39 spherical mirror ray diagram
Ray diagrams help us trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object. Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels. Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirrors
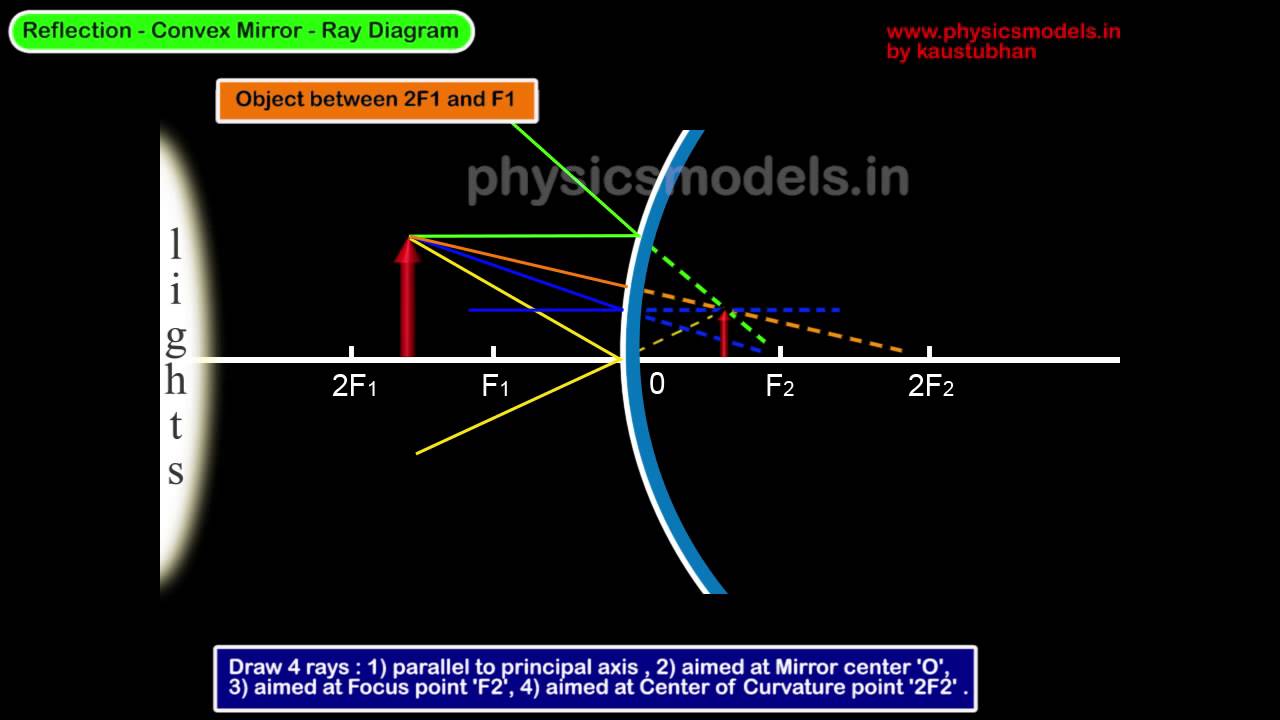
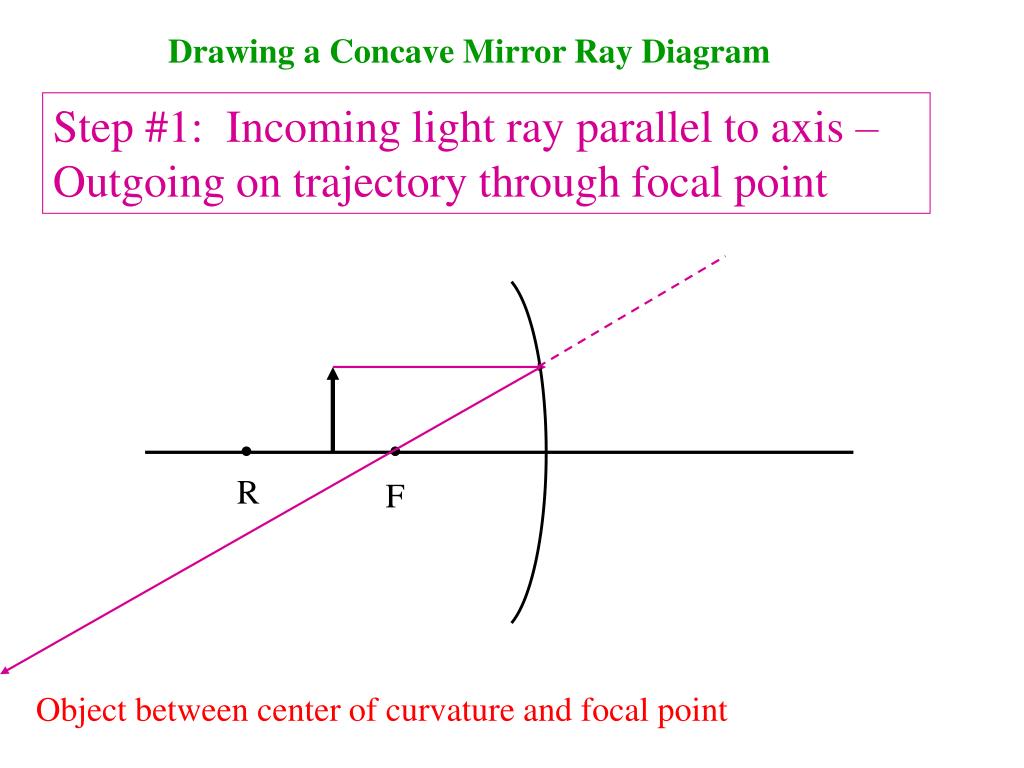
