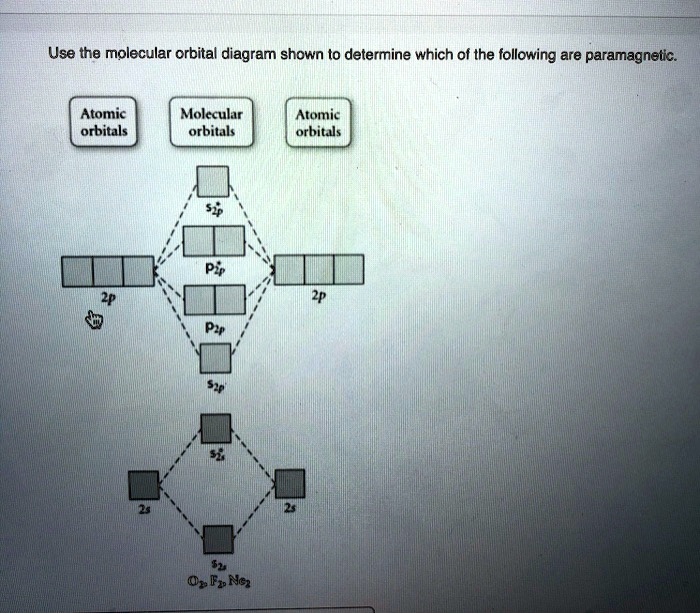
34 use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic.
FREE Answer to Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. N22+ B22+...1 answer · Top answer: Electronic configuration of nitrogen is as follows N (7): 1s'2s 2p Nitrogen has five valence electrons, two electrons in 2s orbital and remaining 3 are ...
