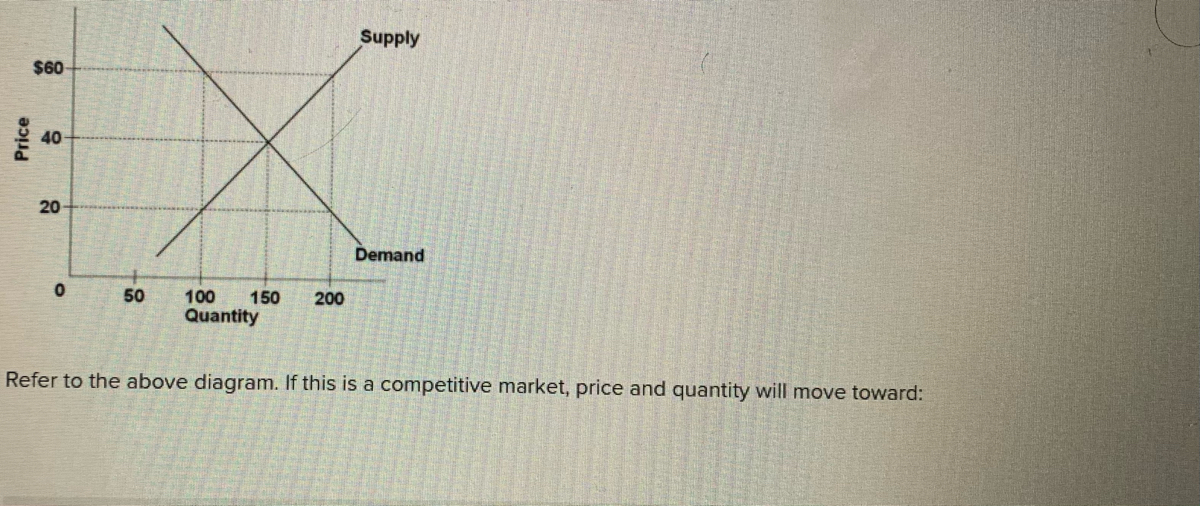
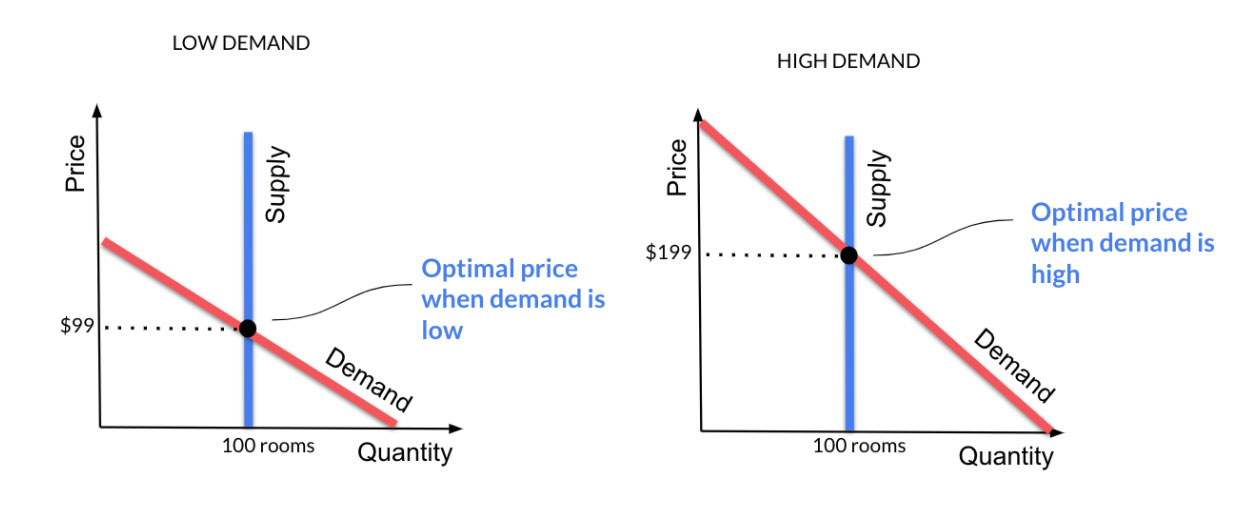
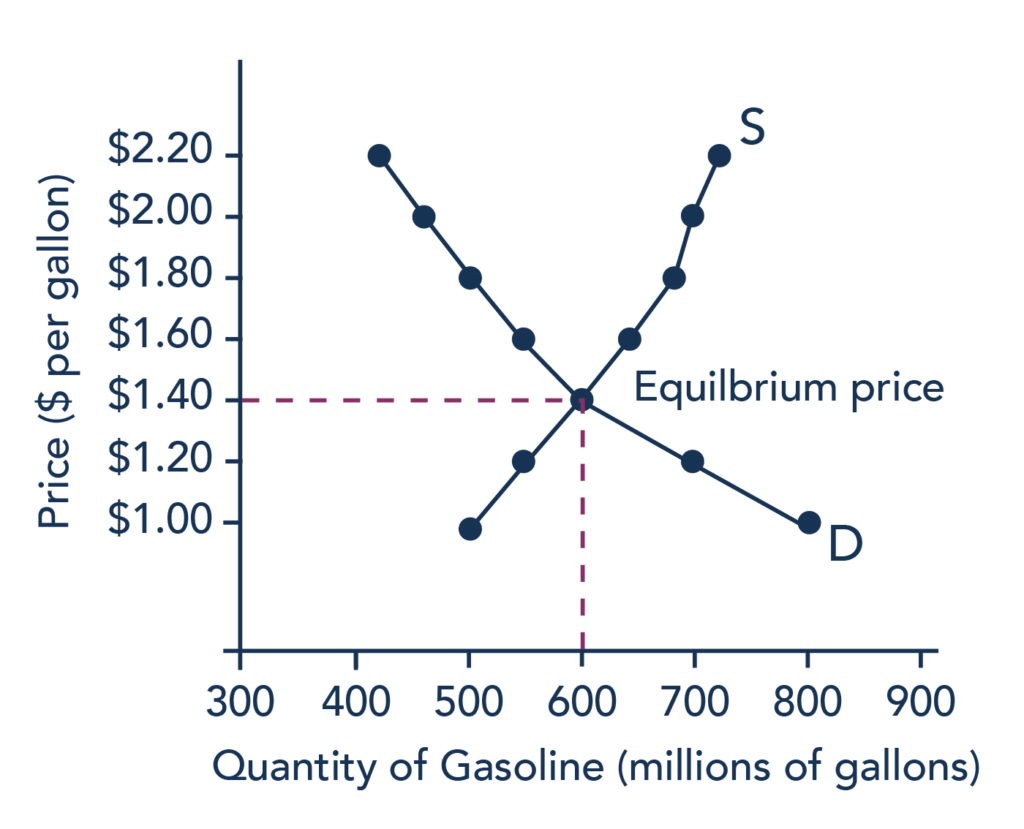
34 refer to the diagram. if this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward
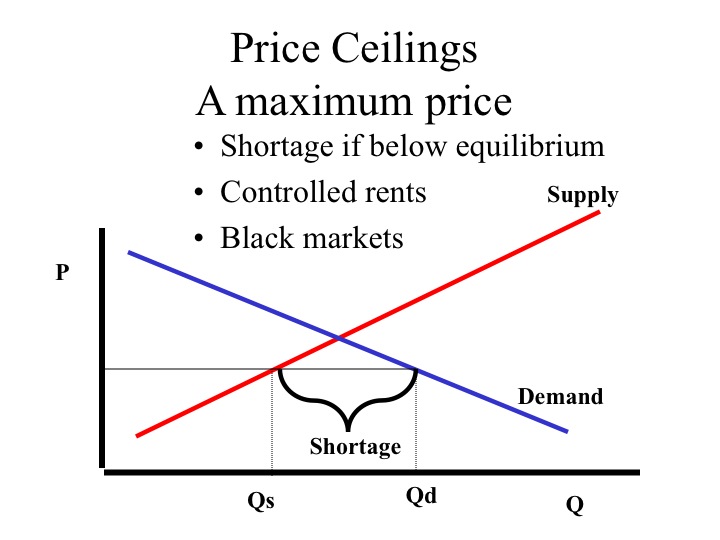
If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: Selected Answer: Correct Answer: $40 and 150 respectively. Question 2 1 out of 1 points College students living off-campus frequently consume large amounts of ramen noodles and boxed macaroni and cheese. some firms leaving an industry. In the above market, economists would call a government-set maximum price of $40 a: price ceiling. A demand curve: indicates the quantity demanded at each price in a series of prices. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $60 in this market will result in: a surplus of 100 units.