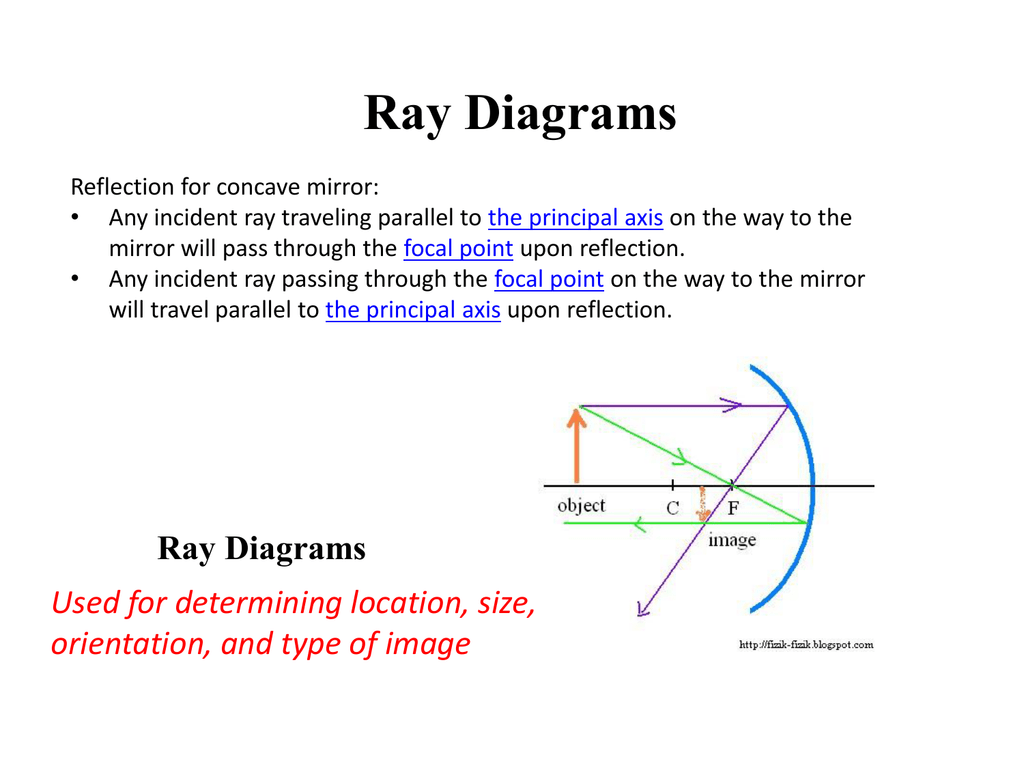
The method for drawing ray diagrams for concave mirror is described below. The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the center of curvature (C) of a concave mirror. Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two ...