1 answera. Only B2 B 2 is paramagnetic. All the others are diamagnetic. Their MO diagrams are shown below. b. For CO, the...
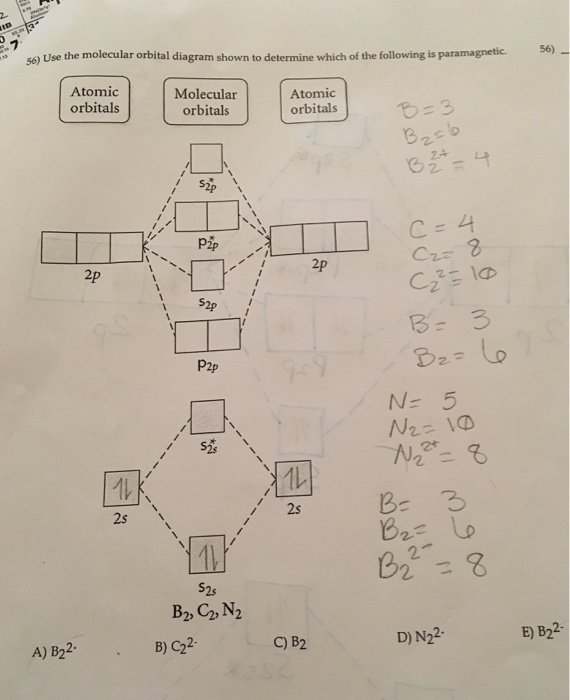
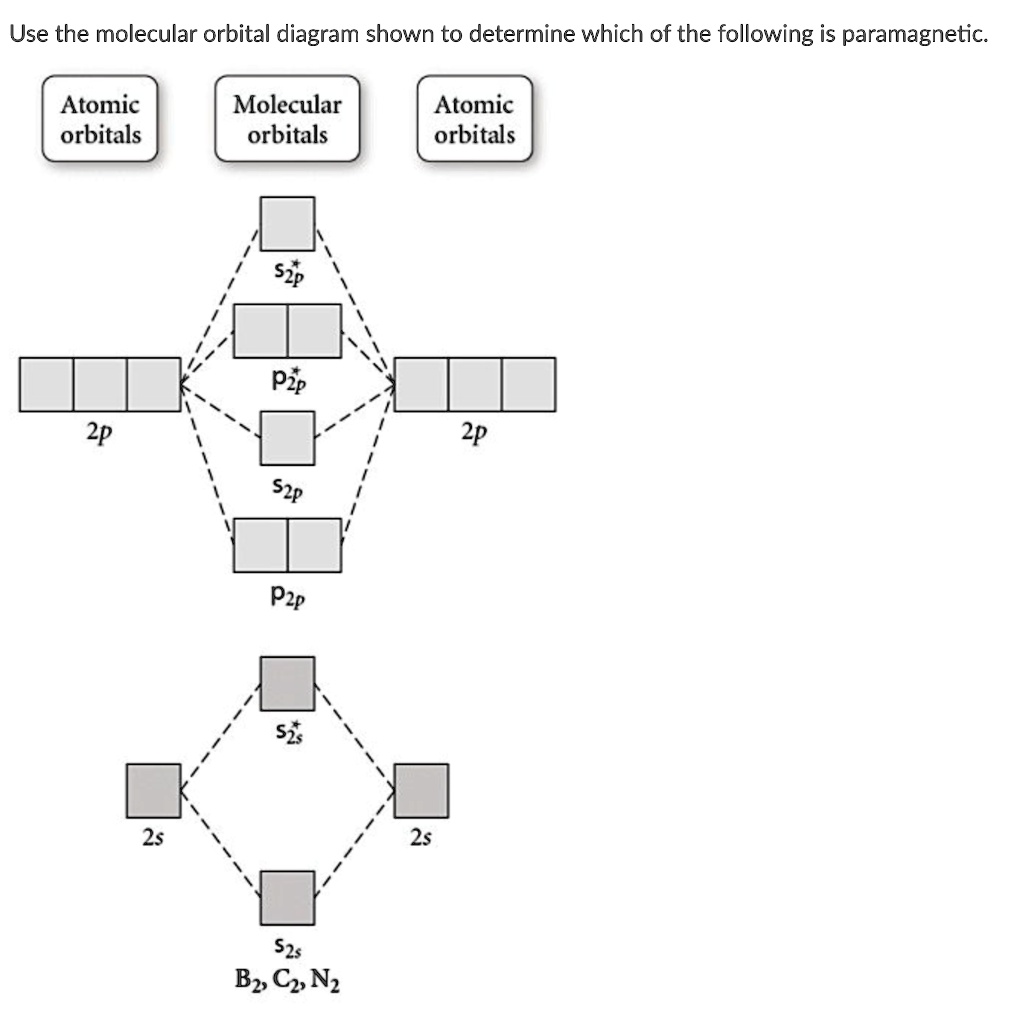
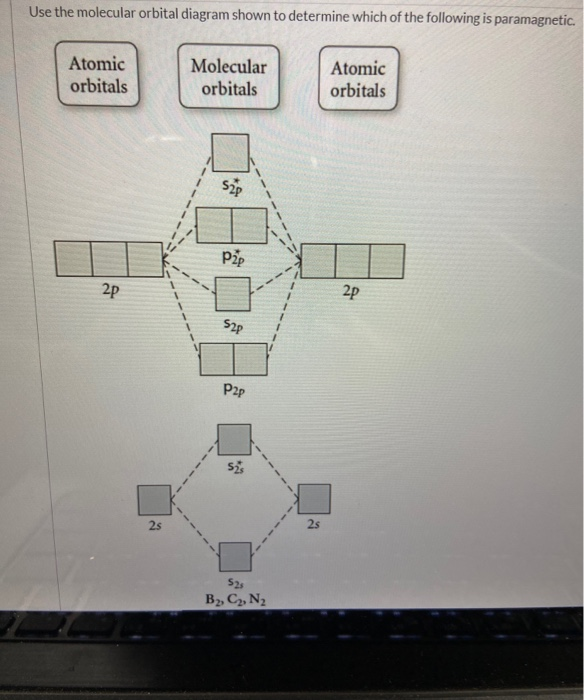
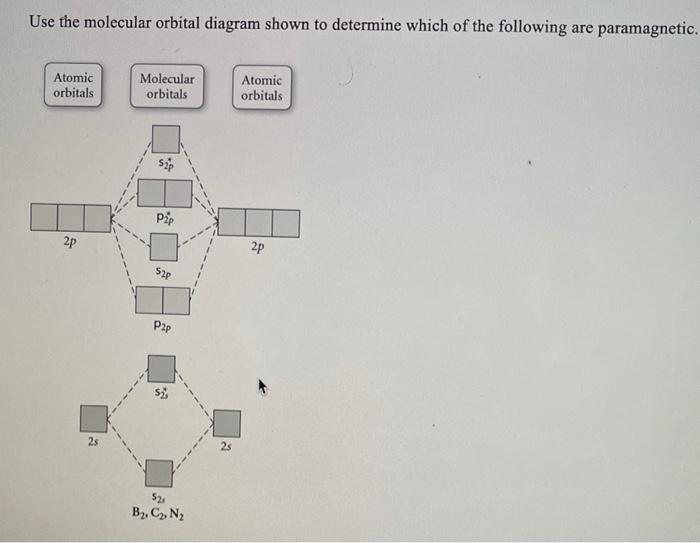
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. a) B2 b) C2^2- c) N2^2+ d) B2^2- e) B2^2+ Use the molecular ...