8. Refer to the above diagram. The highest price that buyers will be willing and able to pay for 100 units of this product is:€ € A.€$20. B.€$40. C.€$60. D.€$30. € 9. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $20 in this market will result in a:€ € A.€surplus of 50 units. B.€shortage of 50 units. C.€shortage of 100 units. D ...
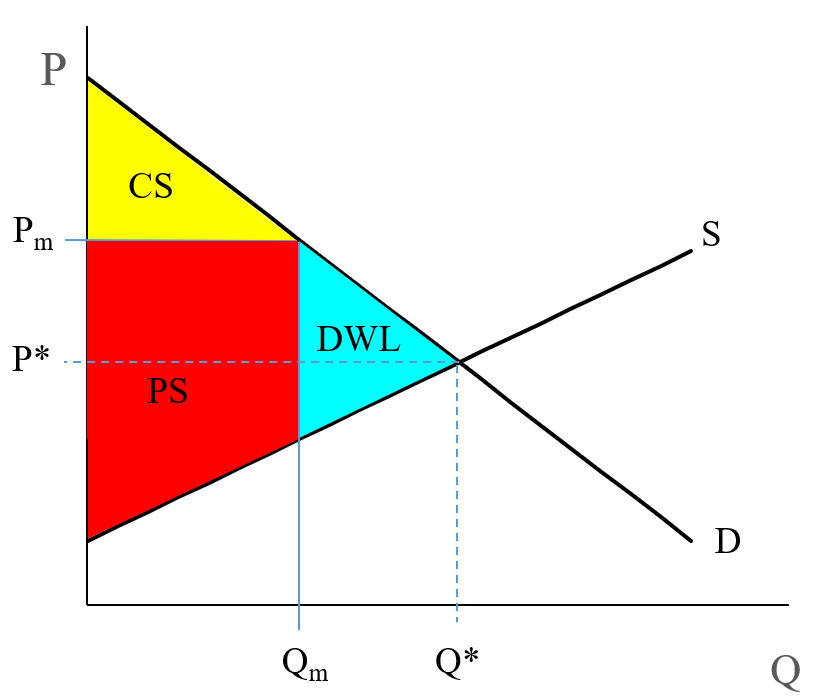
Refer to the diagram. if this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward
Refer to the above diagram. The highest price that buyers will be willing and able to pay for 100 units of this product is: A) $30. B) $60. C) $40. D) $20. 34. Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A) $60 and 100 respectively. C) $40 and 150 respectively. B) $60 and 200 respectively. D. increase equilibrium price and decrease equilibrium quantity. 96. Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100 respectively. B. $60 and 200 respectively. C. $40 and 150 respectively. D. $20 and 150 respectively. Refer to Exhibit 2-3. If PPF 1 is the relevant production possibilities frontier, society may move to PPF 2 as a result of. a. an increase in resources. b. a decrease in resources. c. ... If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will gravitate toward. a. $6 and 10 units, respectively. b.
