38 concave lens ray diagram notes
central axis. And the green ray reflects from the mirror at the central axis, so the reflected ray is symmetric about the central axis. distance i in terms of the object distance p and the focal length f: 1 p + 1 i = 1 f. (1) Note that this relation is valid no matter what are the signs of f and i. (The sign of p is always positive.) Steps to a Concave Lens Ray Diagram. Start the First Ray: Start with your pencil on the top of the object (black thick arrow tip) and draw a line parallel to the principle axis to the center of the lens. Keep your pencil on the paper here ... (Note: some lens ray diagrams follow three rays as seen in the lab interface but the end result is the ...
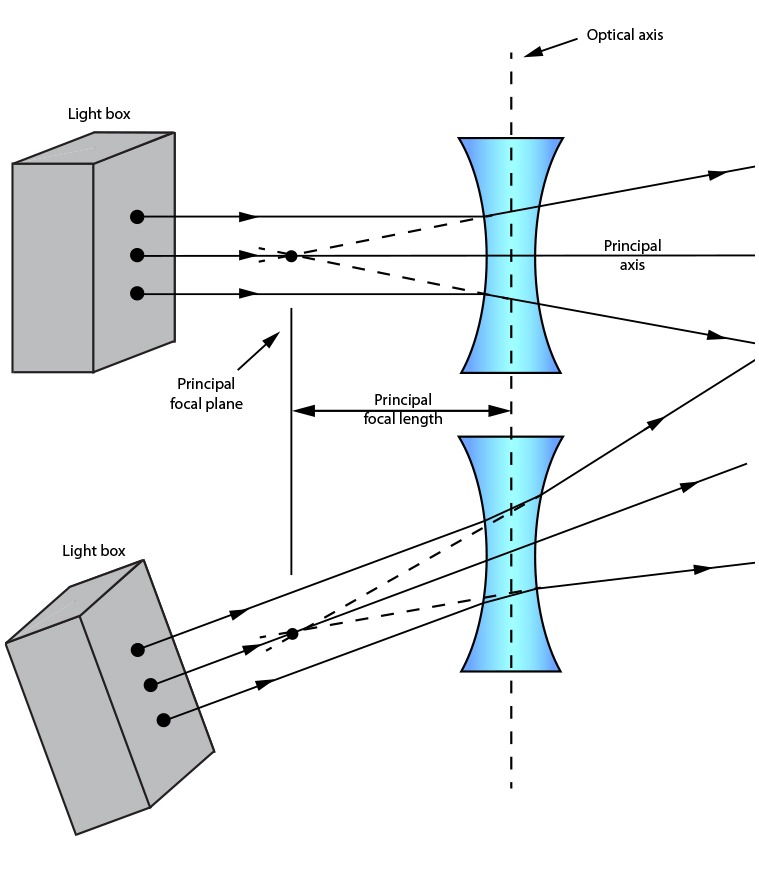
Lecture Notes on Geometrical Optics (02/18/14). 2.71/2.710 Introduction to Optics –Nick Fang 6 Example 2: matrix of a ray propagating in a medium (changes x but not ) Example 3: refraction matrix through a thin lens (combined refraction)
Concave lens ray diagram notes
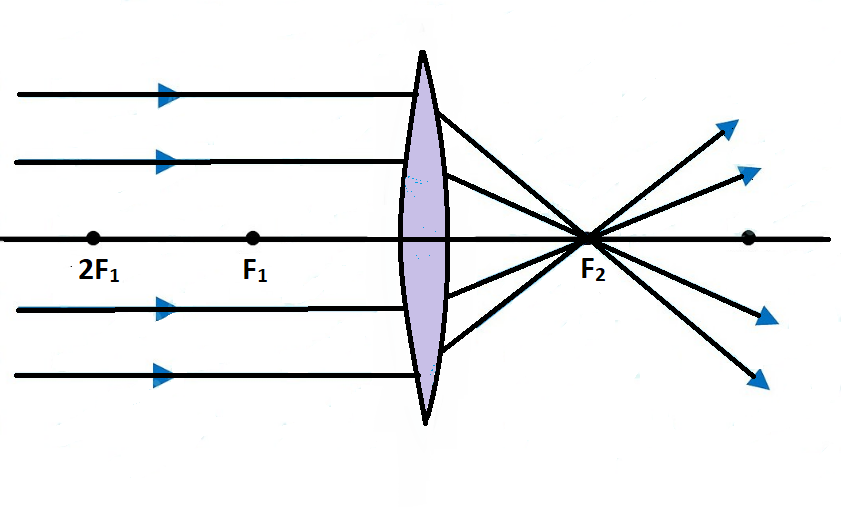
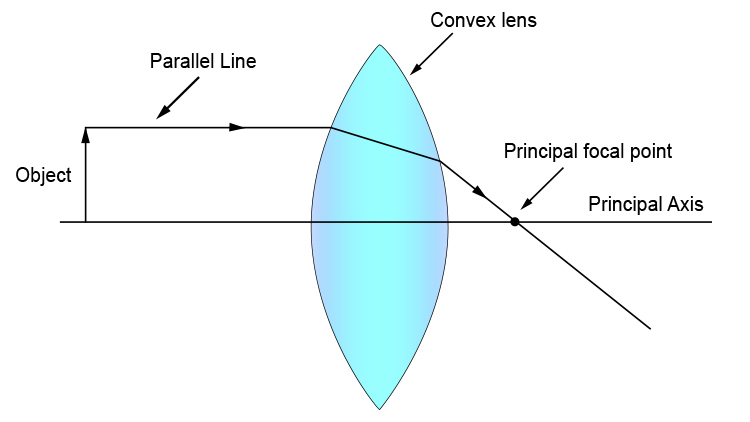
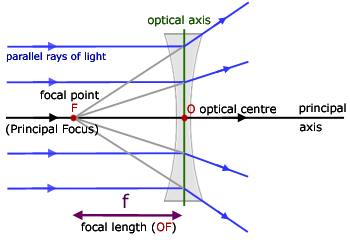