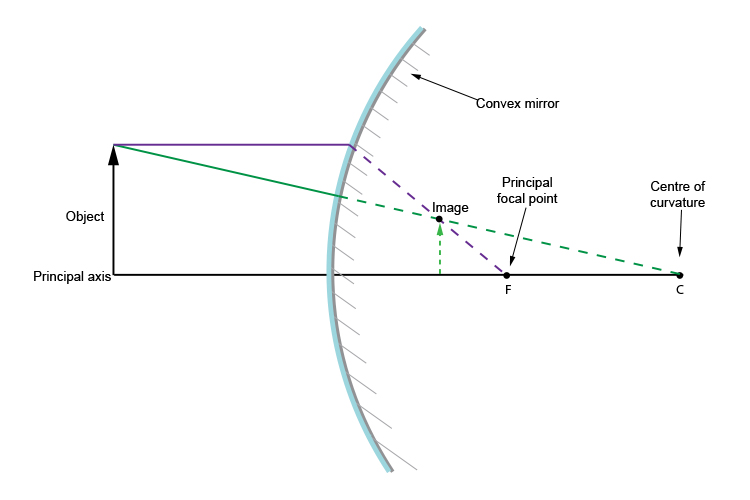
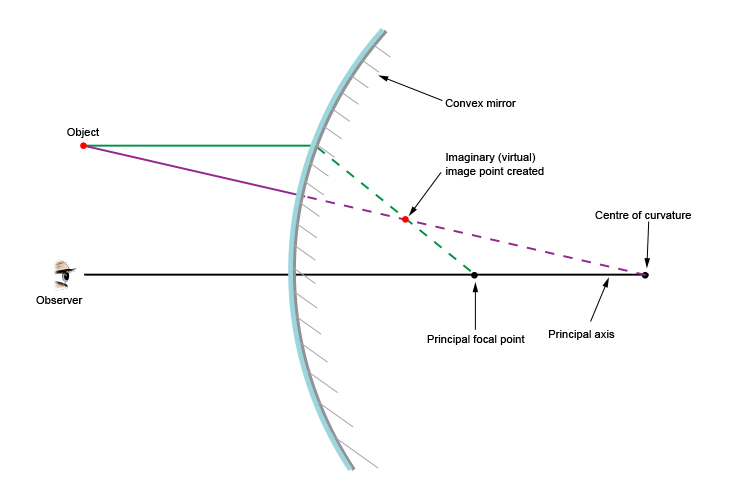
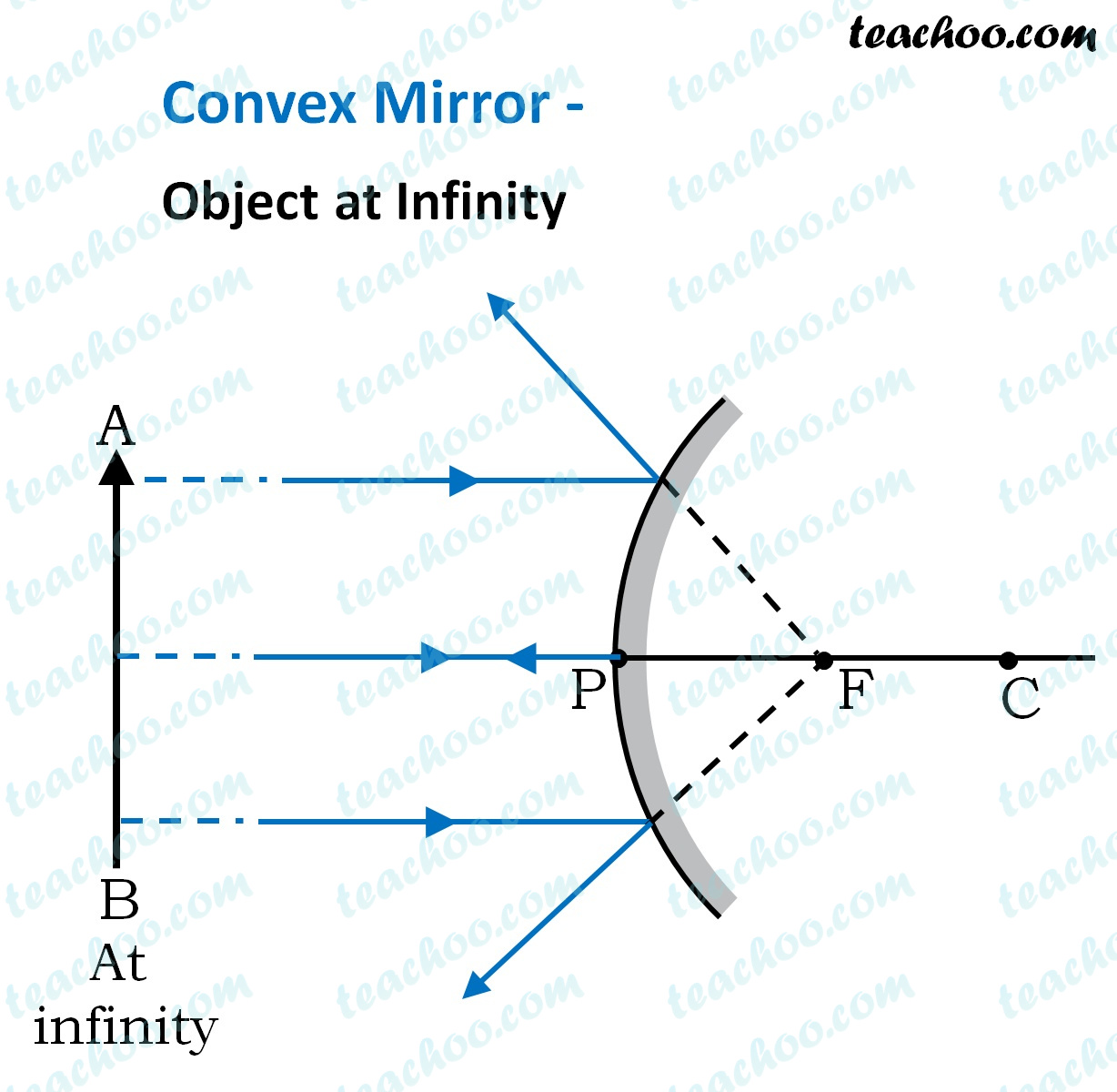
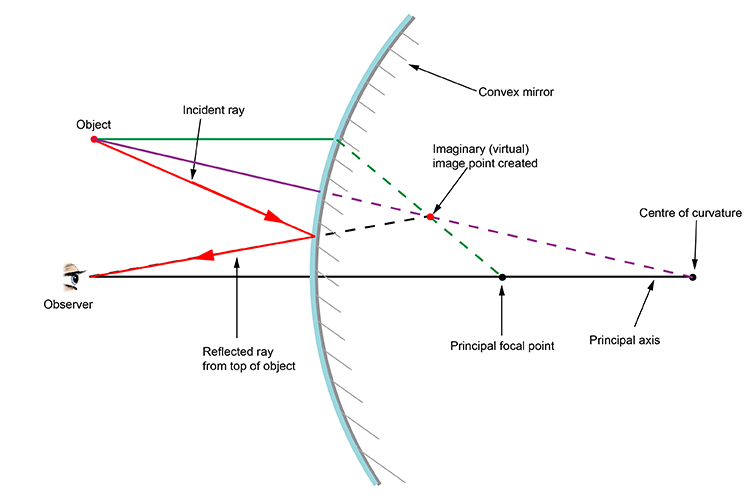
Convex Mirror Image. A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here.. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror.