Refer to the diagram. if this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward. For a perfectly competitive firm, total revenue ( TR) is the market price ( P) times the quantity the firm produces ( Q ), or. TR = P x Q. The relationship between market price and the firm's total revenue curve is a crucial one. Panel (a) of Figure 9.2 "Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue" shows total revenue curves for ... Figure 12 - 5 shows cost and demand curves facing a typical firm in a constant - cost, perfectly competitive industry. 4) Refer to Figure 12 -5. If the market price is $20, what is the firm's profit - maximizing output? 4) A) 750 units B) 1,100 units C) 1,350 units D) 1,800 units 5) Refer to Figure 12 -5. Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100 respectively. B. $60 and 200 respectively. C. $40 and 150 respectively. D. $20 and 150 respectively. AACSB: Reflective Thinking Skills Bloom's: Application Learning Objective: 3-3 Topic: Equilibrium; rationing function 122. Refer to the diagram if this is a competitive market price and quantity will move toward. 60 and 200 respectively. Pic35 60 and 100 respectively. 40 and 150 respectively. 20 and 150 respectively 40 and 150 respectively. 20 and 150 respectively. Chapter 03 demand supply and market equilibrium appendix 110.
PAUL;WELLS KRUGMAN (ROBIN.) · 2017A competitive market is in equilibrium when price has moved to a level at which the quantity demanded of a good equals the quantity supplied of that good. Refer to diagram below. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $20 and 150 respectively. B. $60 and 100 respectively. C. $60 and 200 respectively. D. $40 and 150 respectively. In this diagram, we have a price cap, PC, which is a horizontal line below the equilibrium price, P*. The quantity demanded, Q(d), is the amount at which the price cap and the demand curve intersect. The quantity supplied, Q(s), is where the price cap and the supply curve intersect. From the diagram, you can see that Q(d) is greater than Q(s). Refer to Example 2.4 on the market for wheat. At the end of 1998, both Brazil and ... A vegetable fiber is traded in a competitive world market, and the world price is $9 per ... price, the market-clearing quantity is 2280.65 million bushels. Total revenue has decreased from $6614.6 million to $3709.0 million. Most farmers would worry.
Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100, respectively. B. $60 and 200, respectively. C. $40 and 150, respectively. D. $20 and 150, respectively. Refer to Exhibit 2-5. As more fax machines are produced, the opportunity cost of producing them ... In the simple circular economic flow diagram, if goods produced by business firms flow counterclockwise, then the services of labor flow ... If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will gravitate toward. a. $6 and 10 units ... Refer to the diagram. The highest price that buyers will be willing and able to pay for 100 units of this product is: (Pic34) $30. $60. $40. $20. $60. Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: (Pic35) $60 and 100, respectively. $60 and 200, respectively. $40 and 150, respectively. $20 and 150 ... If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100 respectively. B. $60 and 200 respectively.C. $40 and 150 respectively. D.
Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. ... R-2 F03090. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $20 in this market will result in: A. equilibrium. B. a shortage of 50 units. C. a surplus of 50 units. D. a surplus of 100 units. E. a shortage of 100 units. 8.
7. Refer to the above diagram. Other things equal, this economy will achieve the most rapid rate of growth if: A. it chooses point A. B. it chooses point B. C. it chooses point C. D. it chooses point D. 8. Refer to the above diagram. This economy will experience unemployment if it produces at point: A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D. 9.

Setting The Future Of Digital And Social Media Marketing Research Perspectives And Research Propositions Sciencedirect
Question 3 1 / 1 pts Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: $60 and 100 respectively. $60 and 200 respectively. Correct! $40 and 150 respectively. $20 and 150 respectively.
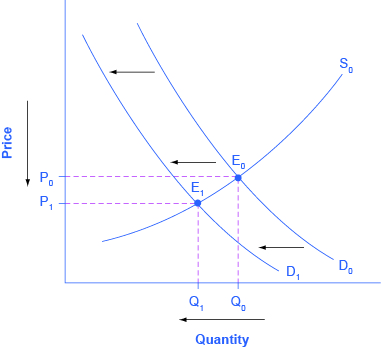
If the supply curve starts at S2, and shifts leftward to S1, the equilibrium price will increase and the equilibrium quantity will decrease as consumers move ...
