39 draw a ray diagram
(a) Draw the ray diagram of an astronomical telescope when ... (a) Draw the ray diagram of an astronomical telescope when the final image is formed at infinity. Write the expression for the resolving power of the telescope. (b) An astronomical telescope has an objective lens of focal length and eyepiece of focal length . (i) Find the angular magnification of the telescope. (ii) If this telescope is used to view the Moon, find the diameter of the image ... Introduction to NVIDIA RTX and DirectX Ray Tracing ... 19/03/2018 · All ray tracing related GPU work is dispatched via command lists and queues that the application schedules. Ray tracing therefore integrates tightly with other work such as rasterization or compute, and can be enqueued efficiently by a multithreaded application. Ray tracing shaders are dispatched as grids of work items, similar to compute ...
How to Draw & Label Enthalpy Diagrams - Video & Lesson ... 07/01/2022 · An enthalpy diagram is a method used to keep track of the way energy moves during a reaction over a period of time. Learn how to draw and label enthalpy diagrams, the definition of an enthalpy ...

Draw a ray diagram
How to Draw a Ray Diagram for a Convex Lens | Physics ... An arrow is drawn on a piece of paper and is placed 20 cm away from a convex lens which has a focal length of 30 cm. Draw the ray diagram for the image of the arrow. Step 1: Identify the focal... Concave Mirror - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table Apr 23, 2020 — ... away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes t. Drawing ray diagrams | IOPSpark The diagrams are drawn in pencil. All rays are drawn with a ruler. All rays carry an arrow showing the direction of travel of the light. When you draw ray diagrams on the board or on a transparency: Always use a ruler. Always insert direction arrows. This is definitely a case of the teacher setting the example to be followed!
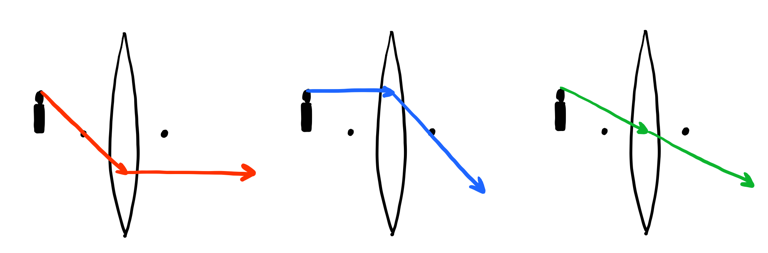
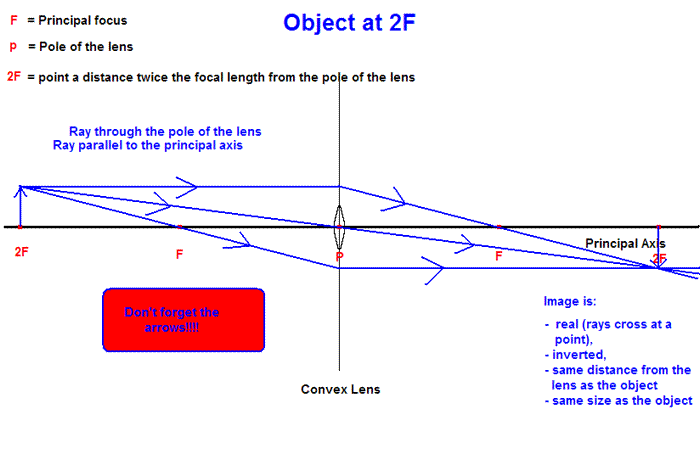
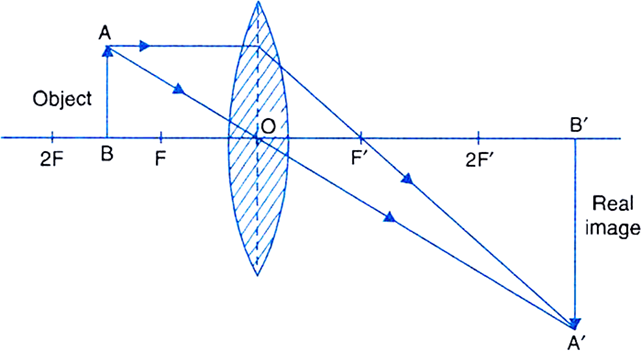
Draw a ray diagram. Ray Diagrams - Physics Classroom The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the lens. Concave Lens - Ray diagram, Images Formed - with Steps ... 26/04/2020 · Concave Lens - Ray diagram. Last updated at April 26, 2020 by . For a Concave lens, There are only 2 cases They are Object is Placed at Infinity Object is Placed between Infinity and Optical Center Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity In this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance) So, we draw rays parallel to principal axis Since ray parallel … GCSE Physics - How to Draw Ray Diagrams #70 - YouTube This video covers:- How to draw ray diagrams for convex and concave lenses - How to comment on whether an image is real or virtual, upright or inverted, and ... PDF Physics 1 - Convex and Concave Lens Ray Diagrams Practice 10. Draw a ray diagram for a 3.0 cm tall object placed 10.0 cm from a convex lens having a focal length of 15.0 cm. 11. Draw a ray diagram for an object placed 6.0 cm from the surface of a convex lens with a focal length of 12.0 cm. 12. Draw a ray diagram for a concave lens that has a focal length of -10.8 cm when an object is
