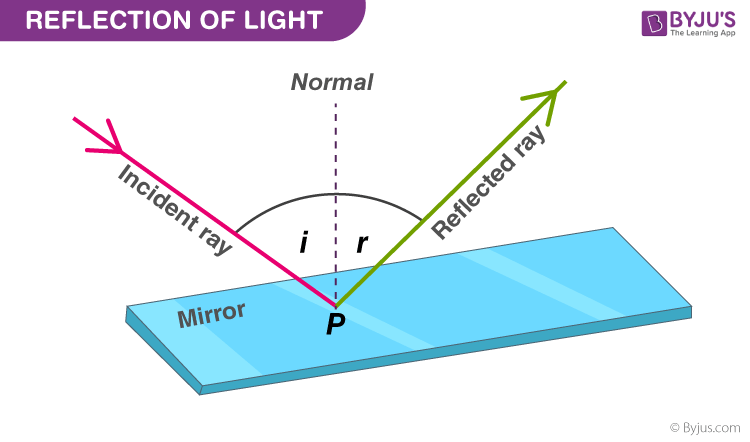
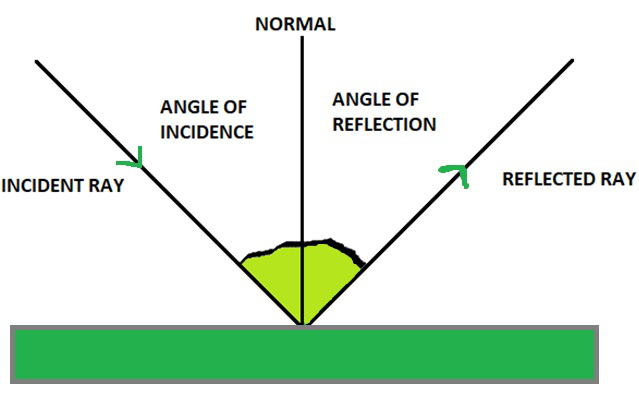
37 the diagram shows the reflection of light from a mirror. the value of x in the diagram is °.
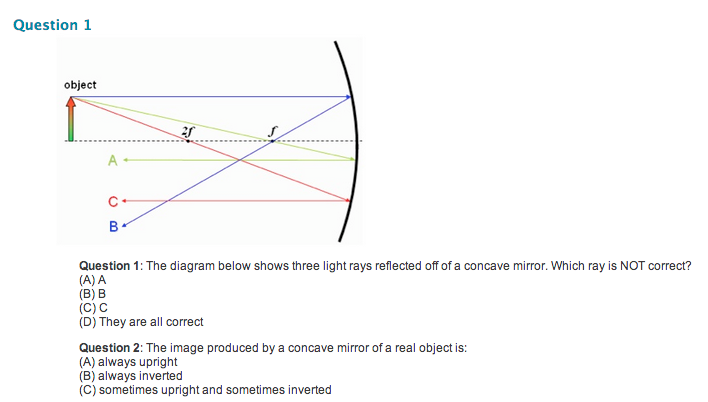
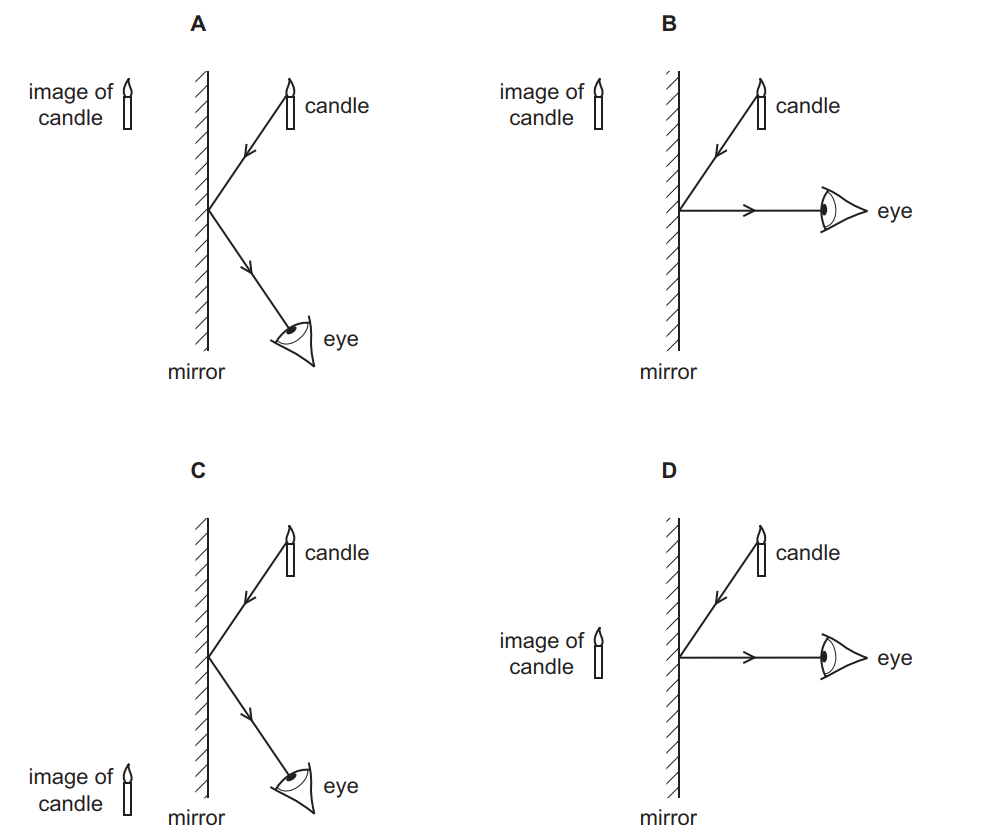
The diagram shows an object located vertically on the principal axis of a diverging lens. A student looks through the lens and can see an image of the object. (a) Using a pencil and ruler to draw construction lines on the diagram, show how light from the object enters the student's eye and the size and position of the image. (3) A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Incident rays - at least two - are drawn along with their corresponding reflected rays. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Every observer would observe the same image location and every light ray would follow the law of reflection.
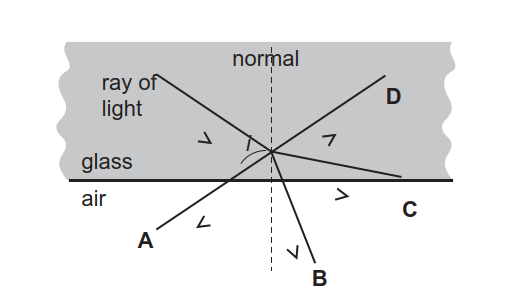
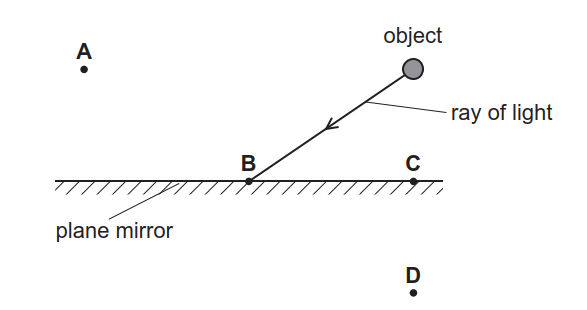
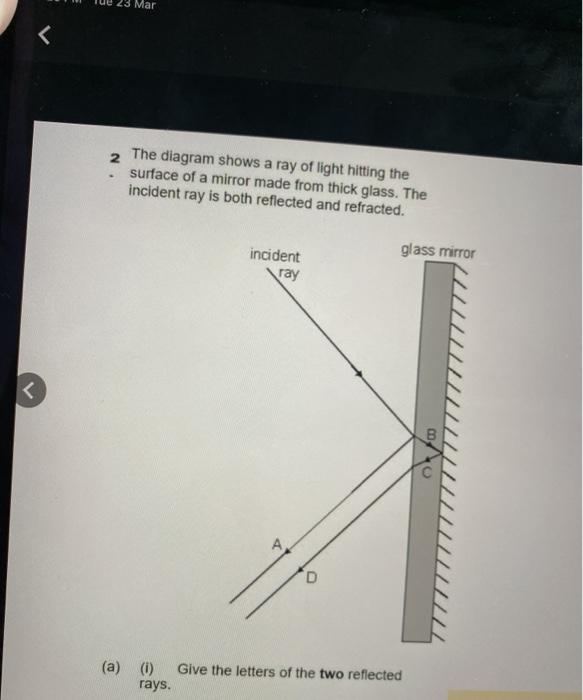
The diagram shows an object in front of a plane mirror. At which labelled position is the image of the object formed? ... The diagram shows a ray of light inside a glass rod. The critical angle for the light in the glass is 42°. ... the angle of reflection from a mirror equals the angle of incidence. waves incident on a mirror are partially ...