Convex Lenses. In a convex lens, parallel rays of light are brought to a focus . This point is called the principal focus; This lens is sometimes referred to as a converging lens; The distance from the lens to the principal focus is called the focal length. This depends on how curved the lens is; The more curved the lens, the shorter the focal length Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts as if from F. Ray 2 heads towards F' before refracting parallel to the axis. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. image is always virtual, upright and reduced O F I F' Ray diagram for diverging lens Ray Diagram Examples •Note the changes in the image as the object moves through the focal point. Section 23.3. Ray Diagram for Concave Mirror, p > R •The object is outside the center of curvature of the mirror. ... Ray Diagrams for Thin Lenses •Ray diagrams are essential for understanding the overall
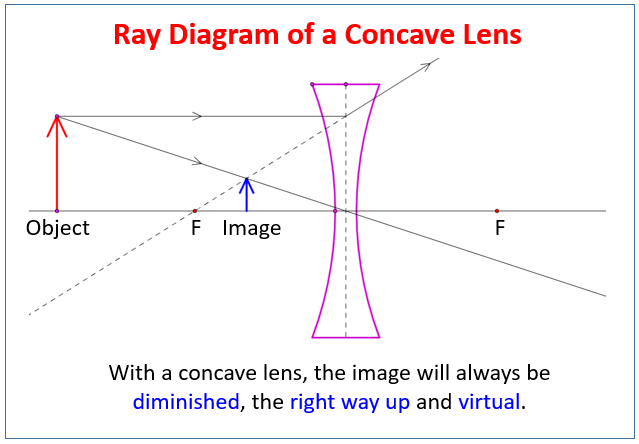
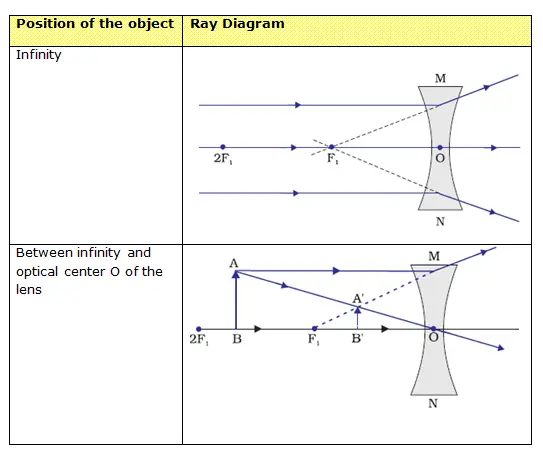
Concave lens ray diagram notes. Ad Download over 20000 K-8 worksheets covering math reading social studies and more. Drawing Ray Diagrams for Convex Lenses Science Start Practising In this worksheet we will practice drawing diagrams of light rays interacting with convex lenses. Physics Notes Learn Physics Science Formulas Lenses - Ray Diagram Construction Worksheet. Lens