36 blank molecular orbital diagram
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond Or... Construct the molecular orbital diagram for dichlorine. x y z z y 3 x y z z y 4 Showing the p orbitals. Showing the s and p orbitals. ORBITALS AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION 11. CARBON ORBITALS Methane Ethane METHANE AND ETHANE C H H H H CH4 C C H H H H H H C2H6 1 2 Color conventions: Hydrogen atoms are shown in gray.
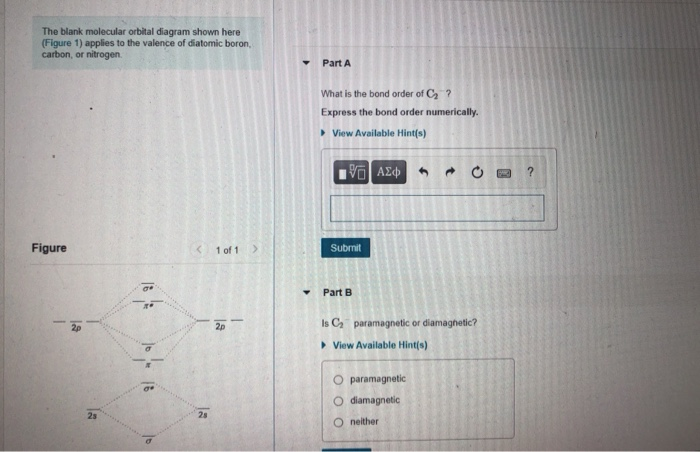
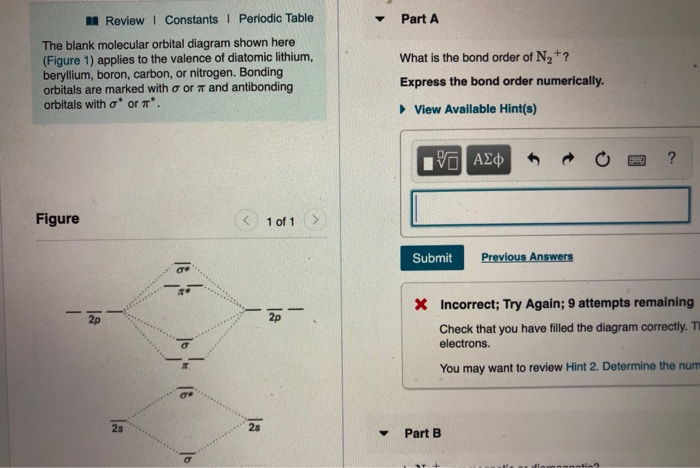
A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. FREE Expert Solution 84% (340 ratings) View Complete Written Solution Problem Details Arrange the following in order of decreasing bond energy.

Blank molecular orbital diagram
for the molecular orbitals with high d orbital character. metal d orbitals xz yz x2-y2 xy z2 1.125e 2.75e b. For consideration of L as a -acceptor in the axial position, the identical energy level diagram is obtained regardless of whether L is assigned to position 1 or 6. The xz and yz orbitals are each stabilized by e . xz yz x2-y2 xy z2 1.125e Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. The blank molecular orbital diagram for #"O, F"#, and #"Ne"# is. Molecular orbitals for #"O"_2#. Each #"O"# atom has 6 valence electrons, so the #"O"_2# molecule has 12 valence electrons.. We use the Aufbau Principle and Hund's rule to place these electrons in the atomic and molecular orbitals.
