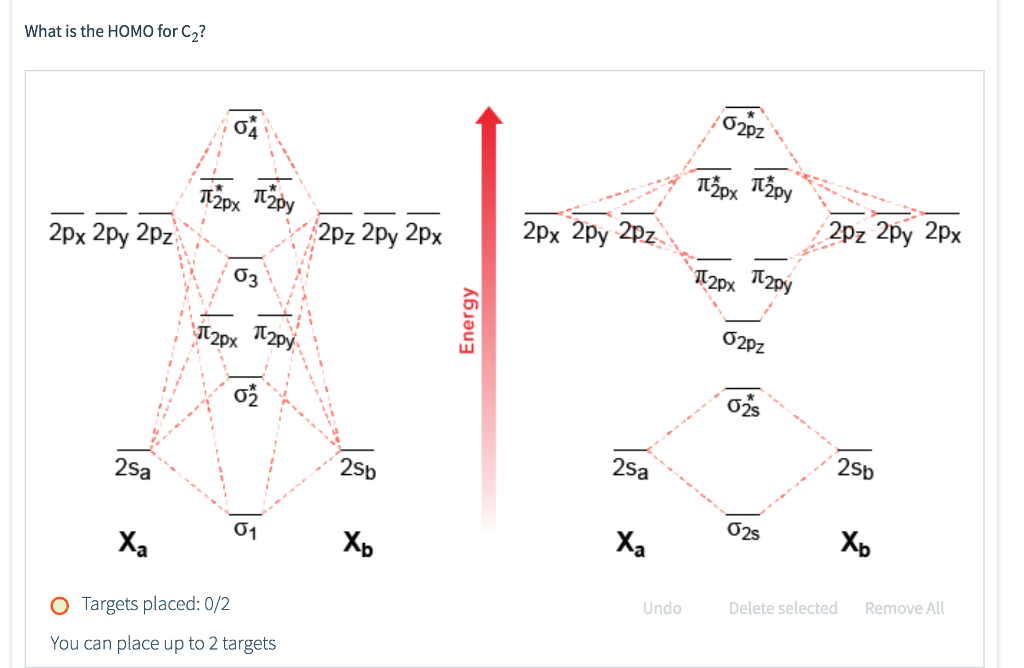
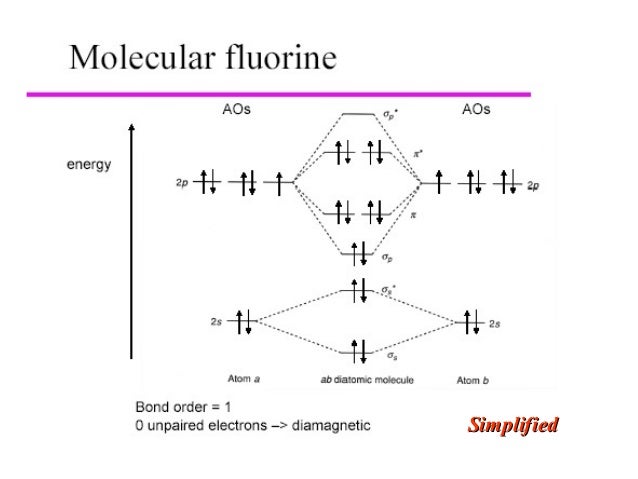
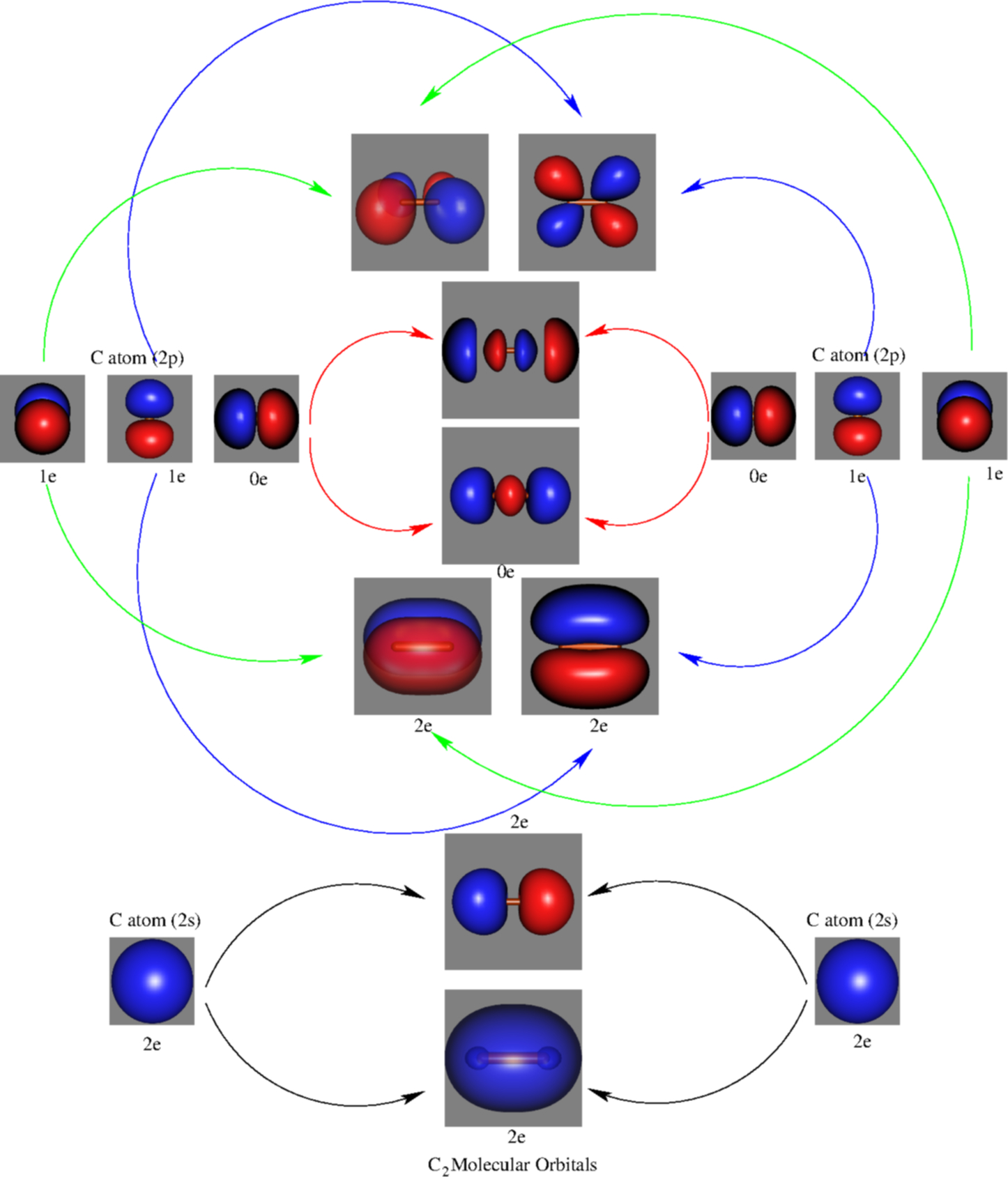
Feb 26, 2018 · Asked by futureisbright051101 26th February 2018, 3:12 PM. Answered by Expert. Answer: The molecular orbital diagram for C 2 molecule is : The electronic configuration of C 2 is K K (σ2s) 2 (σ * 2s) 2 n (2px) 2 n (2py) 2. The C 2 molecule is diamagnetic because all electrons are paired there are no unpaired electrons.
C2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
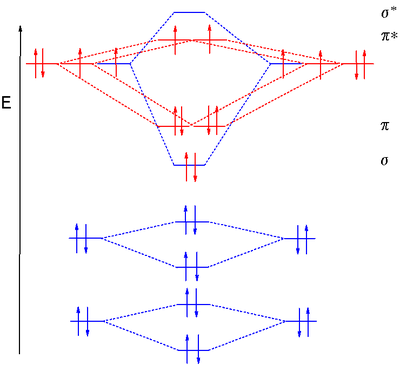
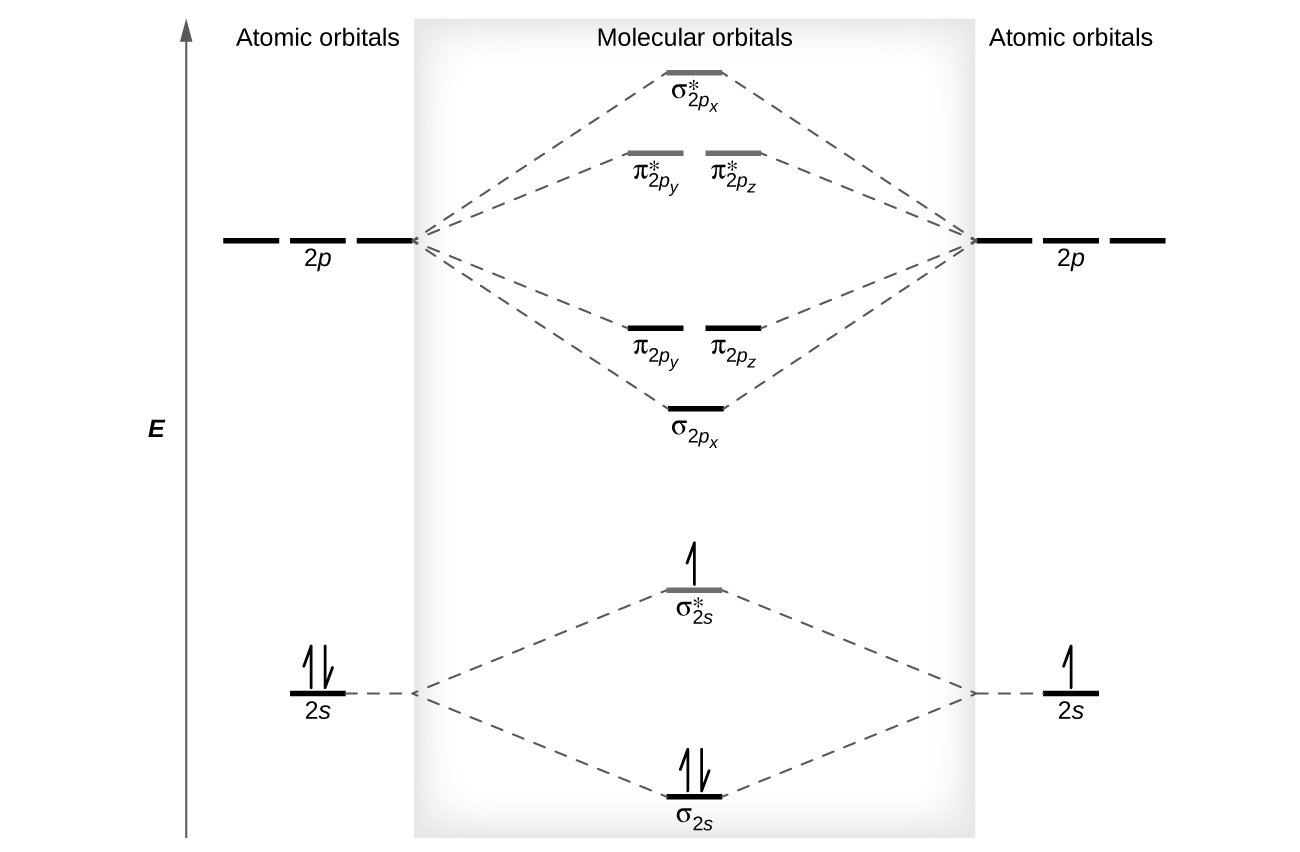
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... A bond involving molecular orbitals which are symmetric with respect to rotation around the bond axis is called a sigma bond σ bond. The result