38 molecular orbital diagram for cn
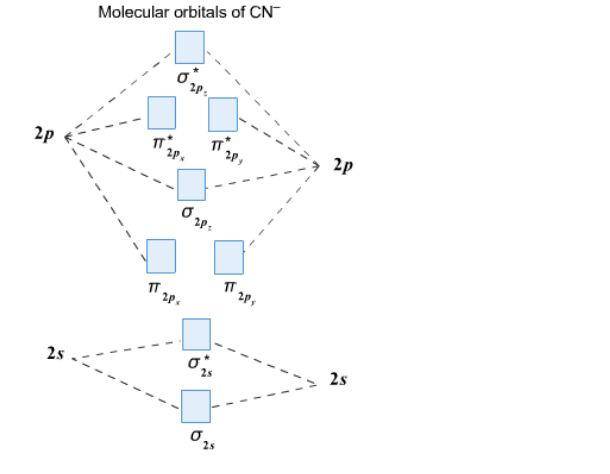
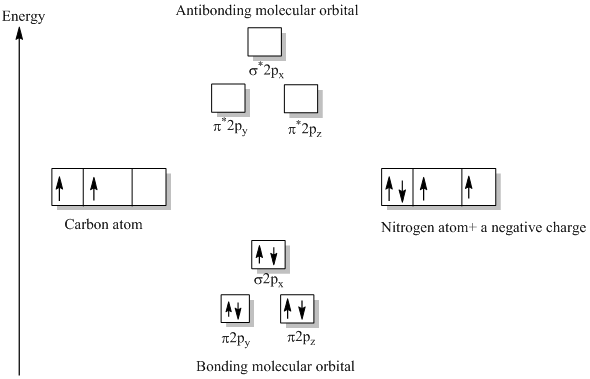
Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of. Although we have ignored the remaining p-orbitals, their inclusion in a molecular orbital treatment does not lead to any additional bonding, as may be shown by activating the fluorine correlation diagram below. Another type of MO (the π orbital) may be formed from two p-orbitals by a lateral overlap, as shown in part A of the following diagram ...
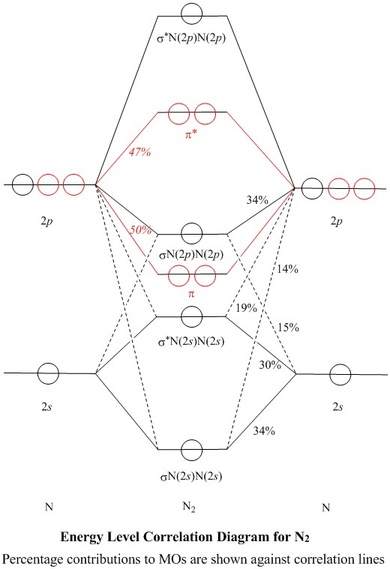
The molecular orbital energy diagram for N₂ is shown below. Based on this diagram, what is the bond order of N₂? D) 3-- BO=12 (number of bonding electrons − number of antibonding electrons) BO =12 (number of bonding electrons − number of antibonding electrons) BO = 12(10−4)=3 . What is the mass percentage of O in CO₂? 72.71%. What is the mass percentage of Cl in hydrochlorothiazide ...