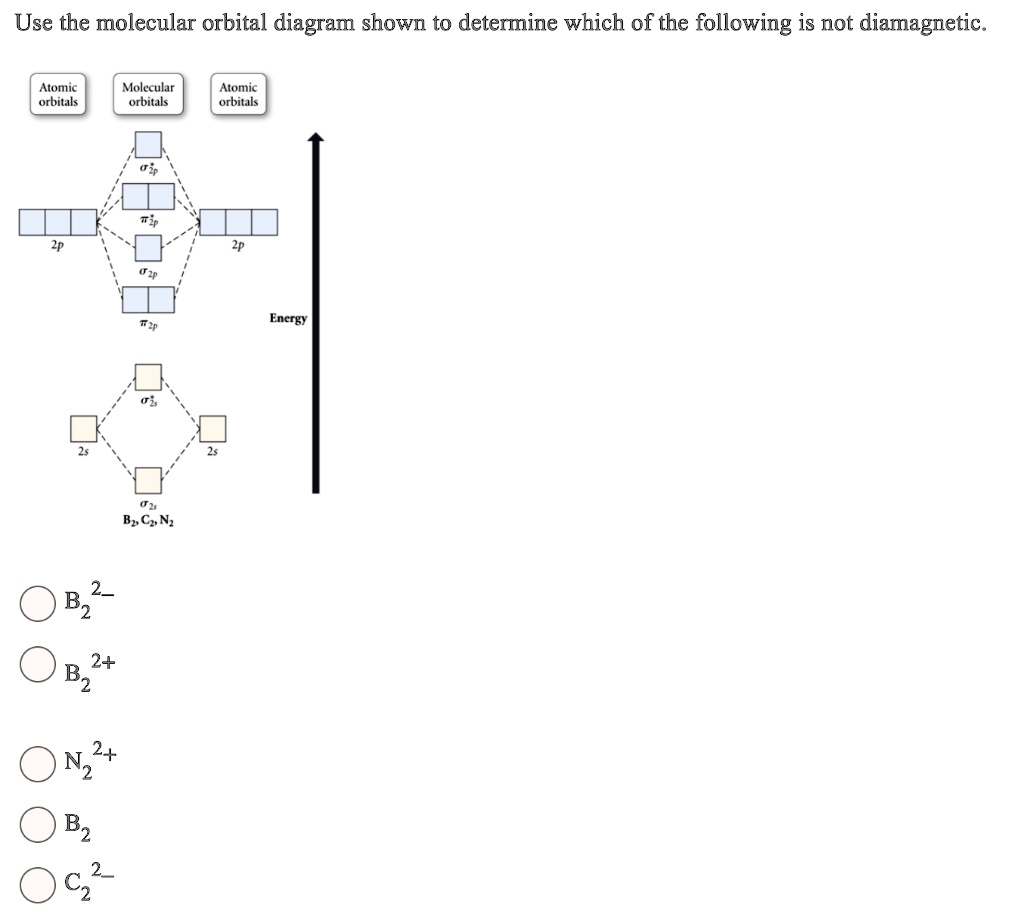
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic.
Transcribed image text: 10. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals ...
