38 convex mirror ray diagram object at infinity
Homework Statement An object is in front of a convex mirror. We then obtain an erect image whose height is equal to 25% of the height of the object. What is the distance between the object and the mirror if we know that the focal distance is equal to 0.2m? Homework Equations M = Yi/Yo = q/p...
If you make an object transparent and shine a laser on it the light will reflect and refract according to physical laws.Point objectsA point object reflects light in all directions but we are only interested in the rays that pass through the lens so don"t have to draw a million rays.Distant objectAs you move away from a point object the angle between rays that pass through a lens becomes ...
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual magnified image of an object by a convex lens. In your diagram, the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus should be shown clearly. (c) Three convex lenses are available having focal lengths of 4 cm, 40 cm and 4 m respectively.

Convex mirror ray diagram object at infinity
Explanation - when object is placed between focus point and pole of the mirror, then image formed is virtual and enlarged and erect also. 2. For the formation of a ray diagram, in case of a concave or convex mirror, the following rule should be kept in mind
2) Geometric centre of the spherical mirror is pole . 3) Nature of the images formed by a convex mirror is smaller, virtual and erect. 4) The mirror used by the ophthalmologist to examine the eye is concave mirror. 5) If the angle of incidence is 45° , then the angle of reflection is 45 °. 6) If an object is placed between two mirrors which ...
View Images Library Photos and Pictures. Images formed by concave mirror using ray diagram | Class 10, Light-Reflection and Refraction NCERT Chapter Notes Class X Science Light - Reflection and Refraction 3 | ENTRANCEINDIA Image Formation by Concave and Convex Mirror Class 10 Notes | EduRev Draw a Labelled Ray Diagram to Show the Formation of Image in a Convex- mirror When the Object is at ...
Convex mirror ray diagram object at infinity.
Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear - view mirror in vehicles ? ... At twice the focal length at infinity (c) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus. ... Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. Solution. Range of object distance = 0 cm to15 cm.
As the object moves towards the mirror the image location moves further away from the mirror and the image size grows (but the image is still inverted). When the object is that the focal point, the image is at infinity. How do you find the image in a convex mirror? Step-by-Step Procedure for Drawing Ray Diagrams
The correct answer is Convex mirror. 20. A ray of light starting from air passes through medium A of refractive index 1.50, enters medium B of refractive index 1.33 and finally enters medium C of ...
Plane mirrors are the only type of mirror for which a real object always produces an image that is virtual, erect and of the same size as the object. Virtual objects produce real images, however. The focal length of a plane mirror is infinity; [4] its optical power is zero. Concave and Convex mirrors (spherical mirrors) [5]
(d) cannot be ascertained as size of image depends upon the focal length of the convex mirror. Answer: (C) The magnification produced by a convex mirror is always: (a) Equal to +1 (b) Equal to -1 (c) Greater than +1 (d) Smaller than +1 Answer: (D) The image formed by a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm is a quarter of the object.
A convex mirror always produces an erect image of the objects. The image formed in a convex mirror is highly diminished or much smaller than the object, due to which a convex mirror gives a wide field of view of the traffic behind. A convex mirror enables the driver to view such larger area of the traffic behind him. Page Number: 171. Question 1
Convex lens forms real image because of positive focal length and concave lens forms virtual image because of negative focal length. In mirrors , images are formed through reflection but lens es form images through refraction . This is explained with the help of ray diagram s as follows 1. Introduction (Refraction and Lens es) 2. The Lens Equation 3. Concave Lens es 4.
If the object is at the focus, the image is formed at the infinity. And the spherical mirrors produce virtual images only when the image is formed behind the mirror. In the given case, the concave mirror produces only the diminished image as the object is at infinity. When object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens the location of images?
By drawing ray diagrams, explain the formation of image when an object is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens at the following positions:(i) At infinity(ii) Beyond 2F1 (iii) At To Find Image Distance For Varying Distance Of A Concave Lens NCERT Class 10 Science Lab Manual Image Formation by a Convex Lens - CBSE Tuts
Concave mirror reflection ray diagram. A concave mirror is used to focus the light rays to a single point which is used as a furnace. The above shows light is focused to burn a piece of paper. The parallel rays of light from the sun are focussed at a point using a concave mirror which is used to burn paper from the above diagram.
