33 diagram of muscle fiber
Label this diagram of a muscle fiber, using these terms: myofibril, Z line, T tubule, sarcomere, sarcolemma, sarcoplasmic reticulum. Step-by-step solution Chapter 39, Problem 19TY is solved.
bundle and a single axon may innervate a few to 100's of muscle fibers at same time each muscle organ is composed of 1000's of motor units whole motor unit responds as "all or none" muscle cells cannot "partially" contract the fewer muscle cells/ motor unit more precise movement the muscle can make eg. eye: 10-23 fibers/axon hand: few
FG fibers are used to produce rapid, forceful contractions to make quick, powerful movements. These fibers fatigue quickly, permitting them to only be used for short periods. Most muscles possess a mixture of each fiber type. The predominant fiber type in a muscle is determined by the primary function of the muscle.

Diagram of muscle fiber
7. $15.00. Zip. Human Anatomy Muscle Organ Diagrams by Julie Ridge are part of my human anatomy series. This set contains the following 10 diagrams: Full body muscles, both anterior and posterior diagrams; Actin Myosin 5-step cycle; Muscle fiber diagram showing the muscle, fascicle, muscle fibers, myofibril, and.
Muscle Fiber Diagram Unlabeled is a high-resolution transparent PNG image. It is a very clean transparent background image and its resolution is 1210x849 , please mark the image source when quoting it.
SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBER DIAGRAM. Image: Skeletal Muscle Fibers. When viewing the I bands within the myofibril, it can be clearly seen that I bands are considered to run from one edge of the stack of filaments to the next. They take on a lighter shade due to the thin fibers of their creation. Despite the appearance of a distinctive border, the I ...
Diagram of muscle fiber.
Muscle Charts of the Human Body For your reference value these charts show the major superficial and deep muscles of the human body. Superficial and deep anterior muscles of upper body
Figure 9.13b A motor unit consists of a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates. Branching axon to motor unit Muscle fibers Axon terminals at neuromuscular junctions (b) Branching axon terminals form neuromuscular junctions, one per muscle fiber (photomicrograph 330x).
Muscle fibers are single muscle cells. When grouped together, they work to generate movement of your body and internal organs. You have three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
Muscle Fiber Diagram.Diagram with myofibril and muscle fibers. Diagram of the Structure of a Muscle Cell (also called a muscle fibre). PT on the Net (Esther Aguilar) Diagram with myofibril and muscle fibers. There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take.
In the diagram, individual muscle fibers are covered by this layer. a) K b) I c) L d) M e) A. c. In the diagram, one of the components of a myofibril is the structure labeled _____.? a) G b) H c) B d) J e) None of these choices are correct. b. In the diagram, what is the basic functional unit of a myofibril? a) B
Diagram of part of a muscle fiber showing the myofibrils. One myofibril extends from the cut end of the fiber. Small part of one myofibril enlarged to show the myofilaments responsible for the banding pattern. Each sarcomere extends from one Z disc to the next. Enlargement of one sarcomere (sectioned lengthwise).
The diagram provided shows how a sarcomere changes when a muscle fiber contracts. Which of the following best describes how the sarcomere changes? [A] The sarcomere shortens as the myosin pulls the actin filaments toward the M line. [B] The sarcomere extends as the actin filaments pull the myosin away from the M line.
Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched and are connected to one another at their ends by intercalated discs. An intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave-like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump. Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.
Start studying Anatomy: Muscle Fiber Diagrams. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Muscle Fiber Diagram Unlabeled. 1210*849. 0. 0. PNG. Images For Ear Anatomy Diagram Blank - Unlabelled Diagram Of The Ear. 1280*975. 0. 0. PNG. 6th Grade Muscle Diagram. 591*684. 0. 0. PNG. Small - Chloroplast Diagram Unlabeled. 516*596. 0. 0. PNG. The Peripheral Nervous System Is The Part Of The Nervous - Nervous System Diagram Unlabeled.