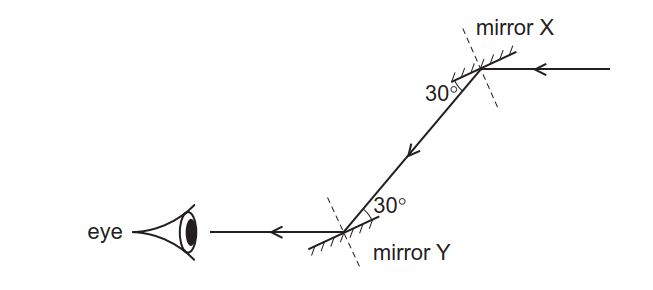
The diagram shows the reflection of light from a mirror. the value of x in the diagram is °.
When light ray is incident on plane mirror it undergoes reflection. When the light ray is incident normally on the plane mirror then by using laws of reflection angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection. Hence, as the angle of incidence is zero degree angle of reflection is zero degree. Find an answer to your question The diagram shows the reflection of light from a mirror. The value of x in the diagram is °. zabrianna zabrianna 05/02/2018 Physics High School answered The diagram shows the reflection of light from a mirror. The value of x in the diagram is °. 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement is the light coming away from the mirror; A ray diagram for reflection at a mirror. In the ray diagram: the hatched vertical line on the right represents the mirror
The diagram shows the reflection of light from a mirror. the value of x in the diagram is °.. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus. The diagram shows light travelling from air into glass. Four angles v, w, x and y are shown. ... C The angle of reflection at mirror X is 120°. D The angle of reflection at mirror Y is 0°. ... [0, 0], [[970, 250], [970, 90], [728, ... The diagram below in figure shows an object XY in front of a plane mirror MM 1. Draw on the diagram, path of two rays from each point X and Y of the object to show the formation of its image . Draw on the diagram, path of two rays from each point X and Y of the object to show the formation of its image . Complete and copy the diagram to show how light bends when it travels from the liquid to the glass and back to the liquid, (i) If the light slows down in the glass, (ii) If the light speeds up in the glass. Answer: Question 10: Show with the help of a diagram how a total reflecting prism can be used to turn a ray of light through 90°. Name an ...
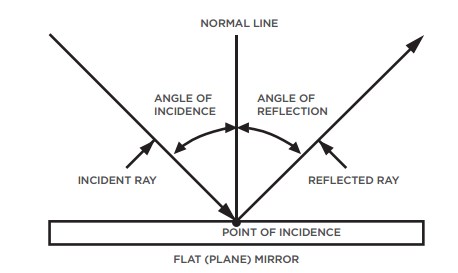
A woman is looking at her reflection in a flat vertical mirror. The lowest part of her body she can see is her knee. If she stands closer to the mirror, what will be the lowest part of her reflection she can see in the mirror. A) Above her knee B) Her knee C) Below her knee If the light doesn't get to your eye then you can't see it The total internal reflection taking place in an object done clear. D) The ... Identify the value of persistence of vision. A) ... The diagram shows the path of a light ray X, directed at a plane mirror. Solution. First, we consider reflection, as shown in the diagram below for a light wave striking a surface. We identify the incoming ray as the incident ray and the outgoing ray as the reflected ray. Concomitantly, the angleθ i. that the incoming ray makes with a line (dashed in the diagram) normal to the surface is called the angle of incidence. The diagram shows the principal axis, focal point (F), and center of curvature for both a concave and convex spherical mirror. Spherical mirrors are either concave (converging) mirrors or convex (diverging) mirrors, depending on which side of the spherical surface is reflective.