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Song - YouTube Emerson Foo ( ) & Wong Yann ( ) made an original music video on the Electromagnet... Ray Diagrams for Lenses - Wolfram Demonstrations Project This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The rays parallel to the principal axis and the ray through the center of the lens are drawn. [more] Contributed by: Ernest Lee (November 2007) The reflection and refraction of light - Boston University The first step is to draw the ray diagram, which should tell you that the image is real, inverted, smaller than the object, and between the focal point and the center of curvature. The location of the image can be found from the mirror equation: which can be rearranged to: The image distance is positive, meaning that it is on the same side of the mirror as the object. This agrees with the … An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a ... - BYJUS An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed. Given that. The height of object = 5cm. Position of object, u = – 25cm. The focal length of the lens, f = 10 cm. We need to find . The position of the image, v =? Size of the image. Nature of the image. …
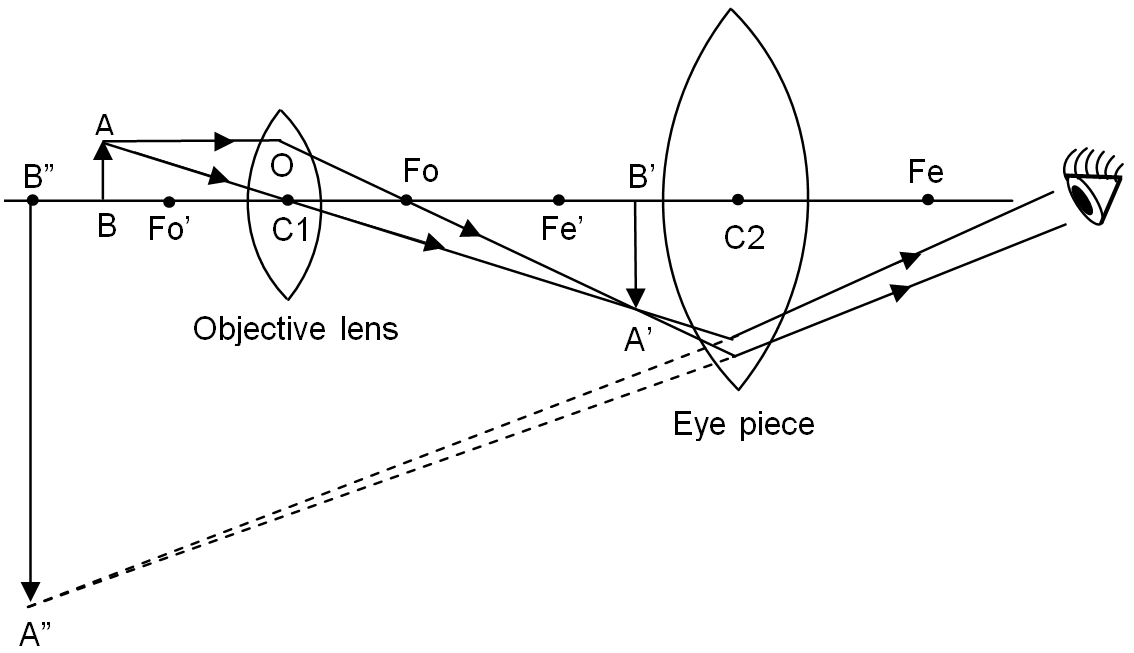
Draw a ray diagram of a compound microscope. Write the ... Ray diagram of a compound microscope.When the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision,For the image formed at infinity, ue = feand By making focal length of the objective small, the magnifying power can be increased. Draw a ray diagram of astronomical telescope for distance ... Draw a ray diagram of astronomical telescope for distance object in normal adjustment. What is the expression for its magnifying power. - Get the answer to this question by visiting BYJU'S Q&A Forum. Draw a ray diagram of reflecting type telescope and class ... Hint:Draw the proper ray diagram for the reflecting type telescope.Recall the various advantages that a reflecting telescope gives over the other types of telescopes. Mention the advantages of the reflecting type telescopes due to the use of mirror, parabolic mirror, small optical instruments used in it and its cost. Ray diagrams - Lenses and ray diagrams - OCR Gateway ... It is important to be able to draw ray diagrams to show the refraction of a wave at a boundary. To draw a ray diagram: Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis ...