Molecular orbital diagram for cn
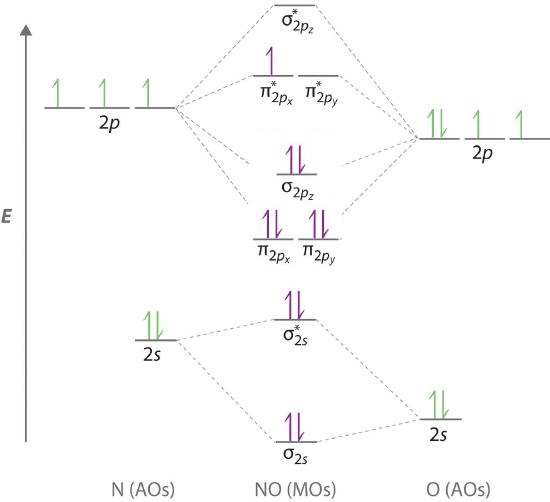
According to Merriam-Webster and the Online Etymology Dictionary, the word "molecule" derives from the Latin "moles" or small unit of mass.. Molecule (1794) – "extremely minute particle", from French molécule (1678), from New Latin molecula, diminutive of Latin moles "mass, barrier". A vague meaning at first; the vogue for the word (used until the late 18th century only in Latin form) can ... The CN– energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the antibonding π* electron. b. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons. c. The HOMO is the 2p orbital, which can interact with the 1s of the H+, as in the diagram at right. The bonding orbital has an energy near that of the π orbitals; the antibonding orbital becomes the highest energy orbital. 2s 2s ... 10:14Dr. Shields shows you how to draw the MO correlation diagram for cyanide (CN-), calculate the MO bond ...25 Jan 2015 · Uploaded by Shawn Shields
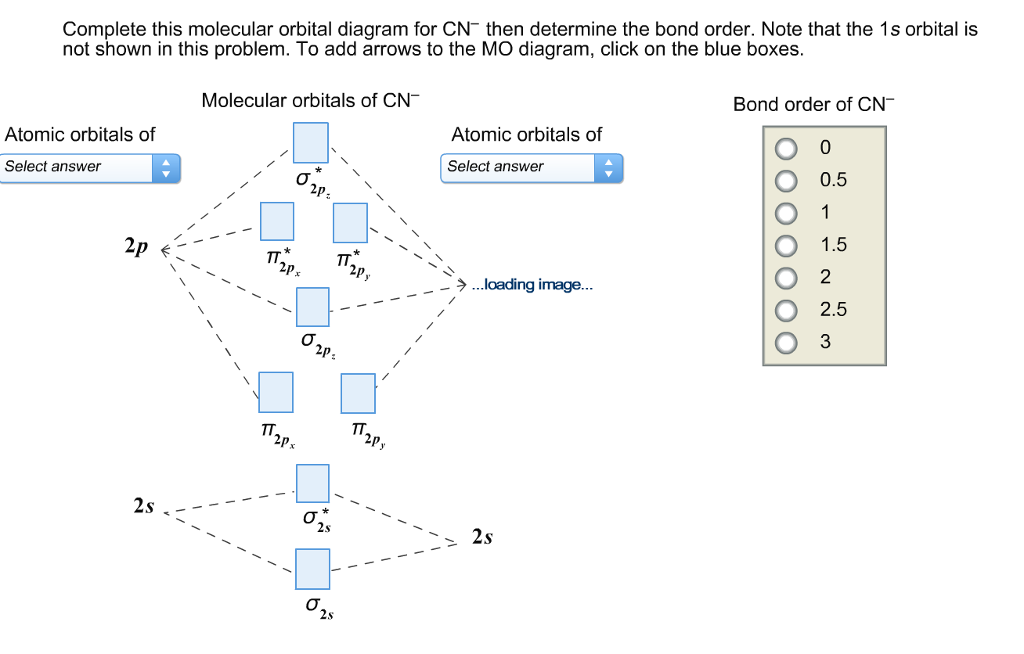
Molecular orbital diagram for cn. 21 May 2014 · 3 answersHere is the MO for CN-, just take away a single electron from the MO since CN is neutral. Vijayta Gupta is right, the N atom is lower in energy. Molecular orbital diagram of dinitrogen molecule, N 2. There are five bonding orbitals and two antibonding orbitals (marked with an asterisk; orbitals involving the inner 1s electrons not shown), giving a total bond order of three. Atomic nitrogen, also known as active nitrogen, is highly reactive, being a triradical with three unpaired electrons. Free nitrogen atoms easily react with most ... Also, using the Molecular orbital diagram of CN-we can also find its bond order which helps us to predict its bond length and stability as well. Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. Problem: Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN– then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. FREE Expert Solution. 93% (316 ratings) FREE Expert Solution. We’re being asked to complete the molecular orbital diagram of CN-and then determine the bond order.