Convex mirrors always produce virtual images . It cannot be used to produce images on the screen. Concave mirrors produce real images on the screen in all cases except when the object is between pole and focus , therefore students should use a concave mirror because it forms real images.
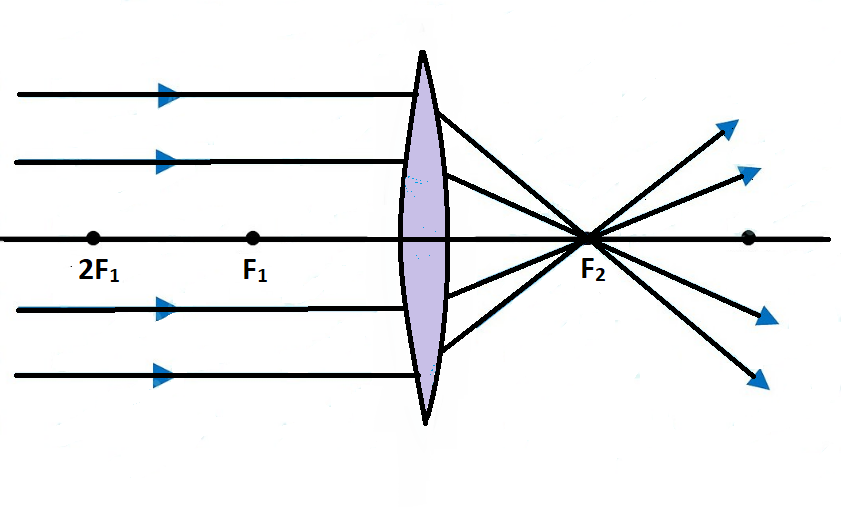
By mirror formula, The image formed by convex lens (when object is at infinity) is at focus, real and inverted. In case (A), the beam of light is coming parallel to principal axis while in case (B) the beam of light incident on lens is not parallel to principal axis but the converging point is focus of the lens. 46. Given, i = 90 0 - 60 0 = 30 0
A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. The light ray will pass through the focus of the spherical mirror after reflection. Redraw the diagram given below in your answer book and show the direction of . In this practice worksheet students will ray diagram on a flat mirror and then on concave and convex mirrors ...
The ray diagram shows the image formation, A', of an object placed in front of a plane mirror, A. Plane mirrors are flat mirrors. Most common mirrors, such as those in a restroom or dressing room, are plane mirrors. The rules of plane mirrors are straight-forward and only explicitly stated so they may be modified for spherical mirrors.
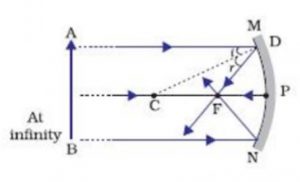
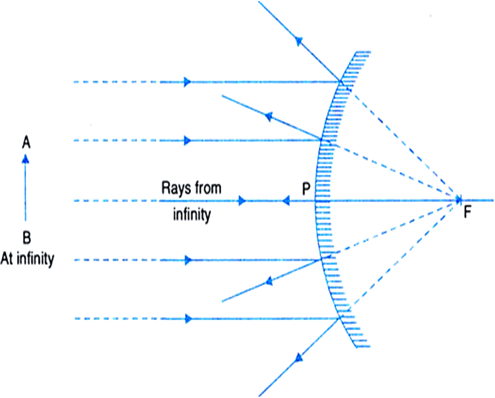
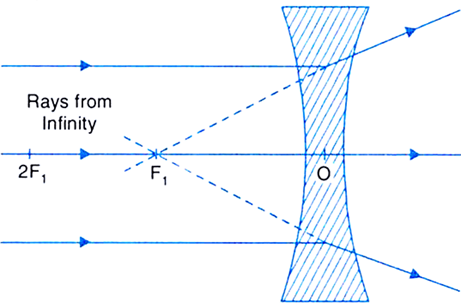
(a) Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image in a convex mirror when the object is at infinity. Mark clearly the pole and focus of the mirror in the diagram. (b) State three characteristics of the image formed in this case. (c) Draw diagram to show how a convex mirror can be used to give a large field of view. Solution :
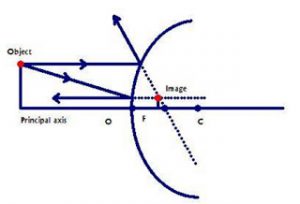
Object at infinity:- Since parallel rays coming from the object converge at principal focus, F of a concave mirror; after reflection. Hence, when the object is at infinity the image will form at F. Real and inverted.When an object is at infinity,then the rays coming from it is almost parallel to principal axis.
Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity. In this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance). So, we draw ray s parallel to principal axis. Only RUB 220.84/month. Ray Diagram s for Lens es (Concave). STUDY. Flashcards. Concave Lens es. Thinest in the middle and makes the light ray s diverge ( spread out). If the ray s ...
The ray diagram of a convex mirror is shown below. The focal length of a convex mirror can be determined by introducing a convex lens between the object and the convex mirror. An image can be obtained with the help of a convex lens side by side with the object when the convex mirror reflects the rays along the same path, i.e., when the rays ...
In each diagram use an arrow 10 cm tall pointing upwards as the object. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. Concave And Convex Mirrors Ray Diagram For Convex And Concave Mirror. Converging mirror ray diagram. The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located […]
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object.
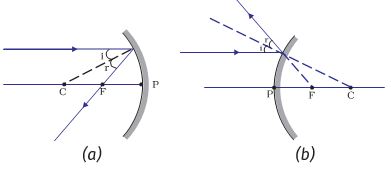
Ray diagram for Convex mirror. Before drawing a ray diagram for the convex mirror, first look at the rules for drawing a ray diagram in a convex mirror. You can also navigate to the exercise section. The image of an object is formed behind the convex mirror. The image is formed by a convex mirror that is always virtual, erect, and diminished.
When the object is placed in between P and infinity, the image is formed behind the mirror, which is virtual, erect and diminished. Uses of Convex Mirrors. Used in Rearview mirrors in vehicles, as it provides an erect and wider view. Convex mirrors installed on roads as traffic safety, in bends, mountain passes. Also used in blind spots in shops.
23 Apr 2020 — Convex Mirror - Ray diagram · Object is Placed at Infinity · Object is Placed between Principal axis and Infinity ...Position of the object: Position of the imageAt infinity: At the focus F, behind the mirror
For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t
Hey guys, so after hours of study/confusion (idk maybe I'm just like...physics challenged and had trouble...that happens often to me with topics)...I've boiled it down to the following. Hopefully, it can help you all solve these kinds of problems; NS Content review goes over how to draw the diagrams, etc., but I really doubt any of us will be drawing diagrams on test day. Things to be aware of that don't have to do with the 5 steps: --> Snell's Law and refraction/reflection (i.e. what ...






![View 29+] Image Formation By Concave Mirror When Object Is ...](https://funscience.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/PositionOfImageWhenObjectIsPlacedAtInfinityInConvexMirror.png)
















![Expert Answer] draw ray diagram showing the image formation ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/da6/df9a8f074ab806f4a42890238eed5c3f.jpg)


0 Response to "38 convex mirror ray diagram object at infinity"
Post a Comment