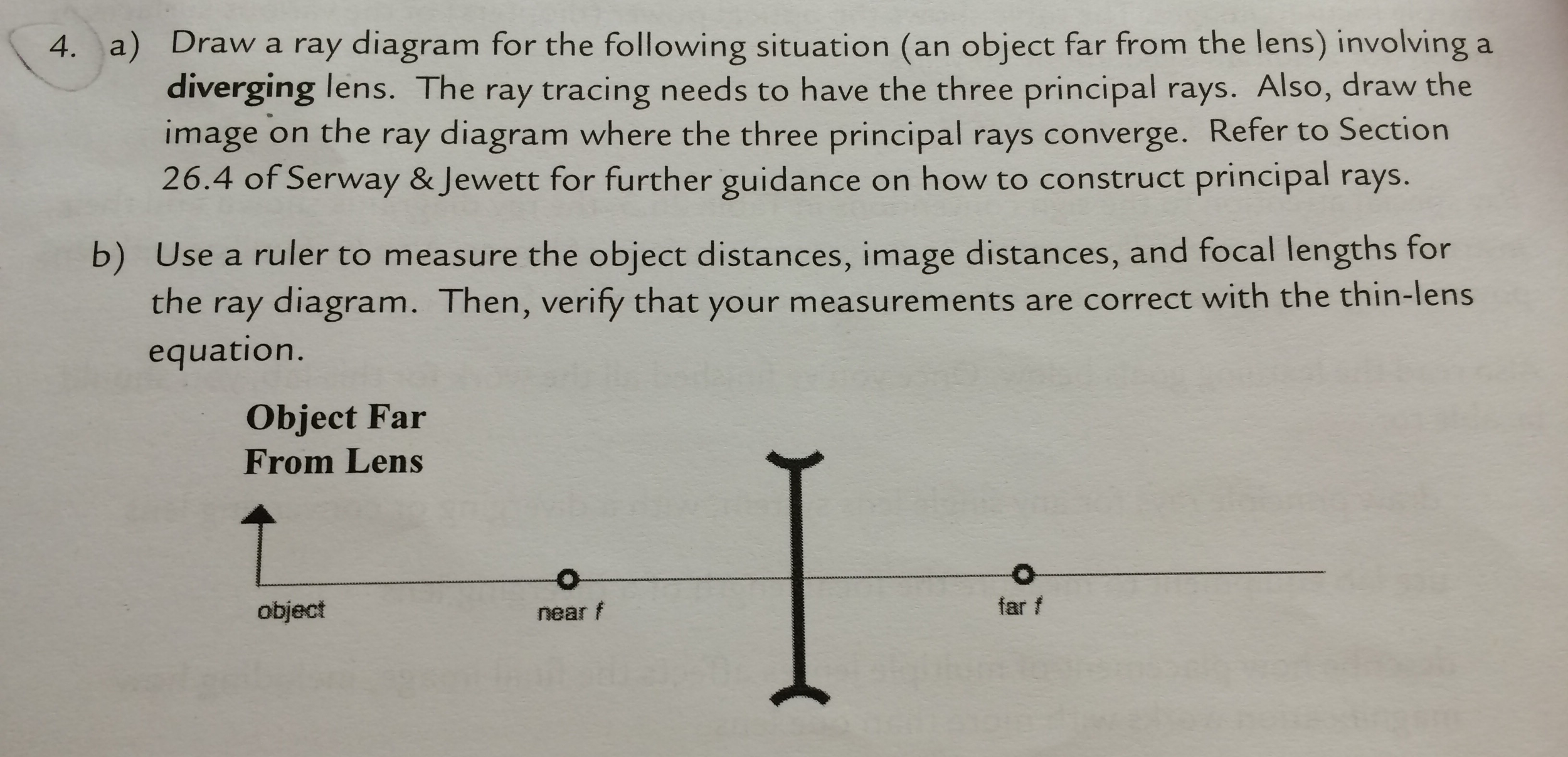
PDF Converging & Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams (10) Draw a ray diagram for a 3.0-cm tall object placed 10.0 cm from a converging lens having a focal length of 15.0 cm. (11) Draw a ray diagram for a diverging lens that has a focal length of -10.8 cm when an object is placed 32.4 cm from the lens's surface. (12) Draw a ray diagram for an object placed 6.0 cm from the surface of a converging lens with a focal length
Ray diagrams (practice) - Khan Academy Ray diagrams and curved mirrors Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization.