The human body has three different types of muscles. They include: skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, cardiac muscles. Skeletal muscles. Your skeletal muscles are attached to your bones via tendons. Each muscle is comprised of thousands of muscle fibers that are bundled together. Skeletal muscle is predominantly involved in movement.
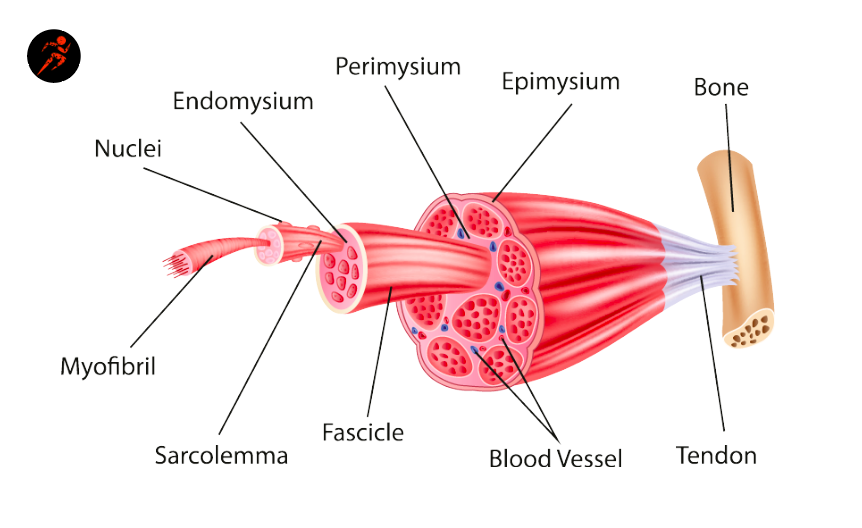
Figure 10.2.2 - Muscle Fiber: A skeletal muscle fiber is surrounded by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma, which contains sarcoplasm, the cytoplasm of muscle cells. A muscle fiber is composed of many myofibrils, which contain sarcomeres with light and dark regions that give the cell its striated appearance.
