35 convex lense ray diagram
This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The rays parallel to the principal axis and the ray through the center of the lens are drawn.Locators allow you to drag both the object and the lens. You can change the focal length using a slider.
Convex Lens - Ray diagram Concave Lens - Ray diagram You are here. Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens Lens Formula Power of a lens NCERT Questions → Class 10. Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1) Concepts ...
Biconvex lenses. A biconvex lens is one that is convex on both sides of the lens, as shown below: Treating this and drawing ray diagrams for a biconvex lens is essentially two refractions (one on the way into the lens and the other on the way out) along curved surfaces. So let's look at the steps necessary to draw the ray diagram for light ...
---teachoo.png)
Convex lense ray diagram
"A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element. A compound lens is an array of simple lenses (elements) with a common axis; the use of multiple elements allows more optical aberrations to be corrected than is possible with a single element. Lenses are typically made of glass or transparent ...
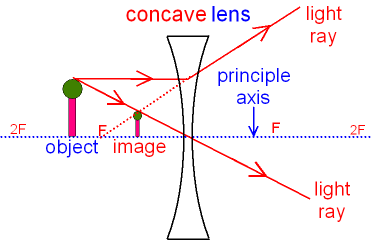
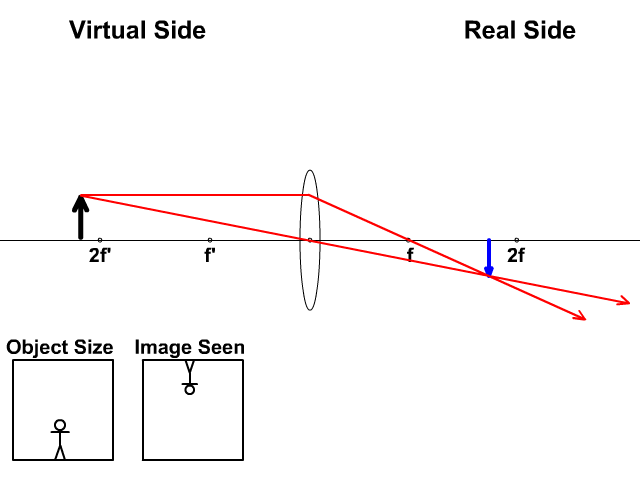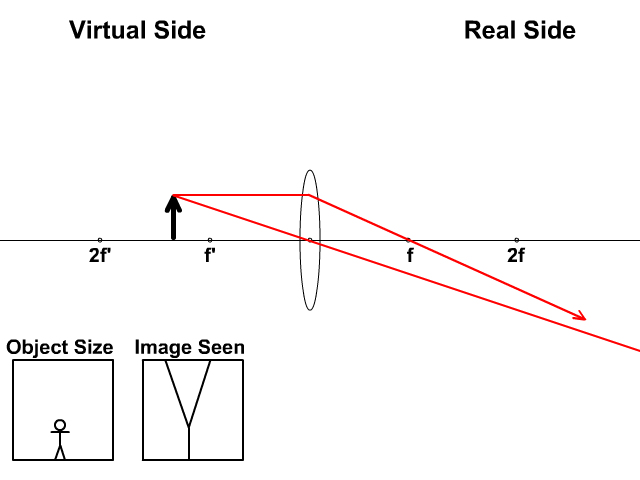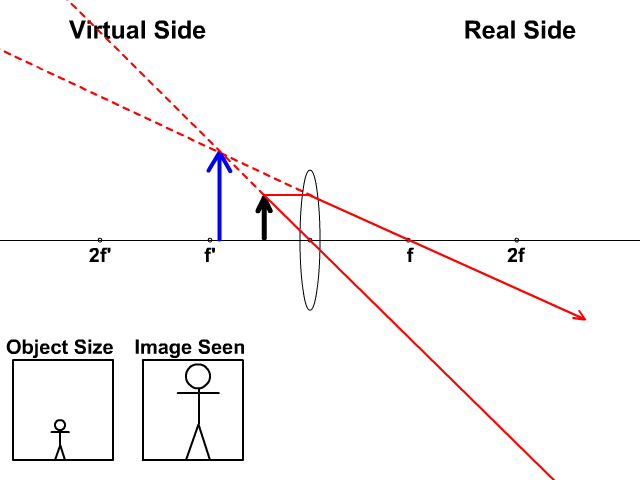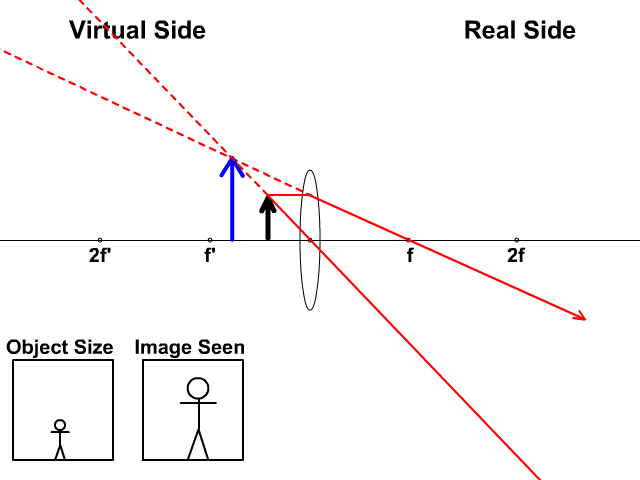
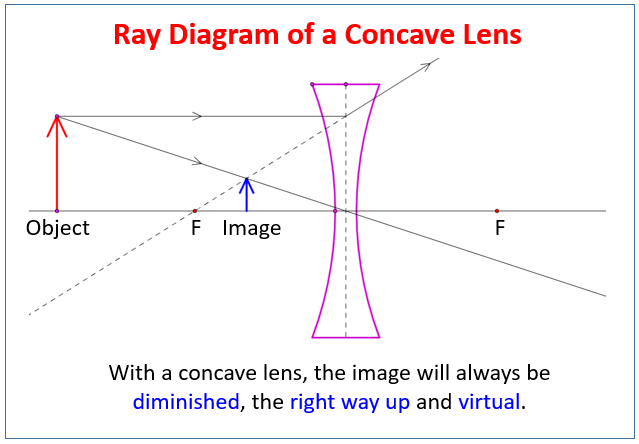
But you really don't need to remember this, the only thing to remember is: From the object. 1. Pass a parallel line through the principal focal point on the same side as the object. 2. Pass a ray line through the centre of the concave lens. Notice how similar this is to the two rules of refraction for converging lenses (convex lenses).
Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscienc...
Convex lense ray diagram.
Basic Types of Lenses Convex Lens Concave Lens Type of Image Convex Lens Ray Diagram for Convex Lens Rules for Ray Diagrams for Convex Lens PowerPoint Presentation Summary for Convex Lens Sign Convention Magnification Lens Equation Concave Lens Summary for Concave Lens PowerPoint Presentation ...
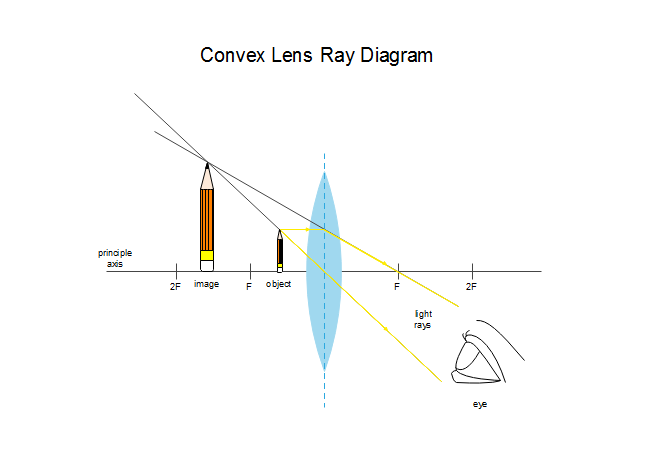
A convex lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a convex lens. To draw a ray diagram and find the location of the image that would be created on a screen you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "The two rules of refraction for converging lenses".
Convex Lenses and Ray Diagrams. A series of free GCSE/IGCSE Physics Notes and Lessons. The following diagrams show the ray diagrams for convex lens: for objects at different distances from the lens. Convex Lenses.
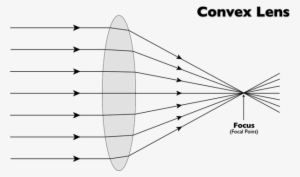
The convex lens is a lens that converges rays of light that convey parallel to its principal axis (i.e. converges the incident rays towards the principal axis) which is relatively thick across the middle and thin at the lower and upper edges. convex lens can converge a beam of parallel rays to a point on the other side of the lens.
Uses of convex lens. These are used for a variety of purposes in our day-to-day lives. For example, The lens in the human eyes is the prime example. So the most common use of the lens is that it helps us to see. Another common example of the use of this type of lens is a magnifying glass. When an object is placed in front of it at a distance ...