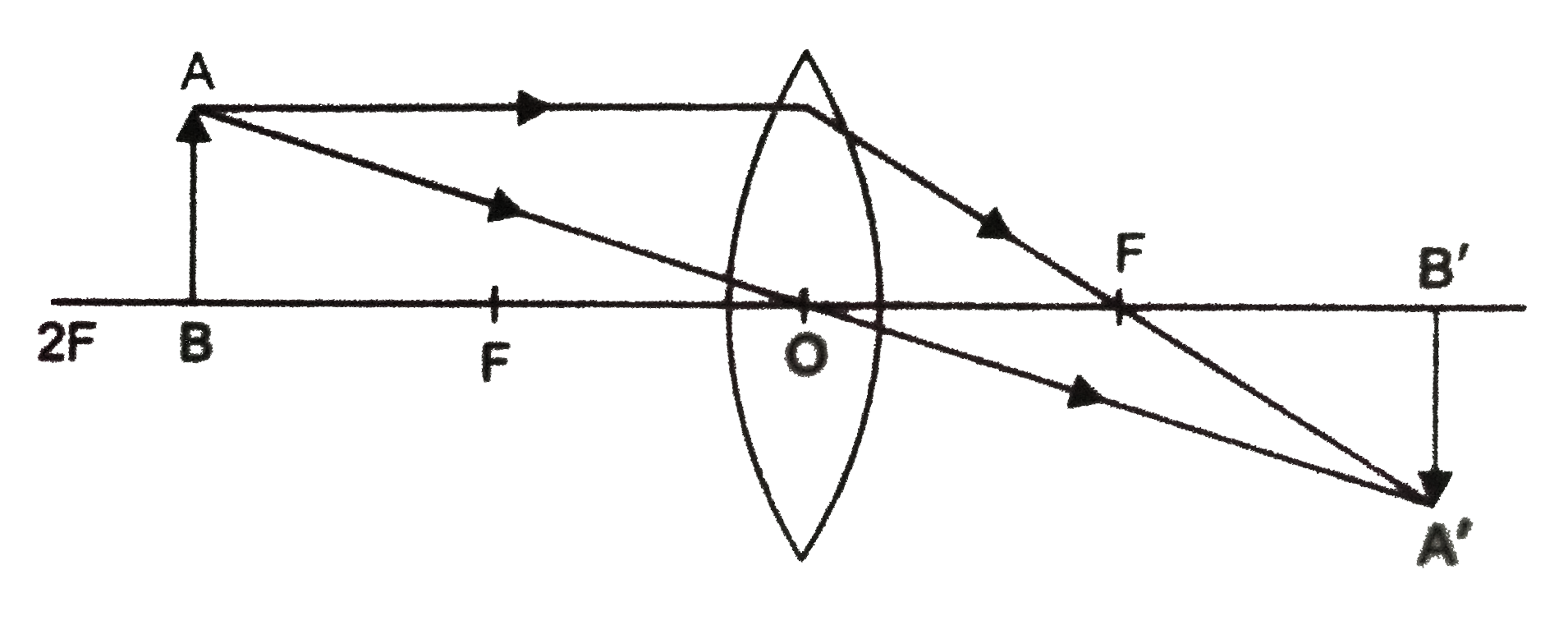
Convex Lens - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table - Teachoo First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis So, it passes through focus after refraction We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center So, the ray will go through without any deviation Where both refracted rays meet is point A' And the image formed is A'B' This image is formed between beyond 2F 2 We can say that Image is Real
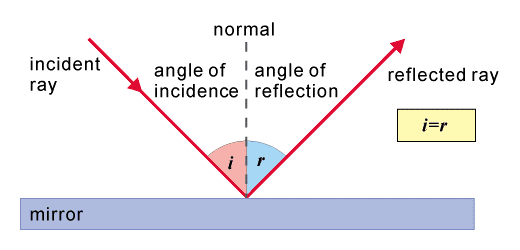
Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors - Mini Physics ... This is a short tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Click on the images to view a larger version. Initially, we have an object in front of a plane mirror. First, we draw an image of the object on the other side of the mirror Distance A is equal to distance B and the image size is the same size as the object size.
How To Draw Ray Diagrams For Lenses? - How To Draw How do you draw a perfect ray diagram? Drawing Ray Diagrams: A Step-by-Step Guide Draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror from a point on the top of the object. Once these incident rays strike the mirror, reflect them using the two rules of reflection for concave mirrors. Mark the image of the top of the object.