Q10. Describe with a suitable diagram, how a convex mirror diverges a parallel beam of light rays. Mark clearly the pole, focus, and the centre of curvature of convex mirror in this diagram. Answer: After the reflection, the light rays diverge from the principal focus and that is why convex mirror is also known as diverging mirror. The diagram shows the reflection of light from a mirror. The value of x in the diagram is ____°. 50. How does a concave mirror form an image? it bounces the light toward a focal point. The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. According to the law of reflection, which statement must be true? Draw a diagram showing the reflection of a light ray from a plane mirror. Label on It the Incident ray, the reflected ray, the normal, the angle of Incidence I and the angle of reflection r. Uses of Ray Diagrams. Ray diagrams can be particularly useful for determining and explaining why only a portion of the image of an object can be seen from a given location. The ray diagram at the right shows the lines of sight used by the eye in order to see a portion of the image in the mirror.
Q4) Draw a diagram showing the reflection of a light ray from a plane mirror. Label on it the incident ray, the reflected ray, the normal, the angle of incidence i and the angle of reflection r. Looking to do well in your science exam ? Learn from an expert tutor. Book a free class! Hello, welcome to Reno today. We are going to draw a diagram ...
The diagram shows the reflection of light from a mirror. The value of x in the diagram is. 50. Which building material would provide the best surface for viewing a reflection? glass.
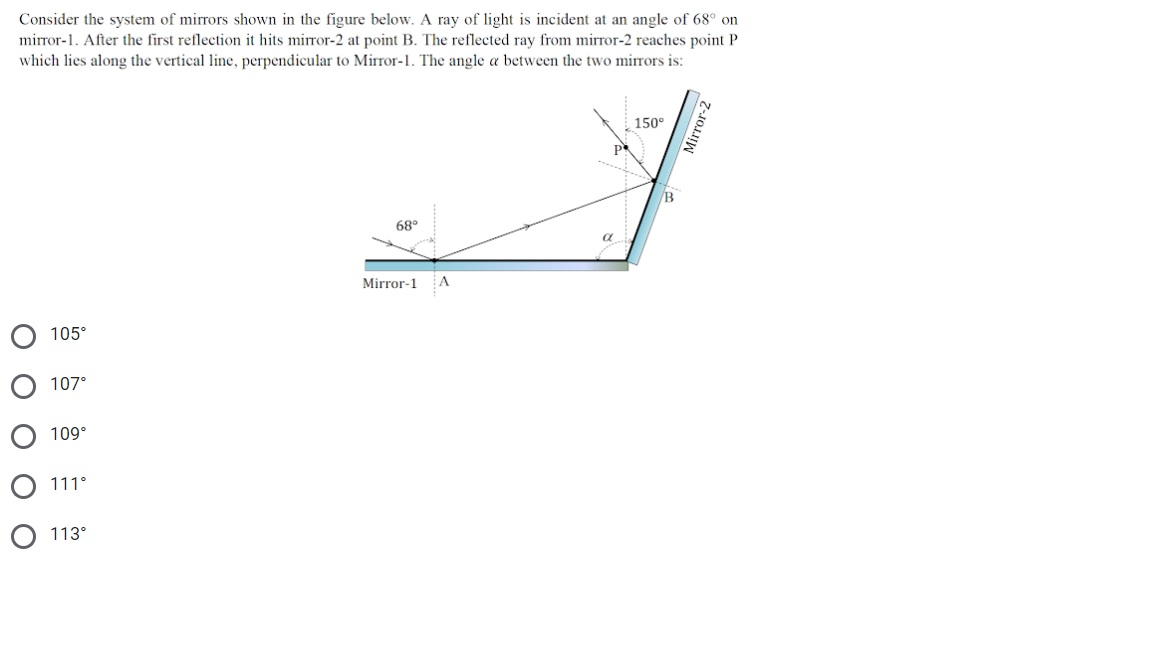
B. The angle of incidence at mirror Y is 60°. C. The angle of reflection at mirror X is 120°. D. The angle of reflection at mirror Y is 0°. Light 29 30. 4. The diagram shows a child using a periscope to look at an object on the other side of a wall. Light 30 31. Which diagram shows a correctly drawn ray of light from the object? Light 31 C 32.