Spherical mirror ray diagram
in a previous video we saw that if you take a mirror which is a part of a sphere then we call such mirrors as spherical mirrors and if this mirror is small enough meaning if it's a small enough part of the sphere then if you incident parallel rays of light it will almost get focused at a single point in this video we'll talk about some details …
Sample Plot Chart Templates 5 Free Documents In Pdf. com 6 hours ago · Spherical mirror ray diagram worksheet. Identify the population and the sample: a) A survey of 1353 American households found that 18% of the households own a computer. conflict or contrast of character, especially one int ended to be acted on the stage; ...
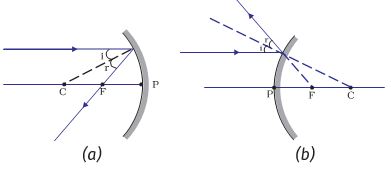
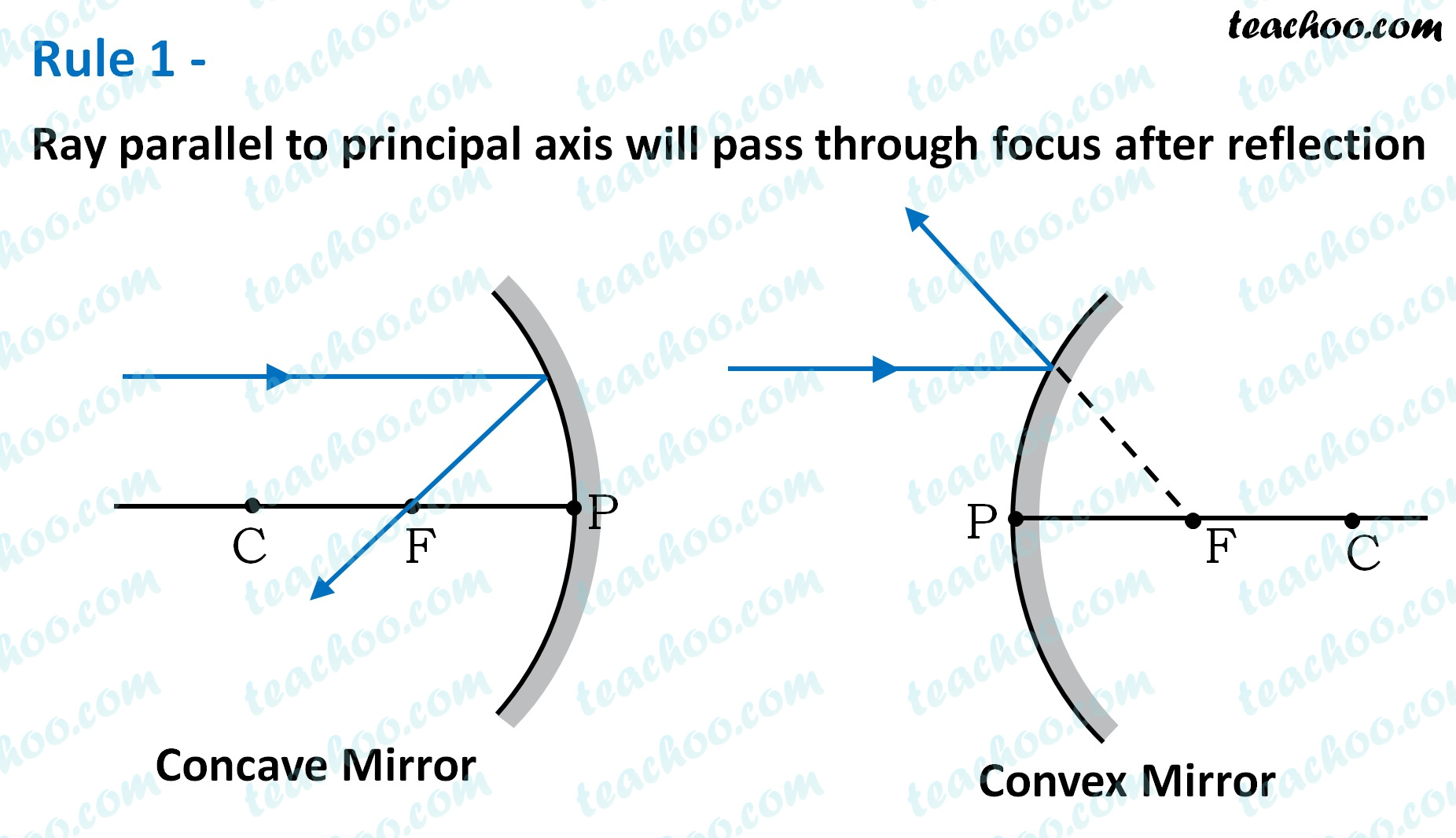
Rules For Making Ray Diagrams By Spherical Mirror (i) A ray passing to the principal axis, after reflection, will pass through the principal focus in case of a concave mirror or appear to diverge from the principal focus in case of a convex mirror. CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10
Spherical mirror ray diagram.