is. The o2 mo diagram will have one more electron compared to o2 and the o2 mo diagram will have one fewer electron compared to o2. Bonding order is 2 and it is diamagnetic. C2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules ... Molecular orbital diagram for n2 o2 c2 f2 also h2o this problem has been solved. A diatomic molecular orbital diagram is used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. Orbitals of similar but unequal energies can interact if they have the same symmetry the 2s and 2pzorbitals form mos with the same symmetry σ g and σ u.
C2 molecular orbital diagram bond order. Antibonding orbital is type of molecular orbital (MO) that weakens the chemical bond between two atoms, whereas bonding orbital is used in molecular orbital (MO) theory to describe the attractive interactions between the atomic orbitals of two or more atoms in a molecule.Thus the bond order of C2^- is 1/2 x (9-4) = 2.5 The bond order of C2− ... This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the C2(2-) molecule. The bond order of C2(2-) is also calculated and the meaning of t... 10.8K answers. 116M people helped. Bond order = 1/2 (number of electrons in bonding orbitals - number of electrons in antibonding orbitals) Therefore, Bond order of C2+ = 1/2 (5 - 2) = 3/2 = 1.5. Bond order of C2- = 1/2 (7 - 2) = 5/2 = 2.5. Bond order of C2 = 1/2 (6 - 2) = 2. Highest bond order means highest bond energy and shortest bond length ... This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the C2(2+) molecule. The bond order of C2(2+) is also calculated and the meaning of t...
