38 stratified cuboidal epithelium diagram
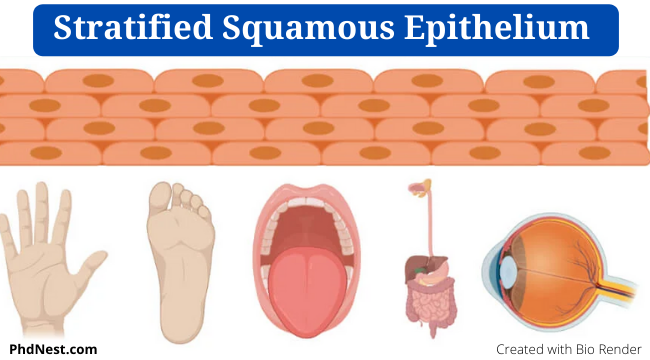
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium is a form of stratified squamous epithelium in which the apical segment of the cells has a stiff coating of keratin and numerous layers deep to it. Keratin is an intracellular protein that protects the skin and underlying tissues from heat, pathogens, and pollutants. Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium. Of unknown organism, from personal collection. Stratified cuboidal epithelial tissues are more rare comparing to other epithelial types. This picture was taken from salivary gland and the duct showed that the inner most layer, or right around the lumen, contains cuboidal cells but the rest of the layers may or ...
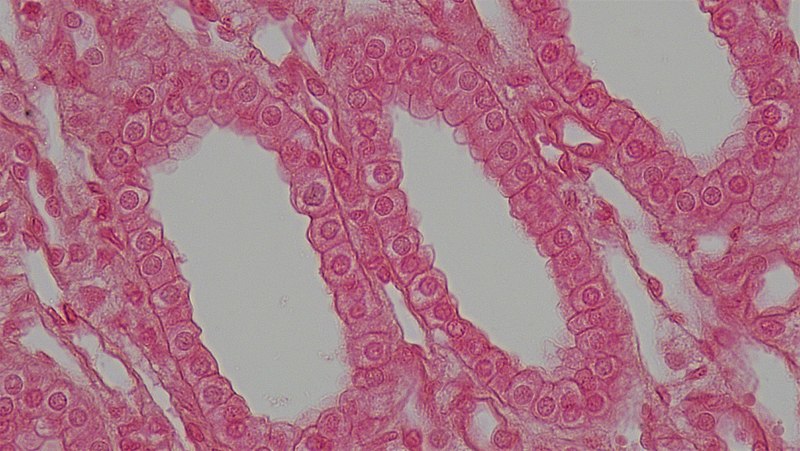
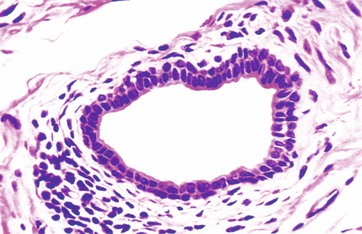
Stratified cuboidal epithelium (40x objective lens) This section shows the stratified cuboidal epithelium that forms the walls of the ducts of sweat glands. Two ducts cut in cross section can be seen in the upper half of this image. Note that the wall of the duct is composed of two layers of cuboidal cell.

