39 convex mirror ray diagram
Concave and Convex Mirror: In this article, we will discuss what are Concave Mirror and Convex Mirror, how they are formed, Concave and Convex Mirror differences, examples, ray diagrams, uses, and much more.But before understanding what is a Concave and Convex mirror, let's understand what is a Mirror. Take Mock Test On Reflection And Refraction Now Ray Diagram for a Convex Mirror •The object is in front of a convex mirror. •The image is virtual. •The image is upright. •The image is smaller than the object. Section 23.3. Notes on Images •With a concave mirror, the image may be either real or virtual.
The ray parallel to the principal axis and the ray that hits the center of the mirror are drawn. This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for concave and convex spherical mirrors. By manipulating the object and mirror locations, you can create real or virtual images.

Convex mirror ray diagram
Convex Mirror Image. A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here.. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror. In this video from The Physics Classroom's video tutorial series, Mr. H demonstrates how to draw a ray diagram for objects located in front of convex mirrors... Description of how to draw ray diagrams for convex mirrors for grade 10 science
Convex mirror ray diagram. While making ray diagrams, these two rules are important for students. The purpose of drawing ray diagrams is to find the location, size, direction, and type of image formed by a convex mirror. The steps involved in drawing ray diagrams are quite simple and easy to understand. A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram. Hi, in this video, I have created an animation to show the travel of Rays, to explain where they start from, where they end up. The concept explanation helps... Spherical & parabolic mirrors. Spherical mirrors, radius of curvature & focal length. Convex & concave mirror ray diagrams. This is the currently selected item. Practice: Ray diagrams. Practice: Ray diagrams and curved mirrors. Mirror formula derivation. "Objects in the mirror are ..." actually images in the mirror.
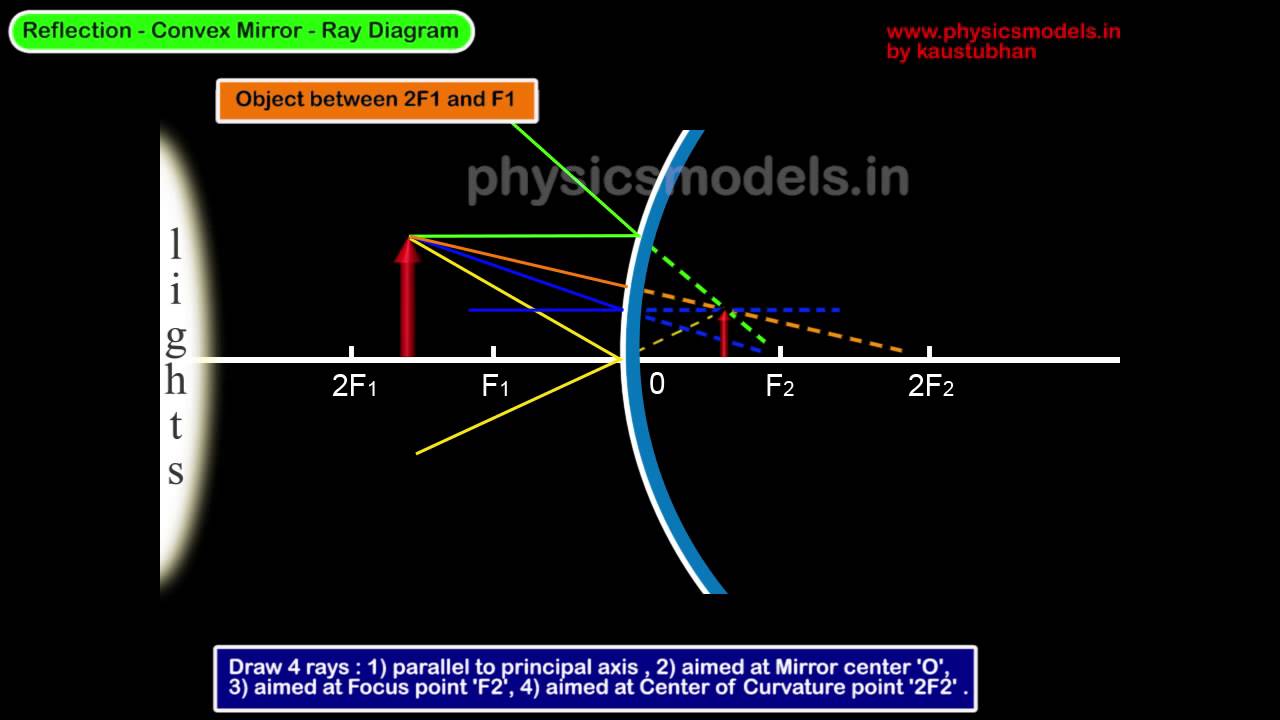
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray. A ray diagram that shows the position and the magnification of the image formed by a convex mirror. The animation illustrates the ideas of magnification, of real and virtual images. Click and drag the candle along the optic axis. Click and drag its flame to change its size. Convex Mirror - Ray diagram. Last updated at April 23, 2020 by Teachoo. For a Convex Mirror, The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirror So, there will only be 2 cases. They are Object is Placed at Infinity Object is Placed between Principal axis and Infinity Virtual, erect, and diminished images are always formed with convex mirrors, irrespective of the distance between the object and the mirror. Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors. Guidelines for Rays Falling on the Concave and Convex Mirrors. When a ray strikes concave or convex mirrors obliquely at its pole, it is reflected obliquely.