Calculate The Bond Order Of C2, H2 And N2. The difference between the total number of bonds and anti bonds is defined as the bond order. It is a number of chemical bonds present between a pair of atoms. Bond order (B.O) = half the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons. B.O = 1 2[N b-N a] 1 ... According to molecular orbital theory, the atomic orbitals having comparable energy overlap and result in the formation of the same number of molecular orbitals. The molecular orbitals having the same sign combine and give bonding molecular orbitals. We have to draw the molecular orbital diagram for ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule. Bond order is a measurement of the variety of electrons concerned in bonds between two atoms in a molecule. It’s used as an indicator of the steadiness of a chemical bond. Often, the upper the bond order, the stronger the chemical bond. …. Exceptions happen when the molecule incorporates antibonding orbitals. Might 29, 2020. The bond order of C2+ is A 1 B 2 C dfrac32 D dfrac12. Hint: To solve this question, we first need to know what is bond order. The number of chemical bonds through which a pair of atoms are bonded is known as the bond order.
Answer (1 of 6): Bond order is the number of Chemical bonds between a pair of atoms and indicates the stability of a bond. In a Covalent Bond ( as in case of C2 ) between two atoms, a single bond has a bond order of one, a double bond has a bond order of two, a triple bond has a bond order of th... Nov 27, 2015 · Molecular Orbital C2- Diagram, Bond Order, Magnetism. Postby Brooke Tobias 1B » Fri Nov 27, 2015 7:31 pm. A video explaining the molecular orbital diagram and notation of C2- along with the bond order and magnetism. You do not have the required permissions to view the files attached to this post. Top. Molecular orbital diagram for carbon dimer c2. For the ion c22. Give the molecular orbital configuration for the valence electrons in cec22. A draw the molecular orbital diagram. N 2 has a bond order of 3 and is diamagnetic. Bonding order is 2 and it is diamagnetic. Interact and form molecular orbitals. B calculate the bond order. C2 molecular orbital diagram. A diatomic molecular orbital diagram is used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. Get 11 help now from expert chemistry tutors. Fill from the bottom up with 8 electrons total. They also give insight to the bond order of the molecule how many bonds are shared between the two atoms.