Stratified cuboidal epithelium diagram
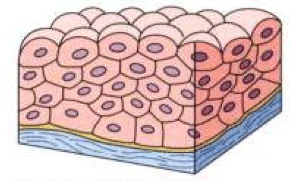
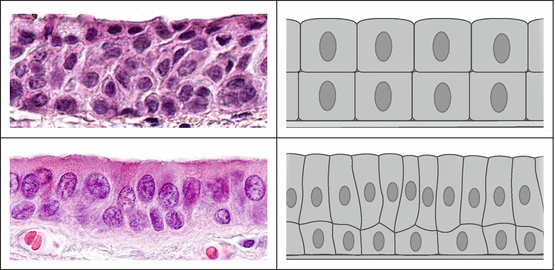
In this image, you will find basement membrane, cuboidal epithelial cells, duct lumen in Stratified cuboidal epithelium. Stratified cuboidal epithelium description: generally two layers of cubelike cells. Stratified cuboidal epithelium function: protection. Stratified cuboidal epithelium location: largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary gland, and salivary glands. Tissue Types, Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium - the surface cell,…: Tissue Types (Connective, MUSCLE, Epithelium, Nervous), Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium - the surface cell, Transition epithelium - lines a few organs and are rounded and domelike. They can slide past one another and change shape All the surfaces of our body, except the teeth and joints, are covered with some type of epithelium. Our bodies are made up of different types of tissues or materials. These include the bones and blood (connective tissue), different types of muscles (muscle tissue), and the brain, nerves, and spinal cord (nervous tissue). However, the surface of our body needs to be protected from elements like sunlight and wind, and so do our delicate organs which are located in empty spaces. At the same time, the body needs to control which substances are present inside it, and which are being removed. All these roles are played by a kind of thin tissue called the ‘epithelium.’ However, this epithelium may be made of a single layer of cells called simple epithelium, or several layers called stratified epithelium. In the following sections, we will learn about a type of simple epithelium, called the simple cuboidal epithelium.
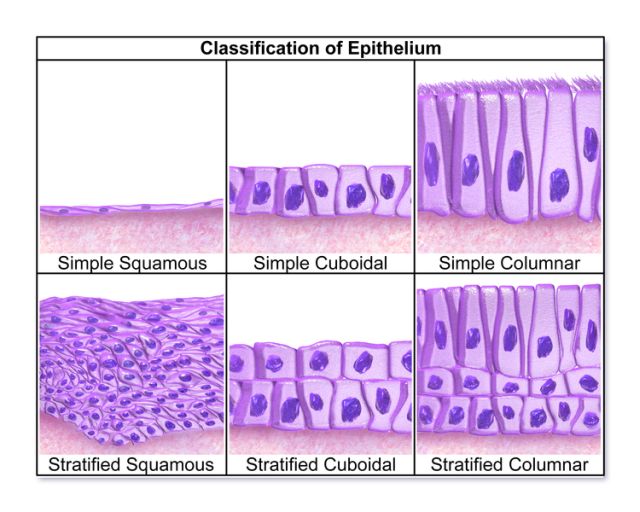
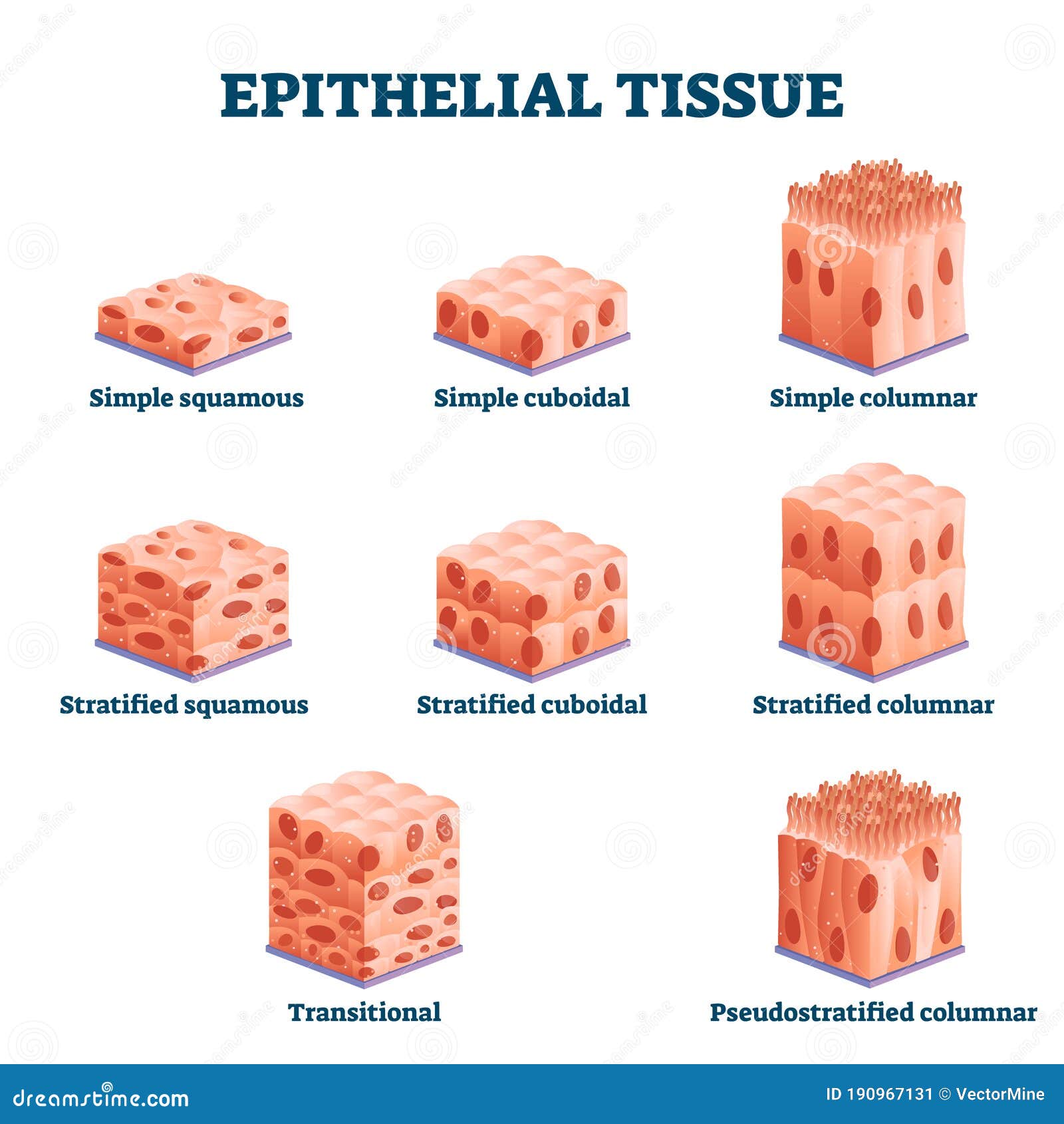
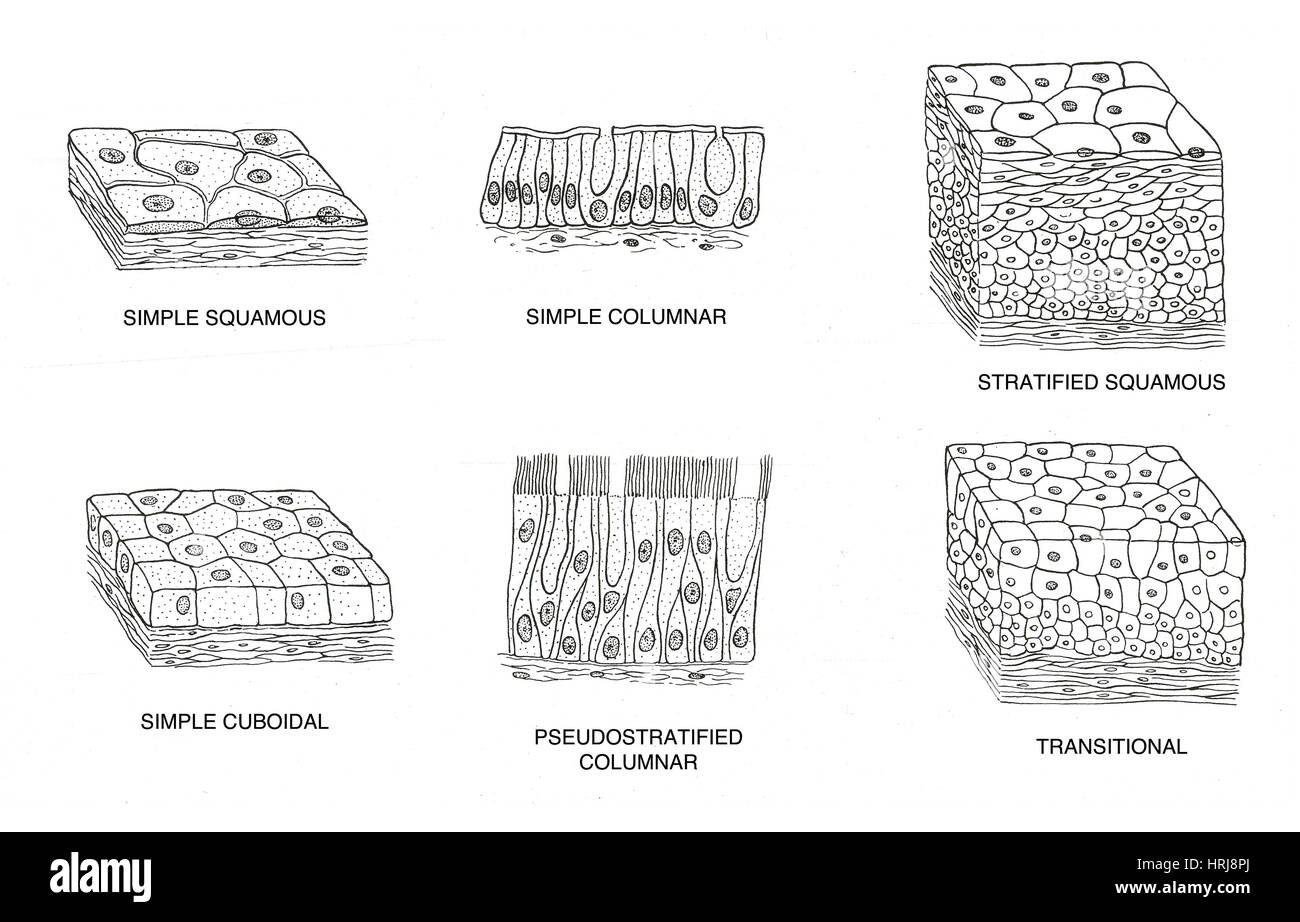
Stratified cuboidal epithelium diagram. Stratified Epithelium. A stratified epithelium consists of multiple stacked layers of cells. This epithelium protects against physical and chemical damage. The stratified epithelium is named by the shape of the most apical layer of cells, closest to the free space. Stratified squamous epithelium is the most common type of stratified epithelium in the human body. The apical cells appear squamous, whereas the basal layer contains either columnar or cuboidal cells. Stratified squamous epithelium definition. The stratified squamous epithelium consists of several layers of cells, where the cells in the apical layer and several layers present deep to it are squamous, but the cells in deeper layers vary from cuboidal to columnar. Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium •Largest ducts of sweat, mammary and salivary glands. Identify the tissue type and a location where it is found. Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium •Trachea and most of the upper respiratory tract. Identify the tissue type and a Sep 30, 2021 · Stratified cuboidal epithelium is quite thin, consisting of two or three layers of cuboidal cells. This type is relatively rare, occurring specifically in the lining of excretory ducts, such as salivary and sweat glands. Its main function is structural reinforcement, since it is not significantly involved in absorption or secretion. Stratified columnar epithelium
Simple Epithelium- it is composed of one layer of a cell and mostly has a secretory or an absorptive function. Compound (Stratified) Epithelium- it is made up of two or more than two layers of cells and mostly has a protective function. The glandular epithelium is made up of cuboidal or columnar cells. They are specialised for secretion. The simple squamous epithelium is different from other types of epithelial tissue such as simple cuboidal, simple columnar, and stratified squamous epithelium in that it is only made of one layer ... Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Stratified cuboidal epithelium usually consists of only two or three layers of cuboidal cells. This type of epithelium is confined to the linings of the large ducts of sweat glands, salivary glands, and the pancreas, where its stratification probably provides a more robust lining than would simple epithelium. Transitional Epithelium Functions, Location and Diagram. Transitional epithelium is also called Uroepithelium or Urothelium (because it lines the urinary system), and it is a type of stratified epithelial tissue in which the surface cells change shape from being rounded to squamous in nature. Transitional epithelium is located in the urinary ...