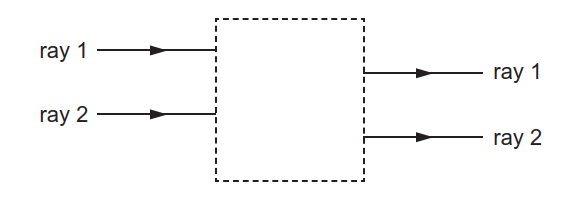
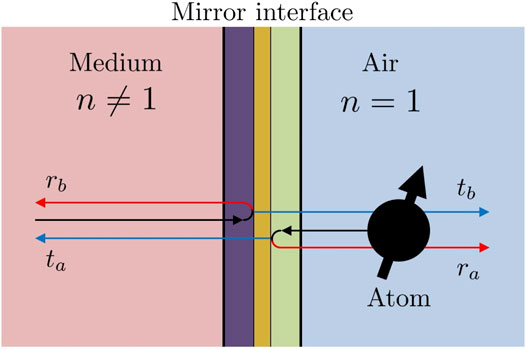
Learn about the laws of reflection and refraction. Ray diagrams. A ray diagram shows how light travels, including what happens when it reaches a surface.
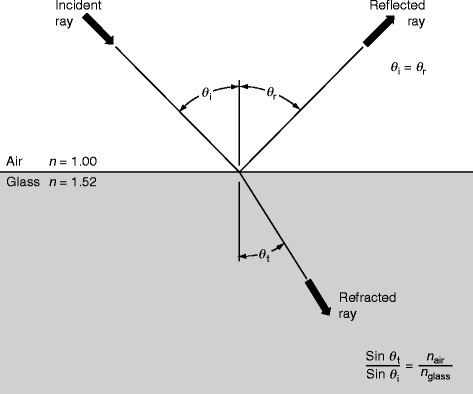
State the two laws. answer choices. Laws of Reflection. 1. The angle of incidence = angle of reflection. 2. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal (line perpendicular to the plane of the mirror/ reflective surface) all lie in the same plane. Laws of Mirror. 1.
When light reflects from the surface of a plane mirror, the angle of incidence is ..... the angle of reflection. (ii) The diagram shows two rays of light coming from an object. Continue the two rays and add further lines to the diagram to show how an image is formed by a plane mirror. (2)
The diagram below shows the apparatus a student used to investigate the reflection of light by a plane mirror. The student drew four ray diagrams for each angle of incidence. The student measured the angle of reflection from each diagram. The table below gives the student's results. € € € Angle of reflection
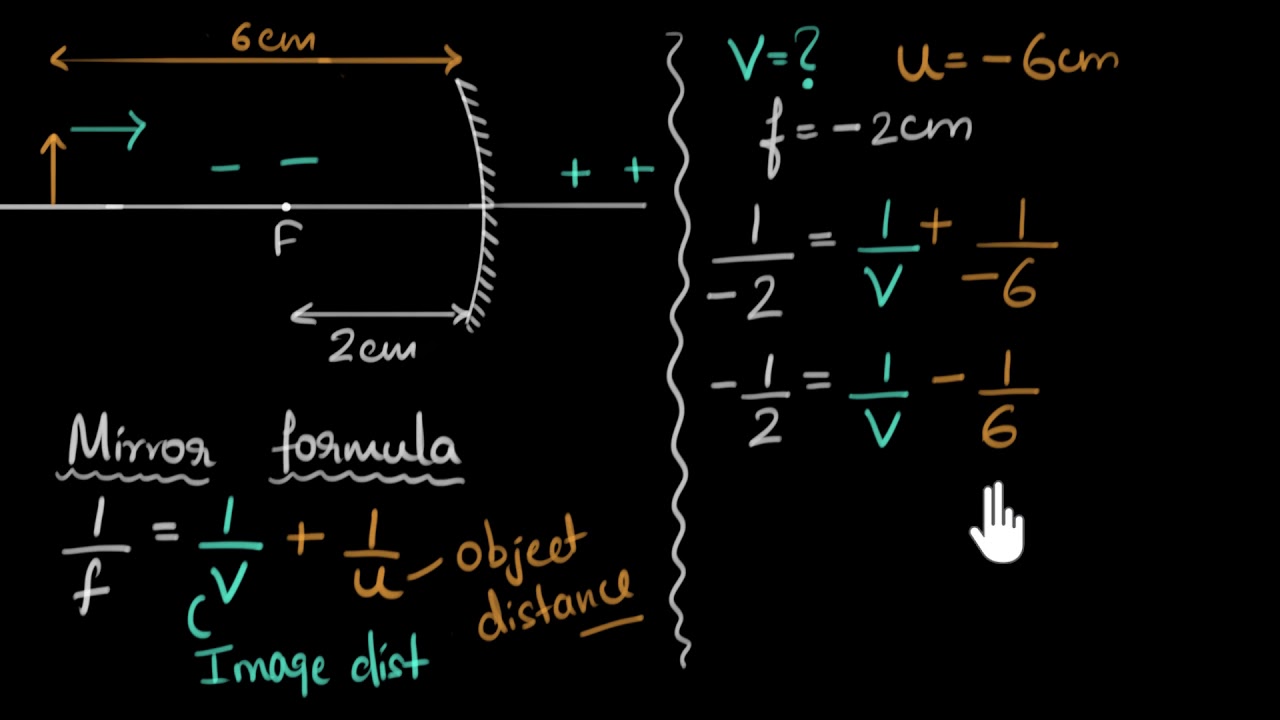
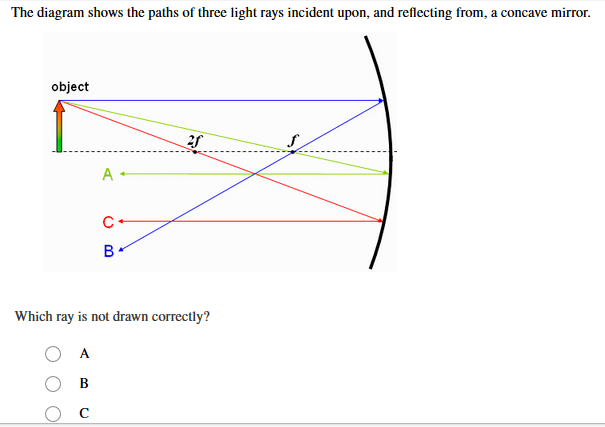
24. What is the minimum number of rays required for locating the image formed by a concave mirror for an object. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual image by a concave mirror. [Delhi] Answer. 25. The refractive index of water is 1.33 and the speed of light in air is 3 x 108 ms-1.