The molecular orbital diagram for c22 this problem has been solved. From the molecular orbital diagram of n 2 predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. The molecular orbital diagram for c22 question. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules ...
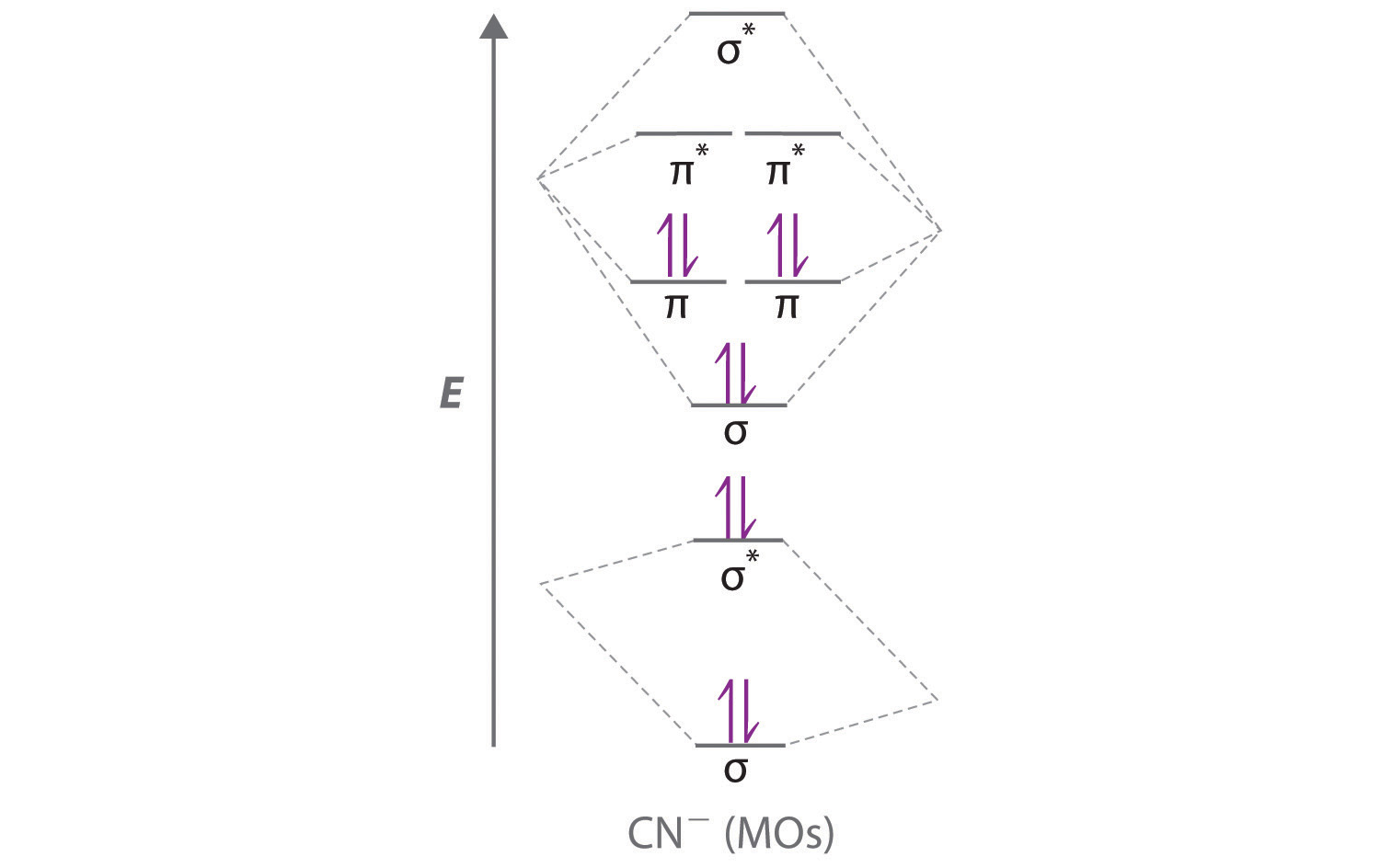
d. NO+ Bond order = 3 shortest bond (106 pm) NO Bond order = 2.5 intermediate (115 pm) NO- Bond order = 2 longest bond (127 pm), two electrons in antibonding orbitals. 5.8 a. The CN- energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the antibonding π* electron. b. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons. c.
Molecular electron configuration for o2 σ2σ2σ2π4π2 we can also calculate the oo bond order. Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules introduction. Electronic configuration of c2 molecule is σ 1s2 σ1s2 σ2s2 σ2pz 2 2px 1 2py orbitals what is the origin of differences between mo schemes o₂ and n₂ chemistry stack exchange c22 ...
The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4. The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be.
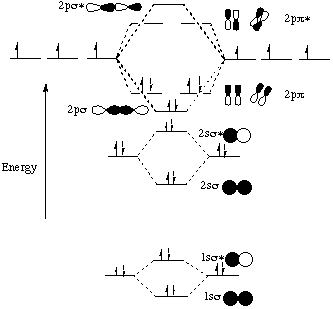
Molecular orbital diagram for c2. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules. Molecular orbitals are formed combining similar atomic orbitals. Just because some chemical species shows integral value of bond order doesnt mean that it should exist. Molecular orbital diagram for the molecule oxygen o2.
Nov 16, 2016 · Re: MO Diagram/ Bond Order (C2)^2-. The molecular diagram you would use is the Z<8 one because carbon's atomic number is 6, however when filling in the valence electrons you would use 10 because it is two carbons (C2) (4+4) with a negative 2 charge so (+2 valence electrons). The bond order of this would be calculated using the middle pi and sigma bonds.
bond orderthe number of overlapping electron pairs between a pair of atoms. antibondingan atomic or molecular orbital whose energy increases as its constituent atoms converge, generating a repulsive force that hinders bonding. Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms; in diatomic nitrogen (N≡N) for example, the bond ...
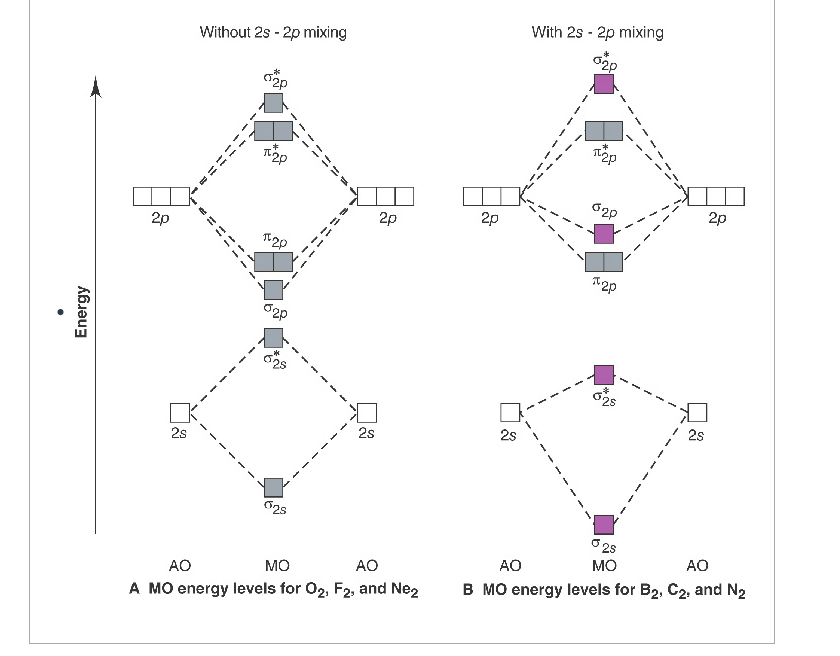
Answer to Draw a molecular orbital energy diagram for Li2. What is the bond order? Is the molecule likely to be stable? Explain. Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals.