Convex lens ray diagram worksheet. Which diagram correctly shows the path of the ray after it has passed through the lens. Both word and pdf worksheets available. 4b a 15 0 cm object is placed 25 0 cm from a convex lens which has a focal length of 15 0 cm. For case 4 merely construct the ray diagram.
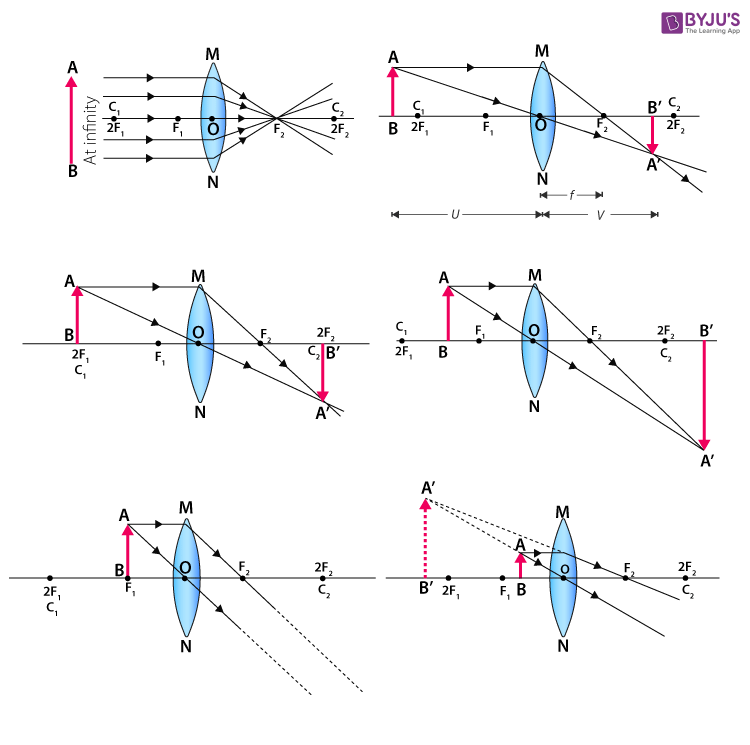
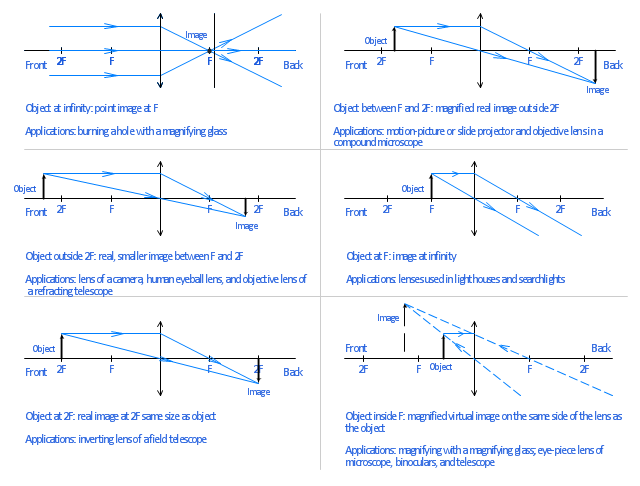
Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, the real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus. The size of the image is the same as compared to that of the object.
"A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element. A compound lens is an array of simple lenses (elements) with a common axis; the use of multiple elements allows more optical aberrations to be corrected than is possible with a single element. Lenses are typically made of glass or transparent ...
The ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces; Snell's law and refraction principles are used to explain a variety of real-world phenomena; refraction principles are combined with ray diagrams to explain why lenses produce images of objects.