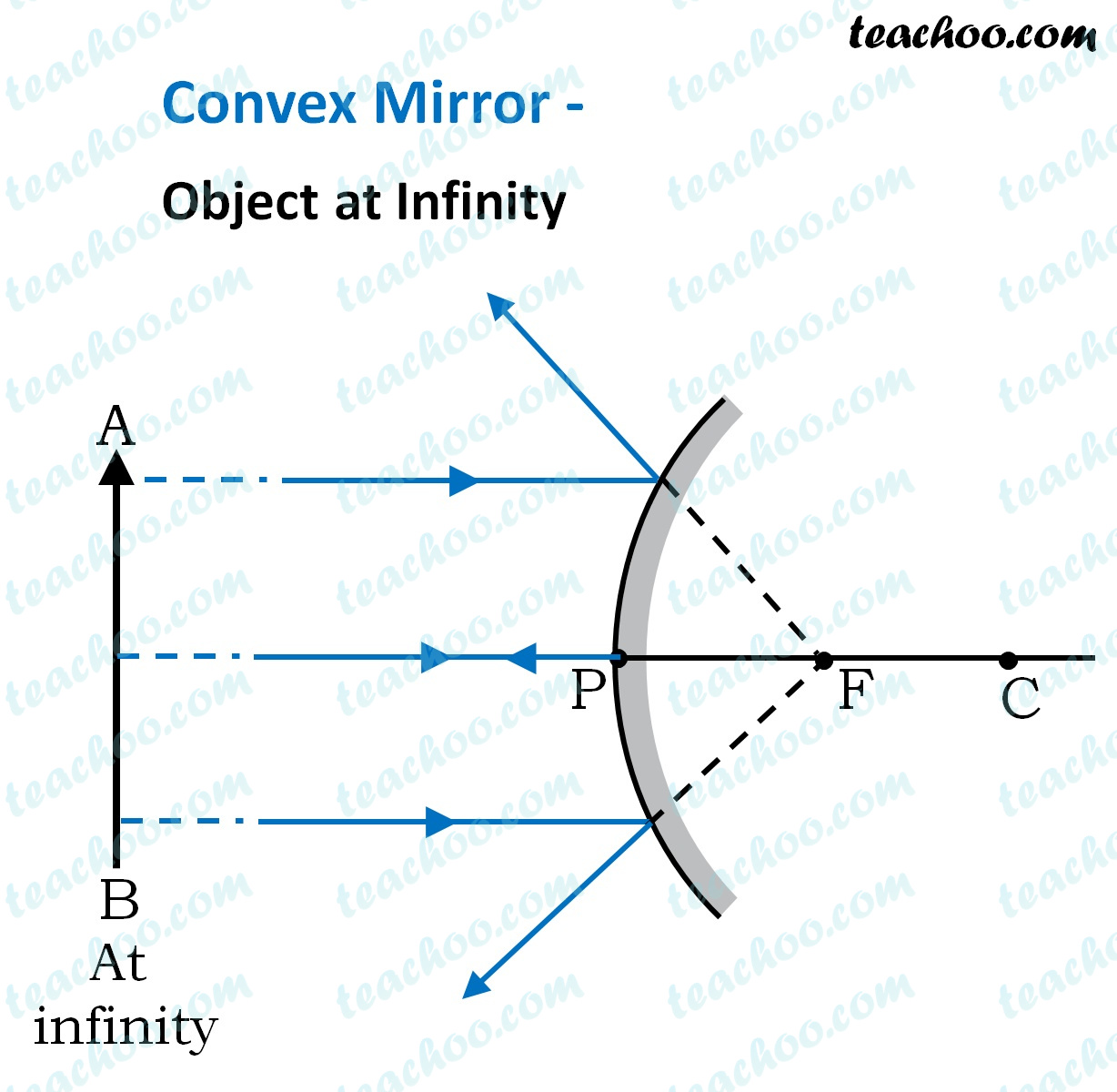
How to Draw a Ray Diagram for an Object In Front of a ... An arrow drawn on a piece of paper is placed 20 cm away from a convex mirror, which has a center of curvature of 20 cm. Draw the ray diagram for the image of the arrow. Step 1: Identify the...
Answered: Draw the shear and moment diagram for… | bartleby Solution for Draw the shear and moment diagram for the beam. close. Start your trial now! First week only $4.99! arrow_forward. learn. write. tutor. study resourcesexpand_more. Study Resources. We've got the study and writing resources you need for …
Concave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors - Image Formation, Ray ... Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels. Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirrors Mirrors are made into different shapes for different purposes. The two of the most prominent types of mirrors are: Plane Mirrors Spherical Mirrors
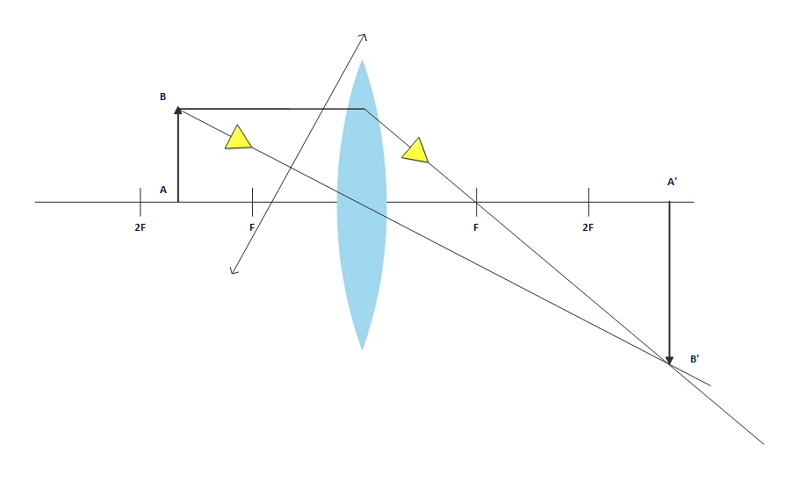
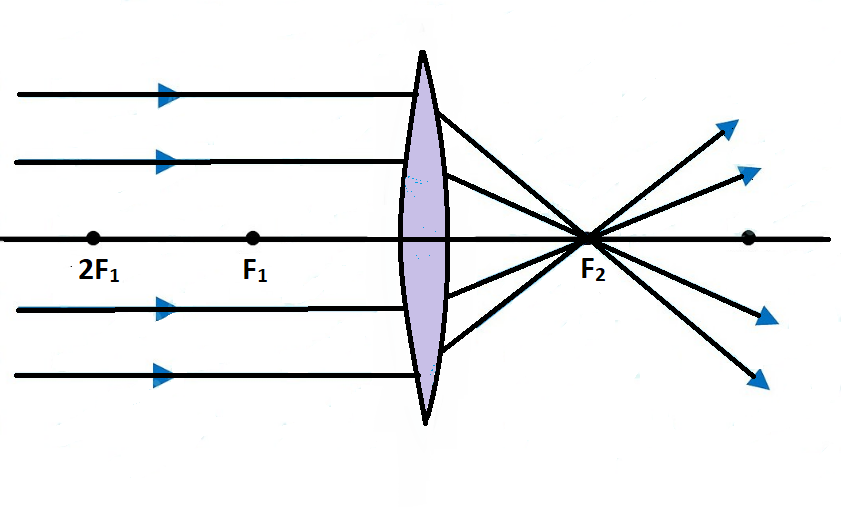
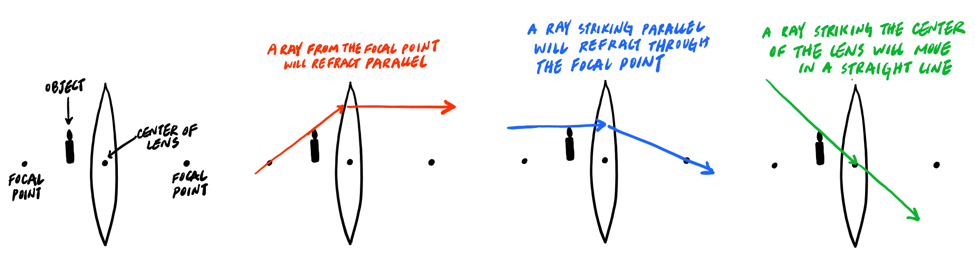
Ray Diagrams for Lenses - Georgia State University Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: A ray from the top of the object …