Sep 22, 2021 · Definition of Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium. An epithelium with cuboidal cells inside the apical layer and columnar cells with in deeper layer is called stratified cuboidal epithelium. Because of this, cells inside the deeper layers of squamous epithelium could vary from those in the top layer. Position as well as role of the epithelial tissue influence the apical surface modification. A. Simple columnar epithelium. Slide 29 (small intestine) View Virtual Slide Slide 176 40x (colon, H&E) View Virtual Slide Remember that epithelia line or cover surfaces. In slide 29 and slide 176, this type of epithelium lines the luminal (mucosal) surface of the small and large intestines, respectively. Refer to the diagram at the end of this chapter for the tissue orientation and consult ... Stratified squamous keratinising epithelium. This type of epithelium is protective against chemical and mechanical damage, and water loss, and is found in skin, and oral epithelia. This is an example of thin skin. There are around 8-10 layers of cells. It's difficult to see the basal lamina in the region of the dividing cells, in the basal layer. Form the Outer Covering of the skin and some internal organs. Form the Inner Lining of blood vessels, ducts and body cavities, and the interior of the respiratory, digestive, urinary and reproductive systems. Glandular epithelia. Constitute the secretory portion of glands. Simple squamous epithelium. Most delicate epithelium.
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Definition. Stratified cuboidal epithelium is a type of epithelial tissue found mainly in glands, which specialize in selective absorption and secretion by the gland into blood or lymph vessels. In general, epithelial tissue is any group of cells lining a body cavity or body surface. Stratified cuboidal epithelium describes an epithelial tissue with two aspects.
Sep 28, 2020 · Stratified cuboidal epithelium definition. Stratified cuboidal epithelium has multiple layers of cells in which the apical layer is made up of cuboidal cells while the deeper layer can be either cuboidal or columnar. As in the case of stratified squamous epithelium, the cells in the deeper layers might be different than the layer on the top. The modification of the cells on the apical surface is based on the location and function of the epithelial tissue.
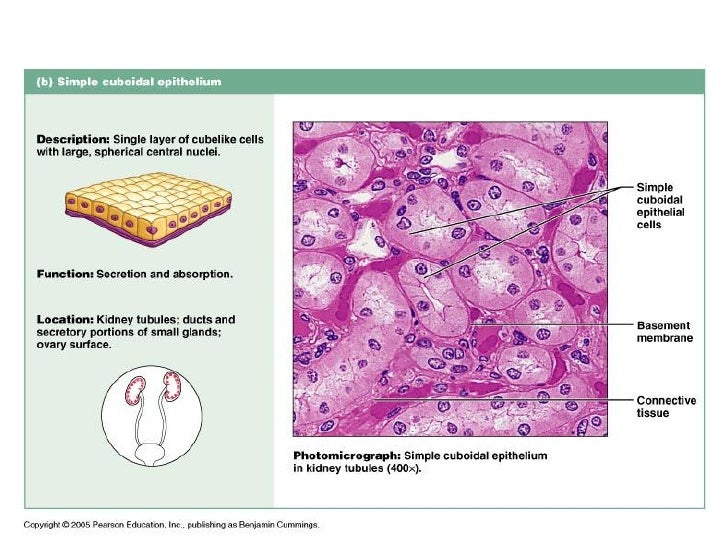
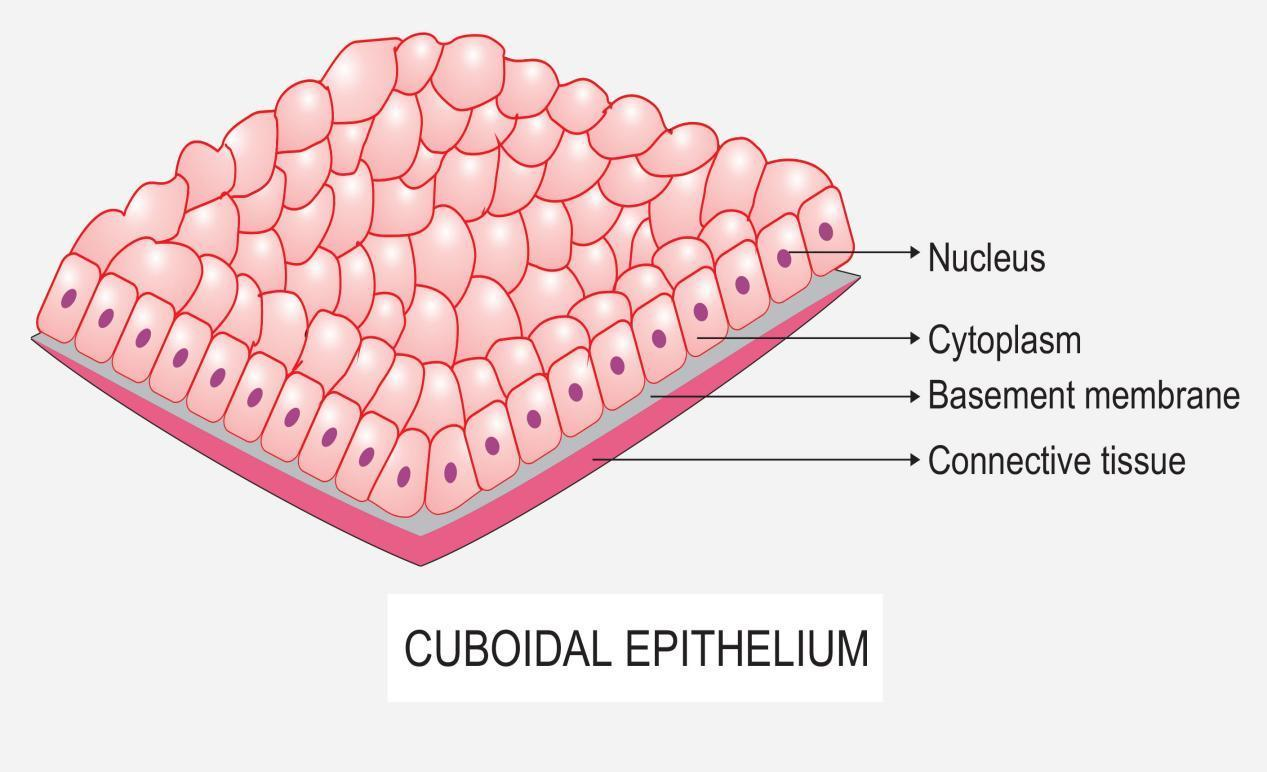
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium (Figure 4.3b) Simple cuboidal epithelium consists of a single layer of cube-shaped cells. This epithelium forms the secretory cells of many glands, the walls of the smallest ducts of glands, and the walls of many tubules in the kidney. Its functions are the same as those of simple columnar epithelium.