ray diagram worksheet. This optics bundle contains everything you need for teaching ray diagrams, the thin lens equation and magnification for convex and concave lenses and mirrors. For each of the topics included in this bundle you get a complete set of clearly written, concise notes that can be used as handouts for your Method for drawing ray diagrams – Concave lens. A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as “the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses”. Apr 26, 2020 · For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
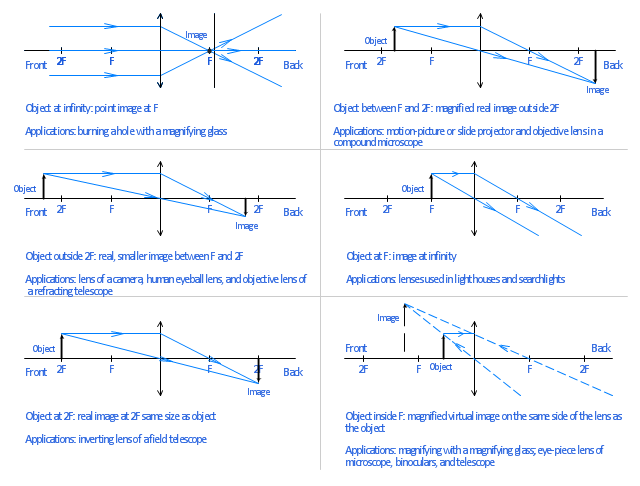
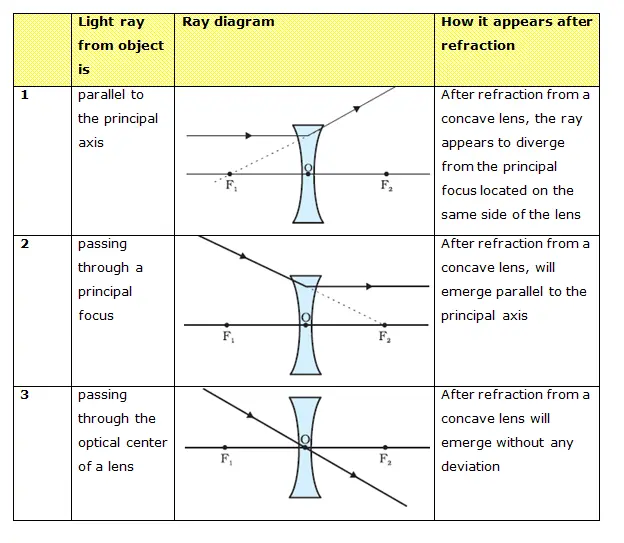
Convex lens ray diagram for when object is a distance between F and 2F from lens. Ray diagram 4 (below): The formation of a real image by a convex lens when the object O is a distance from the convex lens between F and 2F.. 4a converging lens. You construct this ray diagram 4a as exactly described for ray diagram 3.. Apart from the axis line, this is essentially a 2 ray diagram for an object ... diverging lens? Any lens that is thicker in the middle is a converging or convex lens Any lens that is thinner in the middle is a diverging or concave lens Worksheet of lens ray diagrams… Ray diagrams for multiple lenses • When