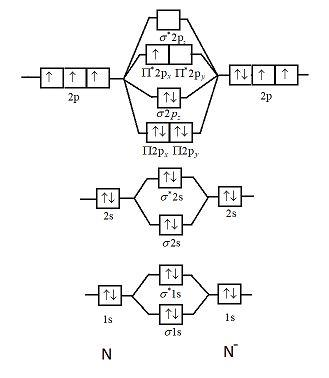
From the MOs generated on the prior page, the following two Molecular Orbital Diagrams are created. (Note: To simplify this content, some instructors only use one MO Diagram shown below instead of two for all 2nd period diatomic molecules. …
Apr 05, 2020 · 3 draw the molecular orbital diagram needed and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A asdfasdf b asdfasdf c asdf d f2 2 e none of the above are paramagnetic. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stablea n22 b b2c b22d c22 e c22 problem use the molecular orbital diagram shown to ...
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic..
Transcribed image text: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals ...
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory is the final theory pertaining to the bonding between molecules. In contrast to VSEPR and valence bond theory which describe bonding in terms of atomic orbitals, molecular orbital theory visualizes bonding in relation to molecular orbitals, which are orbitals that surround the entire molecule. The purpose of MO theory is to fill in the gap for some …
388 chApTer 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories • Count the number of electrons in a delocalized p system.(Section 9.6) • Explain the concept of bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals and draw examples of s and p MOs. (Section 9.7) • Draw molecular orbital energy-level diagrams and place electrons into them to obtain the bond orders and electron configurations …
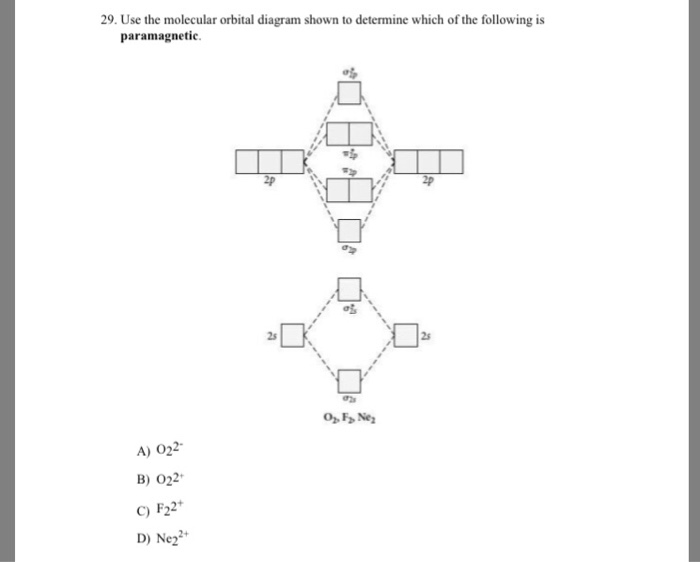
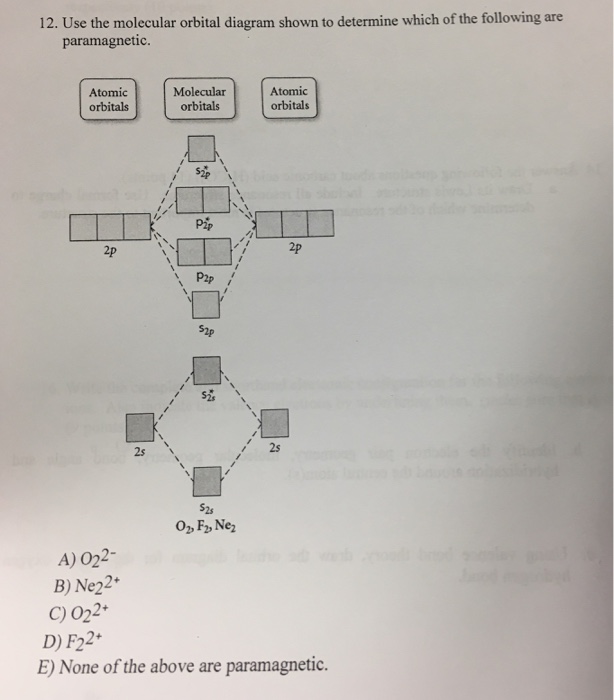
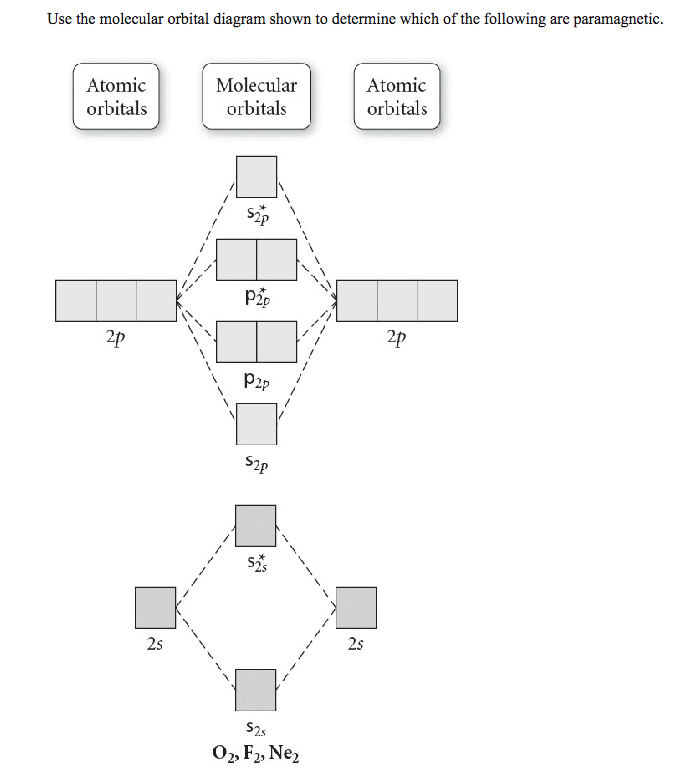