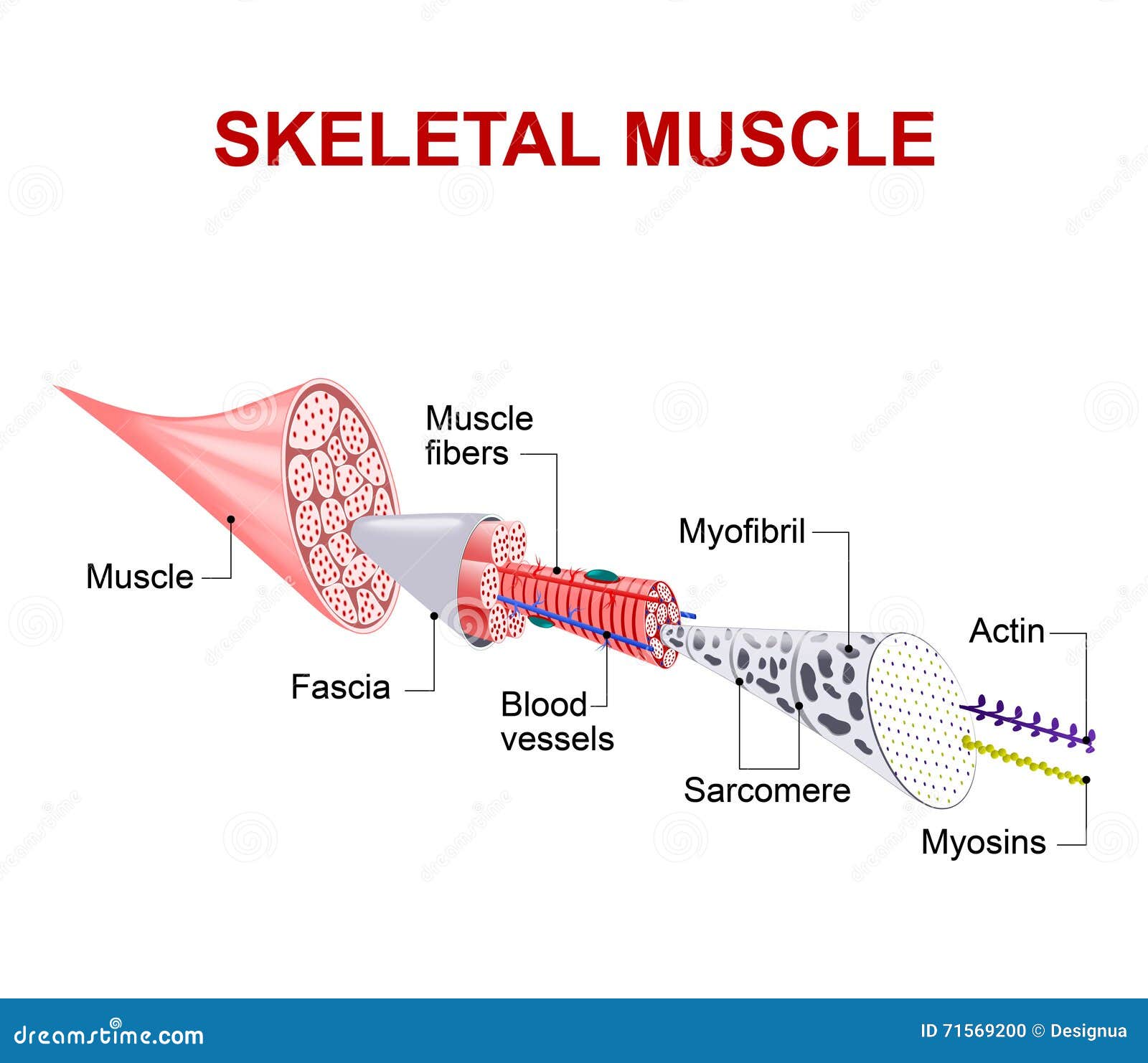
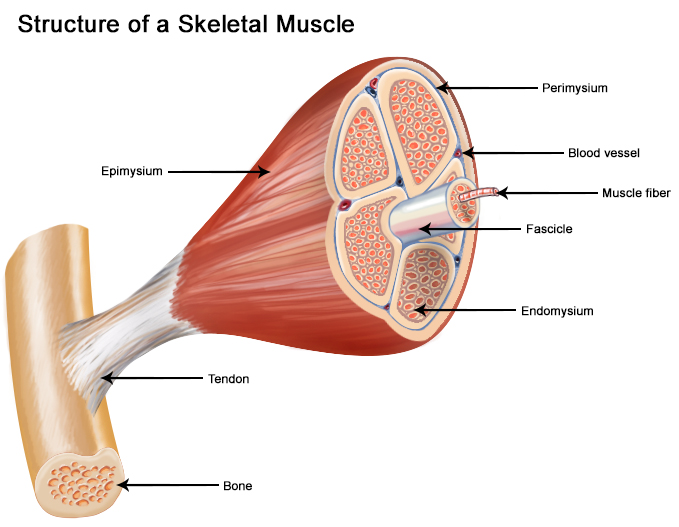
Skeletal muscle is made up of thousands of muscle fibres that run the length of the muscle. Each muscle fibre consists of many contractile units called myofibrils which run the length of each muscle fibre. Individual muscle fibres are wrapped with fascia and then further bound together by more fascia into bundles called fascicules.
Browse 845 muscle fiber stock illustrations and vector graphics available royalty-free, or search for muscle or maze to find more great stock images and vector art. muscle tissue seamless pattern Muscular tissue seamless pattern. Stock vector illustration of muscle cells in rows.