there are two lenses, the image from the first lens becomes the object for the second • Ex 32-10 Concave Lens Ray Diagrams. Concave (diverging) lenses can also be used to form images, although the images are always virtual in this case; If an object is placed further from the lens than the focal length f then a concave lens ray diagram will be drawn in the following way: Light - Reflection and Refraction Notes (ii) A ray passing through the principal focus of a concave mirror or a ray which is directed towards the principal focus of a convex mirror, after reflection, will emerge parallel to the principal axis (iii) A ray passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror or directed in the
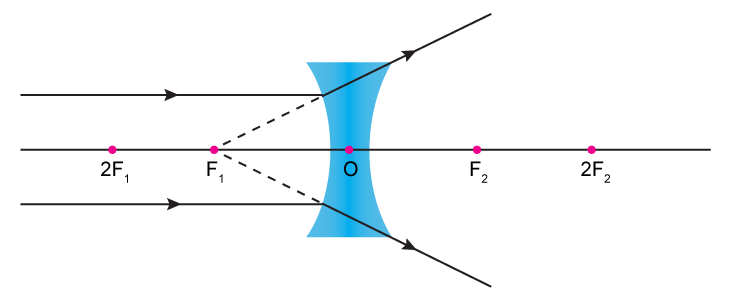
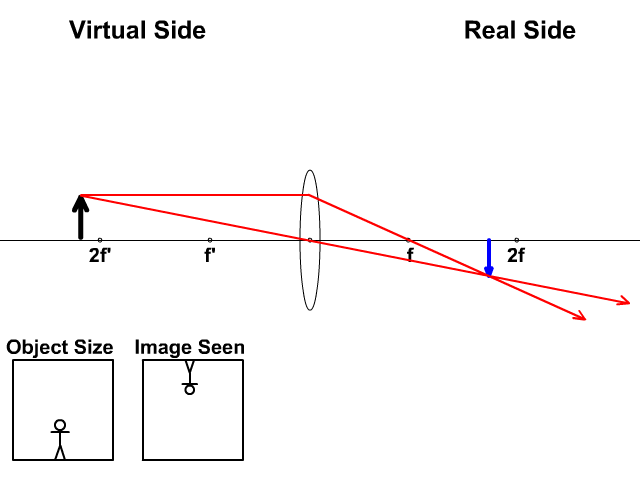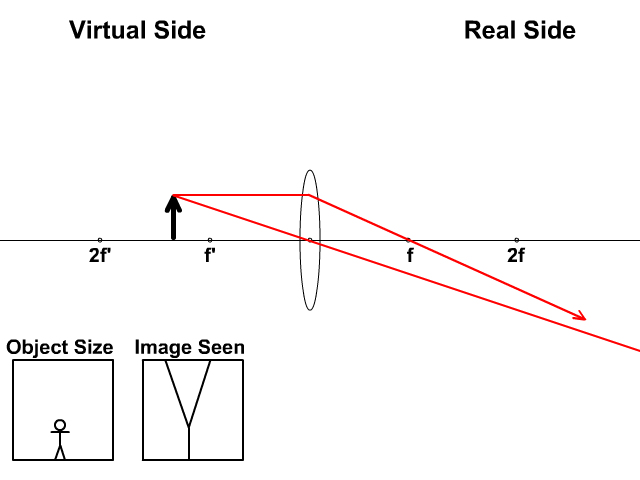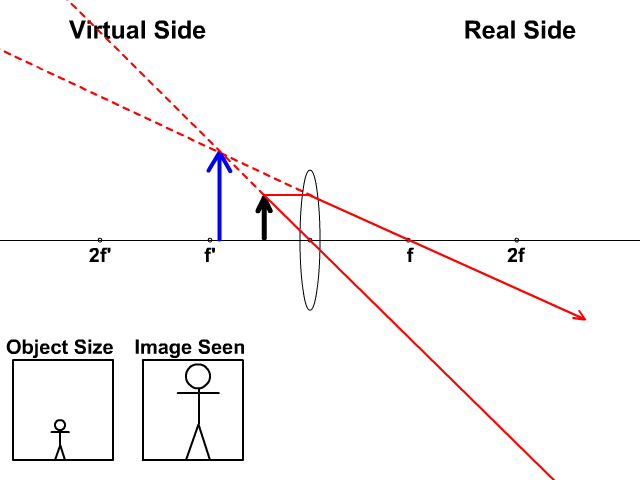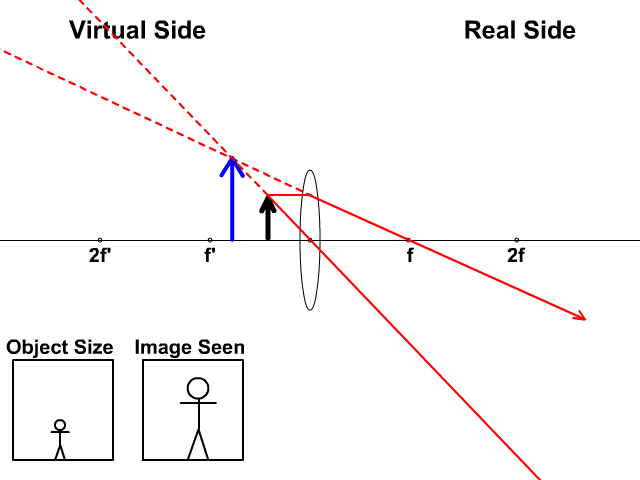
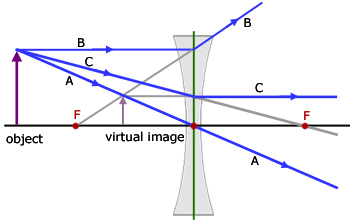
Case II. When the incident light ray emerges from the first focus F 1 of a convex lens, or appears to emerge from the second focus F 2 of a concave lens. In this case, light after refraction from both the lenses will move parallel to the principal axis. Case III. When the light ray passes through the optical centre (O) of a lens. In this case ... Section 3: Concave Lenses 12 3. Concave Lenses Concave lenses always produce upright, virtual images. For aconcave lens, the lens equation is the same but the value of fis nownegative. Ray diagrams for such lenses are drawn using: a ray from the top of the object through the middle of the lens; a ray from the top of the object parallel to the ... The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a double concave lens will be located at a position behind the double concave lens. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram. Home Science Lens NCERT Lens Science Chapter Class 10 Note. A transparent material bound by two surfaces, of which one or both surfaces are spherical. Convex lens: It is a lens which is thicker at the center and thicker at the edges. Concave lens: It is a lens which is thicker at the center and thicker at the edges. Terms related to a lens:
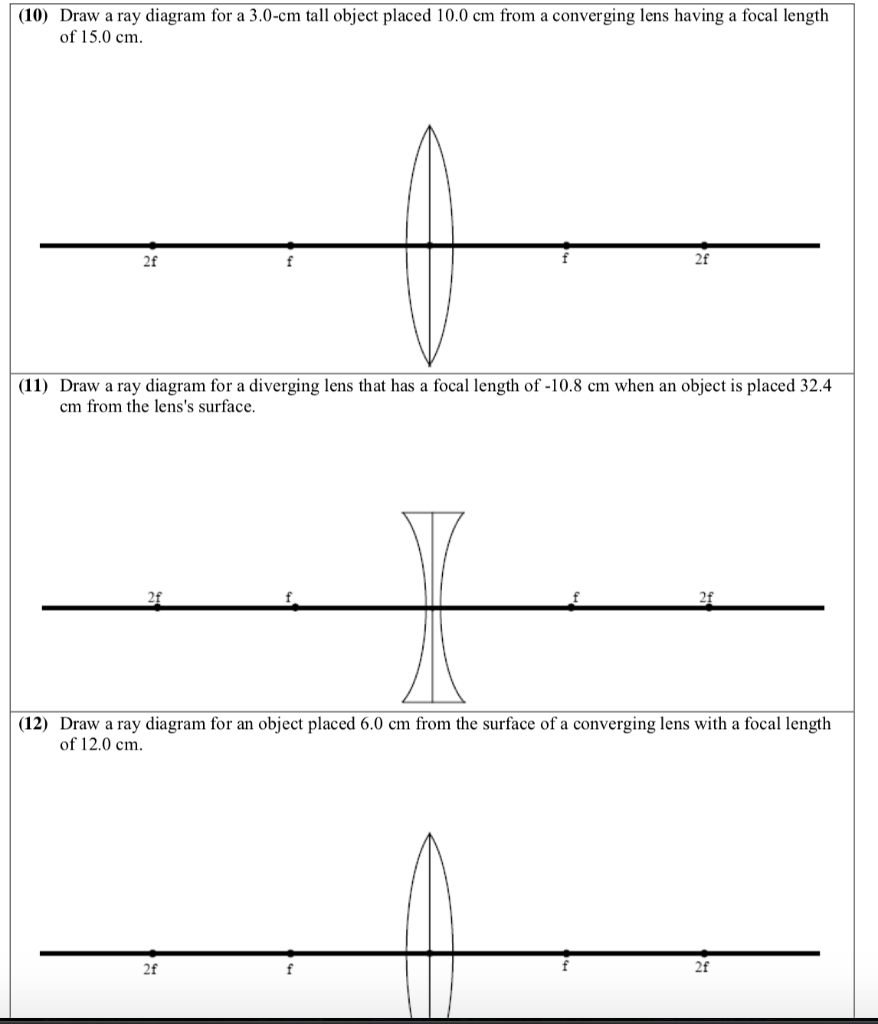
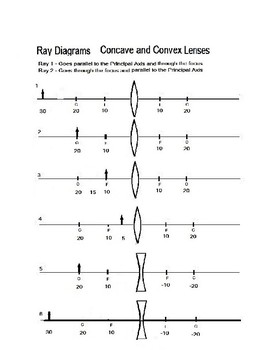
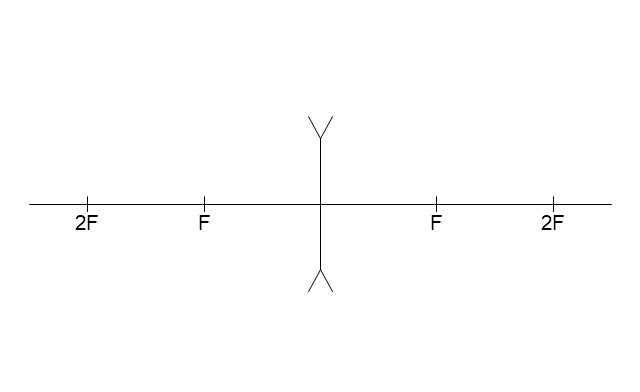
Part 3 - Ray Diagrams 1. Complete the Concave Lens Ray Diagram Worksheet. Use the following values for ALL ray diagrams. f = ± 3 cm object height = 1 cm 2. Use the following rules to construct your ray diagrams. Each ray diagram requires three rays of light.
A converging lens that is curved on both sides (there are two types of converging lens- concave and convex.) A converging lens causes the light rays that are travelling parallel to its principal axis to refract and cross the principal axis at a fixed point called the focal point. (This is explained in more detail below). (A ray diagram is given ...
Convex concave ray diagrams. 1. J.M. Gabrielse Ray Diagrams. 2. J.M. Gabrielse Spherical Mirrors (concave & convex) 3. J.M. Gabrielse Concave & Convex (just a part of a sphere) C: the centre of curvature (centre point of the sphere) F: the focus (focus) of the mirror (halfway between C and the mirror) • C • F Principal Axis Curved Surface. 4.
What Is The Ray Diagram Of Concave Lens When Object Is Placed At Infinity Please Explain In Detail Physics Topperlearning Com Fyblb6ii
Reflection of LightPlane MirrorCurved MirrorThe Ray Diagram and the Types of ImageRefraction of LightSnell's LawRefractive IndexNatural Phenomenon due to Refraction of LightTotal Internal Reflection and Critical AnglePhenomena Related to Total Internal ReflectionLensesPower of LensesConvex LensCharacteristics of the Image Formed by a Convex Lens Concave LensCharacteristics of the Image Formed ...