Blank molecular orbital diagram. Problem: The blank molecular orbital diagram shown here (Figure 1) applies to have valence of diatomic boron, carbon, or nitrogen. What is the bond order of ...1 answer · Top answer: We’re being asked to determine the bond order of C2-. For this, we do the following:Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present.Step ... The molecular orbital diagram below may be used for the following problem(s). However, the diagram will still yield the correct bond order and magnetic ...2 pages 5.7 a. The energy level diagram for NO is on the right. The odd electron is in a π2p* orbital. b ...29 pages The blank molecular orbital diagram shown here (Figure 1) applies to the valence of diatomic lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, or nitrogen. Bonding orbitals are marked with sigma or... Posted one year ago
F2 Polarity A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equilvalent, overlap them. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help F2 F2 Lowest bond energy Highest bond energy The correct ranking cannot be determined. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in A blank molecular orbital diagram (Part A 1 figure) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. F2, F2+, F2- Chemistry - Bond Order What is the bond order of the diatomic molecule BN and is it paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Science
a blank molecular orbital diagram (part b 1 figure) has been provided to you. drag the formulas to the appropriate magnetic bin : c2^2+,li2-,b2^2- Answers: 1 Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in L a T e X by means of the package MOdiagram.For information about the more traditional molecular structure diagrams see our documentation about chemistry formulae. a molecular orbital is a region of space in a covalent species where electrons are likely to be found. the combination of two atomic orbitals always forms two molecular orbitals; the bonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, and the antibonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, than the original atomic orbitals Once you have drawn and labelled molecular orbitals, you fill them in the same order as you fill atomic orbitals. The rules you use for filling atomic orbitals are: 1. Aufbau Principle You place electrons in the lowest energy orbitals available. 2. Pauli Exclusion Principle No orbital may hold more than two electrons, and they must have opposite spin. 3. Hund's Rule Every orbital in a subshell ...
Procedure: draw Lewis Structure, determine Steric Number (SN), Molecular Geometry and Hybridization SN = # of atoms bonded to the central atom plus # of lone pairs on the central atom (SN = the effective number of electron pairs surrounding a central atom). Note: If one s and one p orbital hybridize, they form two sp hybrid orbitals.
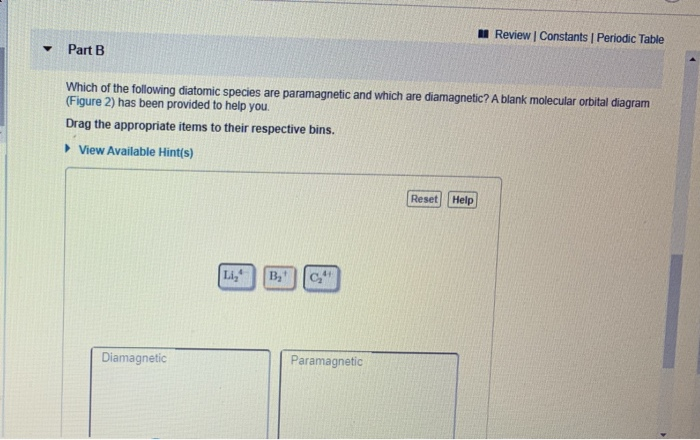
which of the following diatomic species are paramagnetic and which are diamagnetic? a blank molecular orbital diagram (figure 2) has been provided to you. Categories Question-Answer. Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. a blank molecular orbital diagram (part a 1 figure) has been provided to you. rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. to rank items as equivalent, overlap them. f2, f2+, f2-
A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equilvalent, overlap them. View Available Hint (s) Reset Help F2 F2 Lowest bond energy Highest bond energy The correct ranking cannot be This problem has been solved! See the answer
Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from 180 o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram Water 104.5 ° X H H H O H
Printable Blank Atom Diagram Automotive Wiring Diagram Chemistry Worksheets Bohr Model Atomic Structure . In this theory each molecule has a set of molecular orbitals. Blank orbital diagram worksheet. Guided worksheet assigning electrons using orbital diagrams for elements in energy levels 1 and 2. Read Pgs 291 299 Pg 300 Q 1 - 4.
A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 2) has been provided to help you. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. View Available Hint(s) Li2 C24 Paramagnetic Diamagnetic Li2 . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. 1.
A blank molecular orbital diagram (Part A 1 figure) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. To rank items as equivalent, overlap science Based on the figure, imagine two new species, E and F, descended from species C, and two new species, G and H, descended from species D.