Putting the supply and demand curves from the previous sections together. These two curves will intersect at Price = $6, and Quantity = 20. In this market, the equilibrium price is $6 per unit, and equilibrium quantity is 20 units. At this price level, market is in equilibrium. Quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded ( Qs = Qd).
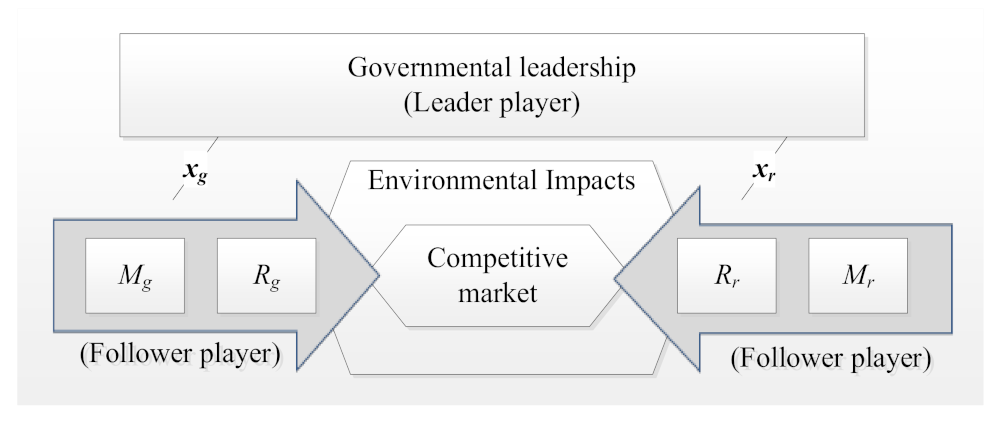
Sustainability Free Full Text Environmental Policy Making In Supply Chains Under Ambiguity And Competition A Fuzzy Stackelberg Game Approach Html
Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A.$60 and 100, respectively. B.$60 and 200, respectively. C. $40 and 150, respectively. D. $20 and 150, respectively.
However, if a market is not at equilibrium, then economic pressures arise to move the market toward the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. This happens either because there is more supply than what the market is demanding or because there is more demand than the market is supplying. This balance is a natural function of a free-market ...

Chapter03 6 110 Refer To The Diagram If This Is A Competitive Market Price And Quantity Will Move Toward A 60 And 100 Respectively B 60 And 200 Course Hero
Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward. $40 and 150, respectively. The table below shows the weekly demand for hamburger in a market where there are just three buyers. ... Assuming a purely competitive market for the product, the new equilibrium price will be between.
Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward:
f) Suppose this market was a perfectly competitive market (i.e., the monopolist's demand curve is still the market demand curve, but now there are many firms providing gas for the market). Given the market is perfectly competitive, what would be the equilibrium price (Ppc) and quantity (Qpc) in this competitive market? 20 b 40
gallons, and there were 267 million consumers. Multiplying the quantity demanded at that price by each individual consumer gives us the market quantity demanded at that price: 267 million × 41 gallons = 10.9 billion gallons. Similarly, the market quantity demanded at a price of $1.50 would be 267 million × 50 gallons = 13.4 billion gallons.
Refer to the above diagram. The highest price that buyers will be willing and able to pay for 100 units of this product is: A) $30. B) $60. C) $40. D) $20. 47. Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A) $60 and 100 respectively. C) $40 and 150 respectively. B) $60 and 200 respectively.
Both intersect at E which is the equilibrium point. OP is the equilibrium price at which OQ equilibrium quantity is bought and sold. If the price falls from OP to OP 2, demand P 2 d > P 2 s 1 supply and s 1 d 1 represents the excess demand. Since demand is greater than supply, competition among buyers will raise the price from OP 2 to the equilibrium price OP. ...
In Image 1, both buyers and sellers are willing to exchange the quantity Q at ... When either demand or supply shifts, the equilibrium price will change.
Question: QUESTION 4 Supply $60 Price 40 20 Demand O 50 200 100 150 Quantity Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market price and quantity will move toward $60 and 100, respectively. $40 and 150, respectively, $60 and 200, respectively $20 and 150, respectively,
Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100, respectively. B. $60 and 200, respectively.