Ray Diagram for Convex and Concave Mirror. A mirror is a part of a smooth and highly polished reflecting surface. Most commonly used mirrors are plane mirrors. A spherical mirror is a part of a spherical reflecting surface. There are two types of spherical mirrors - convex mirror and concave mirror. Convex Mirror- Ray Tracing. Convex Mirror- Ray Tracing. Log InorSign Up. a = − 4. 4 7. 1. f = 2. 1 4. 2. focal point. 3 ... Answer (1 of 2): As with a concave lens (negative/diverging element), there is only one typical use case for a convex mirror. For all real objects (real = in front of the mirror) you get a diminished, erect=uninverted and virtual image (virtual = inside of the mirror). The range goes from M=0 - ... Convex Mirror Ray Diagram Draw And Explain The Ray Diagram Formed A Convex Mirrora When A. Convex Mirror Ray Diagram Ray Diagrams When An Object Is Placed Opposite To A Concave Mirror All Six Cases. Convex Mirror Ray Diagram An Object Is Placed At A Distance Of 10 Centimetres From A Convex.
oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Concave and Convex Mirrors. Concave and Convex Mirrors - GeoGebra Materials. Description. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror.
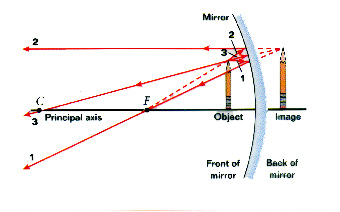
The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a convex mirror will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.
Ray diagrams can be used to determine the image location, size, orientation and type of image formed of objects when placed at a given location in front of a mirror. The use of these diagrams was demonstrated earlier in Lesson 3 and in Lesson 4.Ray diagrams provide useful information about object-image relationships, yet fail to provide the information in a quantitative form.
Set your child up for success with Lido, book a class today! Our top 5% students will be awarded a special scholarship to Lido. Q40) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors Ray 1: parallel to the axis then from F. Ray 2: Vertex. Ray 3: from C. • image is virtual, upright, and smaller than object Ray 4: towards F, then parallel. Concave mirrors: Shaving and makeup mirrors Solar cookers Satellite dishes (for EM waves)
CONVEX MIRRORS Extra Practice Worksheet a) Draw a ray diagram for each to locate the image. b) State the characteristics (SALT). *note- diagrams are not to scale S A L T: 1) 2) 3) SNC 2D - Light and Geometric Optics S A L T: 4) 5) 6) Author: Louise Macwilliam Created Date ...
Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a convex mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and to learn the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. The intersection of these two reflected rays gives the position of an image of the object. In case of a convex mirror any ...
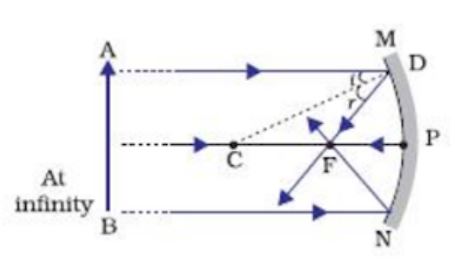
For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t
The Physics Classroom » Curriculum Corner » Reflection and Mirrors » Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors. The document shown below can be downloaded and printed. Teachers are granted permission to use them freely with their students and to use it as part of their curriculum. Visit the Usage Policy page for additional information.
Draw The Ray Diagram And Find The Position Nature And Size Of Image Formed By A Convex Mirror If The Object Is Placed I At Infinity Ii Between Infinity And The Pole
Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams A spherical mirror is a reflective segment of a sphere with a radius of curvature R. It can be convex (outside surface of a sphere) or concave (inside surface). First we will consider a concave spherical mirror. The mirror has a radius R, and the distance from the mirror to the object is p.
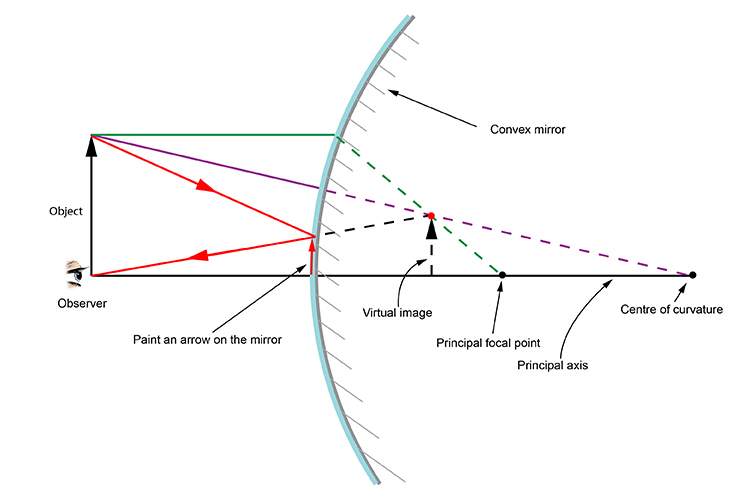
There are, again, two alternative methods of locating the image formed by a convex mirror. The first is graphical, and the second analytical. According to the graphical method, the image produced by a convex mirror can always be located by drawing a ray diagram according to four simple rules: . An incident ray which is parallel to the principal axis is reflected as if it came from the virtual ...
Mirror ray tracing is similar to lens ray tracing in that rays parallel to the optic axis and A convex mirror forms a virtual image. Ray diagrams for mirrors. You must be able to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors, and be able to calculate image and object heights, Spherical Mirrors: concave and convex mirrors.
Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams. Two possibilities of the position of the object are possible in the case of a convex mirror, which is when the object at infinity and the object between infinity and the pole of a convex mirror. Object at infinity. Whenever the object is kept at infinity, we observe that a point-sized ...
Convex Mirrors Mirror equation still holds, but: f& R now negative Virtual image, always upright. Liu UCD Phy9B 07 9 Summary: Signs ... Ray Diagram for Thin Lenses Ray 1 goes out from Q parallel to the axis & passes through F2. Ray 2 goes through the center of the lens unaffected
Below are the ray diagram rules for convex mirrors, which allow you to predict where the light rays from an object will travel and then focus in the eye of an observer. Rule 1. Take a line from an object parallel to the principal axis and where it touches the convex mirror take another line to the principal focal point. Rule 2.
Description of how to draw ray diagrams for convex mirrors for grade 10 science
In this video from The Physics Classroom's video tutorial series, Mr. H demonstrates how to draw a ray diagram for objects located in front of convex mirrors...
Draw Ray Diagrams To Show The Principal Focus Of A A Concave Mirror B Convex Mirror Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Convex Mirror Image. A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here.. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror.

A To Construct A Ray Diagram We Use Two Light Rays Which Are So Chosen That It Is Easy To Know Their Directions After Reflection Use These Two Rays To Locate The

Ppt Convex Mirrors Diverging Mirrors How To Locate An Image Using Ray Diagrams Powerpoint Presentation Id 2640548

Draw A Ray Diagram To Show The Use Of A Convex Mirror For The Formation Of Images Having The Following Science Light Reflection And Refraction 10787219 Meritnation Com

Draw Ray Diagram To Show The Formation Of Image When The Object In Front Of A Convex Mirror Is At Any Other Position Near The Mirror Snapsolve



















0 Response to "39 convex mirror ray diagram"
Post a Comment