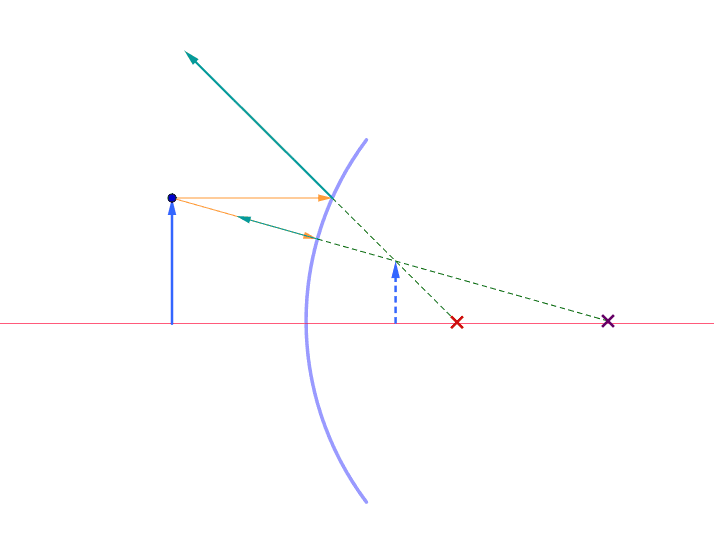
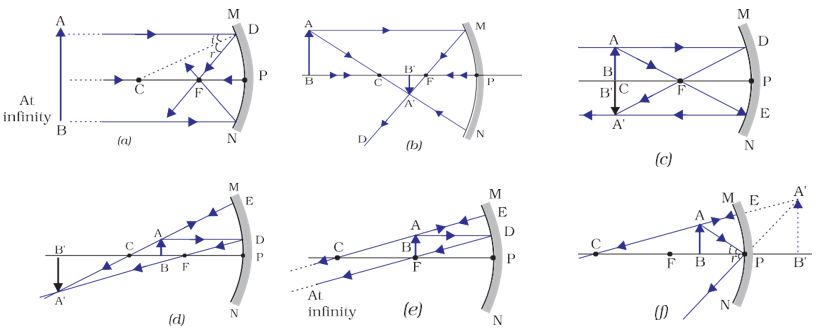
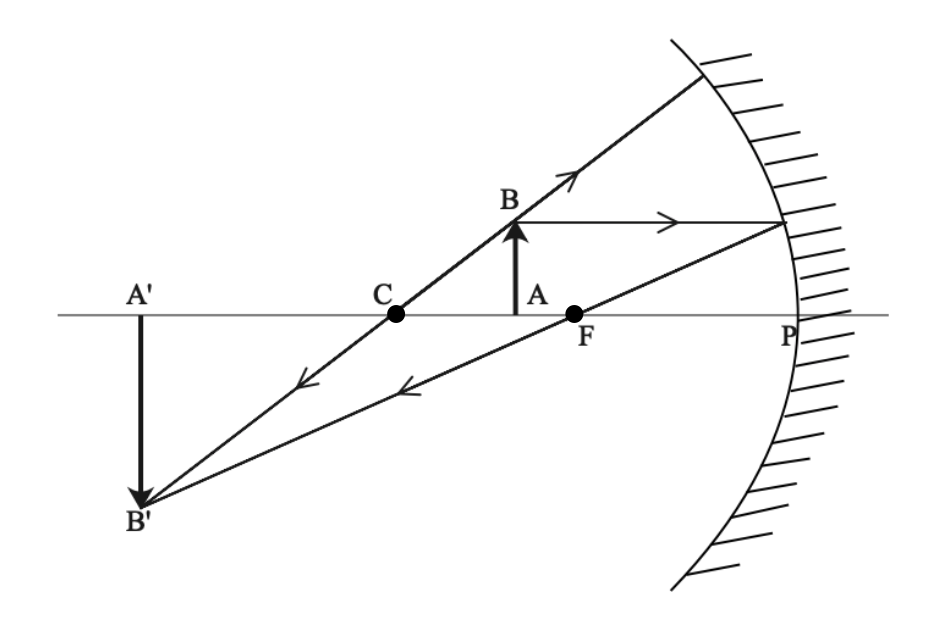
The centre of curvature (C) is the centre of the circle (sphere) of which the mirror is an arc. The focal length (f) and radius of curvature (R) are defined in the diagram at the right. It can be shown that R = 2f. "A" in the diagram is known as the "vertex" (often labeled V). Image formation in spherical mirrors is defined by certain ...
Ray diagram of Concave mirror. The spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outward is called Convex Mirror. Convex mirror used in road, bends to prevent accidents. To study the reflection of light on the curved surface, then we need to know about Centre of Curvature ( C), Pole (P) Ray diagram for Convex mirror.
Glass with any shapes constructed from line segments and circular arcs, including prisms and "spherical" lenses. Glass (Ideal lens) An ideal lens which obeys exactly the thin lens equation (1/p + 1/q = 1/f).
Mirror Ray Diagram Answers. 3 Spherical mirror Ray diagram worksheet. Apparatus Biconvex glass lens spherical concave mirror meter ruler optical bench. When parallel rays are incident upon a spherical mirror the reflected rays intersect but the focal point F For a concave mirror the focal point is in tear of the mirror.
Spherical mirror Ray diagram worksheet: For each of the questions below, you must draw a ray diagram to show the image. 1. The concave mirror shown below has an object placed 20cm in front of it. An image is formed in 35 cm in front of the mirror. What is the nature of the image? Calculate the magnification of the image and the focal