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A. Ne 22+ B. O 22+ C. F 22+ D. O 22- E. None of the above are paramagnetic. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Concept Videos.
Transcribed image text: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. (a) O^2-_2 (b) Ne^2+_2 (c) O^2-_2 (d) ...
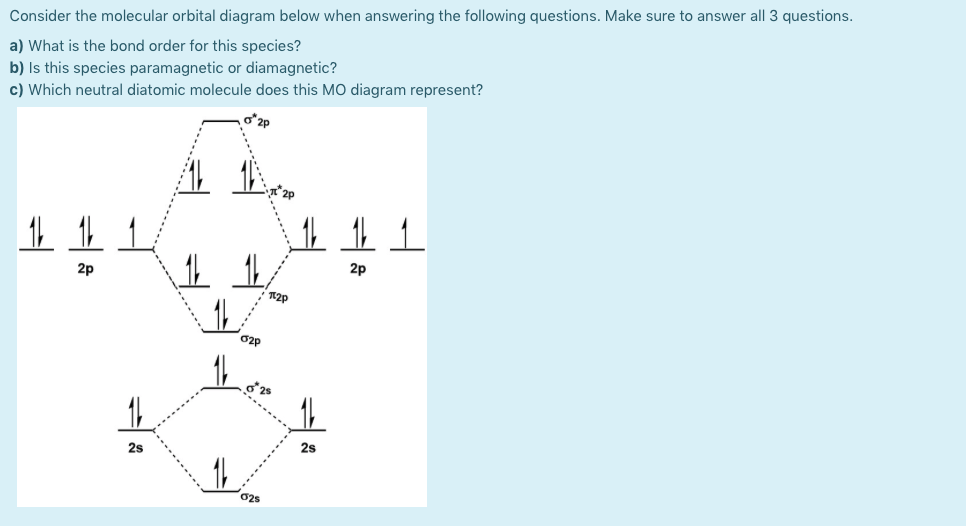
The molecular orbital energy diagram for the valence orbitals of the NO– ion is shown below. Use this diagram to answer the following questions. a) What is the bond order in NO– ? b) Is NO– diamagnetic, or is it paramagnetic? How can you tell? c) Which has the larger bond distance, NO– or NO? * O2p T2p T2p G2s
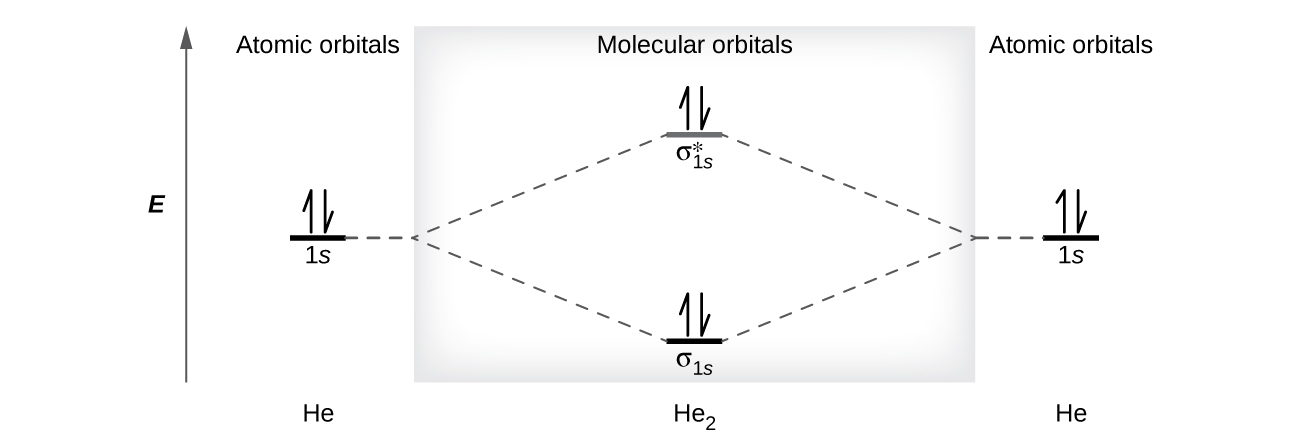
The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram . For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one orbital that can hold two electrons. The molecular orbitals formed by the combination of the atomic …
Transcribed image text: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals ...
For those ions that are paramagnetic, determine the number of unpaired electrons. _____ 9.81 Using Figures 9.35 and 9.43 as guides, draw the molecular orbital electron configuration for (a) B 2 +, (b) Li 2 +, (c) N 2 +, (d) Ne 2 2+. In each case indicate whether the addition of an electron to the ion would increase or decrease the bond order of ...
04.09.2021 · The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Each horizontal line represents one orbital that can hold two electrons. The molecular orbitals …
Mar 09, 2018 · Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. 2 use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. O 2 2 e. A o22 b ne22 c o22 d f22 e none of the above are paramagnetic.