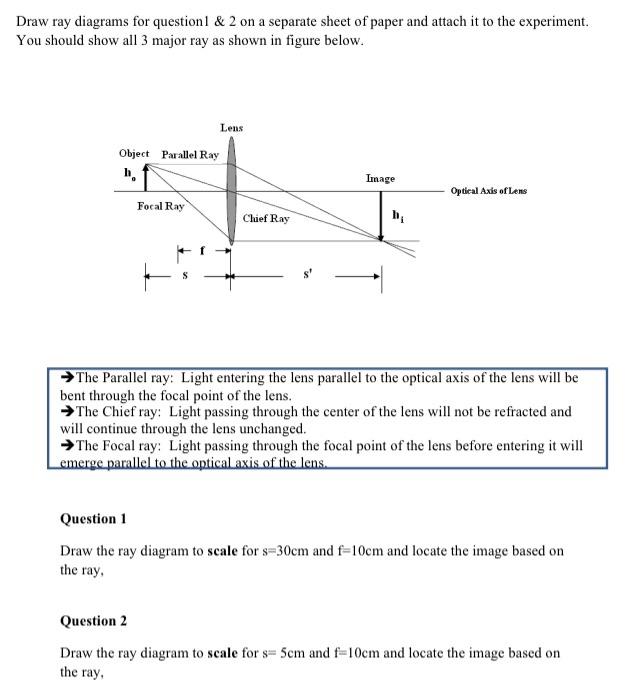
How to Draw Ray Diagrams - Shalom Education In a ray diagram, a convex lens is drawn as a vertical line with arrows pointing outwards in both directions. This is to resemble the shape of a convex lens. Whereas a concave lens is drawn as a vertical line with arrows pointing inwards. This is to resemble the shape of a concave lens. You can see this below:
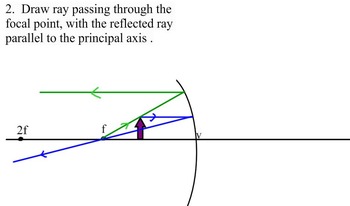
Method for drawing ray diagrams - Concave lens To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses". But you really don't need to remember this, the only thing to remember is: From the object 1. Pass a parallel line through the principal focal point on the same side as the object 2.
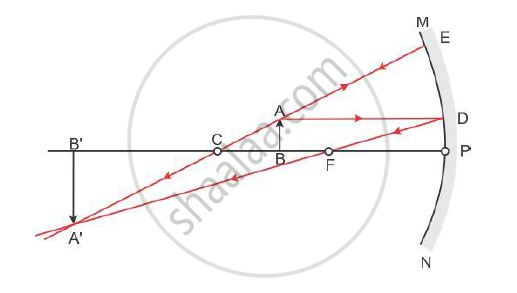
Draw the ray diagram showing the image formation by a ... Draw the ray diagram showing the formation of image when the object is kept beyond centre of curvature (C) of a concave mirror. asked Mar 19, 2020 in Science by Abhinay (62.8k points) class-10; 0 votes. 1 answer. Draw a ray diagram to show the image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed between F and 2F.