Six overlapping p orbitals must form six molecular orbitals . Three will be bonding, three antibonding . Lowest energy MO will have all bonding interactions, no nodes . As energy of MO increases, the number of nodes increases . System symmetric so 2 pairs of degenerate orbitals . 6 atomic orbitals - 6 molecular orbitals
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
which of the following diatomic species are paramagnetic and which are diamagnetic? a blank molecular orbital diagram (figure 2) has been provided to help you. Answers: 2 Show answers Another question on SAT. SAT, 27.06.2019 22:30. Compared with the cost of tuition, fees, and books for a traditional college course, the cost of a clep exam is: ...
A blank molecular orbital diagram has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. Molecular orbital (MO) theory is based in quantum mechanics and treats the orbitals found in a molecule in a manner similar to atomic orbitals in an atom.
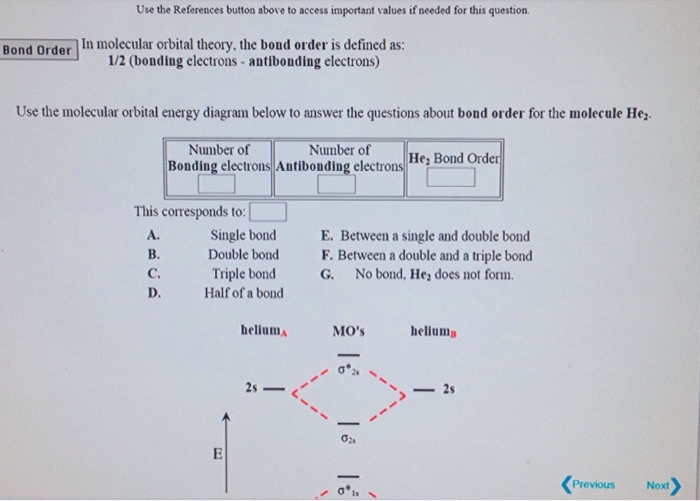
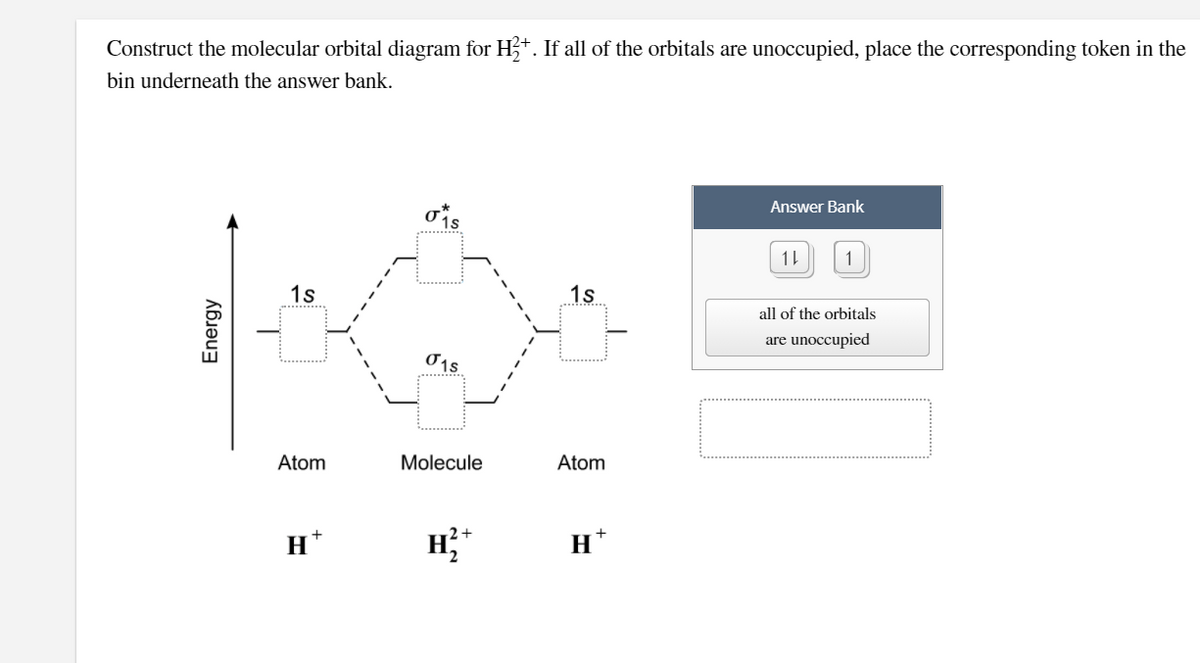
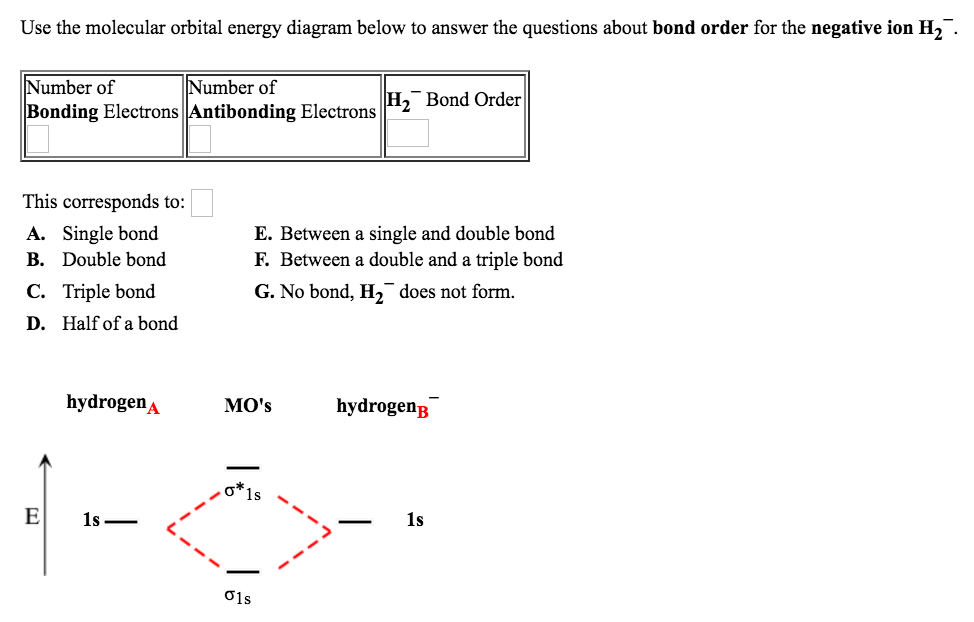
This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic orbitals.
The blank molecular orbital diagram for #"O, F"#, and #"Ne"# is. Molecular orbitals for #"O"_2#. Each #"O"# atom has 6 valence electrons, so the #"O"_2# molecule has 12 valence electrons.. We use the Aufbau Principle and Hund's rule to place these electrons in the atomic and molecular orbitals.