Dec 16, 2021 · Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic.a. ne22+ b. o22+ c. f22+ d. o22- e. none of the above are paramagnetic. Use molecular orbital theory to predict whether or not each ...
Transcribed image text: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic (Recall: molecules with unpaired ...
Molecular orbital energy level diagram of N 2 molecule • Bond order = (8 2)/2 = 3 (N ≡ N)Orbital filling diagram for carbon. All nitrogen atoms in the 1,2,4-triazine ring, N-1, N-2, and N-4, are potential sites for proton attack. Sol: (d) In N-atom, number of valence electrons = 5 Due to the presence of one negative charge, number of valence electrons = 5 + 1 = 6. pairs of electrons …
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. Answer options: B2 B22+ N22+ C22- B22-. Expert Answer.
Practice Use MO theory to explain or decide the Molecular orbital practice problems Ch301 fall 2009 work 7 answer key Molecular Orbital Theory Purdue University April 17th, 2019 - Valence Bond Model vs Molecular Orbital Theory Construct a molecular orbital diagram for the O 2 molecule Click here to check your answer to Practice Problem 9 Bond Order The number of …
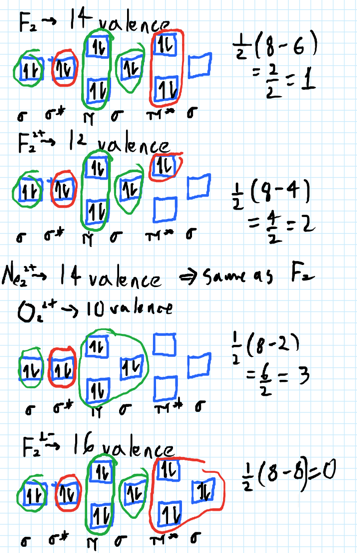
Answer to Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. None of the ions are paramagnetic. F 2 2+ O 2 2- O 2
A molecular orbital is a region of space in a covalent species where electrons are likely to be found. The combination of two atomic orbitals always forms two molecular orbitals; the bonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, and the antibonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy than the original atomic orbitals.