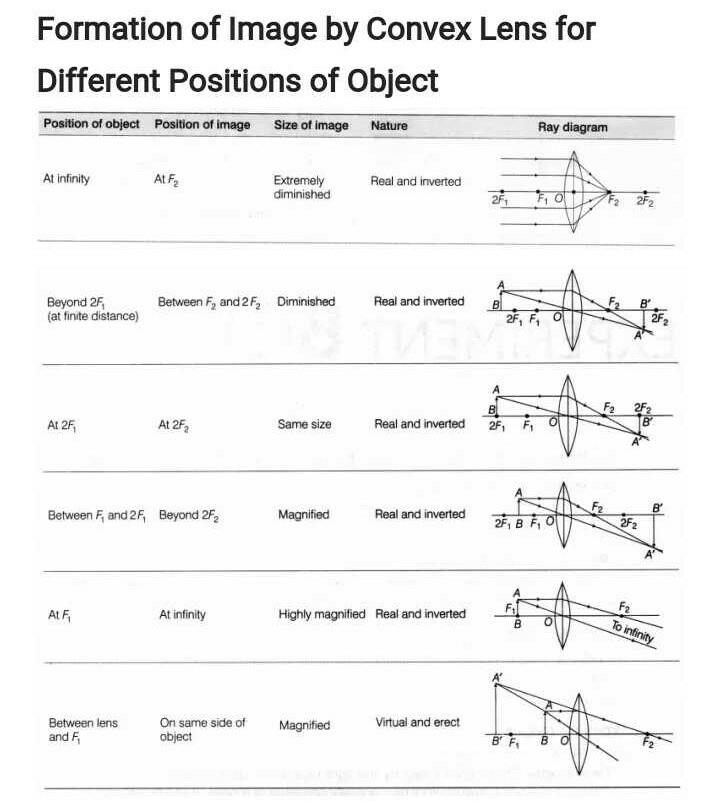
With The Help Of Ray Diagram Illustrate The Change In Position Nature And Size Of The Image Formed If The Convex Lens In Replaced By Concave Lens Of Same Focal Length
From the point of view of the class 10th board, this topic of a spherical mirror is very important. If you know how to draw a ray diagram for concave and convex mirrors, you will be able to create an image. I hope you will understand the given notes of the image formation by concave and convex mirrors. But still, if there is any doubt related ...
A worksheet to construct ray diagrams to show where images are formed by a converging convex lens and a diverging concave lens. Convex lens ray diagram worksheet . Then describe the location of the image orientation upright or inverted of the image the relative size of the image larger or smaller than object and the type of image real or virtual.
Lecture 8 Notes: 07 / 12 Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams A spherical mirror is a reflective segment of a sphere with a radius of curvature R. It can be convex (outside surface of a sphere) or concave (inside surface). First we will consider a concave spherical mirror. The mirror has a radius R, and the
¥Ray diagrams ¥Lenses As usual, these notes are only a complement to the notes on the whiteboard. Types of Images ¥A real image is formed when light rays pass through and diverge from the image point ÐReal images can be displayed on screens ¥A virtual image is formed when light rays do not pass through the image point but only
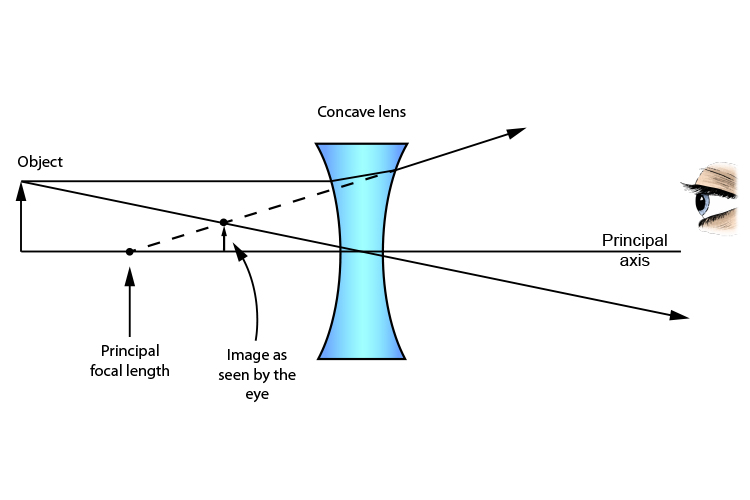
A series of free GCSE/IGCSE Physics Notes and Lessons. The following diagrams show the ray diagram for a concave lens. With a concave lens, the image will always be diminished, the right way up and virtual. Concave Lenses Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed by a concave lens. Describe the properties of an image produced by a concave lens.
convex lens ray diagram with image formation by convex lens image or image formed by convex lens. concave lens ray diagram with image formation by concave lens image or image formed by concave lens. Convex Lenses for Image Formation: Concave lenses . 1. A virtual image is produced at the focus when an object is positioned at infinity.
Ray 1: A ray parallel to the lens axis passes through the far focus of a converging lens or appears to come from the near focus of a diverging lens. Ray 1: Ray 1: A ray parallel to the lens axis passes through the far focus of a converging lens or appears to come from the near focus of a diverging lens. Converging Lens. Diverging Lens. F Ray 1 ...
Ray diagrams help us trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object. Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels. Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirrors
Figure 3 shows a concave lens and the effect it has on rays of light that enter it parallel to its axis (the path taken by ray 2 in the Figure is the axis of the lens). The concave lens is a diverging lens, because it causes the light rays to bend away (diverge) from its axis. In this case, the lens has been shaped so that all light rays ...
The theme of this unit has been that we see an object because light from the object travels to our eyes as we sight along a line at the object. Similarly, we see an image of an object because light from the object reflects off a mirror and travel to our eyes as we sight at the image location of the object. From these two basic premises, we have defined the image location as the location in space where light appears to diverge from. Ray diagrams have been a valuable tool for determining the path taken by light from the object to the mirror to our eyes. In this section of Lesson 3, we will investigate the method for drawing ray diagrams for objects placed at various locations in front of a concave mirror.
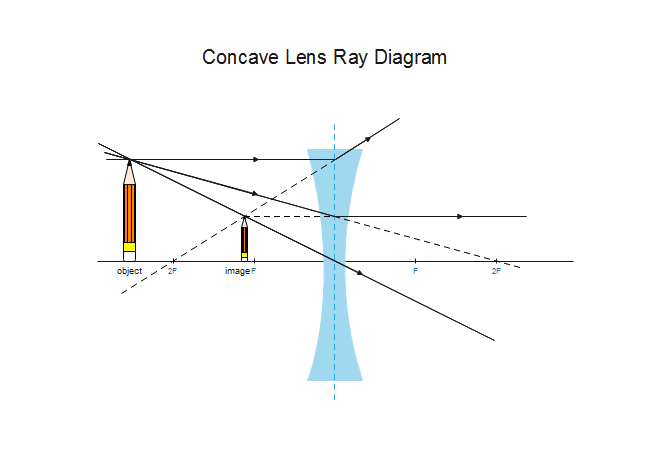
Rule 3 - Ray passing through Optical Center will emerge without deviation. For a both convex and concave lens, we see that ray passing through Optical center emerges without deviation. Next: Convex Lens - Ray diagram→. Facebook Whatsapp.

Convex Lens Concave Lens How To Determine Focal Length Ray Diagrams Image Properties Real Virtual Inverted Size Correction Of Eye Defects Causes Of Long Sight Short Sight Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes
The second ray goes straight through the center of the lens. The light rays don't converge, but the sight lines do. J.M. Gabrielse f Concave Lens (example) • F optical axis The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and refracts from the focal point. The second ray goes straight through the center of the lens.
Guidelines for rays falling on the concave and convex lenses. When a ray strikes concave or convex lenses obliquely at its pole, it continues to follow its path. When a ray, parallel to the principal axis strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray passes through a focus on the principal axis.

Convex Lens Concave Lens How To Determine Focal Length Ray Diagrams Image Properties Real Virtual Inverted Size Correction Of Eye Defects Causes Of Long Sight Short Sight Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes
Ray Diagram Examples •Note the changes in the image as the object moves through the focal point. Section 23.3. Ray Diagram for Concave Mirror, p > R •The object is outside the center of curvature of the mirror. ... Ray Diagrams for Thin Lenses •Ray diagrams are essential for understanding the overall
Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts as if from F. Ray 2 heads towards F' before refracting parallel to the axis. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. image is always virtual, upright and reduced O F I F' Ray diagram for diverging lens
Convex Lenses. In a convex lens, parallel rays of light are brought to a focus . This point is called the principal focus; This lens is sometimes referred to as a converging lens; The distance from the lens to the principal focus is called the focal length. This depends on how curved the lens is; The more curved the lens, the shorter the focal length









---teachoo.png)

0 Response to "38 concave lens ray diagram notes"
Post a Comment