We'll just keep zooming until we get to the molecular level. So this myofibril, which is-- remember, it's inside of the muscle cell, inside of the myofiber. The myofiber is a muscle cell. Myofibral is a-- you can view it as a tube inside of the muscle cell. These are the things that are actually doing the contraction.
Cardiac muscle, in vertebrates, one of three major muscle types, found only in the heart. The neck muscles and massive triangular muscles of the back stabilize the head and shoulders and permit a range of complex movements. The above diagram is an action potential recorded in the ventricular cardiac cell of the heart.
Muscle cells (Muscle Fibers) Myofibrils Myofilaments Page 12. Summary • The three types of muscle cells in the body are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. • Skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue: epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium. • The striations of skeletal muscle cells are due to the organized arrangement of contractile ...
Muscle fibers are classified on the basis of their physiological behavior as fast (or fatigable) or slow (fatigue resistant), largely an expression of aerobic enzyme activity and calcium metabolism, and by myosin heavy chain isoform into type 1, types 2A, 2B and 2 ×. Type 2B is not expressed in human skeletal muscle. With only a few exceptions, each motor unit is composed of fibers of one ...
Relaxing skeletal muscle fibers, and ultimately, the skeletal muscle, begins with the motor neuron, which stops releasing its chemical signal, ACh, into the synapse at the NMJ. The muscle fiber will repolarize, which closes the gates in the SR where Ca ++ was being released. ATP-driven pumps will move Ca ++ out of the sarcoplasm back into the SR.
Diagram the process of cross-bridge cycling The Neuromuscular Junction The process of muscle contraction begins at the site where a motor neuron's terminal meets the muscle fiber—called the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Every skeletal muscle fiber in every skeletal muscle is innervated by a motor neuron at a NMJ.
Most skeletal muscles of the body are a mixture of all three types of skeletal muscle fibers, but their proportion varies depending on the usual action of the muscle. For example, postural muscles of the neck, back, and leg have a higher proportion of type I fibers.