The molecules are said to be stable if the number of electrons in the bonding molecular orbitals is greater than that in anti-bonding molecular orbitals. • Bond ...1 answer · Top answer: Concepts and reason • The molecular orbital theory explains the bonding in terms of the combination and organization of atomic orbitals of an atom which ... Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram. MO Theory: the bonding orbital will be lower in energy, the an7bonding The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in ... Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of Figure \(\ PageIndex{6}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for HCl. to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). mix atomic orbitals on different atoms to get Molecular Orbitals. The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion). Dot structures and molecular geometry. Drawing dot structures . This is the currently selected item. Drawing Lewis diagrams. Worked example: Lewis diagram of formaldehyde (CH₂O) Worked example: Lewis diagram of the cyanide ion (CN⁻) Worked example: Lewis diagram of xenon difluoride (XeF₂) Exceptions to the octet rule. Practice: Counting valence electrons. Practice: Lewis diagrams ...
3 Jan 2021 — Because each alkali metal (M) has an ns1 valence electron configuration, the M2 molecule has two valence electrons that fill the σns bonding ... 2:32Next: · Construction of MO Diagrams for Simple Polyatomic Molecules · Molecular Orbital Diagrams ...21 Jun 2018 · Uploaded by TAP into Chemistry 3:11How to make molecular Orbital diagramhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYC-ndQ6Lww&t=6s.6 May 2018 · Uploaded by BEST CLASSES Molecular orbital Diagram for Cn-mo diagram of cn hunt research group right you have been asked to draw the mo diagram for cn a heteronuclear diatomic don t panic take it one step at a time and you will have a plete mo diagram before you know it this is meant to be an interactive exercise so arrange for some pieces of blank paper a pencil a pen and an eraser molecular orbital theory ...
Complete This Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cn Then Determine The Bond Order Note That The 1s Orbit Not Shown In This Problem To Add Arrows To The Mo Diagram Click On The
3:26Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN– then determine the bond order. 235 views235 views. Feb 23, 2021.23 Feb 2021 · Uploaded by OneClass

How Can One Tell From The Mo Diagram Of The Cyanide Ion That The Homo Is Carbon Centred Chemistry Stack Exchange
Answer (1 of 5): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here’s a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i...

Diagram Orbital Molekul Unduh Gratis Kimia Orbital Molekul Diagram Heteronuclear Molekul Diagram Orbital Molekul Gambar Png
Solved Determine the molecular orbital diagrams from atomic | Chegg.com. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Determine the molecular orbital diagrams from atomic orbitals for CN+, CN, and CN-. (You do NOT need to submit your diagrams). From your molecular orbital diagrams, answer the following questions. 1.
CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram. CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. It belongs to the cyano group and consists of carbon and a nitrogen atom having a triple bond. It carries a charge of -1 and is a conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide (HCN).
Orbital Structure 35 Images The Effects Of Orbital Overlap On The Electronic Band Molecular Orbital Diagram Cn Untpikapps Electronic Orbitals
10.11.2021 · The molecular orbital diagram of BeCl2 will be drawn by combining atomic orbitals of beryllium atom and group orbitals of chlorine atom having similar energy and symmetry around a molecular axis. The 3s group orbitals of chlorine atom will remain non-bonding because their energy is very low as compared to the 2s and 2p atomic orbitals of beryllium atom. Similarly, 3px* and 3py* …
10:14Dr. Shields shows you how to draw the MO correlation diagram for cyanide (CN-), calculate the MO bond ...25 Jan 2015 · Uploaded by Shawn Shields
The CN– energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the antibonding π* electron. b. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons. c. The HOMO is the 2p orbital, which can interact with the 1s of the H+, as in the diagram at right. The bonding orbital has an energy near that of the π orbitals; the antibonding orbital becomes the highest energy orbital. 2s 2s ...
According to Merriam-Webster and the Online Etymology Dictionary, the word "molecule" derives from the Latin "moles" or small unit of mass.. Molecule (1794) – "extremely minute particle", from French molécule (1678), from New Latin molecula, diminutive of Latin moles "mass, barrier". A vague meaning at first; the vogue for the word (used until the late 18th century only in Latin form) can ...

Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagrams For The Following Diatomic Molecules Polyatomic Ions Indicate Their Bond Orders And Rank Them In Order Of Increasing Bond Strength A Cn B Co C F 2 D N 2
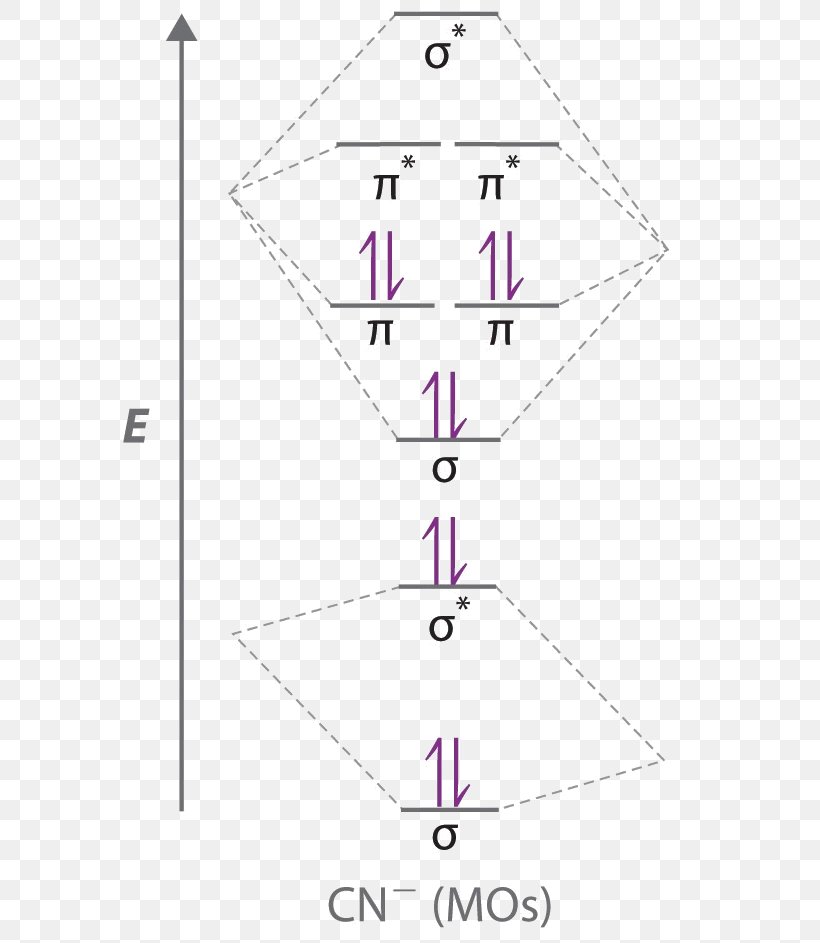
Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic Orbital Cyanide Png 631x943px Diagram Anion Area Atomic Orbital Bond Order Download
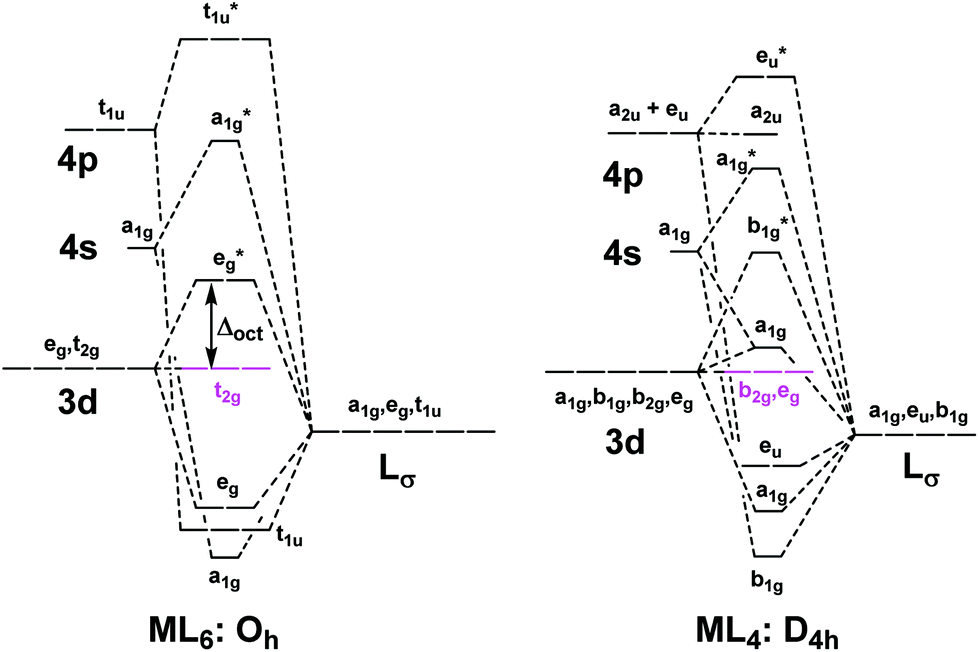
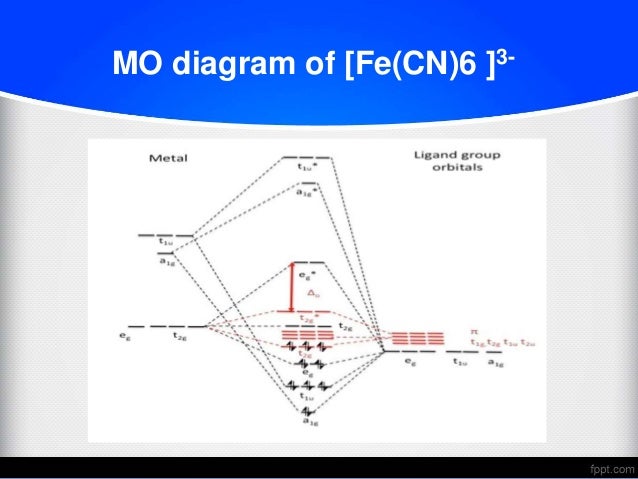
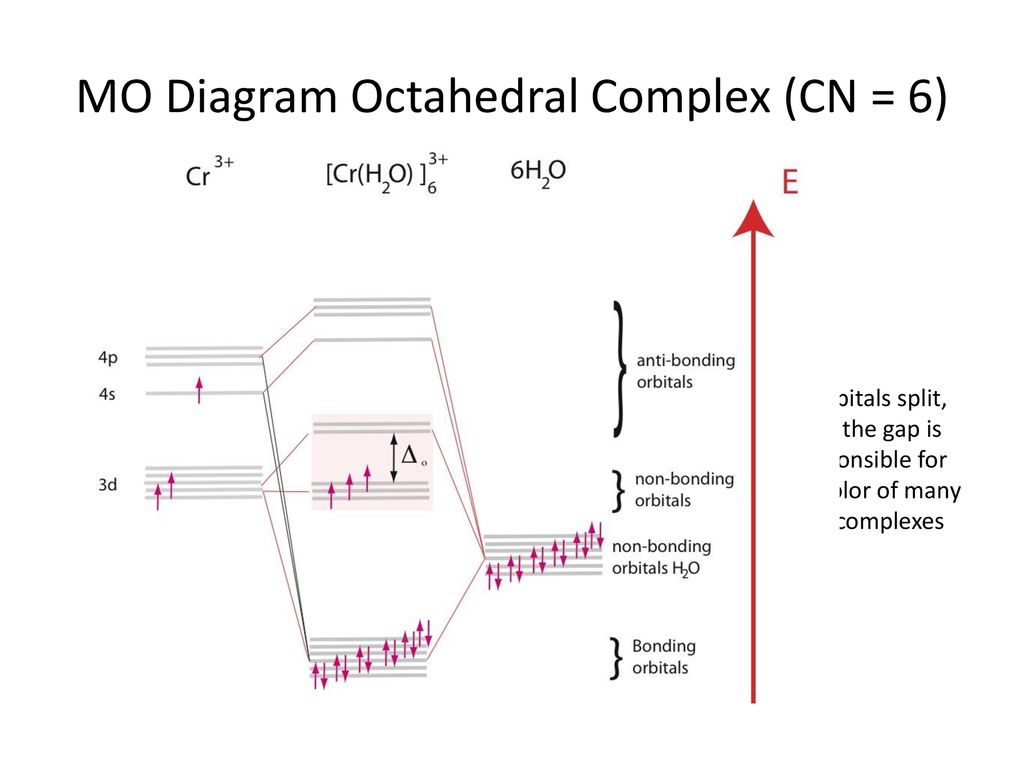
D Orbital Energy Levels In Planar M Ii F 4 2 M Ii Nh 3 4 2 And M Ii Cn 4 2 Complexes The Nature Of M L












0 Response to "38 molecular orbital diagram for cn"
Post a Comment