Spherical mirrors; and Refraction 3-26-99 Sections 23.3 -23.5 A ray diagram for a convex mirror. What happens with a convex mirror? In this case the ray diagram looks like this: As the ray diagram shows, the image for a convex mirror is virtual, and upright compared to the object. A convex mirror is the kind of mirror used for security in ...
Describe image formation by spherical mirrors. Use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to calculate the properties of an image in a spherical mirror. The image in a plane mirror has the same size as the object, is upright, and is the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
Spherical Mirrors: Let's learn Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors. How to use ray diagrams to find the image formed by Spherical Mirrors: Concave and Conve...
Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the mirror.
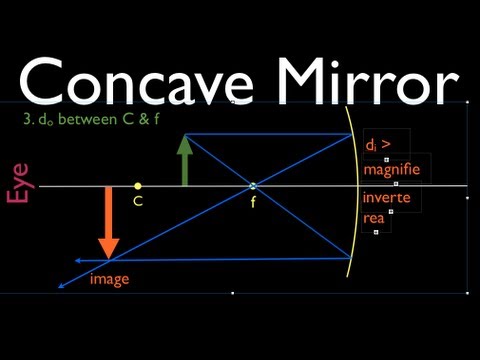
Drawing the ray diagrams is an ideal way to illustrate the formation of images by spherical mirrors. The intersection of at least two reflected rays give the correct position of image of the point object. The following table illustrates the image formed by a concave mirror for different positions of the given object − Uses of Concave Mirror
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1 on a screen placed at a distance of 50 cm from the mirror. (a) Write the type of mirror. (b) Find the distance of the image from the object. (c) What is the focal length of the mirror ? (d) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams A spherical mirror is a reflective segment of a sphere with a radius of curvature R. It can be convex (outside surface of a sphere) or concave (inside surface). First we will consider a concave spherical mirror. The mirror has a radius R, and the distance from the mirror to the object is p.