Each skeletal muscle fiber is a skeletal muscle cell. Within each muscle fiber are myofibrils, long cylindrical structures that lie parallel to the muscle fiber.Myofibrils run the entire length of the muscle fiber. They attach to the plasma membrane, called the sarcolemma, at their ends, so that as myofibrils shorten, the entire muscle cell contracts (Figure 16.18).
The musculoskeletal system comprises one of the major tissue/organ systems in the body. The three main types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle groups.[1][2][3] Skeletal muscle attaches to the bone by tendons, and together they produce all the movements of the body. The skeletal muscle fibers are crossed with a regular pattern of fine red and white lines, giving the ...
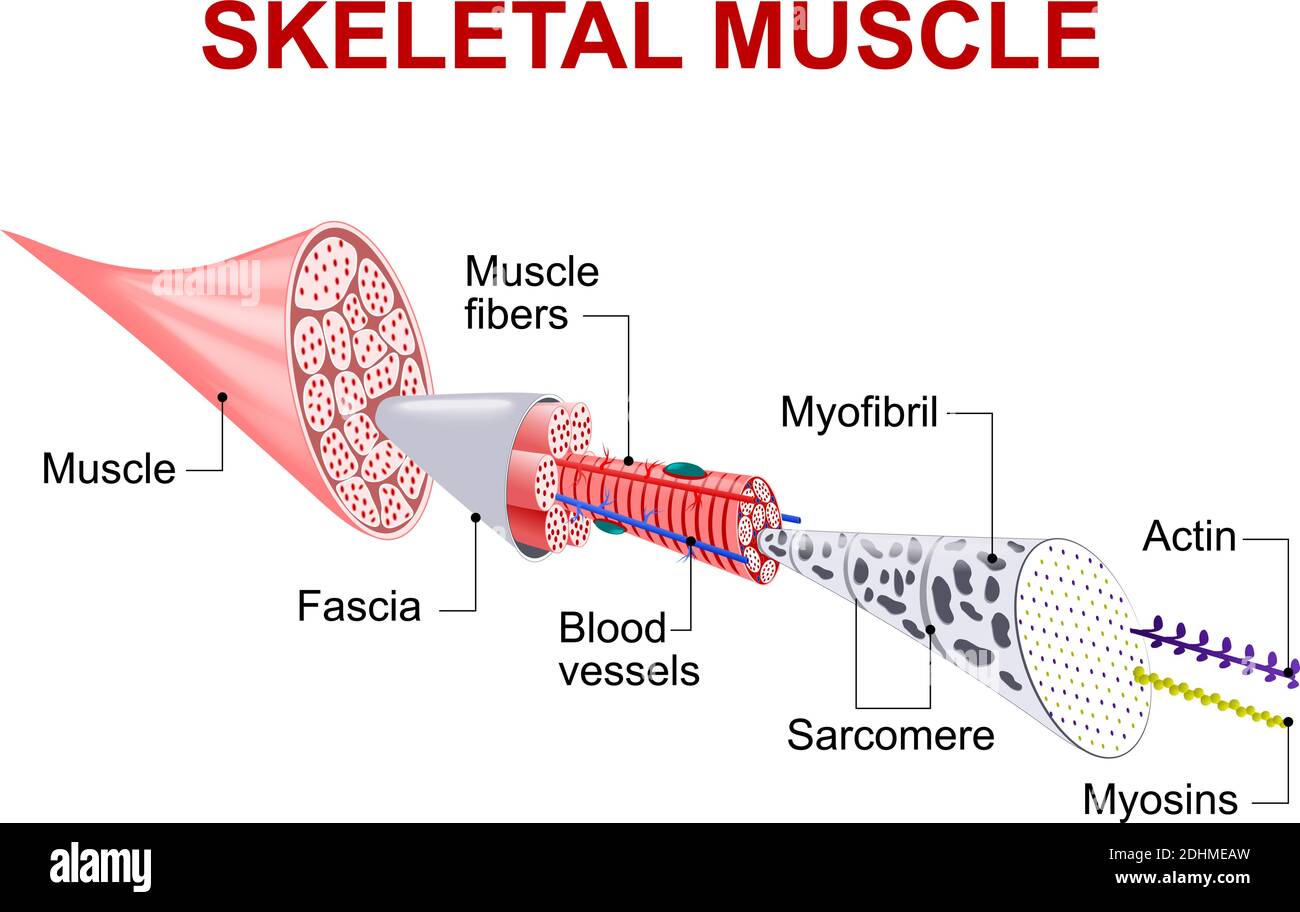




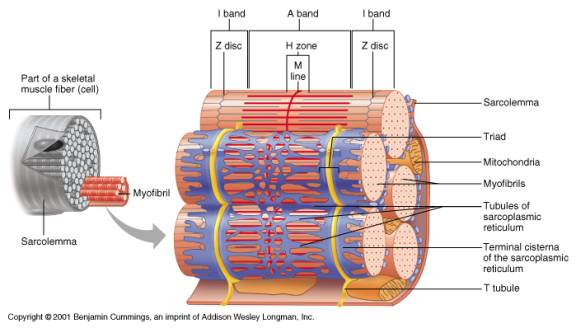


![3: Structure of a muscle fiber. Image: [Spe98] | Download ...](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Kolja-Kaehler/publication/47861059/figure/fig2/AS:669428580642827@1536615619762/Structure-of-a-muscle-fiber-Image-Spe98.png)

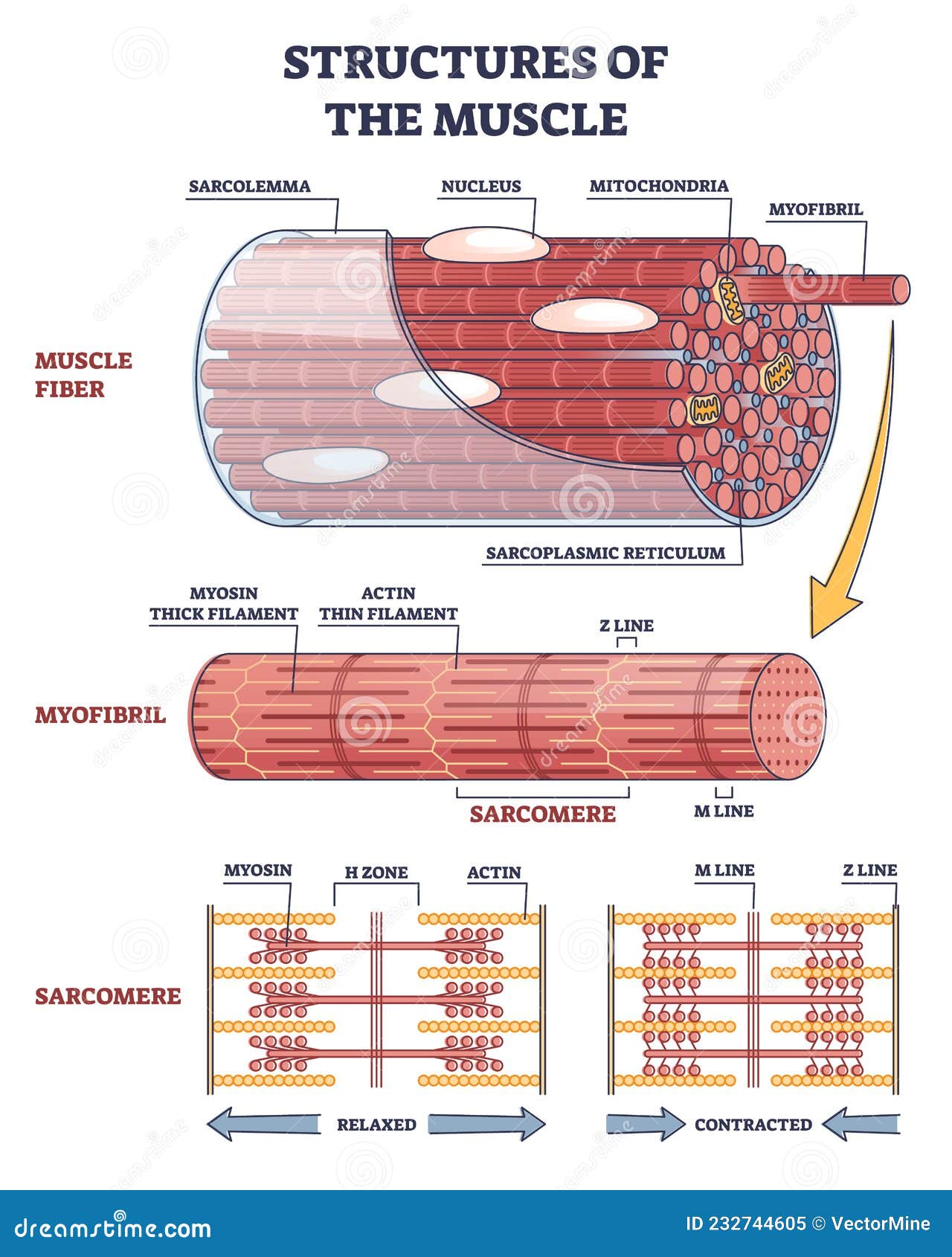



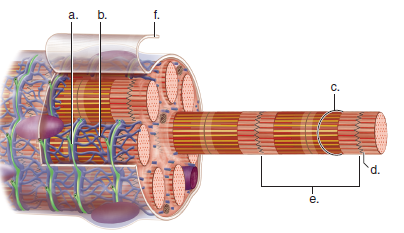








0 Response to "33 diagram of muscle fiber"
Post a Comment