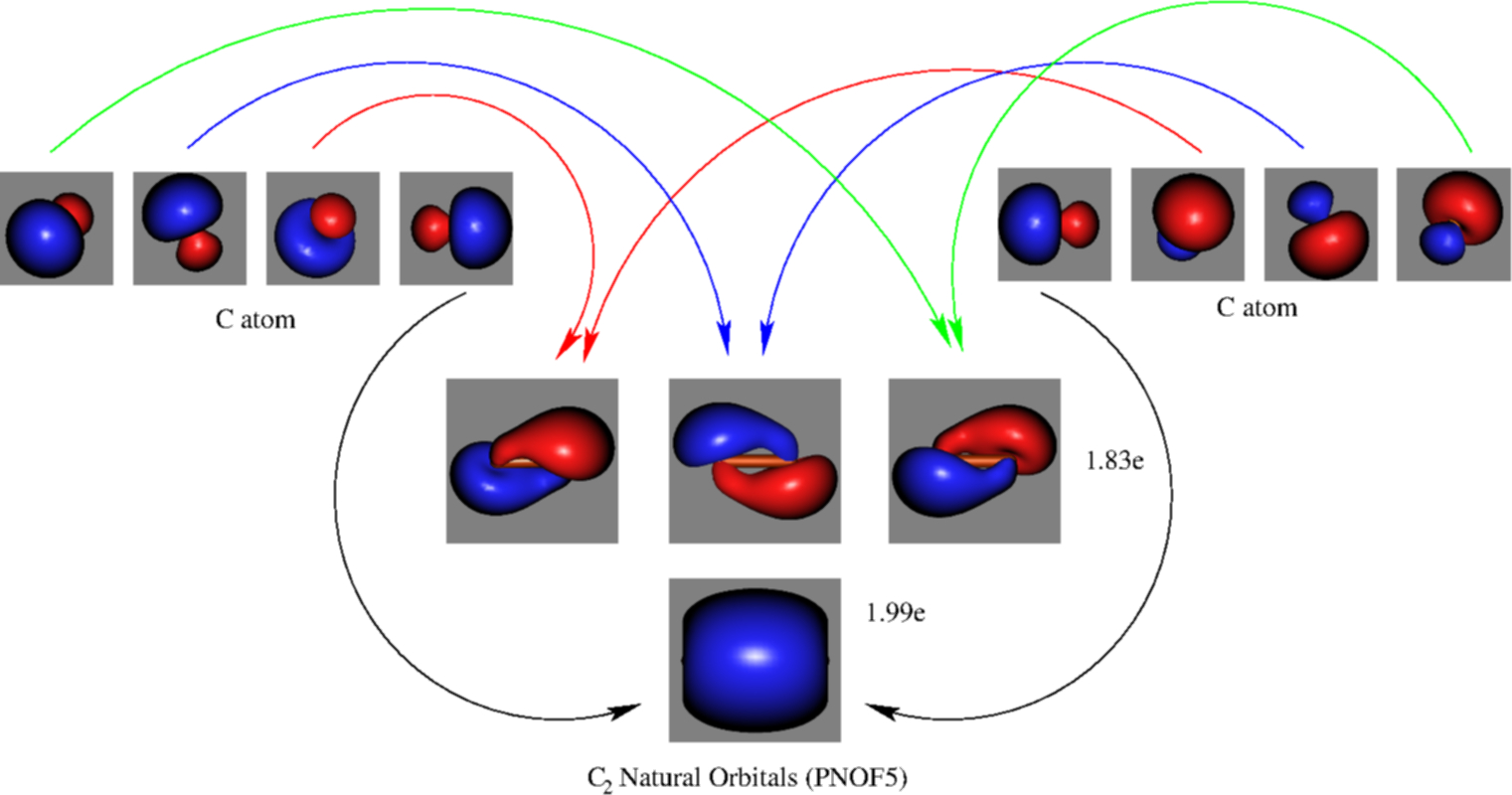
A diatomic molecular orbital diagram is used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. Schematic picture of the molecular orbital diagram obtained from pnof5. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. They also give insight to the bond order of the molecule how many bonds are shared between the two atoms.