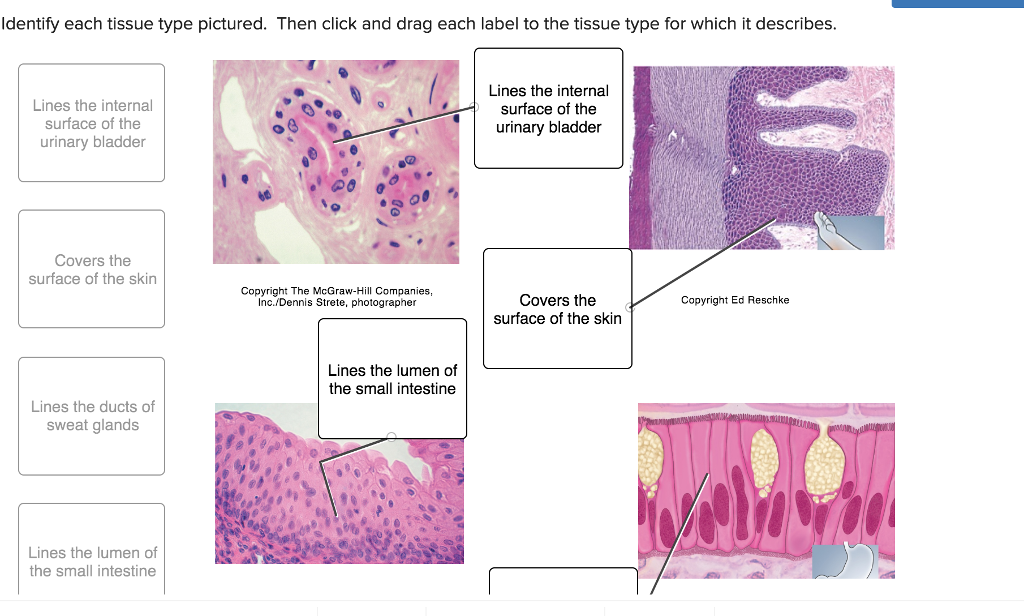
Stratified cuboidal. Stratified squamous epithelium. Simple columnar epithelium. Simple squamous. Tags: Question 8 . SURVEY . 60 seconds . ... Q. Which type of epithelial tissue stretches and is found in the bladder and other urinary organs? answer choices . Transitional. Simple Cuboidal.

10 Integumentary System Skin Ideas Integumentary System Anatomy And Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology
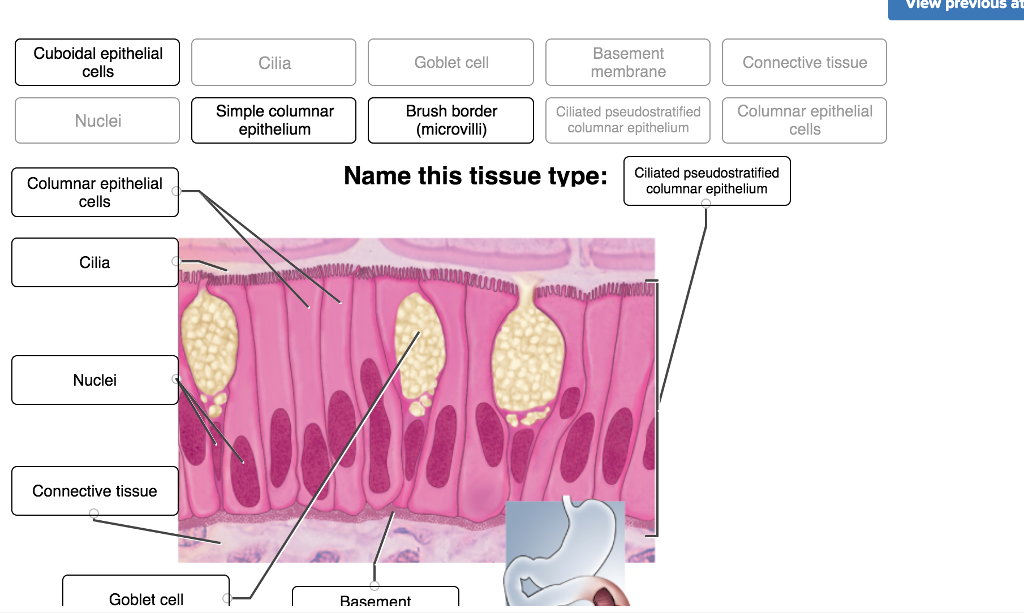
Question: 50 pm 4. Identify the type of epithelium indicated by the diagram below: a. Simple columnar b. Stratified columnar c. Pseudostratified columnar d. Stratified cuboidal 5. Identify the structures indicated by the black arrows: a. Microvilli b. Cilia c. Villi d. None of the above 6.
J. Bean In women, stratified cuboidal epithelium can be found in the ovaries. Stratified cuboidal epithelium is one of the many types of epithelial tissue. It is less common than other types of epithelial tissue, and it has several locations in the body: sweat gland ducts; egg-producing vesicles, or follicles, of the ovaries; and sperm-producing ducts, or seminiferous tubules, of the testis.