Spherical mirror ray diagram question. Ask Question Asked 7 years, 2 months ago. Active 6 months ago. Viewed 1k times 2 $\begingroup$ why does a ray, parallel to the principle axis, intersect the principal axis at half the radius of curvature, i.e. focus? EDIT. I was taught that in a spherical concave mirror, the rays parallel to the principle ...
Free PDF download of Class 10 Science Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction Revision Notes & Short Key-notes prepared by expert Science teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books. To register Science Tuitions on Vedantu.com to clear your doubts.
An object is placed 20.0 cm from a concave spherical mirror having a focal length of magnitude 40.0 cm. (a) Use graph paper to construct an accurate ray diagram for this situation. (b) From your ray diagram, determine the location of the image. (c) What is the magnification of the image? (d) Check your answers to parts (b) and (c) using the ...
Practice: Ray diagrams and curved mirrors. This is the currently selected item. Mirror formula derivation. "Objects in the mirror are ..." actually images in the mirror. Cartesian sign conventions mirrors. Practice: Sign convention. Solved example: Mirror formula. Practice: Using the mirror formula.
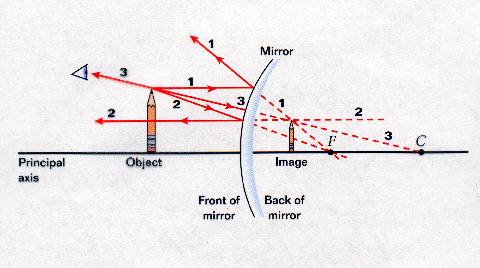
A ray that strikes the vertex of a spherical mirror is reflected symmetrically about the optical axis of the mirror (ray 4 in Figure 2.9). We use ray tracing to illustrate how images are formed by mirrors and to obtain numerical information about optical properties of the mirror.
This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for concave and convex spherical mirrors. By manipulating the object and mirror locations, you can create real or virtual images. The ray parallel to the principal axis and the ray that hits the center of the mirror are drawn. Contributed by: Ernest Lee (March 2011)
Ray Diagrams to Represent Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors When we place an object in front of a mirror, each point of it emits a ray of light. But for convenience, only two rays coming out of the ends of the object are considered. The intersection of at least two rays gives the position of the image formed by the mirror.
Rule 2 - Ray passing through focus will become parallel to principal axis after reflection. For a concave mirror , we see that ray passing through focus becomes parallel to principal axis after reflection. For a convex mirror, since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel to principal axis.
23 Apr 2020 — For a Concave mirror, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this ...
Lecture 37: Lenses and mirrors •Spherical lenses: converging, diverging •Plane mirrors •Spherical mirrors: concave, convex The animated ray diagrams were created by Dr. Alan Pringle.
Curved mirrors come in two basic types: those that converge parallel incident rays of light and those that diverge parallel incident rays of light. One of the easiest shapes to analyze is the spherical mirror. Typically such a mirror is not a complete sphere, but a spherical cap — a piece sliced from a larger imaginary sphere with a single cut.
oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Concave and Convex Mirrors. Concave and Convex Mirrors - GeoGebra Materials. Description. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror.
Well, torches have special spherical mirrors which make the light focused in the direction you want to go. Let's find out the mechanism involved in the image formation by spherical mirrors… Suggested Videos Ray Diagrams Ray diagrams are used to depict the image formation by tracing the path of light rays i.e. incident rays and reflected rays.
121 - Ray Diagram - MirrorsIn this video Paul Andersen explains how ray diagrams can be used to determine the size and location of a reflected image. Ray di...













0 Response to "39 spherical mirror ray diagram"
Post a Comment