The Modernization Of The Rice Value Chain In Senegal A Move Towards The Asian Quiet Revolution Soullier Development Policy Review Wiley Online Library
... Supply $60 Price Demand 50 200 100 150 Quantity Refer to the diagram. If this is a competitive market price and quantity will move toward: $60 and 200, ...
Refer to Exhibit 2-3. If PPF 1 is the relevant production possibilities frontier, society may move to PPF 2 as a result of. a. an increase in resources. b. a decrease in resources. c. ... If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will gravitate toward. a. $6 and 10 units, respectively. b.
D. increase equilibrium price and decrease equilibrium quantity. 96. Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A. $60 and 100 respectively. B. $60 and 200 respectively. C. $40 and 150 respectively. D. $20 and 150 respectively.
Refer to the above diagram. The highest price that buyers will be willing and able to pay for 100 units of this product is: A) $30. B) $60. C) $40. D) $20. 34. Refer to the above diagram. If this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward: A) $60 and 100 respectively. C) $40 and 150 respectively. B) $60 and 200 respectively.

Effect Of Exchange Depreciation On A Country S Export Price Level In Imf Staff Papers Volume 1950 Issue 001 1950


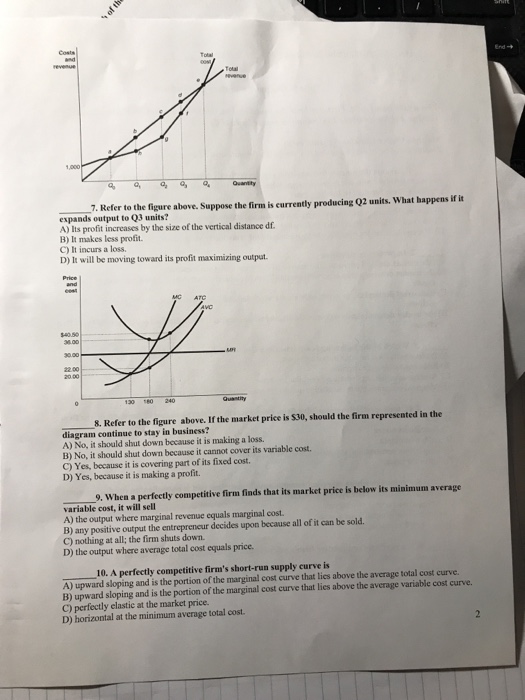
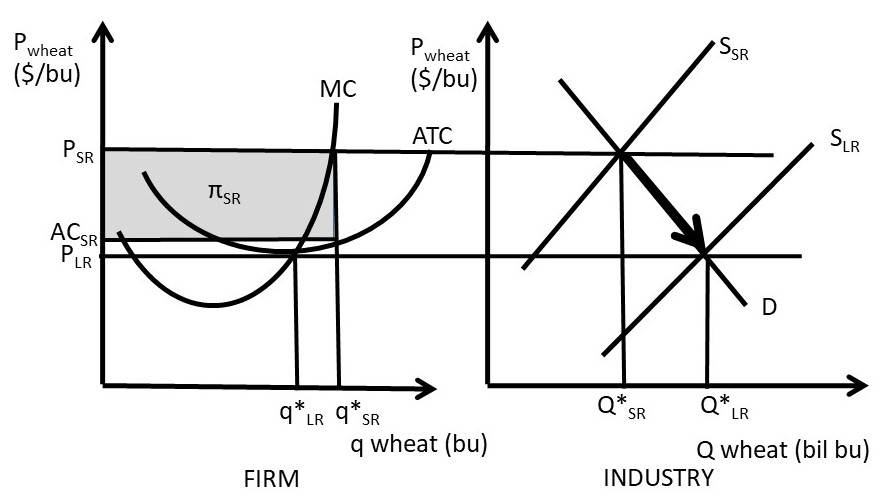










0 Response to "34 refer to the diagram. if this is a competitive market, price and quantity will move toward"
Post a Comment