The diagram shows a ray of light being reflected by a plane mirror. The angle of reflection is: ? 55 o ? 20 o ? 110 o ? 70 o ? 35 o; An object that gives out its own light is called ? luminous ? non-luminous ? effervescent ? translucent The angle of incidence at a plane ...
Common Refer to the diagrams above and give the names for the following: terminology of reflection of 1.Centre of curvature ,C = The geometric centre of a hollow sphere of which the concave or light on a convex mirror is a part. curved mirror 2.Pole of mirror, P = The centre point on the curved mirror 3.Radius of curvature ,r = CP = radius of ...
is the light coming away from the mirror; A ray diagram for reflection at a mirror. In the ray diagram: the hatched vertical line on the right represents the mirror
Find an answer to your question The diagram shows the reflection of light from a mirror. The value of x in the diagram is °. zabrianna zabrianna 05/02/2018 Physics High School answered The diagram shows the reflection of light from a mirror. The value of x in the diagram is °. 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement
When light ray is incident on plane mirror it undergoes reflection. When the light ray is incident normally on the plane mirror then by using laws of reflection angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection. Hence, as the angle of incidence is zero degree angle of reflection is zero degree.









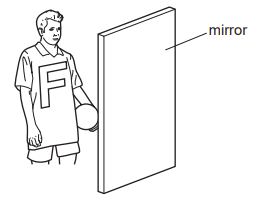


0 Response to "37 the diagram shows the reflection of light from a mirror. the value of x in the diagram is °."
Post a Comment