on C22- Molecular Orbital Diagram. The problem provides you with the MO diagram for the C2 molecule, so all you really have to do here is add an electron to that diagram. It is sigma2s (2)sigma2s* (2)sigma2p (2)pi2p (4)pi2p* (4) Bond order 1. It is stable. In fact, it's the perioxide ion. Check me out.
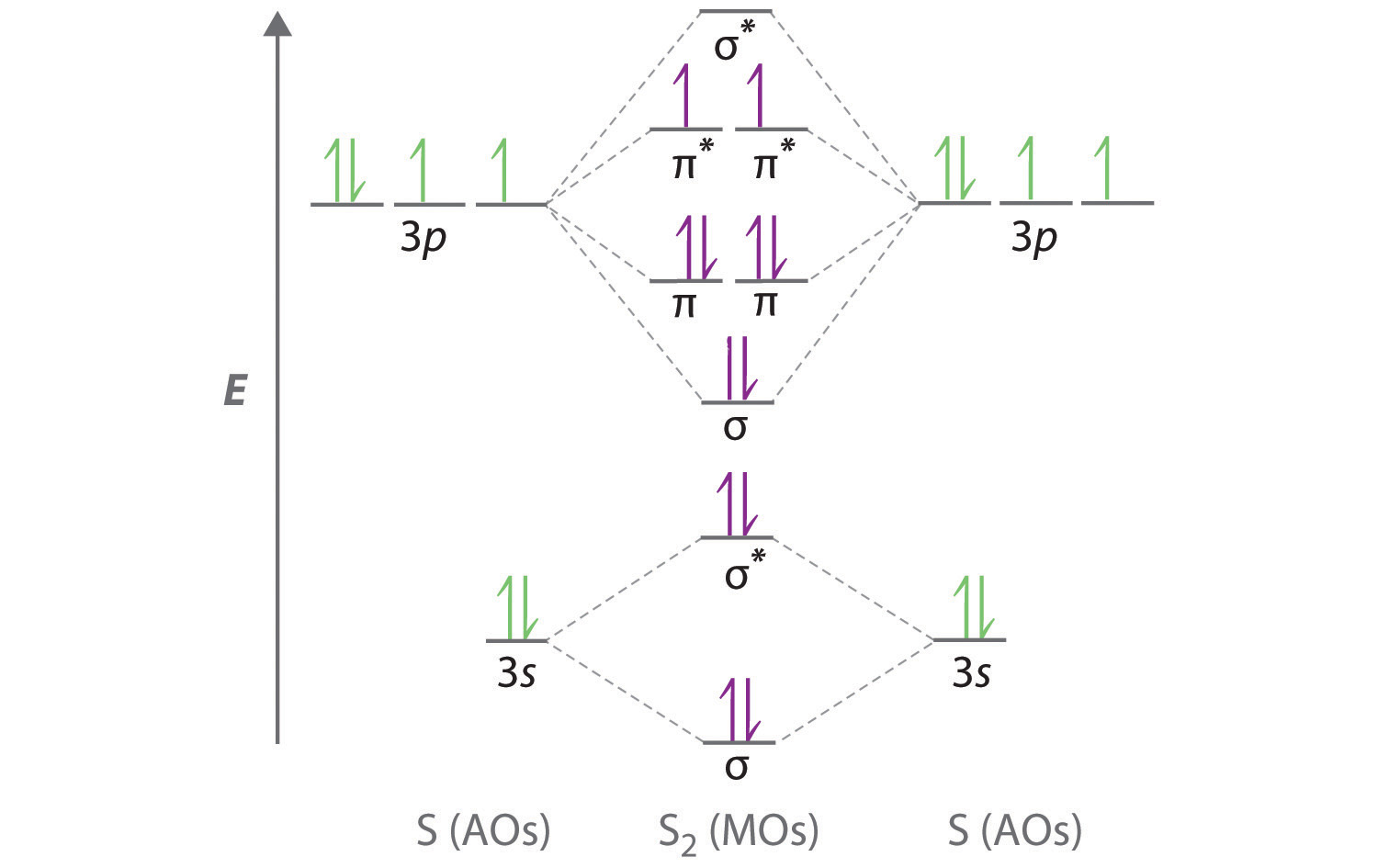
Electron Configurations and Bond Orders Just as with atoms, we can write a molecular electron configuration for O2 σ2σ*2σ2π4π*2 We can also calculate the O–O bond order: BO 1 2 # bonding e # anti-bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 LCAO MO theory also predicts (correctly) that O2has two unpaired electrons.