Q.3. Assertion : Urinary bladder can considerably expand to accommodate urine. Reason : It is lined by stretchable squamous epithelium. Answer Answer: (c) Urinary bladder is not lined by squamous epithelium but by transitional epithelium which is a stretchable compound epithelium. It has a single layer of cuboidal cells at the base, 2-3 middle layers of large polygonal cells and a superficial ...
Epithelium is a tissue that lines the internal surface of the body, as well as the internal organs. Simple epithelium is one of the types of epithelium that is divided into simple columnar epithelium, simple squamous epithelium, and simple cuboidal epithelium. Bodytomy provides a labeled diagram to help you understand the structure and function of simple columnar epithelium.
Epithelial Tissue. It is the protective tissue of animal body.The cells are tightly packed,form continuos sheet,very little or no intercellular spaces,covers most of the organs. They lie on a delicate non-cellular basement membrane which contain special form of matrix called collagen. 2)Form lining of mouth and alimentary canal,protect these ...
Epithelium (/ ˌ ɛ p ɪ ˈ θ iː l i ə m /) is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue.It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with little intercellular matrix.Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities ...
PLAY. Match. Gravity. Draw out 8 types of epithelial tissue diagram. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. Simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, nonkeratinized stratified squamous, keratinized stratified squamous, stratified cuboidal, stratified, columnar, pseudo-stratified columnar, transitional.
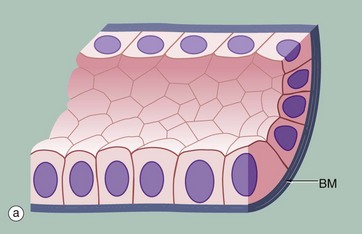
Stratified Columnar Epithelium Anatomy. In this image, you will find basement membrane, stratified columnar epithelium, underlying connective tissue, urethra in Stratified columnar epithelium anatomy. Stratified columnar epithelium description: several cell layers, basal cells usually cuboidal; superficial cells elongated and columnar.
Transitional epithelium is a stratified tissue made of multiple cell layers, where the cells constituting the tissue can change shape depending on the distention in the organ. When the organ is filled with fluid, cells on the topmost layer of this epithelium can stretch and appear flattened. Alternately, they can also appear cuboidal with a ...
A stratified squamous epithelium is a stratified epithelium with squamous (flattened and scale-like) epithelial cells in the top layer. Cuboidal or columnar cells may be seen in the deeper layers. Some stratified squamous epithelia are extensively keratinized, whereas others are keratinized either minimally or not at all.
All the surfaces of our body, except the teeth and joints, are covered with some type of epithelium. Our bodies are made up of different types of tissues or materials. These include the bones and blood (connective tissue), different types of muscles (muscle tissue), and the brain, nerves, and spinal cord (nervous tissue). However, the surface of our body needs to be protected from elements like sunlight and wind, and so do our delicate organs which are located in empty spaces. At the same time, the body needs to control which substances are present inside it, and which are being removed. All these roles are played by a kind of thin tissue called the ‘epithelium.’ However, this epithelium may be made of a single layer of cells called simple epithelium, or several layers called stratified epithelium. In the following sections, we will learn about a type of simple epithelium, called the simple cuboidal epithelium.
Tissue Types, Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium - the surface cell,…: Tissue Types (Connective, MUSCLE, Epithelium, Nervous), Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium - the surface cell, Transition epithelium - lines a few organs and are rounded and domelike. They can slide past one another and change shape
In this image, you will find basement membrane, cuboidal epithelial cells, duct lumen in Stratified cuboidal epithelium. Stratified cuboidal epithelium description: generally two layers of cubelike cells. Stratified cuboidal epithelium function: protection. Stratified cuboidal epithelium location: largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary gland, and salivary glands.


















0 Response to "38 stratified cuboidal epithelium diagram"
Post a Comment