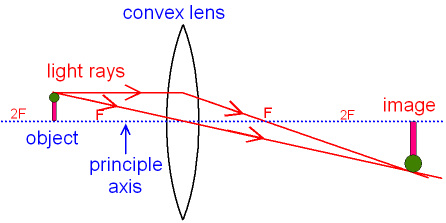
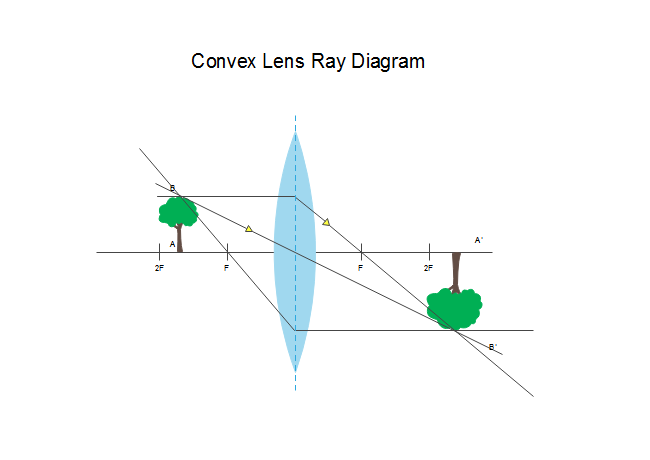
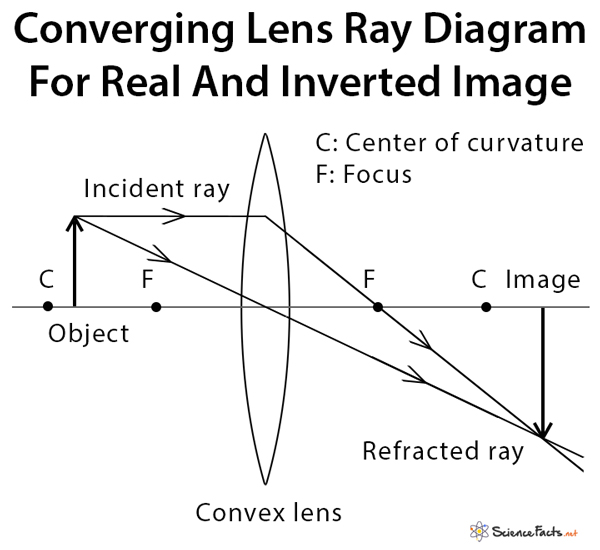
Image formation by convex lens ray diagrams. Image formation in a convex lens can be explained with the help of three principal rays shown in the figure. The ray parallel to the principal axis passes through the focal point after refraction by the lens. The ray passing through optical centre passes straight through the lens and remains undeviated.
Convex Lens - Light Ray Diagram. New Resources. Folding a Paper Airplane; Warm Up: Creating Surfaces of Revolution (1)
Convex concave ray diagrams. 1. J.M. Gabrielse Ray Diagrams. 2. J.M. Gabrielse Spherical Mirrors (concave & convex) 3. J.M. Gabrielse Concave & Convex (just a part of a sphere) C: the centre of curvature (centre point of the sphere) F: the focus (focus) of the mirror (halfway between C and the mirror) • C • F Principal Axis Curved Surface. 4.
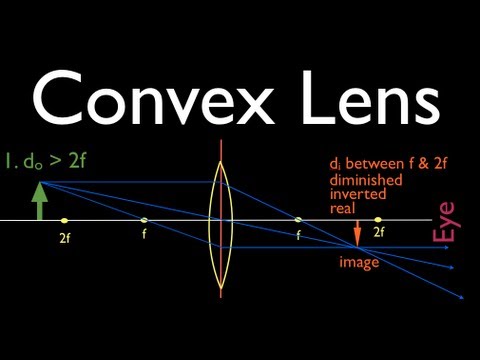
A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ...
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length.
Ray diagrams for convex lenses are based on the principle that convex lenses converge light rays passing through them. The following points are to be kept in mind while drawing ray diagrams for convex lens:-A ray of light passing through the optical center of a convex lens passes through the lens undeviated. A ray of light parallel to the principal axis, on passing through the lens, gets ...
A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.
Description. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave lens.
The convex lens ray diagram shown in the image has been shaped so that all light rays that enter it parallel to its axis cross one another at a single point on the opposite side of the lens. Such a lens is called a converging lens for the converging effect it has on light rays. The point at which the rays cross is defined to be the focal point F of the lens.
Convex Lens - Ray diagram. Last updated at Nov. 18, 2021 by Teachoo. For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positions Hence, we take different cases Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity In this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray.
Figure 16.26 Rays of light enter a concave, or diverging, lens parallel to its axis diverge and thus appear to originate from its focal point, F. The dashed lines are not rays; they indicate the directions from which the rays appear to come. The focal length, ƒ, of a diverging lens is negative.An expanded view of the path taken by ray 1 shows the perpendiculars and the angles of incidence and ...
Digital Teacher Smart Class - Trusted by 7500+ SchoolsDigital Teacher Canvas - Learn @Home, Anytime, Anywhere and Any Device https://bit.ly/3i2bvn5-----...
Correct option is. C. Parallel incident rays converge at focal point, In this case focal length of upper half and lower half are different. Upper half is semi convex lens having one side plane so it has larger focal length than bi-convex lens which is in lower half part. So incident ray from upper part will converge at more distance than ray ...















0 Response to "35 convex lense ray diagram"
Post a Comment