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monoxide, the nitrosyl cation and the nitrosyl anion 1 Order of filling of molecular orbitals in heteronuclear diatomic molecules such as CO. Mar 26, · This video shows the MO diagrams of the C2, N2, O2 and F2 molecules.A molecular orbital (MO) energy level diagram - Parkway C-2Use the molecular orbital ...
C2 molecular orbital diagram. A mo is defined as the combination of atomic orbitals. As for bond orders it is 12e in bonding orbitals e in antibonding orbitals. The only orbitals that are important in our discussion of molecular orbitals are those formed when valence shell orbitals are combined. Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. H 2 n 2 o 2 and f 2.
Molecular orbital diagram for n2 o2 c2 f2 also h2o this problem has been solved. A diatomic molecular orbital diagram is used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. Orbitals of similar but unequal energies can interact if they have the same symmetry the 2s and 2pzorbitals form mos with the same symmetry σ g and σ u.
A bond involving molecular orbitals which are symmetric with respect to rotation around the bond axis is called a sigma bond σ bond. The result is. The o2 mo diagram will have one more electron compared to o2 and the o2 mo diagram will have one fewer electron compared to o2. Bonding order is 2 and it is diamagnetic. C2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules ...
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...

Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H 2 And Then Identify The Bond Order Bond Order A 0 B 0 5 C 1 D 1 5 E 2 Image Study Com

Write The Molecular Electronic Configuration Of F2 And C2 Draw The Energy Level Diagram Calculate Brainly In
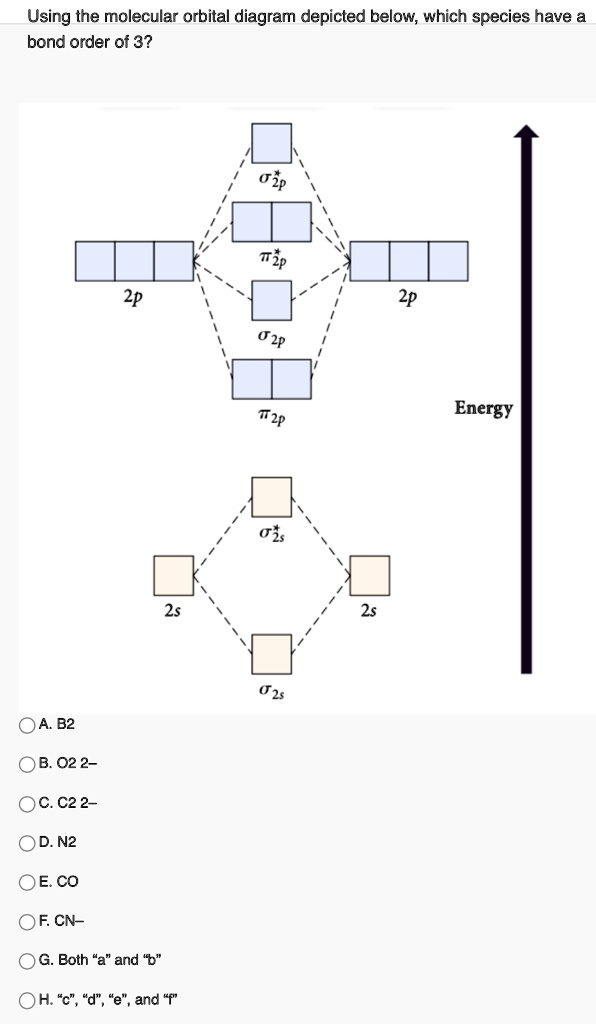
Solved Using The Molecular Orbital Diagram Depicted Below Which Species Have Bond Order Of 3 2p 2p 02p 72p Energy 2s Oa B2 B 02 2 C C22 D N2 Oeco Of Cn G










0 Response to "34 c2 molecular orbital diagram bond order"
Post a Comment