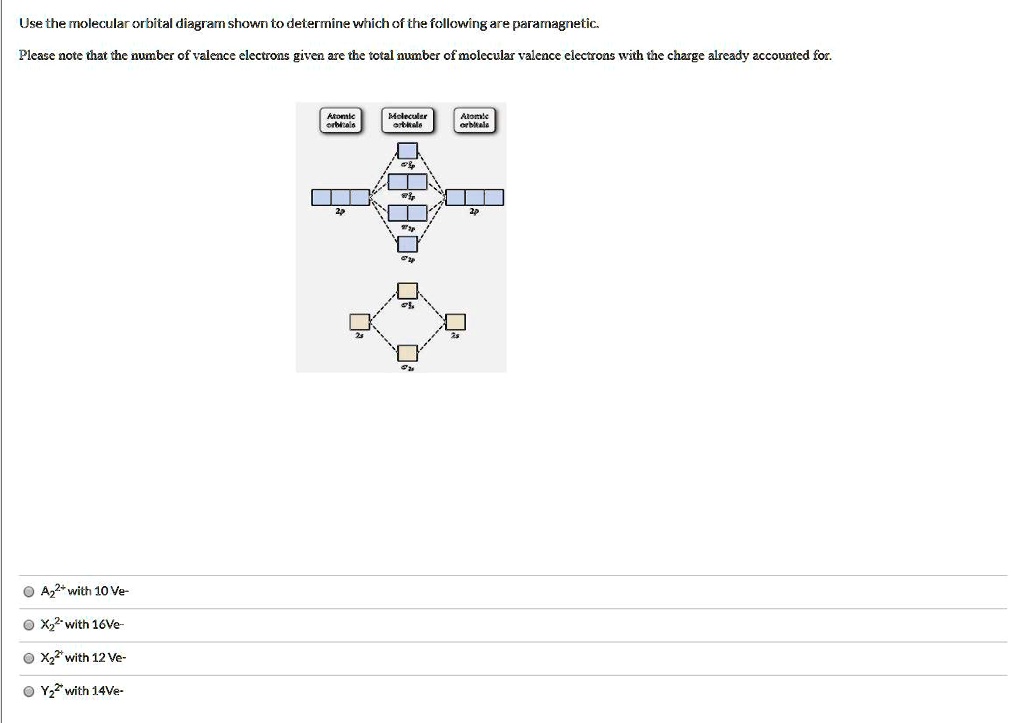
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following ions is fare paramagnetic. X 2+ , Y22+ Consider that Y22+ ion has 12 total valence electrons, and X 2+ ion has 10 total valence electrons Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals PSP 2P 2p PP 2 23 52 Select one: a. Both ions are diamagnetic b.

Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic.a. ne22+ b. o22+ c. f22+ d. o22- e. none of the above are paramagnetic.








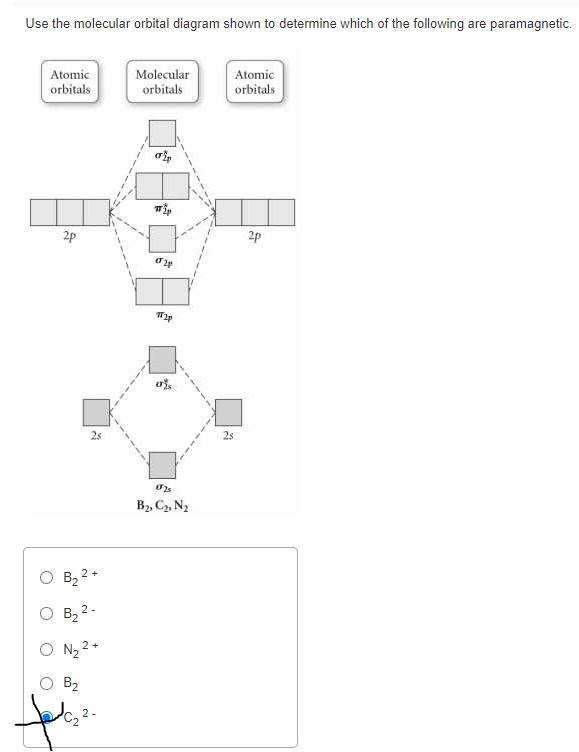







0 Response to "34 use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic."
Post a Comment