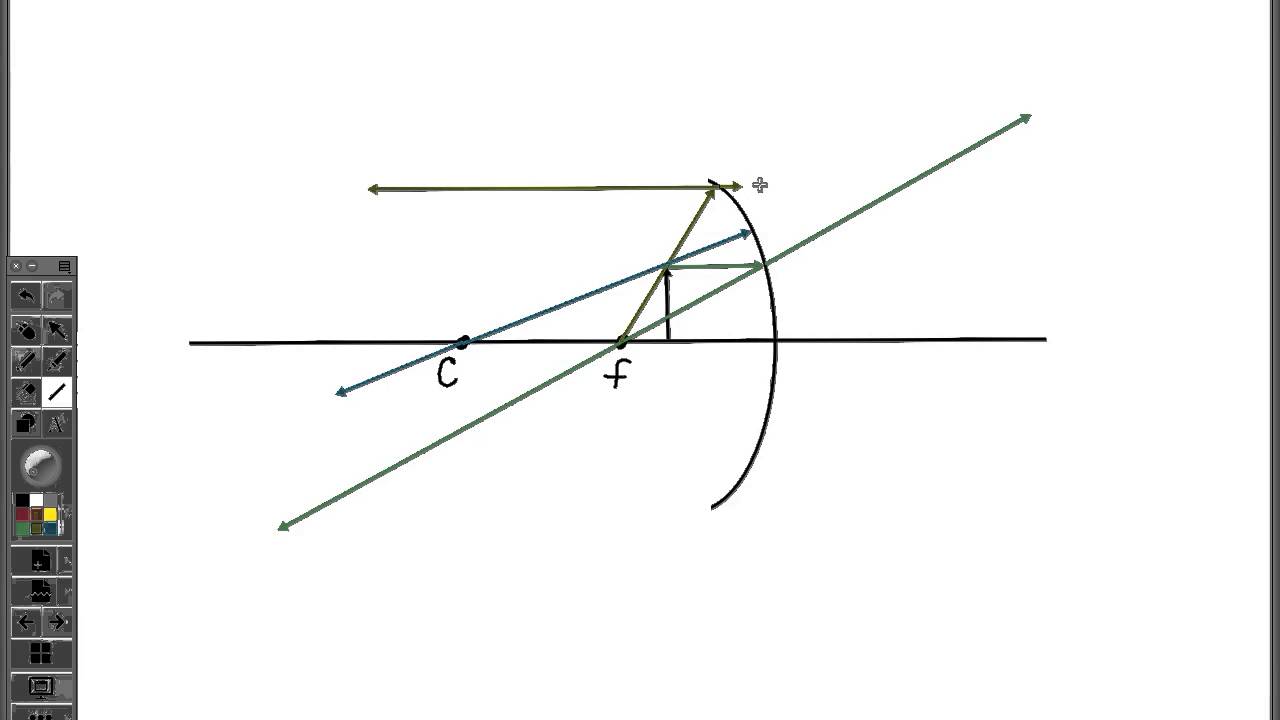
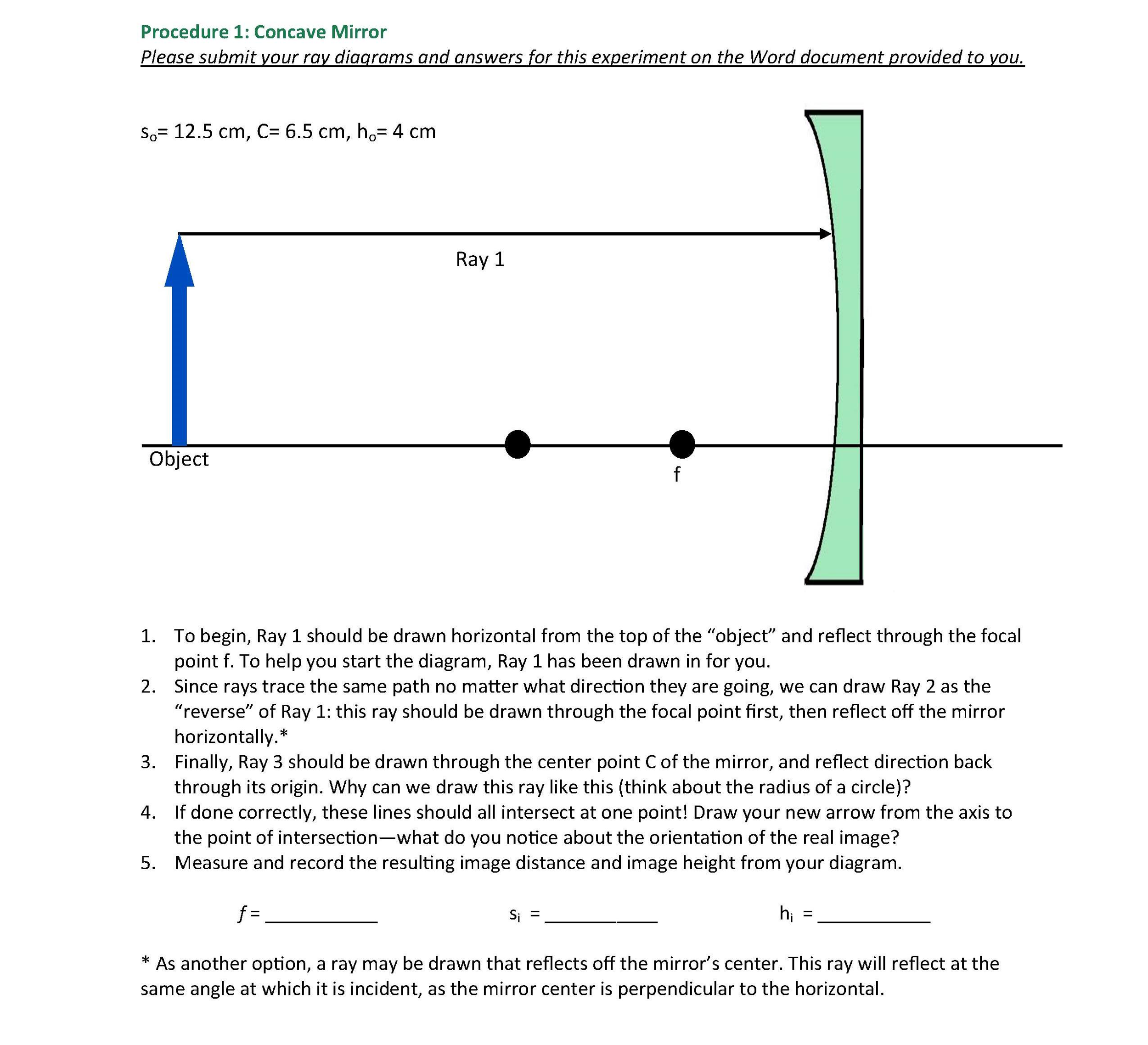
Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors The theme of this unit has been that we see an object because light from the object travels to our eyes as we sight along a line at the object. Similarly, we see an image of an object because light from the object reflects off a mirror and travel to our eyes as we sight at the image location of the object. From these two basic premises, we have defined the image location as the location in space where light appears to diverge from. Ray diagrams have been a valuable tool for determining the path taken by light from the object to the mirror to our eyes. In this section of Lesson 3, we will investigate the method for drawing ray diagrams for objects placed at various locations in front of a concave mirror.
Ray Diagrams - YouTube This physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging lens, diverging l...
Working with lenses and mirrors: how to draw a ray diagram Now you can draw ray diagrams to illustrate this point to yourself! Problem 2: choose the correct ray diagram. Here we have another convex lens, but this time our object is outside of the lens' focal point. Again, let's draw three rays, each emanating from the top of the object.
Draw the labelled ray diagram for the formation of image ... Draw the labelled ray diagram for the formation of image by a compound microscope. Derive the expression for the total magnification of a compound microscope. Explain why both the objective and the eye piece of a compound microscope must have short focal lengths.
Draw a ray diagram of compound microscope, when final ... Draw a ray diagram of compound microscope, when final image is formed at the minimum distance of distinct vision. Easy Solution Verified by Toppr It consist of two convex lenses, one objective of very small focal length with short aperture. And one Eyepiece with moderate focal length and large aperture.