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
for the molecular orbitals with high d orbital character. metal d orbitals xz yz x2-y2 xy z2 1.125e 2.75e b. For consideration of L as a -acceptor in the axial position, the identical energy level diagram is obtained regardless of whether L is assigned to position 1 or 6. The xz and yz orbitals are each stabilized by e . xz yz x2-y2 xy z2 1.125e











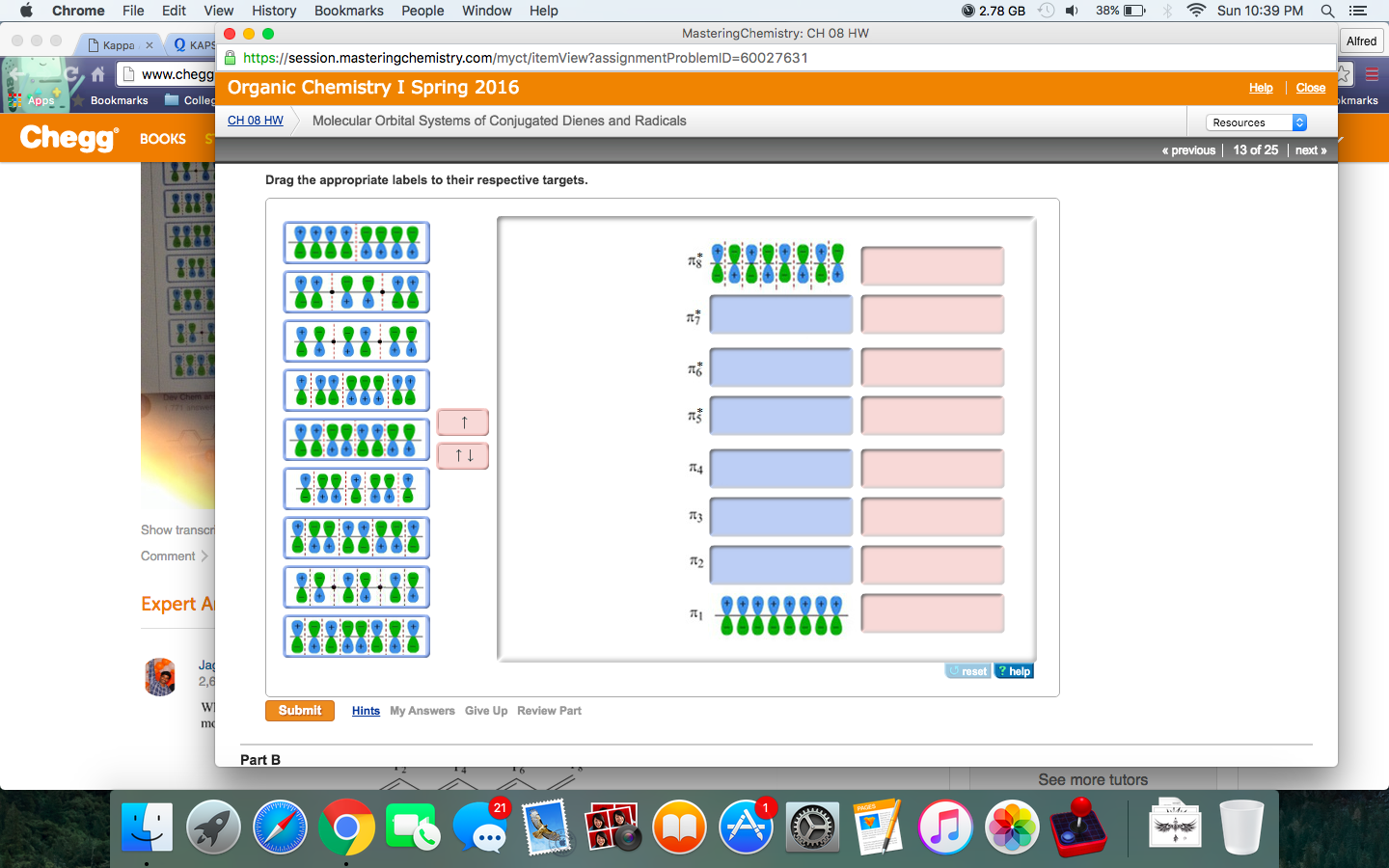




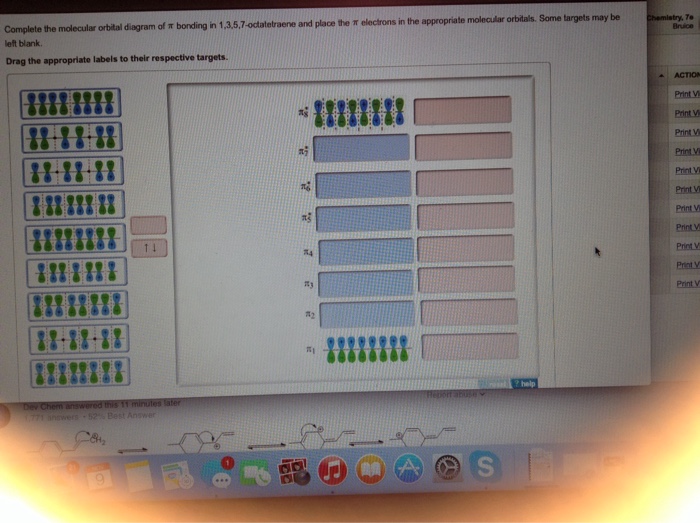


0 Response to "36 blank molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment