36 f2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
Molecular ion (He2)+ has a bond order of 0.5 , while (H2)+ has a bond order 0.5. He2+ is the more stable of the pair because it has two electrons that it can release to form the ion. Is F2 or F2+ more stable? Between F2, F2+, and F2_ which do you think would have the highest bond order, strongest bond, longest bond length. F2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. As per molecular orbital (MO) theory, all the constituent atoms in a molecule contribute to the formation of molecular orbitals. These MOs are a linear combination of the atomic orbitals. Thus, the electrons in a molecule are not individually assigned to atomic orbitals but to molecular orbitals. Let us have a ...
Valence Bond Model vs. Molecular Orbital Theory . Because arguments based on atomic orbitals focus on the bonds formed between valence electrons on an atom, they are often said to involve a valence-bond theory.. The valence-bond model can't adequately explain the fact that some molecules contains two equivalent bonds with a bond order between that of a single bond and a double bond.
F2 molecular orbital diagram bond order
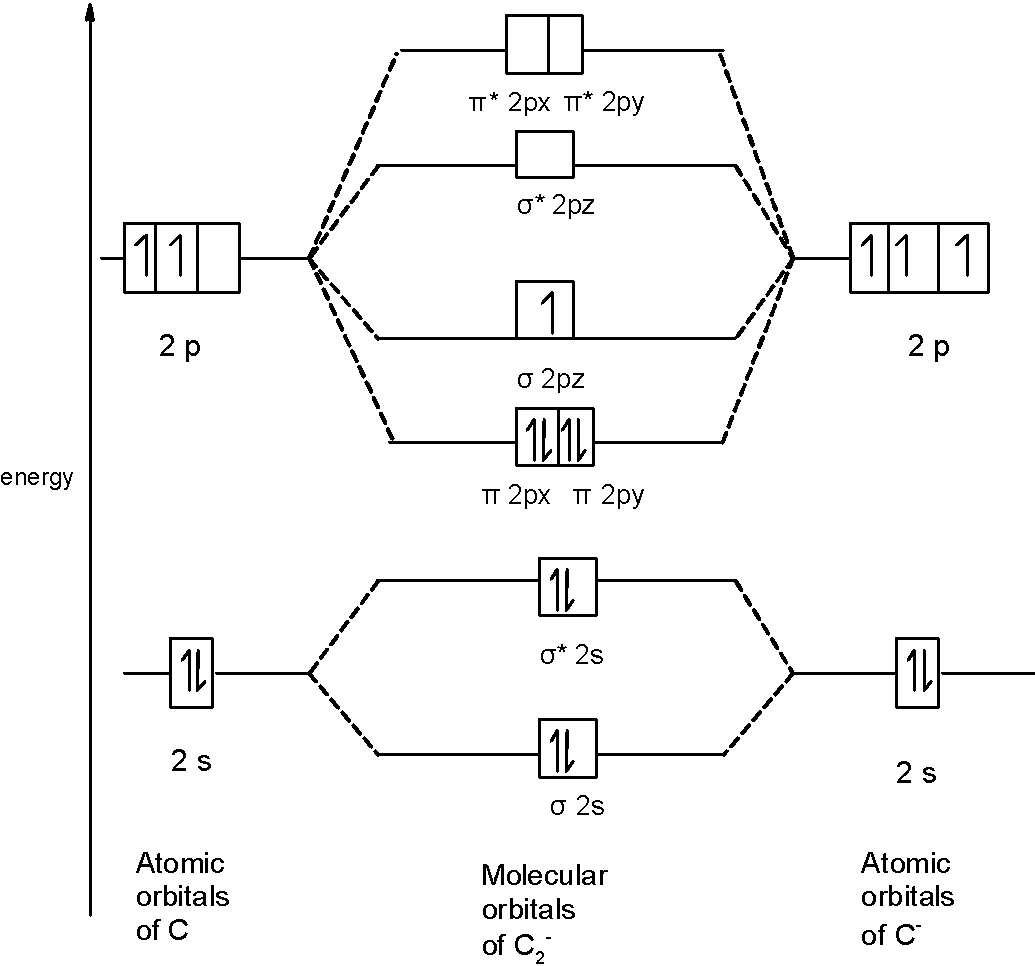
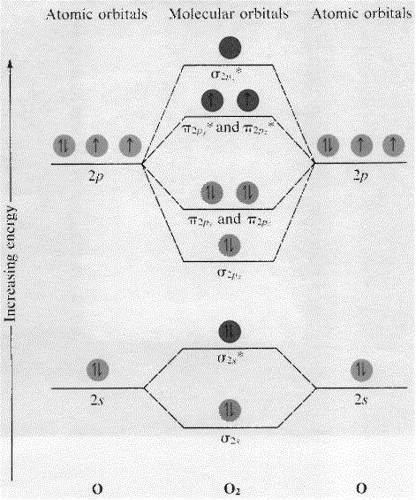
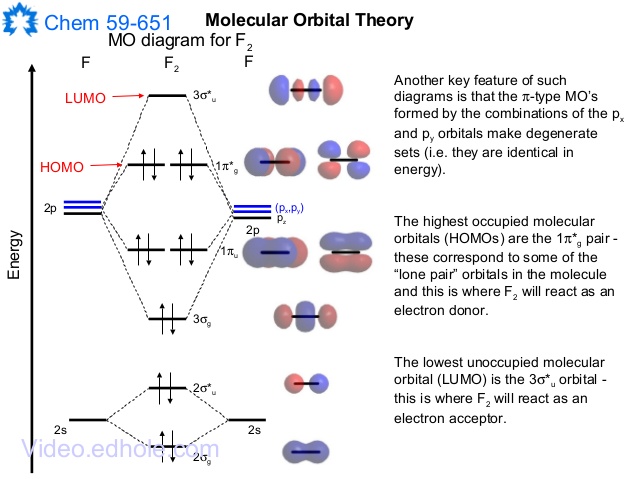
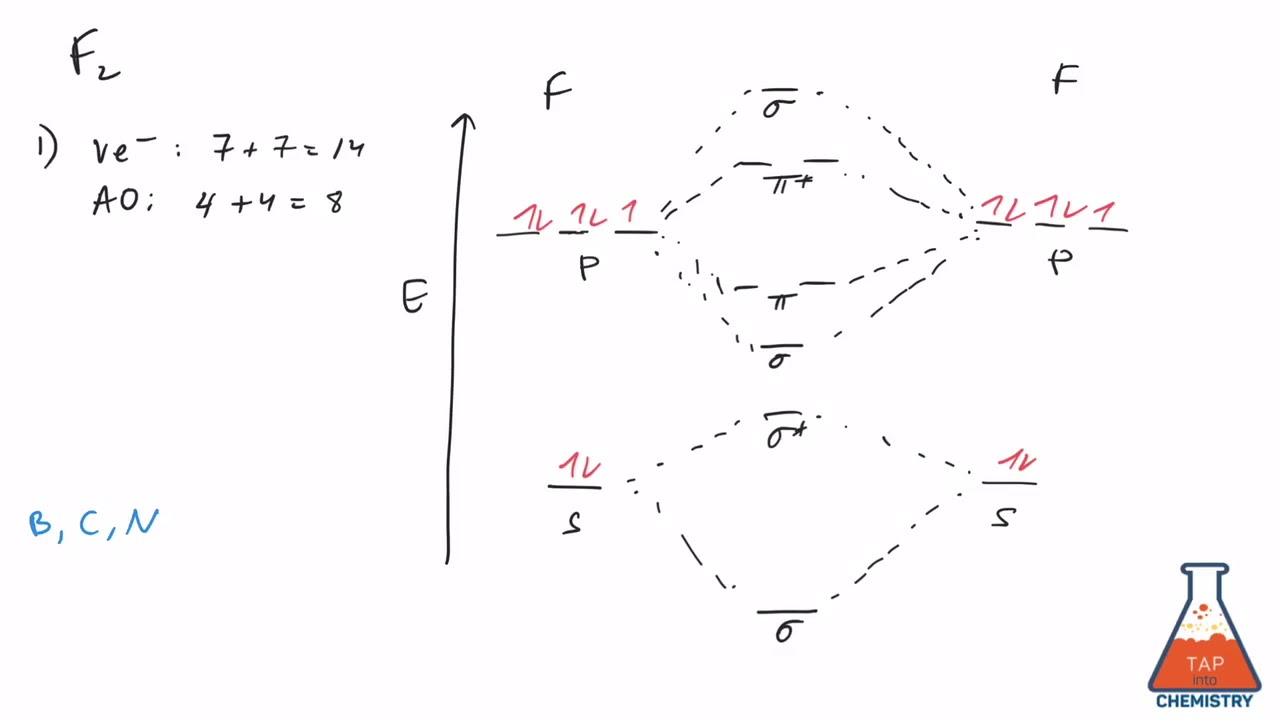
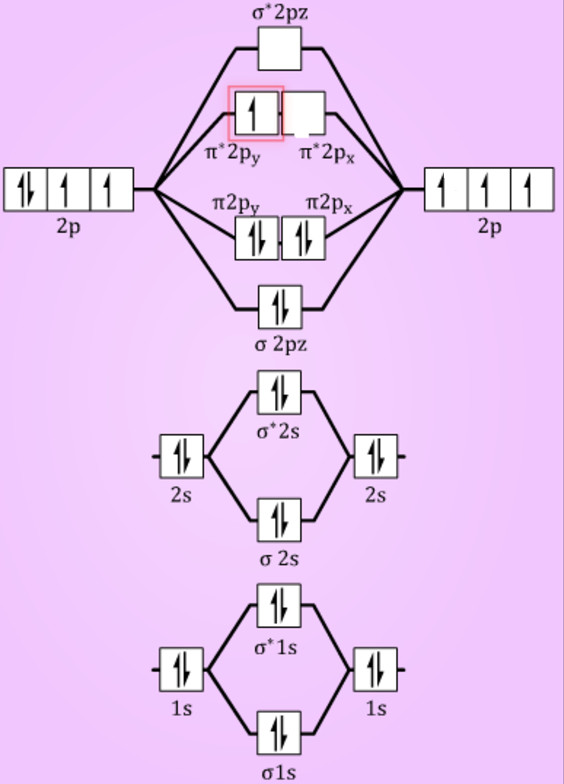
When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so ... d. NO+ Bond order = 3 shortest bond (106 pm) NO Bond order = 2.5 intermediate (115 pm) NO- Bond order = 2 longest bond (127 pm), two electrons in antibonding orbitals. 5.8 a. The CN- energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the antibonding π* electron. b. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons. c. Molecular orbital Diagram F2. molecular orbital theory build f2 for the ion f2 a draw the molecular orbital diagram b calculate the bond order c would this ion exist d write the electron molecular orbital theory c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules this video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules
F2 molecular orbital diagram bond order. Solved question 1 by drawing molecular orbital diagrams solved look at the mo diagrams of corresponding neutral diatom when doing molecular orbitals the pi bonds come before sigma for b2 what is the energy level diagram of n2 and f2 brainly in. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable based on their bond order. Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals O, F, Ne Ne22 F₂2. F2 . 022- • F22 ; Question: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable based on their bond order. Atomic ... Bond order of B2 molecule. So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = .5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond. Molecular orbital diagram for f2. In o 2 and f 2 there is a crossover of the sigma and the pi ortbials. Molecular orbitals mo are constructed from atomic orbitals. The relative energies of the sigma orbitals drop below that of the pi orbitals. The size of the effect depends on the 2s 2p energy difference. It is called a sigma molecular orbital ...
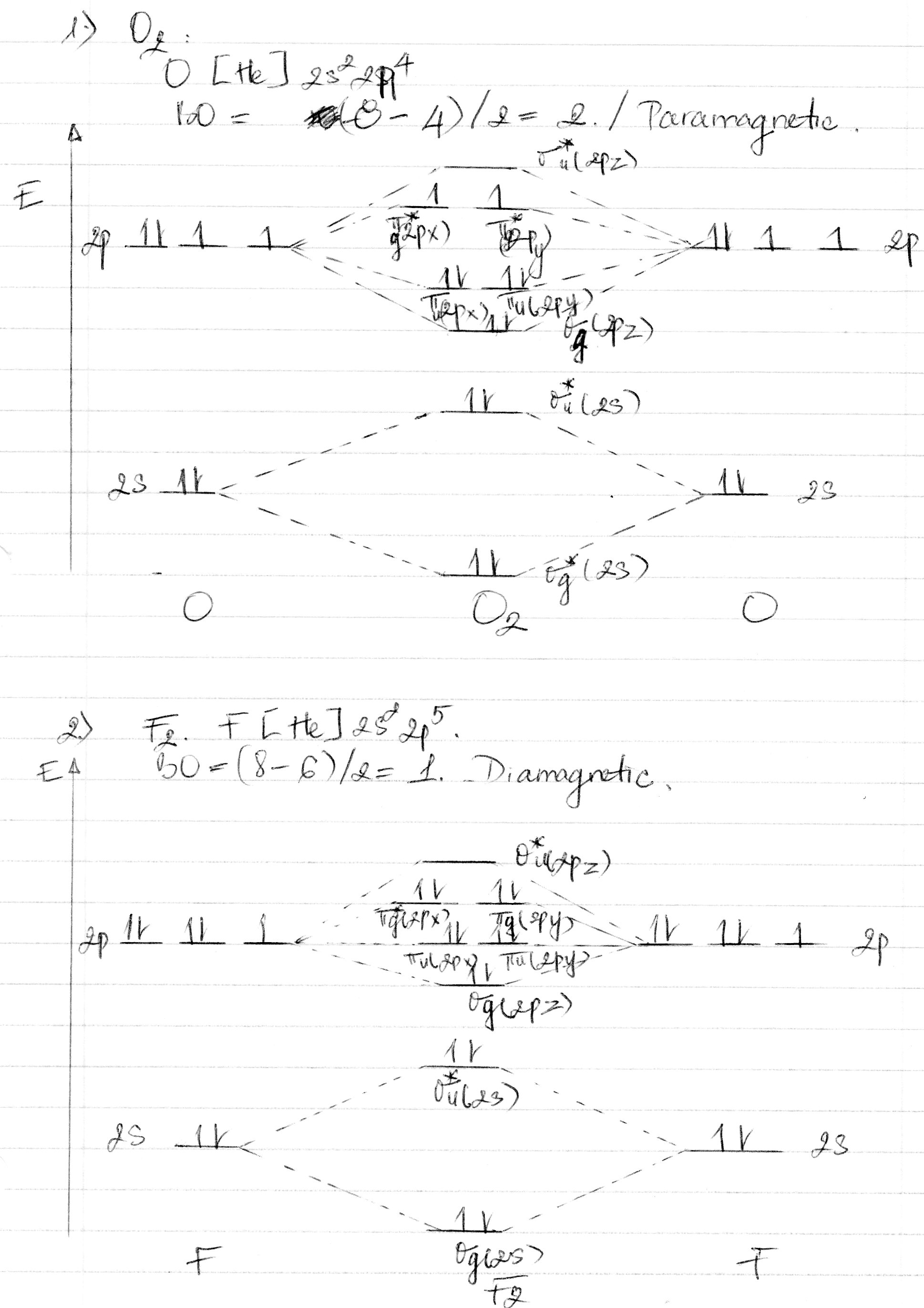
Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic configuration. Thus, the magnetic property can be explained when we know electronic configuration of molecules. Bond order indicates the stability of a bond. In a more advanced context, bond order does not need to be an integer. Bond Order in Molecular Orbital Theory. In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as the difference, divided by two, between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons; this often, but not always, yields the ... If we draw the bond structure of the f2 molecule and distribute the bonding and antibonding electrons using the molecular orbital theory, then we can calculate the bond order of the molecule. In the case of a fluorine molecule has a total of 18 electrons and out of which 14 electrons are valence electrons. If you mean, what is the bond order in the molecule F2, it is 1 (one). If you build the molecular orbitals for the fluorine molecule, the 14 valence electrons of the two fluorine atoms fill the seven lower-energy orbitals, 4 bonding and 3 antibonding; thus you have one net bonding pair, hence bond order = 1, since the bond order is defined as (bonding electrons-antibonding)/2.
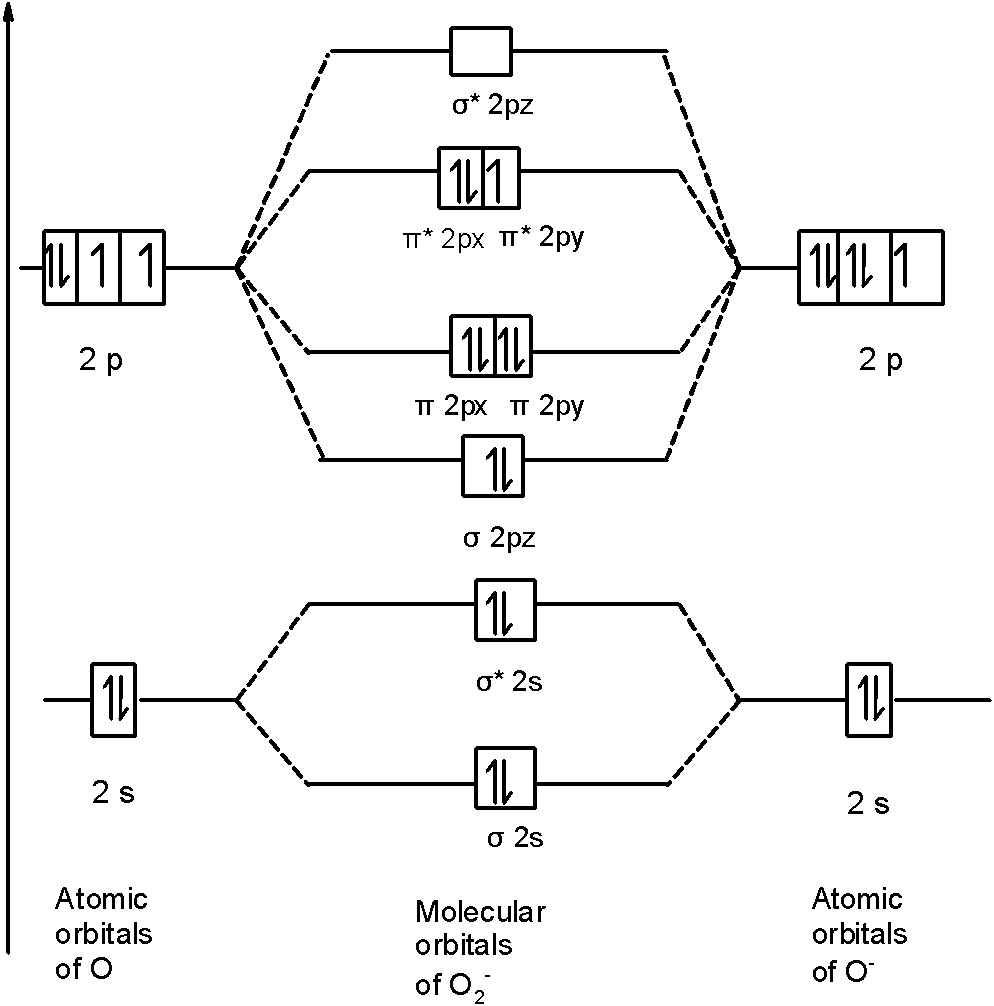
The F₂ molecule is obtained by the linear combination of two F atomic orbitals. When two electrons are supplemented to the antibonding orbitals of the molecule F₂⁻⁻ molecule will be produced. It is identical to Ne. The molecular orbital energy level diagram is given in the attachment. Bond order = 1/2 (Bonding electrons - Antibonding ... Answer (1 of 4): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th... To obtain the bond order, look at the molecular orbitals formed and decide whether they are bonding or antibonding. BO = 1 2 (bonding e− − antibonding e−) = 1 2 [(2 + 2 + 2 + 2) − (2 + 1)] = 2.5. And this should make sense because NO+ is isoelectronic with CO, which has a bond order of 3. With one additional electron in an antibonding ... Answer to Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2. What is the bond order of F2? Oo 0.5 1.5 O O Complete the molecular...
Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN−. Note that the 1𝑠 orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN−. The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of
Solved question 1 by drawing molecular orbital diagrams solved look at the mo diagrams of corresponding neutral diatom when doing molecular orbitals the pi bonds come before sigma for b2 what is the energy level diagram of n2 and f2 brainly in. Information from the mo diagram justify o2s stability and show that its bonding order is 2.
For the ion f2. A draw the molecular orbital diagram. The lumo lowest unoccupied molecular orbital and homo highest occupied molecular orbital of difluorides mo diagram help explain why the molecule is very stable the diagram also tells us that the bond order is 1. The molecular orbital theory mo has been introduced for the diatomic hydrogen ...
Solved 5 Draw Complete Molecular Orbital Diagrams To Compare The Bonding In C2 F2 And Cf A What Is The Bond Order Of Each B Which Of The Thre Course Hero
f2-, f2, f2+ It's a little hard to give a decent answer as you need to see a molecular orbital diagram. Each fluorine atom has 7 valence electrons, and in F2 there are 2 electrons in sigma(2S), 2 in sigma star, 2 in sigma2P, 4 in two pi bonding and 4 in two anti pi bonding.
The bond order describes the stability of the bond. From the completed energy level diagram we can calculate the bond order defined as one half the net number of bonding electrons. 2 know that the higher the bond order the more stable the molecule. Molecular orbital diagram for h2 7. Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of ...
Originally Answered: What is the bond order of F2?In simple terms, since F has 7 valence electrons thus by sharing of electrons with another F it forms a bond to fullfil its octate. You can also find its bond order using advance Molecular orbital theory (MoT). Therefore Bond order of F2 is 1. Mar 26, 2021
Electron Configurations and Bond Orders Just as with atoms, we can write a molecular electron configuration for O2 σ2σ*2σ2π4π*2 We can also calculate the O-O bond order: BO 1 2 # bonding e # anti-bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 LCAO MO theory also predicts (correctly) that O2has two unpaired electrons.
Originally Answered: What is the bond order of F2? In simple terms, since F has 7 valence electrons thus by sharing of electrons with another F it forms a bond to fullfil its octate. You can also find its bond order using advance Molecular orbital theory (MoT). Therefore Bond order of F2 is 1.
Bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons present in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Bond Order = ½ ( N b - Na) The molecule is stable if N b > Na ie. bond order is positive. The molecule is unstable if N b < Na i.e. the bond order is negative or zero. 3) Relative stability of molecule in terms of ...
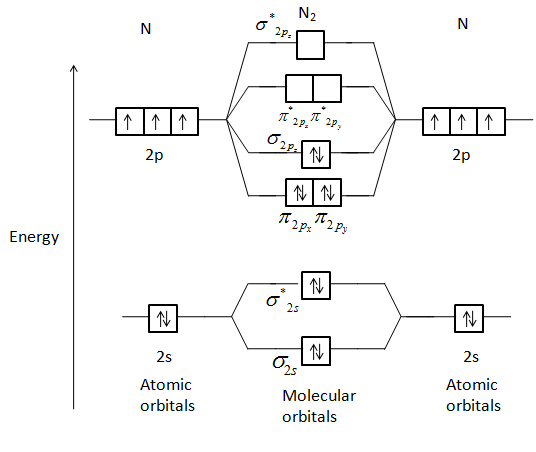
- Bond order: In simple words, It can be stated that bond order is the difference between the number of bonds and antibonds. Bond number also gives an indication of the stability of a bond. Lets calculate the bond order for ${N_2}$ : The total number of electrons present in the ${N_2}$ molecule is 14. Number of electrons in bonding orbitals : 8
Complete the molecular orbital diagram for F2. Do not include the inner shell electrons. (5 pts.) b. Count the number of valence electrons in F2, (2 pts.) c. What is the bond order in F2? (Show your work) (2 pts.) d. What is the bond order in F2? (Show your work) (2 pts.) e. What is the bond order in F2? (Show your work) (2 pts.) f.
In the formation of B 2 molecule, three valence electrons of each boron atom i.e. 6 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies. MO electronic configuration: Bond order: Here Nb = 4, Na = 2 Bond order = The two boron atom is B2 molecules are linked by one covalent bond.
For the ion F2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion.————...
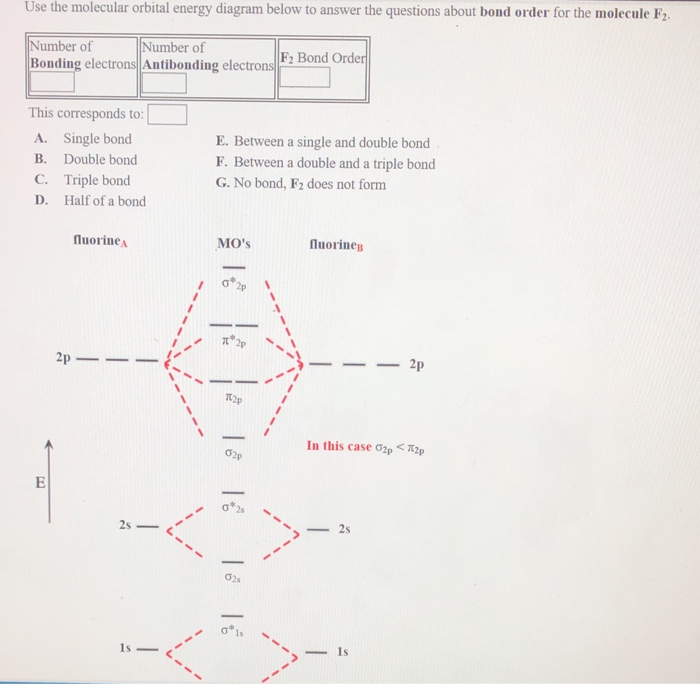
F2 Bond Order 35 Images 33 Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 33 Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 And Find Out The
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Chemistry >> Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure >> Molecular Orbital Theory >> 37. Draw molecular orbital ...
Molecular orbital Diagram F2. molecular orbital theory build f2 for the ion f2 a draw the molecular orbital diagram b calculate the bond order c would this ion exist d write the electron molecular orbital theory c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules this video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules
d. NO+ Bond order = 3 shortest bond (106 pm) NO Bond order = 2.5 intermediate (115 pm) NO- Bond order = 2 longest bond (127 pm), two electrons in antibonding orbitals. 5.8 a. The CN- energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the antibonding π* electron. b. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons. c.
When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so ...

Construct A Molecular Orbital And Energy Splitting Diagram Of The Bonding In Lih Is It Favorable Study Com
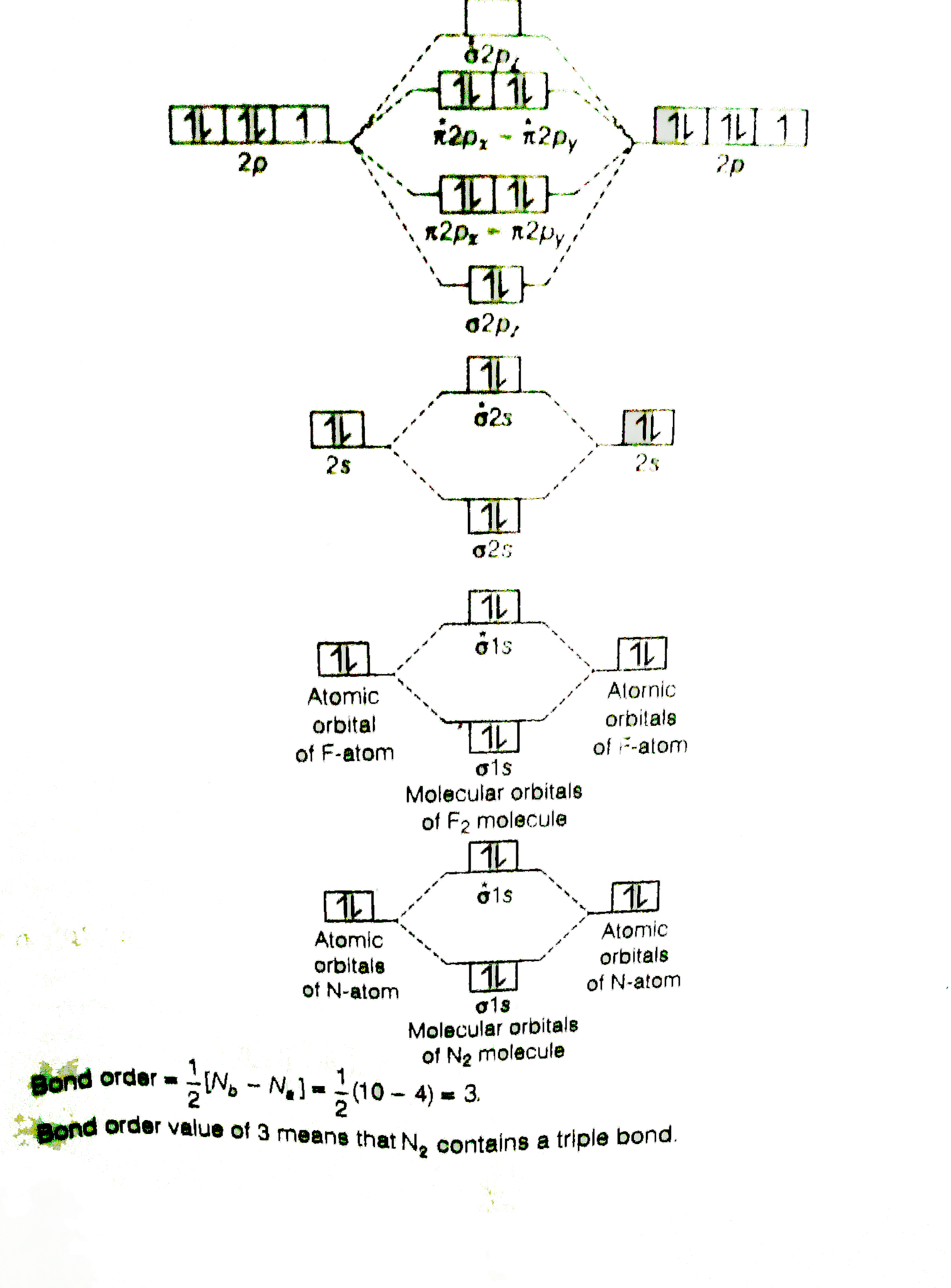
Use The Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram To Show That N 2 Would Be Expected To Have A Triple Bond F 2 A Single Bond And Ne 2 No Bond

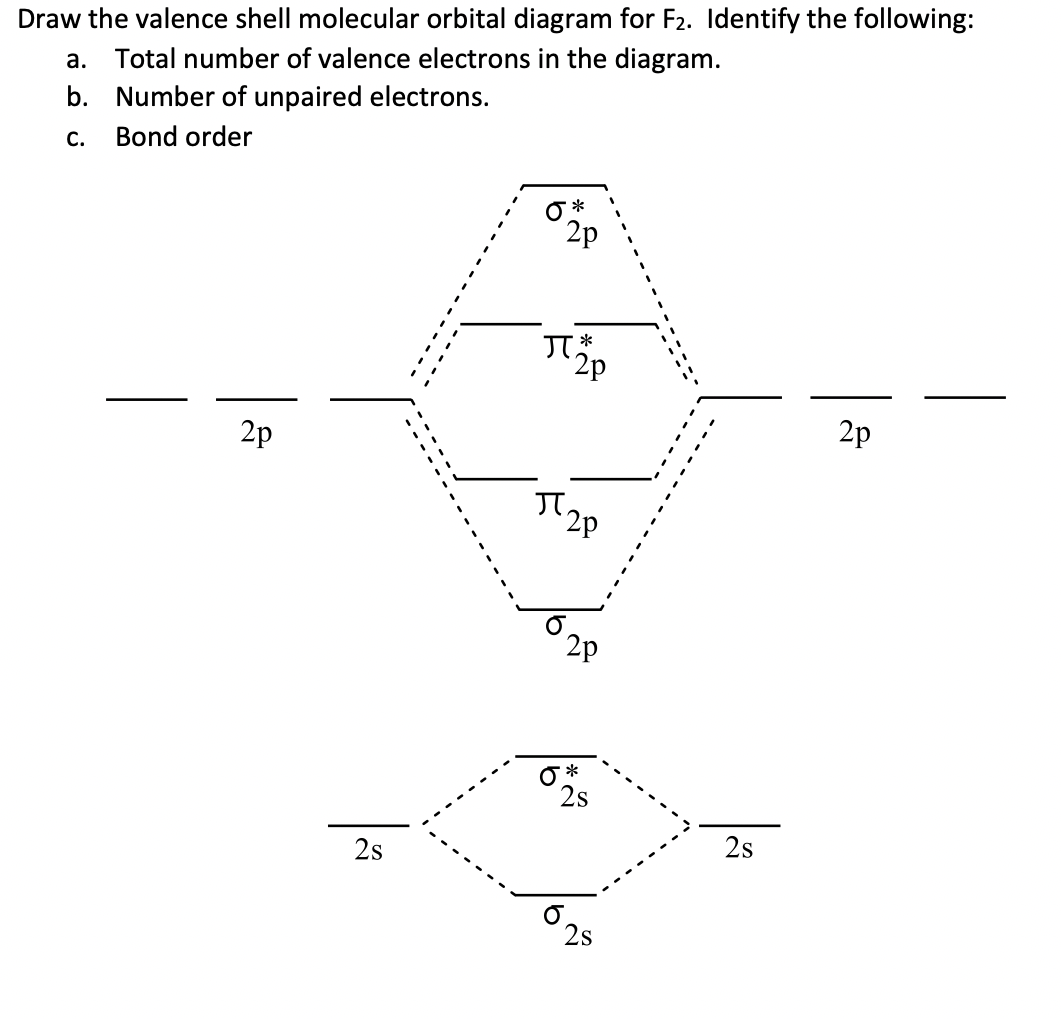













0 Response to "36 f2 molecular orbital diagram bond order"
Post a Comment