Light waves - KS3 Physics Revision - BBC Bitesize In a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: a straight line; with an arrowhead pointing in the direction that the light travels; Remember to use a ruler and …
Draw ray diagram showing the image formation by a convex ... Draw ray diagram showing the image formation by a convex lens when an object is placed at infinity. Verified 104.2k + views - Hint: The property of a convex lens is that it converges the light rays passing through them. The nature of image formed by the lens depends on the distance of the object from the lens.
Convex & Concave Lens Ray Diagrams | How to Draw Ray Diagrams ... Jan 28, 2022 · The steps in drawing a convex lens ray diagram are as follows: Step 1 Draw the first incident ray (Ray 1) from the tip of the object parallel to the principal axis. The refracted ray should pass...
Drawing ray diagrams | IOPSpark The diagrams are drawn in pencil. All rays are drawn with a ruler. All rays carry an arrow showing the direction of travel of the light. When you draw ray diagrams on the board or on a transparency: Always use a ruler. Always insert direction arrows. This is definitely a case of the teacher setting the example to be followed!
Concave Mirror - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table Apr 23, 2020 — ... away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes t.
How to Draw a Ray Diagram for a Convex Lens | Physics ... An arrow is drawn on a piece of paper and is placed 20 cm away from a convex lens which has a focal length of 30 cm. Draw the ray diagram for the image of the arrow. Step 1: Identify the focal...




















0 Response to "39 draw a ray diagram"
Post a Comment